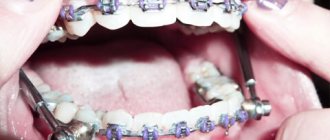
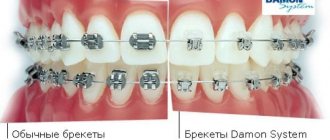
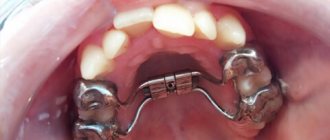
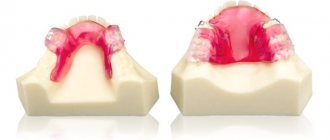
Many patients, when they come to the orthodontist, are determined to receive treatment with braces. But sometimes additional influence is required. One example of such treatment is the non-removable Herbst appliance.
The Herbst appliance helps in eliminating malocclusions. Often the device is effective for distal occlusion defects (incorrect contact of the upper and lower teeth). A distal defect means that the upper row of teeth moves significantly forward in relation to the lower ones. All this is observed with the jaws closed.
Elimination of this defect is necessary not only for physiological reasons (impaired chewing, breathing or speech). Distal bite: protrusion of the upper jaw, curvature of the chin, thinness of the lips. Correction of the bite is accomplished by installing an orthodontic structure.
Features of the Herbst apparatus
- reliability of fixation, which is ensured by two hinges and steel rings;
- the structure is fixed on the supporting teeth;
- getting used to the device occurs in a short time;
- The seemingly massive device does not actually prevent a person from speaking and eating;
- treatment does not require diet;
- with the help of this device you can correct complex bite defects in just a year;
- changes in the patient’s profile occur immediately after installation of the structure;
- high cost of treatment;
- The probability of failure is very low, usually it is minor damage.
Retaining devices (retention)
Such devices are used in cases where it is necessary to keep teeth in place. The most common reason when this may be required is cases of early removal of primary chewing teeth. If the baby tooth could not be saved and had to be removed, and the permanent tooth is still 1-2 years away from erupting, rings with spacers (loops) will come to the rescue. Modifications may vary, but in any case the principle remains the same: a ring to which the element is soldered towards the missing tooth. This structure can remain in the oral cavity until the permanent tooth erupts.
Another option for retaining devices is the Gozgarian palatal clasp or the Nance device. Such devices are used to stabilize the position of molars after treatment with distalizing devices, as well as to prevent loss of space during treatment with tooth extraction. The rigid fixation of the Nance button with rings creates a durable structure to maintain the achieved treatment result.
Advantages
The Herbst apparatus is not used in dentistry as often as before. Today, doctors offer simplified, cheaper designs, but this device has a number of advantages:
- strength and reliability;
- the device rests on the lateral teeth, so it is not noticeable during communication;
- the result is noticeable almost immediately after installing the device;
- continuous impact on the jaw significantly reduces the time to correct the defect;
- the ability to accurately predict the result;
- you don’t need to get used to the device for a long time with pain and discomfort;
- the patient can eat any food, the device will not become dirty;
- the device successfully treats jaw defects that provoke (or were provoked by) respiratory tract diseases;
- The device can be combined with any braces;
- in children under 17 years of age, it can replace surgical correction and treatment with a face bow;
- It is possible to install the device if there are problems with the enamel.
More than 50 examples of successful correction of distal occlusion from Dial-Dent specialists
In the practice of Dial-Dent orthodontists, there are many successful examples of correcting distal occlusion using the Herbst apparatus. In some cases, the Herbst apparatus has become an excellent alternative to surgical correction of the bite. The list below represents just a few of the works.
- Bite correction: lingual braces + Herbst apparatus (Incognito braces)
- An alternative to surgical correction of the bite (Incognito braces)
- Complex orthodontic treatment (Incognito braces and Herbst apparatus)
- Bite correction using the Herbst apparatus (Damon braces)
- Herbst apparatus for correcting deep bite (Damon braces)
An orthodontist will be able to answer all questions about correcting your bite during a face-to-face consultation. Each case is unique, so each patient is given an individual treatment plan. At Family Dentistry, orthodontists work with various equipment, which allows them to choose the most effective and convenient way for the patient to correct the bite.
The clinic has related specialists who will help if it is necessary to treat, remove or replace teeth. Professional dental hygiene is carried out, including hygiene with braces, which helps maintain the health of teeth and gums during orthodontic treatment.
Make an appointment by phone +7-499-110-18-02 or through the form on the website. You can ask questions about correcting your bite to the chief doctor of the clinic, Sergei Vladimirovich Tsukor, at
Types of devices and design elements
The Herbst apparatus is a complex structure. Most of the parts of the device are made of medical alloy, which prevents allergic reactions and damage to the device.
Components:
- crowns for support, which are placed on the side teeth;
- hinged beams (2 pcs.) of a telescopic design, which allows you to open your mouth;
- metal rings for securing the ends of the beams to the crowns;
- curved metal arches (sometimes required for increased stability of crowns).
Types of Herbst apparatus:
- Classical. It is only attached to artificial metal crowns.
- Optimal. Attached to the arch of the bracket system and to the crowns. Allows you to simultaneously correct the bite and correct the dentition.
- Plastic base. The installation of such a structure depends on the initial condition of the teeth. Partial and full basis possible. The design is recommended for people with complete or partial absence of teeth (edentia).
What does it represent?
This device is a complex device whose main purpose is to correct severe occlusions . The main elements of the device are made of medical alloy, which is hypoallergenic and durable.
Design
The main difference between the device and other orthodontic devices is its design. This device includes several elements: support crowns, two hinged beams.
The ends of each beam are attached to the supporting crowns using special metal rings. Crowns are placed on the lateral teeth of opposite dentitions, guaranteeing fixation of the jaw in a given position.
The beams have a telescopic design that moves easily when opening the mouth while talking or chewing.
This is ensured by the uneven length of the rod and the beam tube, where the length of the beam is 2 mm longer than the main tube.
To increase the stability of the crowns, they can be equipped with a special curved metal arc, which is simply welded to them.
Depending on the type of installation, the design is divided into several types with minor differences:
- The classic version , strengthened only on artificial metal crowns.
- Fixed on the orthodontic arch of the bracket system and on crowns . Allows you to combine correction of the jaw position with correction of the dentition.
- Installed on a plastic base .
Depending on the initial state of the dentition, the base can be either partial or complete, with detailed restoration. Such a product requires only fixing the base, without separate installation of the device. This option allows you to correct the position of the jaw for people with partial or complete edentia.
Principle of operation
Visual correction of an abnormal position using this device begins from the moment of its installation.
The principle of operation of the device is constant forced tension of the lower jaw , due to which it gradually moves forward.
While wearing the structure, the ligaments and muscles of the jaw are stretched, due to which the correct position of the mandibular joint is formed.
The speed of the device is ensured by the fact that the device is constantly on the teeth, 24 hours a day. When exposed to the Herbst apparatus, after a short period of time one can notice an improvement in the facial profile and its harmony.
A similar corrective effect is obtained when using Sabbah and Forsus springs.
Areas of use
The design feature allows this device to be used only to correct orthodontic problems caused by underdevelopment of the lower jaw or hypergrowth of the upper jaw .
It can also be used to correct orthopedic problems, in conjunction with other corrective devices.
We provide recommendations on how to tighten the Derichsweiler apparatus in the next review.
In this publication we will talk about methods of treating distal occlusion.
Here https://orto-info.ru/sistemyi-vyiravnivaniya-zubov/individualno-izgotovlennyie-apparatyi/ortodonticheskiy-bryuklya-dlja-korrekcii-prikusa.html we will look at the stages of manufacturing the Bruckle apparatus.
Indications
The main indication for installation is distal class 1 occlusion according to Angle. The design helps to extend the movable lower jaw and fix it. Often, treatment with the Herbst apparatus is combined with the installation of a brace system.
The Herbst apparatus can be used not only for the correction of orthodontic defects that have developed from underdevelopment of the lower jaw and excessive growth of the upper jaw. Sometimes the design is used to treat orthopedic problems, in combination with other devices.
Distal bite and methods for correcting it
A distal malocclusion is a malocclusion in which the lower jaw is strongly pushed back relative to the upper jaw. To correct a deep distal skeletal bite, braces alone are not enough, since the position of the lower jaw must be changed.
There are several methods for changing the position of the lower jaw (correcting distal bite):
- surgery to change the size of the jaws;
- use of neuromuscular technologies;
- use of the Herbst apparatus.
The Herbst apparatus may be an alternative to surgical correction of malocclusion in adults, since not all patients are ready for surgery.
Dial-Dent orthodontists, after in-depth diagnostics and carrying out all the necessary calculations, can accurately say whether the Herbst apparatus can be used as an alternative to surgery to correct the bite, and, if possible, carry out effective orthodontic treatment without surgery.
Commentary by the chief physician of Dial-Dent S.V. Tsukora: “Thanks to the fact that the clinic employs very experienced and competent orthodontists who are proficient in various techniques and can work with various equipment, we can offer our patients a choice of treatment methods. In any case, this will be high-quality treatment, but the patient can choose a more comfortable option. The Herbst appliance, as an alternative to surgical correction of the bite, has helped many patients achieve the desired result without stress.”
Operating principle
The visual result is observed immediately after installation of the device. With constant tension, the lower jaw moves forward. During treatment, the ligaments and muscles of the jaw are stretched, which allows the mandibular joint to be correctly installed.
The effectiveness and surgical treatment is ensured through continuous exposure to the dentition. Within a short time after installation, the facial profile becomes more natural and harmonious. Similar designs are considered to be the Sabbath and Forsus springs.
Examination of the face and oral cavity.
When examining, you need to pay attention to:
- Facial symmetry;
- Skin of the face;
- Opening the mouth;
- The height of the lower third of the face;
- The degree of severity of nasolabial and chin folds;
- Red border;
After examination, according to indications, radiography, graphic recordings of the movement of the lower jaw, recordings of the incisive and articular tracts are performed.
And also, according to indications, special surgical and therapeutic preparation is carried out:
At the same time, the shape of the alveolar process is corrected, plastic surgery of the alveolar process is performed, an artificial socket is created, the vestibule and floor of the oral cavity are deepened, cords and scars of the mucous membrane are eliminated, etc. etc.
Preparing for installation
First, the doctor examines the oral cavity in detail. It is necessary to check the integrity and health of all teeth, especially molars. Preparation for installation consists of treating all teeth, replacing old fillings, and sanitizing the dentition.
Also during this period, the degree of the occlusion defect is assessed, impressions are taken, which are then sent to the laboratory.
Stages of treatment
- Preparation. At this stage, the oral cavity is sanitized and caries is prevented. Sometimes surgical preparation of the cavity for installation of the Herbst apparatus is required. This could be plastic surgery of the labial frenulum, the vestibule of the mouth, or tooth extraction. Additional measures at this stage: consultations with a speech therapist, myogymnastic exercises for the muscles of the mouth and lower jaw, normalization of breathing. Doctors strongly advise getting rid of bad habits.
- Correction. Some patients require alignment of dental arches and correction of jaw position. It is recommended to use removable orthodontic appliances: with springs, to expand the arches.
- Installation. The Herbst appliance can be combined with other orthodontic devices.
- Treatment. Alignment of teeth in both jaws. Retainers allow you to consolidate the result immediately after removing the device. At this stage, it is necessary to achieve tight fissure-tubercle contact (tooth relief).
- Consolidation. Stabilization of the bite is carried out thanks to the correct position of the tongue, muscle functionality, and nasal breathing. To ensure tight jaw contact, removable and non-removable retainers and elastopositioners (special silicone mouthguard) are used.
Fit
- Crown preparation. The sixth tooth is treated on the upper jaw, and the fourth molar on the lower jaw. The procedure is carried out under local anesthesia: 2 mm are removed from the upper surface of the enamel, and 1.5 mm from the sides. This is necessary to ensure that the crown is fixed and does not interfere. Finally, the teeth are treated with a product that increases the porosity of the enamel (phosphoric acids). A substance is also applied that promotes adhesion (bonding of the tooth and crown).
- Installation of crowns. Crowns are placed on the treated molars. For this, high-strength cement or composite is used. Power rods and bushings are secured using bandage rings and C-clamps. If the Herbst apparatus is attached to a bracket system, then first the structure is attached to the arch with special centers. The centers have gaps that allow them to catch on the arc, then the rods are attached to them with mini-screws. The centers should be located near the supporting teeth (on the upper jaw between 5 and 6, on the lower jaw 3-4).
- Correction of bushings and rods. The structure is inspected immediately after the procedure and regularly during treatment. If necessary, you can shorten them. It is necessary to maintain a balance: short rods slip out of the bushings, and long rods injure the mucous membrane.
Wearing rules
- exclude strong mechanical impact;
- watch the C-shaped clamps (if deformed, consult a doctor);
- monitor the traction (partial and complete flight can cause severe injury to soft tissues and the larynx).
Functional
By function, such devices can be divided into:
- Distalizing
. If the baby tooth was removed too early, and the permanent one managed to move forward and take its place, so-called “distalization” is required - moving the tooth back. As a result of this process, we are able to create space for all the permanent teeth without resorting to permanent tooth extraction or separation. For distalization, devices such as Pendulum, Pendex, Distal Jet, etc. are used. - Expanding
. Expansion during the period of primary and mixed dentition occurs as efficiently as possible - since the impact extends not only to the teeth, but also to the jaw itself (a skeletal effect is achieved). At the age of 6-11 years (and sometimes later), the maturation of the bone sutures has not yet been completed and this age is considered the most favorable for obtaining true expansion of the upper jaw.
Using retainers
The duration of treatment depends on the patient's age and the degree of the defect. Often this is 3-6 months with regular orthodontic consultations. Wearing the device for six months allows you to correct complex jaw deformities in children under 15 years of age.
Since the device is aimed at treating complex defects that can only be corrected by surgery, retention is very important. The quick effect of wearing the device is not final. After removing the system, you need to consolidate the results.
Dentists use special devices to keep the jaws straight, called retainers. Wearing retainers prevents teeth from returning to their original position.
After braces, retainers are indicated for several hours a day. After the Herbst apparatus, additional fixation is required for 20 hours a day. This is why permanent retainers are recommended. They are invisible during conversation, but provide fixation of the dentition.
On average, retainers are worn for another 2 years after the device. Sometimes patients have to wear retainers for the rest of their lives. During this period, the muscles and ligaments in the joint are strengthened, and functional adaptation occurs.
Orthodontists offer different retainers to choose from. The most popular are removable transparent aligners or non-removable systems that are attached to the inside of the teeth. The orthodontist can also recommend an LM activator. This is a special type of trainer - a removable silicone device for eliminating dental defects. It must be worn several hours a day and while sleeping.
Orthodontic dentistry
| Name of service | Price |
| Consultation with an orthodontist | 1000 ₽ |
| Diagnostic visit to an orthodontist with drawing up a treatment plan | 4400 ₽ |
| Production of control diagnostic models | 2000 ₽ |
| Single jaw orthodontic plate | 16000 ₽ |
| Double-jaw orthodontic appliance | 23000 ₽ |
| Orthodontic trainer | 17200 ₽ |
| Palatal expansion device | 28000 ₽ |
| Metal bracket system | 35000 ₽ |
| Sapphire bracket system | 55000 ₽ |
| Damon Q bracket system | 65000 ₽ |
| Damon Clear bracket system | 70000 ₽ |
| Activation of the bracket system (1 jaw) | 3000 ₽ |
| Removing the bracket system from one jaw | from 4300 ₽ |
| Retainer installation | 5100 ₽ |
| Diagnostics of treatment using StarSmile aligners Diagnostics includes: taking impressions of the jaws, photo protocol, image analysis (CT and TRG), treatment planning, building a computer model (Setup model) of the final result. You can learn about correcting your bite with orthodontic aligners in the article “You don’t need braces if aligners help!” | 10000 ₽ |
| Treatment with aligners. Correction of “light” defects (5-10 drops) | 80000 ₽ |
| Treatment with aligners. Correction of “medium” defects (11-20 caps) | 190000 ₽ |
| Treatment with aligners. Correction of “complex” defects (more than 21 caps) | 220000 ₽ |
| Re-making the mouthguard | 7500 ₽ |
Cost of the device and patient opinions
The price depends on the type of construction. The minimum cost of a template apparatus with four crowns and rods is 4,500 rubles. Treatment does not include tooth preparation or traction correction. A device with a base and additional elements (for example, springs) costs from 15,000 to 30,000 rubles.
According to patients, the Herbst apparatus is the optimal treatment for complex jaw defects. This treatment gives guarantees and in most cases implements them. The undeniable advantages of the device are the short treatment period and good results. Even in the 21st century, this is one of the best devices for eliminating jaw defects.
Sources used:
- Stancker TG et al. alocclusion influence on balance and posture: a systematic review // Manual Therapy, Posturology & Rehabilitation Journal
- Kurlyandsky V. Yu. Orthopedic dentistry. — 4th, corrected. - M.: Medicine, 1977.
- Official website of the Russian Dental Association
Diagnostics
The main goal of any diagnosis is to identify the cause of the problem. And make a diagnosis. Likewise, the diagnosis of distal occlusion is designed to identify the cause of closure in the second class. In order to separate the flies from the cutlets during treatment, so to speak. That is, dental causes of closure are in the second class from non-dental (maxillary, skeletal).
The main diagnostic methods are:
- Analysis of TRG (teleradiogram) of the skull in a lateral projection. It allows you to clearly determine all the skeletal (jaw) nuances of the problem. Both with the position of the jaws and with their sizes.
- Analysis of plaster models of jaws (for this, casts are taken). It allows you to clarify the “dental” nuances: the size of the teeth, the length and width of the dentition, the features of the relationship (including closure) of the upper and lower teeth
Analysis of TRG (teleradiogram) of the skull in a lateral projection.
Analysis of plaster models of jaws.
It is not recommended to fall below this diagnostic “bar”. Below - just by eye. But this, as we understand, is not the best option.
Diagnostics is the first and key step in the treatment of distal occlusion. Do you want to know why it’s impossible to do without diagnostics?
Impression from the lower jaw
There are six stages of creating a functional impression:
- Setting the workpiece to LF. The visitor closes his mouth and swallows the accumulated secretion. The muscles that compress the pharynx contract. When the spoon is dropped, distal shortening occurs.
- The person presses his tongue on his cheeks one by one. After dropping, the workpiece is shortened along internal oblique lines.
- The patient reaches his tongue to the corners of his mouth. The product is cut in zones 3, 4 and from the mouth.
- A man sticks out his tongue and reaches for the tip of his nose. Then he runs his tongue along his upper lip. The chin muscles become tense. The displaced tray is shortened near the front teeth on the intraoral side.
- The patient strains the pterygomaxillary muscles with the mouth wide open. Distal shortening.
- The cheeks are retracted, and as the position of the spoon changes, shortening is performed near 6, 7 and 8 units. As a result of tension in the mental muscles, the device is reset and created in the corresponding area.