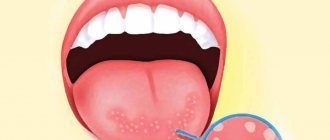
The powerful lymph nodes located around the pharynx cannot cope with the attack of the pathogen, so the body begins to produce antibodies that can find pathogenic bacteria, paralyzing their activity.
As a result, streptococci are defeated, but the child’s body produces so many antibodies that, in addition to foreign cells, the body’s own tissues, primarily the heart and joints, begin to suffer. Therefore, it is always better to entrust the treatment of sore throat in a child to a qualified doctor.
In 10% of cases, sore throat in children can be caused by Staphylococcus aureus, rarely pneumococcus, Haemophilus influenzae, chlamydia and fungal flora. Viral pathogens (adenoviruses, herpes virus) more often attack the body of children under 3 years of age.
How and why does infection occur?
Infection occurs by airborne droplets, from a sick person, by using shared utensils and eating contaminated food, as well as by a number of other factors:
- weakened immunity;
- hypothermia or consumption of cold foods and drinks;
- mouth breathing (for chronic adenoiditis, deviated nasal septum);
- irritation of the nasopharyngeal mucosa with a runny nose;
- recent viral diseases;
- inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs (sinusitis, sinusitis, otitis);
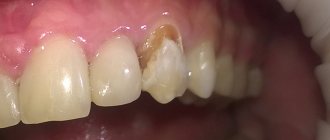
- caries and other oral infections.
Secondary tonsillitis in children can occur against the background of scarlet fever, diphtheria, mononucleosis, as well as blood diseases.
In any case, a sore throat develops rapidly, in a matter of hours, and is especially acute in children, accompanied by the main symptoms—a sore throat when swallowing and an increase in body temperature.
Actions before visiting a doctor
Before seeking medical help, it is recommended:
- Maintaining bed rest. This will make it easier for the body to withstand the increase in temperature and recover.
- Drinking plenty of fluids to speed up the elimination of pathogens from the body through sweat, saliva and urine. Moreover, you can drink not only water, but also warm tea (berry tea is best - raspberry, currant, lemon), compotes, herbal decoctions. When making lemon tea, do not put too much citrus in the drink. You should not give a child with a sore throat soda and sour drinks, as this is fraught with additional painful manifestations in the throat.
- Following a “gentle” diet. The child should eat often, and the portion should be small. During treatment, you need to avoid rough and spicy foods and minimize sweets.
- Gargling. In such a situation, it is better to use gentle herbal infusions, the raw materials for which are sold at any pharmacy. For rinsing, it is recommended to use products based on sage, chamomile, calendula, linden blossom, and eucalyptus. You can prepare the infusion yourself. To do this, you need to pour 3-4 teaspoons of the herb with hot water in a volume of 500 ml and leave to infuse for at least half an hour. It is necessary to gargle before or after eating food. The duration of the procedure is 2-3 minutes. After rinsing, eating and drinking is prohibited for half an hour.
Before starting drug treatment, you should definitely consult a doctor. It is also important to read the instructions for the medicine, which tell you how to dose the drug correctly, taking into account the patient’s weight or age.
Sore throat in children: forms and clinical manifestations
Depending on the nature of the change and the degree of damage to the tonsils, several forms of angina are distinguished.
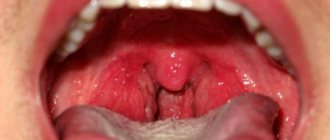
Catarrhal sore throat
A mild form, characterized by enlargement and redness of the tonsils, as well as the absence of purulent lesions. The child feels dry mouth, a whitish coating appears on the tongue, and the cervical lymph nodes are slightly enlarged. In addition to a sore throat that gets worse when swallowing, the child feels a sore and burning sensation. The temperature rises to 38 degrees, children complain of weakness and headache.
Follicular tonsillitis
A serious disease in which the tonsils become covered with purulent pinpoint follicles. On days 2-3, the ulcers open, leaving wounds that heal quickly. There is severe pain in the throat, radiating to the ear, making it difficult to swallow, children refuse to eat and drink. The lymph nodes are enlarged and painful when pressed lightly. Fever and chills are accompanied by a temperature of up to 40 degrees, vomiting, convulsions and fainting are possible.
Lacunar tonsillitis
In the lacunae, between the lobes of the tonsils, islands of yellow purulent plaque appear, which tend to unite into wide purulent foci. The symptoms are similar to those of purulent follicular tonsillitis, but are more pronounced and are accompanied by severe intoxication of the body. It hurts the child to turn his head, his mouth opens with difficulty, which makes speech slurred.
Viral (herpetic) sore throat
Most often, the development of the disease is facilitated by vitamin deficiency and weakened immunity. The tonsils become covered with red blisters, which burst, leaving small ulcers in their place. In addition to a sore throat, symptoms are acute respiratory in nature: cough, runny nose, abdominal pain, indigestion, as well as stomatitis and conjunctivitis. Lack of timely treatment of herpetic sore throat in children can lead to serous meningitis.
Fungal tonsillitis
A relatively mild form of sore throat that occurs in children under 3 years of age. It is distinguished by a coating of white, curdled flakes on the tonsils and, with proper treatment, goes away within a week.
A hoarse voice is one of the signs of laryngitis in a child
14.09.2021
Laryngitis in a child is a common viral infection that tends to recur. This mainly applies to young children,
because a child's larynx is more susceptible to infection and swells more easily than an adult's larynx due to its location and anatomical
buildings. This is usually a minor illness, but in some cases severe acute laryngitis may develop, which may
be life-threatening. Learn about the symptoms of laryngitis in children and how it is treated.
Laryngitis in a child - causes
The disease is caused by viruses, most often: parainfluenza virus, influenza A or B virus, adenovirus, RS virus, metapneumovirus.
There are also cases of bacterial infections, for example, during complications after an untreated cold. As a consequence, there is
damage to the mucous membrane, swelling around the larynx and narrowing of the airway. The disease usually develops in the 1st and 4th quarters
year is a period of increased viral activity, worsening weather conditions and intense heating of apartments. Warm and dry air
promotes the development of infections.
Laryngitis is usually mild and associated with high fever, infection and breathing problems, but is not life-threatening.
The most common type is subglottic laryngitis. It should not be confused with acute diphtheria laryngitis caused by the diphtheria bacillus.
However, life-threatening conditions may include: acute laryngitis and epiglottitis, which are manifested by a large tumor that interferes with breathing.
Why is this happening? Sensitive larynx in a child
Laryngitis and severe complications occur in young children because their airways are slightly different from those of adults.
The submucosa of the larynx in children is looser and contains many blood and lymphatic vessels , which makes it more prone to edema ;
the socket of the larynx is located much higher, the larynx is smaller, the epiglottis is flaccid, and the immune system is not yet formed. All this is done by the larynx in children
vulnerable to infections.
Laryngitis in a child - symptoms
Subglottic laryngitis in children occurs between 5 and 6 months of age, with the greatest incidence in the second year of life. Boys are more likely to get it
type of infection than girls, and affects about 6-8% of children under 5 years of age each year.
Symptoms of laryngitis in children appear suddenly and are preceded by several days of respiratory infections. Most often occurs at night or in the morning, and
symptoms may vary in severity, from mild inflammation, including an intermittent barking cough and hoarseness, to severe inflammation,
requiring emergency assistance.
Symptoms:
• The so-called stridor is a high-pitched sound when breathing due to a narrowing of the airway. • Characteristic barking cough. • Hoarseness. • Rude voice, even silence. • Mild to moderate shortness of breath. • Possible slight fever.
Acute symptoms of subglottic laryngitis:
• Severe shortness of breath, accompanied by increased work of the pectoral muscles. • Blue skin color. • Anxiety. • Impaired consciousness. • Breathing problems.
Narrowing of the airway in the subglottic region can quickly increase and cause severe shortness of breath, so should not be underestimated
infection, but appropriate treatment must be provided as soon as possible. The disease varies in intensity, and the symptoms of laryngitis
in children, initially harmless, can quickly worsen and cause respiratory failure.
Laryngitis in a child - treatment at home
Although the symptoms of laryngitis in children can be worrying, most cases are mild and can be treated well with
using home remedies. What will be effective for childhood laryngitis? Care should be taken to create an atmosphere of calm, because nervousness and
tension will increase the child's fear, which - based on the vicious circle effect - will increase shortness of breath and respiratory failure. To prevent
increased shortness of breath, it is useful to inhale cold, moist air, which reduces swelling of the larynx. It is recommended to open the window wide or remove
take the child to the terrace/balcony and let him breathe in the fresh, cool air. You should remember to dress your baby correctly so as not to catch a cold.
Another way to treat mild laryngitis in a child is to inhale saline and drink drinks. After the attack
shortness of breath stops, you should contact your pediatrician for effective treatment for laryngitis. The doctor knows best what to use to treat the larynx
child and what treatment will be most effective in each case. He will likely prescribe corticosteroids or other medications
to reduce swelling of the larynx.
Published in Pediatrics Premium Clinic
Why is a sore throat dangerous?
As practice shows, only in half of the cases are enlarged tonsils and sore throat caused by purulent sore throat. Many diseases, such as diphtheria or Epstein-Barr virus, have symptoms similar to sore throat. Therefore, only a qualified doctor with modern diagnostic equipment and a well-equipped laboratory can accurately determine the disease and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Each causative agent of sore throat is sensitive to a certain type of antibiotics prescribed by a doctor depending on the diagnosis.
Remember!
Incorrect or untimely treatment of sore throat in children, as well as relying on folk remedies for “red throat” can lead to serious complications and irreversible consequences.
Delay in diagnosis and prolonged treatment provoke the development of rheumatoid arthritis, vascular diseases, heart diseases (including rheumatic endocarditis), renal failure and many chronic diseases leading to disability.
How is the virus transmitted among children?
The influenza virus is transmitted from child to child by sneezing, coughing and talking.
Among children, contact transmission of the virus is common through household items, children's toys, dishes, bedding and various surfaces. The fact is that a virus - for example, the influenza virus - can survive for 2 hours on tables, door handles, pencils, etc. After playing with shared toys or touching the table, the child then touches his face, nose and eyes with his hands.
During epidemic seasons, outbreaks of ARVI and influenza are observed in collective places, most often kindergartens, less often schools.
ICD - pharyngitis:
- J02 - acute pharyngitis
- J02.0 - streptococcal pharyngitis
- J02.8 - acute pharyngitis caused by other specified pathogens
- J02.9 - acute pharyngitis, unspecified
- J31.2 - chronic pharyngitis
- J31.1 - chronic nasopharyngitis
Pharyngitis is rarely isolated as a separate disease; the diagnosis is usually acute respiratory viral disease (ARVI).
ARVI is a general name; the doctor usually specifies how exactly ARVI manifests itself.
This may be rhinitis (runny nose), pharyngitis (red throat), nasopharyngitis (inflammation of the nose and throat), etc.1,2
It is important not to confuse pharyngitis with tonsillitis.
To do this, let's understand the structure of the pharynx and oral cavity.
Classification of pharyngitis
Pharyngitis can be acute or chronic. Acute is inflammation that just arose (suddenly), and chronic is a disease that persists for a long time, and it may not bother a person, but under certain circumstances again cause complaints and anxiety.3
| CLASSIFICATION | A COMMENT | ||
| classification: | Classification of pharyngitis due to its occurrence: | a comment: | viral bacterial fungal allergic traumatic caused by exposure to irritating factors caused by gastrointestinal diseases (gastroesophageal reflux, stomach diseases, etc.) |
| classification: | Pharyngitis associated with specific pathogens: | a comment: | Epstein Bar virus for infectious mononucleosis Yersinia enterocolitica for yersinial pharyngitis gonococcus for gonorrheal pharyngitis Leptotrix buccalis for leptotrichosis of the pharynx |
| classification: | Types of chronic pharyngitis: | a comment: | hypertrophic (enlargement of the mucous membrane) atrophic (depletion of the mucous membrane) catarrhal (standard inflammation) mixed |
Mechanism of disease development
Acute laryngitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the larynx. The larynx is located in the front region of the neck. It connects the pharynx to the trachea and performs three vital functions:
- sound-producing (the vocal apparatus is located in it);
- respiratory;
- protective (prevents food and foreign particles from entering the trachea).
Under the influence of a number of factors (hypothermia, overstrain of the vocal cords, allergies, infectious diseases, etc.), the mucous membrane of the child’s larynx becomes inflamed. As a result, a sharp dilation of blood vessels occurs, edema develops, the lumen of the glottis narrows (or completely closes), speech function is impaired and breathing becomes difficult.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of acute laryngitis is not particularly difficult. The diagnosis is based on the presence of acute respiratory infections symptoms, as well as hoarseness, shortness of breath, and barking cough. Call a doctor: he will listen to complaints, examine the child, measure the temperature, listen to the lungs and make a diagnosis.
Disease prevention
As preventive measures, it is recommended to pay great attention to personal hygiene, strengthen the immune system and monitor a balanced diet. During periods of epidemics, it is advisable to avoid crowded places. But if a child shows the first signs of a sore throat, doing nothing or self-medicating is too careless. Please do not delay your visit to the doctor - call, make an appointment and come. We will be happy to help you!
Always yours, Doctor Zaitsev.
About the author:
ENT doctor of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences. Sci.