What is needed to make a diagnosis for an orthopedic patient?
At the first visit to an orthopedic doctor, the patient is examined. Dentistry and orthopedics provides basic and additional examination methods.
The main examination methods include:
- Collection of complaints: at this point, the doctor asks the patient what the patient is complaining about right now. Accordingly, the doctor clarifies the problems that, from the patient’s point of view, need to be solved: difficulties in chewing food, mobile teeth, sensitivity in certain areas, pain when chewing in the temporomandibular joint, bleeding, pain in teeth covered with orthopedic structures and rubbing or poor fixation denture.
- Collecting an anamnesis of the disease: here the doctor clarifies the time frame - how long ago and how intensely certain complaints are bothering you.
- Collection of general anamnesis:
Past diseases: the general condition of the body, all diseases that the patient suffers from and data on allergic reactions are specified.
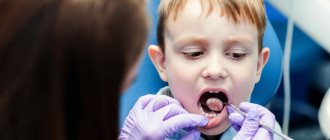
Visual inspection. The doctor examines the patient externally - the skin, the condition of the lymph nodes, whether the mouth opens freely and any external defects.
- The condition of the TMJ is determined without additional examination methods, that is, they pay attention to the degree of opening, uniformity of movement, the presence of clicks, crunching and pain when moving the joint, and also note the condition of the masticatory muscles.
- Next, the oral cavity is examined directly and a dental formula is drawn up. A dental formula is a short table in which, opposite each tooth, the doctor makes a note about caries or other disease, whether this tooth is covered with a crown, whether it is damaged or missing, and the degree of mobility is also noted. Under the table, a note is made about the presence, nature and location of dental plaque.
- Condition of the oral mucosa – the color of the mucosa and its condition are noted: degree of moisture, identified pathologies.
- Next, the doctor focuses directly on examining the teeth that the patient is complaining about - their condition, position in the dentition, abrasion, mobility, whether the roots of the teeth are exposed and whether there is sensitivity during probing or from temperature stimuli, as well as the presence and size of periodontal gum pockets.
They also separately describe the condition of fillings or carious defects, orthopedic structures - both removable and non-removable: the condition of inlays, crowns, removable dentures - the integrity of the prosthesis, fixation of the prosthesis, how well the prosthesis corresponds to the boundaries.
- The doctor also pays attention to the bite - the way the patient closes his teeth. This can provide a lot of data to determine the cause of the pathology.
What are the dangers of missing teeth?
Losing teeth, as it may seem at first glance, causes not only psychological discomfort or an aesthetic defect. The loss of even one tooth can lead to deformation of the dentition, curvature of the remaining teeth, malocclusion, bone tissue atrophy, impaired diction, and the loss of several anatomical units leads to disruptions in the functioning of the entire body. The patient has difficulty chewing food, which leads to problems in the digestive system.
Therefore, it is important to restore the integrity of the dentition as soon as possible, especially since modern orthopedic dentistry offers many treatment options.
Dentists at the multidisciplinary department of orthopedic dentistry in St. Petersburg provide a range of services for dental prosthetics and restoration of the integrity of the dentition. We install ceramic inlays, temporary and permanent crowns on implants and natural teeth, Maryland Visio Ling bridges, clasp dentures, Ti beam structures, veneers, etc. You can make an appointment with a doctor at the Department of Orthopedic Dentistry by calling: 8 (812) 456-15-15 or using the online registration form on the website.
Additional examination methods in orthopedic dentistry include:
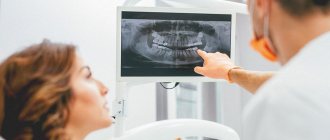
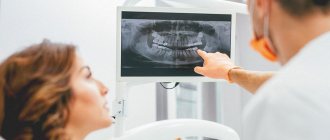
- X-ray image. Typically, orthopedic patients undergo an orthopantomogram, or OPTG as it is called for short. This is a large shot of both jaws and all the teeth. It allows you to see the overall picture and understand what additional examination methods will be needed. To clarify data on specific teeth, targeted intraoral radiographs are taken - small pictures that fit 1-3 teeth. In such photographs, the image of the tooth is larger and clearer, which allows you to see what is invisible in a large panoramic photograph.
- CT scan. This is essentially an advanced X-ray image - thanks to CT, you can get more than just one angle, but immediately look from all sides and see what is not visible on a planar image. To plan large-scale orthopedic work, a CT examination is simply necessary.
As a result, after carrying out all the necessary examinations and examinations, the doctor makes a diagnosis of orthopedics and dentistry based on the data obtained. Next, depending on the diagnosis, a treatment plan is drawn up - each diagnosis has a treatment protocol and objective requirements for the situation in the oral cavity. In orthopedics and dentistry, diagnoses are made only after a thorough examination.
Reliable diagnosis is the key to successful treatment
Dear readers, in this article we will try to tell you as comprehensively and in “simple” language as possible about what diagnostics of dental diseases is, how and why it is carried out, how a plan for the necessary treatment and dental prosthetics is drawn up.
Each clinical case is individual, as well as the required treatment individually. There are no two completely identical people, just like no two identical teeth. Each person in need of restoration of the dental system always needs an individual treatment plan, which can be drawn up based on the examination and diagnosis. One of the keys to successful treatment is diagnosis and careful planning in each specific case. The quality, durability and beauty of your teeth will depend on the correct implementation of these important factors...
As a rule, after the first introductory consultation and filling out medical documentation, diagnostic measures are carried out. The scale and type of diagnosis depends on the complexity and severity of a particular clinical case.
Many diseases that patients had no idea about are detected at various stages of diagnosis, which allows the necessary measures to be taken in time. For example, a person who went to the dentist about a chipped or worn-out tooth would not even think that this was due to an incorrectly formed bite or incorrectly made restorations. Many factors that at first glance are not directly related to the patient’s complaints are, in fact, often the result of another disease or destruction that may not appear immediately; the patient simply does not notice them. If you do not identify the problem, or do not diagnose it at all, but immediately begin to restore this tooth (which was the purpose of the patient’s visit), then the quality of such treatment will be in doubt, moreover, the situation will worsen over time and lead to even greater destruction. The task of any doctor is to diagnose the clinical situation in a timely and detailed manner before carrying out therapeutic or restorative measures.
So, the first diagnostic event is a survey.
Based on your complaints, the dentist collects information about previously suffered diseases, the timing of their occurrence, and their course. Determines your psychological status and readiness for dental treatment. During the interview, try to answer the doctor’s questions in as much detail as possible, listen carefully and do not hesitate to ask if something is not clear. This way you can help the dentist solve your problem. Even during the interview, the dentist pays attention to your face, evaluates symmetry, identifies edema and swelling, studies your articulation and much more, and so begins the next stage of diagnosis - examination.
After the external examination, the dentist begins to examine the oral cavity. In addition to the usual mirror and probe, there are quite a few modern additional examination methods for identifying diseases and making a correct diagnosis. It is believed that a “standard” dental examination of a patient (examination using a dental probe and mirror) will reveal only 30% of the necessary information. Therefore, high-quality diagnostics in modern dentistry is unthinkable without additional examination methods.
The most important and informative methods include visiographic and tomographic studies in dentistry. You can read more about these types of diagnostics in the section on computed tomography.
In addition to identifying various pathologies of the dentofacial area, radiovisiography and computed tomography are an integral part of modern planning of dental prosthetics.
The most accurate calculations for dental implant placement are made using 3D tomographic images. Calculating the exact location of the implant plays a vital role in its functioning and the correct placement of the crown on it. This is a real breakthrough in dentistry. Today it is unthinkable to install implants without preliminary tomographic diagnostics. But tomography is not the entire arsenal of modern diagnostics, which allows you to correctly install an implant, filling or crown.
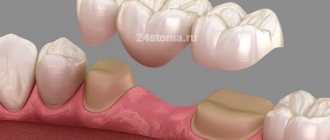
In addition to successfully identifying and treating dental disease, it is necessary to correctly restore the shape of a tooth or an entire row of teeth. After all, after you have had root canal treatment on your tooth, it still needs to be restored. And if you have a tooth removed, then you need to install another one in its place.
Everyone knows that a tooth has a strictly defined shape: cusps, fissures, various ridges and pits. All these elements together determine its shape. Only a properly shaped tooth can ensure proper functioning and each, even the most inconspicuous element on the tooth performs its strictly defined task. If such an element is lost or not created during dental restoration, the entire tooth will suffer, then, like a chain reaction, this will affect the bite, which can subsequently negatively affect the temporomandibular joint, the symmetry of the face, and much more. Each tooth must occupy its specific position in the dental arch and in the bite with an accuracy of fractions of a millimeter.
Let's look at, for example, the destruction of a chewing tooth in the lower jaw
The patient came with complaints about the crown of tooth 46 chipping while eating; the patient does not experience any pain, but he is bothered by the sharp edge of the tooth, which scratches his tongue. The tooth chipped the day before.
The patient denies the presence of chronic diseases, HIV, hepatitis and allergic reactions.
An external examination, examination of the condition of the temporomandibular joint and the condition of the oral mucosa revealed no pathologies. In the oral cavity, the condition of the teeth is satisfactory; no pathologies other than a chipped tooth 46 were identified. The plaque is scanty - the patient had professional oral hygiene a month ago.
The patient's bite is correct and orthognathic.
When examining the chipped tooth 46, we note that the tooth is depulped, while the seal is preserved - an insulating gasket is in place - it protects the filling material of the tooth root canals from infection by oral bacteria. The chip occurred to approximately half the height of the tooth crown on the lingual and distal (back) sides. In this case, the size of the defect in the coronal part of the tooth is more than half the size of the crown.
Next, we move on to additional research methods - we will do an OPTG to identify possible defects on other teeth and assess the condition of neighboring teeth and teeth opposite on the upper jaw and a CT scan in the area of tooth 46 to determine the quality of canal filling and the presence of inflammation in the root area 46.
In the photographs we see that the canals are sealed tightly, up to the apical foramen (that is, to the end) and there are no clearings to suspect the presence of inflammation. The adjacent teeth are vital and do not require treatment.
Gnathology
What is gnathology?
Gnathology is a science
that studies the effectiveness of the dental system in normal and pathological conditions.
Chewing is a vital function of processing and swallowing food. Gnathology - as a field of dentistry
, deals with the identification and treatment of pathology of the temporomandibular joint.
What does a gnathologist treat?
The most important element of the human masticatory apparatus is the paired
temporomandibular joint (TMJ). Movements of the lower jaw occur as a result of the complex interaction of the masticatory muscles, temporomandibular joints and teeth and are regulated by the neuromuscular system. The temporomandibular joint coordinates the movement of the lower jaw in three directions, and any movement occurs with simultaneous sliding and rotation of the heads of the lower jaw. During normal operation of the joint, painless opening and closing of the mouth is ensured by the intra-articular disc, which is a cartilage pad. Dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) interferes with proper chewing of food, speech formation,
and all this is accompanied by pain and a “clicking” of the joint when opening or closing the mouth.
The position of the jaw is disrupted, which leads to improper closure of the dentition. Any deviations in the functioning of the elements of the mandibular joint require competent consultation with a gnathologist. IMPORTANT: A gnathologist-dentist is engaged in functional diagnostics and treatment of dysfunctions of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ).
TMJ dysfunction leads to difficulties in diagnosis, as it has a variety of clinical manifestations. It is important to emphasize that a gnathologist as a specialist must have extensive practical experience in therapeutic and orthopedic dentistry. Incorrectly placed fillings, crowns and orthopedic structures in most cases are the root cause of pathology and a trigger for the malfunction of the dentofacial apparatus. As a specialist, a dentist orthopedic gnathologist will not only determine the cause and degree of dysfunction of the dentoalveolar system, but also propose an optimal treatment plan to eliminate them.
IMPORTANT:
If you need a highly professional consultation with a gnathologist, contact the Dentist dental clinic. Specialists with more than 17 years of experience will explain to you in detail and clearly the cause of your illness and offer a reasonable treatment plan.
Symptoms for which you should contact a gnathologist.
It is no secret that patients mostly turn to the dentist complaining of pain in the teeth. But how do you understand that pain and discomfort in the teeth and jaw are related to the joint? The first signs of dysfunction that you should pay attention to are:
- Rapid fatigue and muscle hypertonicity when chewing.
- Involuntary clenching of the jaws.
- Local or diffuse pain in the masticatory muscles.
- Discomfort when opening and closing the mouth.
- Bruxism (teeth grinding) Unconscious muscle activity not associated with chewing or speaking
Signs indicating the presence of TMJ dysfunction in the later stages:
- Clicking in the joint that occurs when opening the mouth, chewing, or yawning.
- Joint blocking and displacement. The mouth opens in a zigzag or S shape.
- Inability to chew solid food due to pain
- Limited mouth opening.
Patients report severe headaches, migraines of unknown etiology, congestion and tinnitus. Pain and muscle spasms not only in the masticatory muscles, but also in the muscles of the neck and occipital region. With joint dysfunction, dizziness, dry mouth, sleep disturbance, snoring, sleep apnea (breathing stops for 10 seconds) may also occur. IMPORTANT:
When such symptoms appear, treatment of TMJ by a gnathologist is mandatory. Otherwise, the incorrect functioning of the joint will eventually lead to the development of irreversible degenerative processes and immobilization (arthrosis).
Causes of TMJ dysfunction.
Overload of the masticatory apparatus is the basis of dysfunction, but there can be many reasons.
- Occlusal-articulatory
(closing of the dentition) the problem includes:
incorrect prosthetics, placement of flat fillings, single and multiple defects in the dentition,
pathological abrasion of teeth
jaw injuries, malocclusion. All this is accompanied by a decrease (decrease) in the height of the bite. - Another problem is related to mechanical overload of the jaw muscles
and their spasm. Unilateral chewing, bruxism, and heavy speech load ultimately lead to chronic microtrauma of the elements of the TMJ. - And the third important factor is neuropsychic and physical stress
associated with changes in the activity of the central nervous system (CNS).
How does a gnathologist consultation work?
Consultation with a gnathologist-dentist is an important stage in the treatment of TMJ dysfunction and
begins with collecting complaints and anamnesis. Then the doctor proceeds to examine the oral cavity, assesses the closure of the teeth, the functioning of the muscular system, the position of the head, as well as the severity of facial asymmetry. Particular attention is paid to the temporomandibular joint, assessing it in a static position and when performing movements.
A gnathologist, who is maximally focused on obtaining the most effective treatment result, will study all the elements of the muscular-ligamentous apparatus of the neck area, the tension of the back muscles, and the patient’s posture. These elementary examination methods allow a competent specialist to quickly make a preliminary diagnosis and determine the scope of the examination and treatment tactics.
An obligatory part of diagnostics is computer and hardware research. From the variety of studies, the gantologist will select those necessary for treatment.
Often used in the practice of a gnathologist are:
- Orthopantomogram and plain radiograph of the TMJ, allowing to detect
abnormalities in the development of bone tissue of the ligamentous apparatus. - Computed tomography, which provides a layer-by-layer study of the condition of the joint and dystrophic changes.
- MRI of the joint has the greatest diagnostic value for studying the condition of the periarticular soft tissues and articular disc.
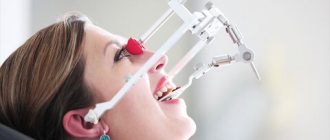
- Graphic research, axiography, method of recording movements of the lower jaw using a special apparatus;
- Analysis of occlusal contacts using an articulator device - a device that reproduces the movements of the lower jaw.
- Diagnostic plaster models of jaws.
Among functional diagnostics, myography is especially in demand - a method for studying the masticatory muscles, the quality of static and dynamic closure of teeth. There are other techniques: electromyography, phonoarthrography, gnathodynamometry. Modern computer programs help speed up the diagnostic process for TMJ lesions, as well as form a more accurate opinion about the mechanism of development of the pathological process. With their help, it is possible to offer optimal correction methods. All of the above methods evaluate the functioning of muscles and joints, determine exactly how the teeth close and help identify the cause of joint dysfunction.
IMPORTANT:
To ensure high quality diagnostics, all these methods can be used by gnathologists at the Dentist clinic.
What treatment methods are used.
Treatment carried out by a gnathologist usually involves an integrated approach. In the treatment of gnathological disorders, it involves the use of therapeutic and diagnostic devices.
- To restore the correct position of the jaw, use special
joint splints
. The technique is effective in combating bruxism, pathological tooth wear, and for relieving muscle tension in the maxillofacial and cervical region. - To stimulate the masticatory muscles of the face and neck, a high-tech system is used - a deprogrammer
. Designed specifically for use in neuromuscular dentistry and gnathology. This unique stimulator allows you to erase (deprogram) the masticatory muscle dysfunction reflex and restore normal tone. - If the dysfunction of the dentofacial apparatus is caused by poorly performed orthopedic treatment, with a serious decrease in the bite, then before repeated prosthetics, an individually made occlusal splint (splint)
, which has a lasting memory effect. Can be installed on one or two jaws at once. Splin not only corrects occlusion (closing), but also solves several functional problems. Evenly distributes the load when chewing, reduces the activity of the muscular system and thereby corrects the direction of movement of the lower jaw.
Dentist orthodontist-gnathologist.
Orthodontists recognize that most malocclusions are caused by problems other than dental problems. Most often, the development of orthodontic problems is caused by such anomalies as violation of the dimensions of individual elements of the jaw apparatus, deviations in the position of the jaws relative to the base of the skull, pathology of the temporomandibular joints or
chewing muscles. Cases of the development of malocclusion due to orthopedic problems of the spinal column are no exception. Malocclusion in 90% of cases is accompanied by pathological abrasion
, and consequently, a decrease in the height of the lower half of the face. Treatment with braces and aligners in such situations is useless and ineffective.
IMPORTANT: Orthodontic treatment cannot restore the previous volume of dental tissue in case of pathological abrasion, it cannot restore single and multiple defects in the dentition, and all this is directly related to dysfunction of the mandibular joint.
When, during a consultation, an orthodontist encounters existing disorders in the functioning of the maxillofacial apparatus, he is obliged to consult with a gnathologist-orthopedist. This will help to avoid mistakes and negative results after orthodontic treatment. If we objectively approach the problems of dysfunction, then an orthodontist-gnathologist
is not the best combination of specializations
. Since orthodontists, as specialized specialists, are very far from therapeutic and orthopedic dentistry and do not have sufficient knowledge and experience necessary for the effective treatment of TMJ dysfunction. The orthodontist corrects the abnormal position of the teeth in the jaw, improves the appearance of the dentition, and restores the correct closure of the dentition, but this is not enough to treat such a complex pathology.
IMPORTANT:
The specialists of the Dentist clinic are well aware that an interdisciplinary approach is very important and the orthodontist acts only as a specialist whose work is necessary in the intermediate stage of treatment of joint dysfunction.
Dentist orthopedist-gnathologist.
The gold standard or standard of a gnathologist is an orthopedic gnathologist.
In a broad sense,
If we consider the specialty of an orthopedist in dentistry, then this particular doctor is in charge of
diagnosing
and correcting defects of the musculoskeletal system. Having extensive experience in eliminating problems associated with the masticatory apparatus during prosthetics and deep knowledge in restoring its functions, this is an ideal candidate for a gnathologist.
The success of orthopedic treatment directly depends on the design of the prosthesis and its ability to evenly distribute the load during chewing. In this case, the condition of the temporomandibular joint and masticatory muscles is taken into account. Uniform distribution of the load and restoration of the correct bite height is the most important stage in the treatment of TMJ dysfunction.
Advantages of contacting specialists at the Dentist clinic.
By contacting the Dentist clinic on Chistye Prudy,
Each patient can count on highly qualified
consultation
with an experienced gnathologist-orthopedist. The center will be able to undergo examination using modern diagnostic methods, as well as carry out all stages of this treatment.
The advantages of the Dentist clinic are:
- High professional level of doctors in this profile.
- The ability to use advanced diagnostic and treatment methods, which will completely eliminate existing symptoms
- At the highest level, carry out orthopedic or orthodontic treatment for TMJ dysfunction.
The price for a consultation with a gnathologist in Moscow varies widely, and often does not correspond to the professional level of the specialist or the diagnostic capabilities of the center.
If you decide to make an appointment with a gnathologist-orthopedist at the Dentist clinic, you will be pleased to discover that, despite the high level of service, the consultation is free .
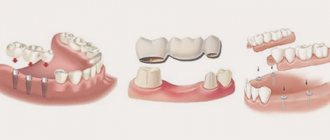
Classification of dentition defects
There are several types of classification. Dentists mainly use three of them:
- Kennedy classification:
- Group 1 - bilateral absence of chewing teeth;
- Group 2 - unilateral absence of a molar;
- Group 3 - unilateral absence of lateral teeth with preservation of distal support;
- Group 4 - defect of the anterior jaw.
- Beltman classification:
- Class 1 - the defect includes edentulous chewing teeth.
a) dentition with unilateral terminal defects;
b) dentition with bilateral terminal defects.
- Class 2 - there is one or more included defects (if the terminal units are present, there may be no teeth in other parts of the row).
a) the number of missing units does not exceed three;
b) the number of missing units is three or more.
- Classification according to the Gavrilov system:
- Group 1 - dentition with terminal one- and two-sided defects;
- Group 2 - dentition with anterior and lateral one- and two-sided defects;
- Group 3 - combined defects;
- Group 4 - single preserved dental units.
Setting goals
Goals of orthodontic treatment:
- achieving the correct jaw ratio;
- elimination of dental distortions;
- restoration of chewing and speech functions;
- elimination of facial asymmetry and other defects.
Planning includes the following activities:
- initial examination and consultation;
- complex of diagnostic studies;
- development of a treatment protocol and agreement with the patient.
Most clinical cases allow for several correction options. The doctor conducts a consultation on each so that the patient can choose the most optimal option.