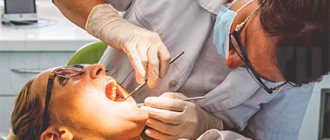
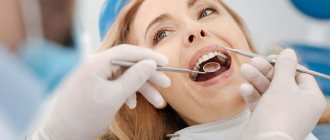
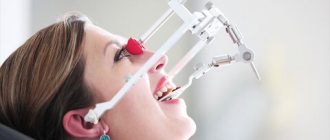
Modern dentistry cannot be imagined without accurate diagnostics. A set of measures to establish a diagnosis is indispensable in the treatment of teeth and gums; it plays a key role in implantation and prosthetics, and is also important during orthodontic treatment.
Diagnostics is carried out at all stages of preventive and therapeutic tasks. The dentist-therapist resorts to full diagnostic measures when the patient comes to the clinic. The specialist also uses operational diagnostic measures as an intermediate stage of treatment after installing a filling. Upon completion of prosthetic procedures, full diagnostics allows you to evaluate the results and correct them in a timely manner.
Dental diagnostics is, without exaggeration, 50% of the success of treatment and prevention.
Diagnostics involves the following activities:
- History - information about the problem from the patient himself. Mandatory primary stage of diagnosis. The patient indicates the area of concern - which tooth hurts, where there is increased sensitivity, etc.
- Introduction to medical history . Modern technologies make it possible to provide a specialist with images and examination results taken earlier. The information in the medical history card can greatly facilitate the doctor’s work when developing the optimal treatment strategy, so it is important to have it with you whenever possible.
- A thorough visual examination and examination of the condition of the teeth and gums. The specialist determines the problem by the appearance of the tissue.
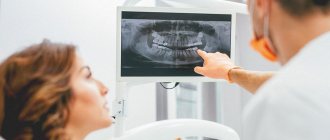
- Instrumental (X-ray) examination is a study using special equipment. A key element of modern dental diagnostics.
X-rays of teeth
Milk, mixed, permanent dentition. Their characteristics.
Milk: 20 teeth, 1 increase in bite during teething 1 mol. molar, shape of dental arches - semicircular, physiological trema/diastema, physiological abrasion of teeth, distal surfaces of second piers. molars form the mesial stage, resorption of the roots of the molars. teeth, reducing the depth of the incisal overlap to a direct ratio, the formation of the TMJ ends.
Replaceable: root resorption, physiological abrasion, trema, eruption of permanent teeth (timing, sequence, pairing), 2nd stage of increasing the bite during eruption 1st post. molars
Constant: 3 increase in bite during the eruption of canines and 2 molars, 32 teeth, upper z.r. - semi-ellipse, lower - parabola, each tooth has two antagonists except (3.1, 4.1, 1.8, 2.8), the upper tooth is in contact with the same and behind the lower one , normally - med.cheek tubercle of 1st molar. located in the fissure between honey. and Wednesday cheeks with cusps of 1 molar of the lower part, and the upper canines are located between the lower canines and premolars, the sagittal gap between the incisors is 1-2 mm, the upper incisors overlap the lower ones by 1/3 (incisal-tubercle contact between them), the upper lateral teeth overlap the lower ones by 1/3 the depth of the longitudinal fissure, the palatal cusps of the upper molars and premolars lie in the longitudinal fissures of the lower ones, the midlines coincide, tight contacts, between the most protruding cusp of the second molar of the mandible and the cutting edge of the lower central incisor there should not be a distance of more than 1.5 mm. (Curve of Spee).
X-ray diagnostics
The use of X-rays and other high-precision equipment in diagnostics allows us to obtain, in real time, accurate images of the desired areas of the oral cavity in optimal resolution.
What equipment is used for instrumental diagnostics:
- Radiovisiograph (visiograph, videograph, dental imaging apparatus) is a device that converts X-ray data into a digital image on a computer in real time. The dentist, using a visiograph, controls the treatment procedure without leaving the chair with the patient. The device allows you to quickly take a photo and obtain an image of the problem tooth.
- Digital 3D orthopantomograph - allows you to take a panoramic image of the desired area of the skull or an individual tooth. The device is indispensable for prosthetics, treatment, implantation, bite correction (orthodontics), etc.
- Rheodentograph is a device for accurately assessing the functional state of the pulp (tissue containing nerve endings) of a tooth according to hemodynamic indications. Allows you to quickly, painlessly and accurately determine the extent of tissue damage. The device is important in the gentle treatment of pulpitis.
- A tool for diagnosing early and latent caries. Pathological processes of hard tissues in the early stages are often difficult to determine. At the same time, treating caries in the early stages allows you to solve the problem with minimal impact on the tissue. The device allows you to effectively identify crisis areas on the tooth.
The capabilities of the equipment allow you to print the results or transfer them to electronic media.
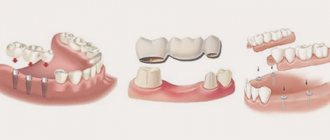
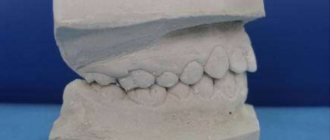
Diagnostic measures include control modeling methods, as well as taking impressions. These methods can significantly increase the effectiveness of orthodontic treatment and prosthetics.
The main task of the dentist is to maintain the health of teeth and gums, maximize tissue preservation, and ensure functionality and aesthetics. All these problems cannot be solved without competent dental diagnostics.
Practical significance of the photo protocol
Creating a photo protocol is necessary for a more detailed assessment of the condition of the dental system. When diagnosing a disease, photography is an integral part of the procedure.
The manipulation is carried out in accordance with the protocol, so even the smallest details are subject to analysis and assessment by a specialist.
According to the object, the photo protocol can be extraoral and intraoral. An important nuance of the procedure is the position of the patient’s head; when creating a series of images, it must remain unchanged.
What information can be obtained as a result of creating an extraoral protocol:
- indicators of tension in the muscular system of the neck and head;
- data on the symmetry (asymmetry) of the dental system;
- information about the individual characteristics of the patient’s appearance.
The intraoral protocol allows:
- analyze the condition of the jaws;
- identify the presence of phenomena such as tooth abrasion or wedge-shaped defect;
- assess the position of the teeth.
The photologging technique is used to evaluate both intermediate and final results.
Hardware methods of functional diagnostics
Detection of dental ailments in the initial stages is carried out using devices such as radiovisiograph and orthopantomograph. The radiation exposure of these devices is within normal limits, so the risk of adverse effects is excluded.
Hardware methods include:
- tomography;
- rheodentography;
- electroodontodiagnostics.
When making a final diagnosis, dentists adhere to the principle of complexity. It is possible to obtain an overall picture of the condition of the patient’s dental system only through a series of diagnostic procedures and their subsequent analysis.
Scanning facial parameters using the Proface scanner
The final stage with the participation of the patient is scanning of facial parameters. There are two options here - use a facial scanner and/or a special application for Mac OS on the iPad.
The Proface scanner or program creates a three-dimensional model of the patient's appearance. For this purpose, a specially developed craniometric analysis algorithm is used (craniometry is a technique for measuring the skull). That is, many points of the skull are calculated - due to this, a copy of the patient’s face and all the bones of the head is transferred to the computer.
In addition, photometry is carried out - photographing the face is necessary to evaluate the result “live” and maintain a digital photo record.
An example of photometry is photographing the face from all angles before and after dental implantation with the installation of a fixed prosthesis immediately
We approach diagnostics wisely! We use the latest developments and artificial intelligence! We make an accurate diagnosis and find the best solution to your dental problems.
Sign up for a consultation
Teleradiography of the skull
Diagnostic methods in dentistry include examination of the skull. Before orthodontic treatment, the doctor needs to see the angle of inclination of the teeth and the degree of their displacement. Using TRG, the doctor can examine in detail all parts of the skull from all sides by rotating the image. During teleradiography, the patient does not touch the device.
Teleradiography of the skull is performed in three projections: frontal, axial and lateral. Frontal projection is a basic photograph of the head, which shows the condition of the teeth, bones, jaws, symmetry or asymmetry, and inflammatory processes. The axial or chin projection helps the implantologist evaluate the structure of the nasal cavity, cheekbones, and sinuses of the upper jaw before implanting the upper teeth.
In Dental Guru clinics, the orthodontist performs teleradiography of the skull in a lateral projection to determine the bite, plan further strategies and tactics for correcting it. After the examination, diagnostic models will be made that will allow you to more accurately plan your treatment and even show the final result.
Computed tomography of teeth
But on an orthopantomogram, since it is a two-dimensional image, nuances are not always visible, and it is impossible to accurately determine the volume and height of bone tissue. Therefore, before implantation and in other cases, the doctor will do a CT scan. This examination is also absolutely safe. The final three-dimensional image of your jaws will show both the canals to the therapist and the volume of bone tissue to the implant surgeon. Based on computer diagnostics in dentistry, a doctor can prepare precise surgical templates for implantation and prosthetics.
Optical strip scanning
This technology shows better results compared to the above. A special grid or stripes are projected onto the object. Based on their distortions, the relief of the scanned surface is determined. In this case, it is enough to determine the coordinates of the object’s surface using one camera and additional structured lighting. This approach is most often used in modern orthopedic dentistry.
Structured light can be different - laser, infrared, visible. The main condition is automatic recognition of these lines by software. The known distance between the projected stripes allows you to calculate the coordinates of the surface points. The more lines, the more accurate the result will be. The more cameras are used, the higher the scanning speed will be.
Development of a prosthesis model in the Proart program
All information obtained during complex functional diagnostics is loaded into a single virtual space and combined into a common model. This may include a CT image of the jaw system (computed tomography data), an axiogram, scans of the face and oral cavity from the inside, virtual prototypes of prostheses, cephalometric analysis data (that is, parameters of the facial skeleton) and much more.
It turns out to be a kind of virtual double of the patient. But, unlike a real person, we can look “under the skin” without any harm and see how the teeth and jaws move and interact, where there are problems and what will change after installing the prosthesis.
We also use the additional Prosthetics software module, which is designed specifically for the orthopedic field. With its help, we can flexibly plan treatment and send complete data about the future prosthesis to our laboratory.
Initial examination
Diagnosis of diseases in dentistry begins with a patient interview and visual examination. It is very important to tell your doctor the symptoms of the disease in detail. These may include: pain, discomfort when eating hot or cold food, sweet or sour taste. If you have allergies to any medications, hereditary or genetic diseases, be sure to tell your doctor. Smoking can also affect the condition of your teeth and gums.
The dentist will examine your mouth using a mirror and probe. For a detailed examination, all Dental Guru clinics have microscopes. If the problem and its solution are obvious, then if you agree, treatment can begin immediately. To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor will conduct the necessary functional diagnostics.
How much does such research cost?
Equipment for functional computer diagnostics of the jaw system is quite expensive. This also increases the price for patients - clinics charge a lot of money for individual procedures even without further treatment. This can also be attributed to the disadvantages of technology. Accordingly, many doctors and laboratories prefer to work with more familiar and accessible mechanical equipment.
In our center, such diagnostics are included in the cost of comprehensive dental restoration on implants, when installing veneers, as well as extended dental bridges. There is no need to pay anything separately - we make sure that our patients receive a guaranteed treatment result and are satisfied with the new prostheses, both in terms of aesthetics and their functional side. If you need functional diagnostics as a separate service, then its cost varies from 15,0000 to 30,000 rubles, depending on the amount of data required.
Types of scanners
- Stationary, or extraoral. They appeared earlier than the others and became widespread. The scanning field is 80 x 90 or 90 x 90 mm, which covers the plaster model of the entire dentition. Some modifications have limited scanning height. Accuracy – 5-15 microns.
- Intraoral. They appeared later, but are actively replacing their extraoral counterparts. Such scanners save the dentist’s time, since with their arrival in the dental laboratory there is no longer a need to stir the plaster and wait for it to harden, install pins, make collapsible models, and plaster them for scanning. However, intraoral scanners are still inferior to stationary scanners in accuracy (their indicator is from 30 microns).
- Facial. These devices stand apart from the previous ones and allow you to obtain a three-dimensional image of the face for planning the treatment of pulpitis, periodontitis, caries, taking into account aesthetic requirements.
The emergence of new diagnostic devices in orthopedic dentistry has simplified the doctor’s task and also reduced the time required to make a diagnosis and draw up a treatment regimen. Three-dimensional technologies have significantly increased the accuracy of therapeutic and orthopedic manipulations at all stages of exposure.
Diagnocat artificial intelligence: fast CBCT analysis, accurate diagnosis
Only in our clinic, Diagnocat artificial intelligence is used for CBCT analysis! The program uses 3D images to determine the condition of the teeth, finds problems and suggests how to treat them. In just a few minutes, Diagnocat will examine your CT scan, identify problem areas, and generate a report for each tooth. And the doctor will make an accurate diagnosis! More about Diagnocat here.
How long does a comprehensive diagnosis take?
Diagnostics using digital equipment and preliminary analysis of the results last from 30 to 60 minutes. All data is instantly transferred to the computer memory with simultaneous calculation and construction of virtual models.
Depending on the manipulation, clinical picture and stage of treatment, the set of diagnostic data may vary. For example, during complex restoration of teeth on implants, data is collected gradually, since there is a period of adaptation, and the creation of a full-fledged axiography is advisable at the stage of installing a permanent prosthesis.
However, basic parameters are taken BEFORE treatment. Thanks to them, the doctor will show preliminary results on the computer screen: whether there are any abnormalities in the bite and functioning of the joint. Optimal treatment options can also be assessed. This is a fairly fundamental question for many patients. After all, the doctor sees the clinical picture and the permissible “corridor” of manipulations, and can say whether, for example, it will be necessary to remove or move teeth if we are talking about partial prosthetics. This is also important for those patients whose teeth have been removed a long time ago and need to gradually restore obvious disorders of the jaw joint and bite relationships.
Are there any disadvantages to digital diagnostics?
The disadvantages of high-precision digital solutions include their low prevalence due to the high cost of the equipment, as well as the time spent by the doctor. The technologies are relatively new and are just beginning to come into practice. There are still few doctors who have a full range of equipment and can carry out the analysis inside and out. Most are just learning new products and using only individual devices - for example, myographs or face arcs. That's why you won't see them in every clinic.
Smile-at-Once is so far the only clinic in Moscow with a full diagnostic range of devices and programs for planning orthopedic treatment and creating prosthetics.
The importance of condylography in identifying dysfunction of the dentoalveolar system
Condylography is a method used to analyze the position of the temporomandibular joint. The main task of the manipulation is to establish the trajectory or, more simply put, the path of movement of the jaw. The technology significantly simplifies the diagnostic procedure and helps identify pathological processes.
Note! The information obtained as a result of condylography can be used not only when making a diagnosis, but also to implement the prosthetic procedure. Thus, the availability of data on the individual indicators of the patient’s TMJ movement trajectory allows the orthodontist to make the most suitable design.