December 3, 2020
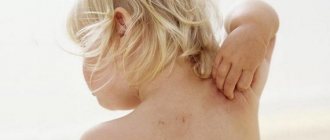
Contact dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin in an area that has come into contact with an irritating substance or environmental factor. Children under 12 years of age are most susceptible to the disease. The point is the structural features of children's skin and the weakness of its protective mechanisms. The disease manifests itself in any area that has been in contact with the irritant, but more often on the face, arms, neck, and groin area.
If the provoking agent is recognized in time and the child is protected from it, the inflammation is well treated and the symptoms quickly pass. When the cause is difficult to identify or parents do not consult a doctor on time, the course of the disease becomes more severe.
Contact dermatitis occurs:
- simple - local irritation by some factor;
- allergic.
The second option will appear when the child has an increased sensitivity to this substance. The first interaction with it is outwardly unnoticeable, but chemicals are formed in the skin that bind to immune cells - T-lymphocytes. Immune cells remember the stimulus. Upon repeated contact, which can occur after a long time, T-lymphocytes trigger an allergic reaction and cause skin symptoms.
How to recognize allergic contact dermatitis in a child
The contours of the inflammation often coincide with the outlines of the object that caused the irritation. The rash spreads little beyond the area of skin that came into contact with the causative factor. The skin here becomes red and swollen, very itchy, blisters, wounds and crusts appear.
Fungal and bacterial infections easily attach to wounds and suppuration occurs. Babies may experience an increase in general temperature.
Frequent exacerbation in the same places leads to unpleasant outcomes: areas of increased or decreased pigmentation, scars, thickening and roughening of the skin.
If you notice a rash or red spots on your child’s skin, be sure to see a doctor to get tests done to determine the exact cause and begin treatment.
The disease may worsen. To prevent this from happening, you need to find and eliminate the provoking causes.
Diagnostics
There is no specific test or examination to confirm the diagnosis of atopic dermatitis; the diagnosis is made clinically. The doctor will examine the rash and ask about the child's symptoms and family history of atopy and allergies. A history of eczema in family members (either as a child or still today) will be an important clue.
Your doctor will rule out other conditions that may cause your skin to become inflamed or itchy. In case of difficulties with diagnosis or severe course of the disease, the pediatrician will refer the child to a pediatric dermatologist or pediatric allergist.
The doctor may ask you to eliminate certain foods (such as eggs, milk, soy, or nuts) from your child's diet for 2 to 3 weeks before reintroducing them and monitoring symptoms. If the diet leads to relief of the rash, and provocation leads to its obvious exacerbation, this will confirm the diagnosis and the need for a diet.
Since there are no accurate laboratory methods for confirming the diagnosis of atopic dermatitis, there are criteria for standardizing the clinical diagnosis (the best known are the Hanifin and Raika criteria).
The criteria are divided into “large” and “small”. To make a diagnosis of atopic dermatitis, it is necessary and sufficient to detect three major and three minor criteria in the patient.
The big ones include:
- itching;
- dermatitis affecting the flexor surfaces in adults, or the face and extensor surfaces in infants;
- chronic or recurrent dermatitis;
- a personal or family history of skin or respiratory allergies.
Small ones include:
- specific facial features: facial pallor, erythema, hypopigmented spots, dark circles under the eyes, cheilitis, infraorbital folds, recurrent conjunctivitis, anterior neck folds;
- typical triggers: emotional factors, environmental factors, food, skin irritants;
- typical complications: susceptibility to skin infections, impaired cellular immunity, predisposition to keratoconus and anterior subcapsular cataracts, immediate skin reactivity;
- other signs: early age of onset, dry skin, ichthyosis, hyperlinearity of the palms, piliary keratosis, dermatitis of the hands and feet, nipple eczema, white dermographism, white pityriasis, perifollicular accentuation.
An explanation of each of these symptoms is beyond the scope of this article; The criteria are given here to help you understand what the doctor is guided by when making a diagnosis of atopic dermatitis.
There are also various scales for assessing the severity of atopic dermatitis used by doctors and scientists, the most famous of which is the SCORAD scale. In this scale, the doctor must note the number, prevalence and severity of symptoms of atopic dermatitis, express them in points, sum up the points and, based on this sum, set the severity of the disease.
External causes of the development of allergic dermatitis in children
The disease can be caused by one of the factors or a combination of several.
- Physical - friction or pressure on the skin of fabrics, leather products, high or low temperatures, humidity, electric current, ultraviolet or x-rays.
- Chemical - various acids and alkalis, substances included in creams and hygiene products, medicines, tobacco smoke.
- Biological - sap and pollen of plants, bites and secretions of insects and animals.
Of the plant agents, the most dangerous are the juice of celandine, hogweed, nettle, pollen of meadow and weeds.
In industrial cities in winter, there are widespread cases of contact dermatitis under the eyes and on the hands of children. Three factors are combined here: cold, chemical impurities in the air and touching the skin with wet mittens.
In infants, allergic inflammation can be caused by a combination of high humidity in diapers, fabric friction and the action of inappropriate cream.
A special type of contact dermatitis is phototoxic, when sunscreens degrade in sunlight and cause allergic damage to the epidermis.
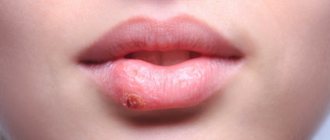
What is oral allergy syndrome?
Another little-known reason why a child's palate itches is oral allergy syndrome. It occurs in patients with pollen allergies (50-75% of cases). The syndrome is accompanied by itching and subsequent swelling of the mucous membrane of the lips and oral cavity, including the palate, after eating vegetables, fruits or nuts.
This health problem occurs because the proteins found in some fruits and vegetables are very similar to the proteins found in pollen. They can confuse the immune system, causing an allergic reaction or worsening existing symptoms, which is called cross-reactivity.
When oral allergy syndrome develops, children and adults may react to different foods depending on what type of seasonal allergy they suffer from. For example, if you are allergic to birch pollen, apples, celery, carrots, almonds and hazelnuts can cause a reaction. If your child's palate is red and itchy after eating nuts, you should consult an allergist, as mild symptoms may only be the beginning of a more serious allergic reaction to nuts.
Children with grass allergies may have the same reaction to peaches, tomatoes, melons and oranges. Those who react to ragweed may experience itching and swelling of the oral mucosa when eating foods such as banana, cucumber, melon and zucchini.
Dermatitis in a child and psychosomatics
Skin health directly depends on a person’s mental well-being. Stress changes hormonal levels and metabolism, causing disruptions in the functioning of the immune system. Therefore, a calm emotional state will prevent exacerbation of the disease and delay the first appearance of symptoms.
When faced with contact dermatitis, analyze the causes and identify the allergen that caused it.
It's not always easy. To be sure of the correct diagnosis, conduct the necessary tests and receive treatment, come for a consultation at our center. In addition to treatment, you will learn how to properly prevent this disease. December 3, 2020
Author of the article: dermatologist Mak Vladimir Fedorovich
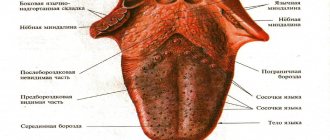
The main causes of itchy tongue
The cause of itching of the tongue can be: an inflammatory process, traumatic damage to the mucous membrane, nervous disorders or other infectious, viral, bacterial diseases.
Glossitis
This damage to the tongue, which is inflammatory in nature, occurs both as an independent disease and as a symptom of other pathologies.
The disease has acute and chronic forms.
Glossitis occurs as a consequence of impaired capillary circulation of the mucous membrane.
Most often, glossitis is a combination of various causes. It begins from the sum of problems of the oral cavity and digestive tract that arise as a result of a burn or injury.
There are several types of the most common glossitis:
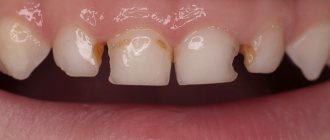
- Catarrhal - the tongue becomes bright red, becomes smooth and shiny. There is a thick coating on the tongue. The patient experiences a feeling of pain, burning of the tongue, loss of taste. The causes of this type of glossitis are: influenza, acute respiratory infections, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, multiple caries.
- Ulcerative is one of the signs of such a disease as ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis. Occurs against the background of a sharp decline in immunity, forming erosions and ulcers, a dirty gray coating and bad breath.
- Desquamative – experts consider it as a symptom of systemic pathologies of the body: disturbances in the functioning of digestion, hematopoiesis, failures of metabolic processes (metabolism), kidney disease, dysbacteriosis, etc. It is expressed in the form of bright red shiny spots, or areas of thickening of the papillae of the tongue.
- Tongue abscess - occurs and develops when the tongue is injured. This type of glossitis lasts quite a long time and is difficult. With an abscess, the tongue swells, and some parts of it become red. If the lesions are located deep at the root of the tongue, difficulty swallowing and breathing may occur.
The second classification divides glossitis into 3 groups:
Inflammatory – infectious in nature:
- viral;
- herpetic;
- candida;
- bacterial.
Selected pathologies:
- surface;
- deep;
- catarrhal
Non-inflammatory are symptoms of other diseases:
- desquamative;
- median rhomboid;
- atrophic;
- Gunter's;
- folded;
- interstitial;
- villous.
Glossitis occurs in acute and chronic forms. The acute form appears as inflammation of the tongue, change in color and structure. Chronic glossitis has more varied symptoms, but, as a rule, the disease is diagnosed by the presence or absence of papillomas.
Signs of glossitis are:
- the appearance of uneven plaque spots on the tongue;
- ulcers;
- change in tongue color;
- swelling and presence of teeth marks on the lateral surfaces of the tongue;
- difficulty moving the tongue;
- bad breath;
- impaired salivation.
Mechanical injury
A child can easily injure his tongue while eating, or when chewing on another rattle.
Often in babies, injuries can occur during teething.
Lollipops (and other solid foods) can cause tongue injury in older children if not taken care of.
And sometimes even when talking, you can damage your tongue by biting it.
In addition, you can get injured:
- dental instruments – bur, probe;
- exposure to a sharp object - fork, bone, knife;
- biting the tongue during an epileptic seizure;
- injuries from a blow to the face.
Due to mechanical trauma, ulcers and erosions form on the surface of the tongue.
Mechanical injuries to the tongue are usually not treated; they heal on their own over time. The recovery period for injured tissue depends on the depth and location of the tongue lesion.
Nervous disorders
Experts do not give a definite answer, but are inclined to believe that disorders of the nervous system and its malfunctions can also cause itching and worsening of the condition.
If a person is in a state of depression, then the volume and composition of his saliva changes.
If a child has become overly aggressive, or, on the contrary, is silent and shows nervousness, then it is necessary to pay close attention to this point.
Talk to him, find out the reason for this behavior, provide the child with psychological relief so that the accumulating negative energy does not destroy the baby’s nervous system, lead to a breakdown, and subsequent deterioration of his condition.
Deficiency of nutrients
As a rule, in the spring, the body of a child, and even an adult, begins to lack some vitamins. As a result, itching of the tongue can begin due to a deficiency of nutrients in the body. A lack of iron, vitamin B12 and folic acid can provoke various types of pathologies in the body.
If there is a lack of vitamins of various groups, in addition to itching on the tongue, the following may appear:
- white and red pimples;
- the tongue may become inflamed;
- small cracks appear on the lips, and peeling around;
- lack of vitamins B2 and B6 can cause conjunctivitis;
- Itching and inflammation can also result from a lack of niacin and vitamin C.
To make up for the deficiency, you need to follow your diet. Meals should be balanced, eat more fruits and vegetables and walk outdoors more often.
Candidiasis
This is an infectious disease of the oral mucosa, also known as thrush. It is caused by the Candida fungus due to extremely low immunity, and as a concomitant disease with problems of the gastrointestinal tract. Oral thrush in children is caused by yeast flora.
Candidiasis exists in 2 forms - acute and chronic. The acute form is typical for children.
You can get a candidiasis infection in 3 ways:
- contact;
- airborne;
- intrauterine.
The development of candidiasis can also be stimulated by:
- increased acidity in the oral cavity;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- use of hormone-containing drugs.
If a child has contracted the candidiasis virus, then it is easy to determine it yourself, but you must immediately consult a doctor to prescribe effective treatment, and not do it yourself. A strong white coating appears on the gums, the inner surface of the cheeks, and on the tongue, under which damaged tissue is hidden. Foci of inflammation can spread to the tonsils, pharynx, corners of the mouth and lip contour.
Associated symptoms expressed by older children may be complaints of pain in the oral cavity when eating, itching, burning in the oral mucosa.
Children show discomfort by refusing to eat, excessive tearfulness, irritability, and sleep disturbances.
How to treat seasonal allergies in children?
Over-the-counter antihistamines are most often used for allergy symptoms. Typical antihistamine active ingredients found in over-the-counter medications include diphenhydramine, loratadine, cetirizine, or chlorpheniramine. Most often, antihistamines that do not have a sedative effect are used for children - loratadine or cetirizine.
Over-the-counter allergy medications should only be used in children over 6 years of age. If your child is under 6 years of age and has allergy symptoms, talk to your pediatrician about prescribing the best medications available at the lowest appropriate dose.
What are pinworms in children?
Infection with worms is often caused by eating unwashed fruits.
Enterobiasis is a disease caused by the appearance of pinworms in the small and large intestines of the body. Pinworms are also called worms. These parasites look like small white worms. They are small in size: females up to 1.5 cm, and males up to 5 mm. Their color is always white. The habitat in the human body is the intestines, but there are exceptions when they live in other organs. The female parasite reproduces quite quickly. Every day at night, she can lay eggs near the anus or in the folds of the skin. The affected areas may be the perineum.
During the process of the emergence of worm embryos, the child experiences severe itching as the infected area of the skin becomes vulnerable. Nematodes mature quite quickly and penetrate the intestine and attach themselves to the intestinal walls. After the female has laid eggs, she dies. Girls have a hard time coping with this disease. Worms, crawling out, can penetrate the mucous membrane of the external genitalia, causing additional infections. This does not mean that the disease does not need to be treated. During a short lifespan, a female can lay many eggs. The disease is gaining new momentum and the baby’s condition is worsening.
If no treatment is given, the parasite dies after 50 days.
Treatment of pinworms in children using traditional methods
Traditional medicine allows the use of natural ingredients. But this does not mean that it can cure the disease. It can be used as an addition to the doctor’s main prescriptions and after his approval. The most popular home methods:
- Garlic juice. This juice is mixed with water in equal proportions and given to the child before bedtime. You should drink it with a large glass of water. The procedure is carried out over 3 days.
- Onion. The onion is brought to a mushy state and seasoned with sunflower oil. Give to children before bedtime with plenty of water. Use the pulp for 5 days.
- Pumpkin seeds. Raw pumpkin seeds are crushed and seasoned with olive oil. Give a tablespoon three hours before breakfast to children.
- Beetroot juice. Drink half a glass in the morning and before bed. The course lasts 2 weeks.
- Wormwood tincture. Brew a teaspoon of chopped herbs into 300 ml of boiling water. Let it brew for about 10 minutes. After straining, the child should drink the decoction. Carry out the procedure within 4 days. Green vegetables and fruits. It is believed that such products, due to their taste, destroy a favorable environment for the development of parasites.
Food allergies
Hives and facial swelling are the most common symptoms of food allergies. Hives appear as raised pink bumps with pale centers, similar to insect bites. Other symptoms include itching and swelling in the mouth, runny nose and cough, vomiting and diarrhea. Life-threatening allergic reactions may also include difficulty breathing and/or swallowing. The medical name for this phenomenon is anaphylaxis. Most of these reactions occur suddenly within 10-20 minutes. All this happens within 2 hours after eating a certain food containing allergens.
Diagnosis of enterobiasis in children
Some believe that infection occurs from pets
If they detect signs of pinworms in their children, parents contact their pediatrician. He, in turn, can prescribe an examination himself, or send him for a consultation with a gastroenterologist and parasitologist. First of all, the specialist will conduct a survey, including basic questions to determine a possible diagnosis. Key questions will include:
- Main complaints
- First symptoms and when they appeared
- How many family members have similar symptoms?
- Does the family practice good hygiene?
The next step will be to assign research:
- Examination of feces. The laboratory takes a stool test for worm eggs. For the analysis to be reliable, it is necessary to take the biomass to the laboratory within an hour after defecation. It is necessary to prevent urine from coming into contact with feces. Analysis from different parts of the stool is collected in a disinfected container. 2 teaspoons are enough for an accurate diagnosis. If the basic rules are not followed, the result may be unreliable.
- Scraping in the anal area. The study is carried out in the morning. The patient should not go to the toilet before this and should not wash himself. The procedure is quite simple: a special film is applied to the skin area. Helminth eggs stick to it, which can be detected under a microscope.
- Blood tests. A general blood test is done. In the presence of enterobiasis, eosinophilia is detected - an increase in eosinophils in the blood. In rare cases, anemia is detected, a decrease in hemoglobin and red blood cells. This disease can be caused by a large number of helminths and a simultaneous infectious disease
If there are any signs of enterobiasis, it is recommended to immediately visit a doctor and undergo the necessary tests. Timely detection and treatment of the disease eliminates the development of complications.
Pinworms - Baby food
“Sadikov's disease” - enterobiasis?
When a child’s body is affected by worms, the mother must take care of the baby’s specific nutrition. Eating the right foods can speed up the healing process. It is worth including in the diet:
- Spicy dishes. Pepper and spicy dressings worsen the habitat for pinworms.
- Sour vegetables and fruits. In an acidic sphere, parasites die faster.
- Horseradish with mustard. Not all kids will like such a specific product. But it undermines active reproduction and temporarily paralyzes the worms.
- Walnuts, flax seeds, pumpkin seeds. Such products help destroy parasites in the intestines.
- Olive and vegetable oil. Relieves irritation of the intestinal walls.
- Dairy products. With their use, medications are better absorbed and the intestinal microflora is not disturbed.
During the period of illness, it is recommended to exclude sweets, fatty foods, and foods with a chemical composition - the consumption of harmful foods creates all the conditions for the further proliferation of pinworms in the child’s body.
What else do parents need to know?
One in five people suffers from allergies at some point in their lives. Hay fever is the most common type of allergy. It is easily treated by avoiding allergens, washing the child in the shower after returning from outside during flowering season, over-the-counter medications, and sometimes additional prescription medications. Most children with hay fever only need allergy medication during seasonal outbreaks.
Allergy symptoms often change with age. Allergy symptoms can worsen during early childhood and often disappear as people get older.
Drug labels list the ingredients of allergy medications. Use the lowest dose possible to treat symptoms, and check with your child's doctor if he is younger than 6 years old before giving him an over-the-counter antihistamine.