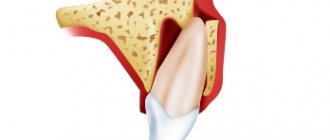
Untimely treatment of caries in children leads to the development of pulpitis - inflammation of tooth tissue, including blood vessels and nerve bundles. The lower molars are most often affected, but the disease occurs even on the anterior elements. Therefore, pulpitis in children occurs even more often than in adults. This is due to a number of factors:
- thin weak enamel;
- large volume of pulp;
- wide root canals;
- less mineralization;
- weak immunity.
In addition to caries, pulpitis can be caused by trauma, including poor treatment.
Symptoms
Inflammation occurs in acute and chronic forms. Acute occurs less frequently, but has more severe symptoms and occurs in two stages:
- serous. The inflamed pulp is filled with serous fluid. There are complaints of severe pain in the tooth, intensifying at night and when chewing. The pain, as a rule, is intermittent, appears once and subsides. Most often, the process occurs in teeth with unformed or absorbable roots. After 5–6 hours, a transition to another stage occurs;
- purulent. Pus forms in the tissues, which begins to melt cells and tissues. The severity of the condition is influenced by immunity, dental condition, and bacterial activity. If the pus has an outlet in the form of a carious cavity or fistula, then the pain is mild. In the absence of outflow, the pain syndrome is bright and long-lasting, intensifying when chewing or eating cold or hot food. The general condition may worsen and fever may appear.
Chronic pulpitis occurs after acute pulpitis or on its own and is characterized by vague symptoms. Pain can only occur under unfavorable factors - cold or hot, too sweet food. The child begins to chew on one side, an unpleasant odor appears, and a bursting and pressing sensation occurs.
The danger of this form is that it is almost asymptomatic. Because of this, inflammation affects more and more tissues. Chronic pulpitis is of three types:
- fibrous. The lightest and most common form. Fibrous tissue grows, the pulp may bleed, and episodic pain appears from mechanical and thermal contact;
- hypertrophic. Develops with severe destruction of the tooth crown. Pathological growth of pulp tissue occurs, which fills the carious cavity;
- gangrenous. The most severe form, accompanied by pulp necrosis. The tooth becomes gray and bad breath appears due to tissue decomposition.
What diseases cause inflammation of dental canals?
Root canals can become inflamed due to the development of the following diseases:
- caries;
- pulpitis;
- periodontitis.
An accurate diagnosis of inflammation of the pulp and canals of the tooth can only be determined by a dentist after X-ray diagnostics and a visual examination of the oral cavity.
How to recognize the problem and is emergency treatment required?
Due to the reduced sensitivity of the pulp, pain during inflammation may be mild and not cause severe discomfort. In this case, the process of tissue destruction occurs rapidly. It is important to visit the dentist regularly and not ignore your child’s complaints of pain when chewing or when eating cold and hot foods.
Treatment for pulpitis should be immediate. The disease is dangerous due to complications - periodontitis or periostitis. It can also spread to a permanent tooth that has not yet erupted and destroy it.
Symptoms
If periodontitis is diagnosed in children, symptoms and treatment depend on the form of the disease (acute or chronic). In acute periodontitis, there is a sharp initial and severe, increasing and incessant pain. The intensity of pain increases when pressure is applied to the damaged tooth. Other signs include:
- The gums near the diseased chewing element swell noticeably.
- The child's body temperature rises.
- The appearance of weakness and attacks of nausea are noted.
- The lymph nodes become enlarged and pain is felt when pressing.
In case of chronic periodontitis, a child’s primary tooth, which is treated in a clinic, does not have characteristic signs. Painful sensations can occur if you press on a sore tooth, or during contact with hot or cold food. In addition, there are the following symptoms:
- A fistula forms on the gum if the disease develops into a granulating form.
- The child becomes drowsy, gets tired quickly, and general weakness appears.
- Appetite worsens.
- Increased body temperature.
Treatment methods
The treatment of primary teeth in general does not differ from the treatment of permanent elements. If the child’s condition is serious, there is a threat of infection spreading throughout the body, amputation is performed. In most cases, the tooth is preserved to prevent malocclusion. Therapy is carried out in different ways:
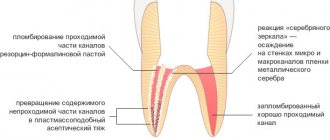
- traditional. Involves treatment in three visits. During the first one, the nerve is opened, a devitalizing paste with arsenic is applied for 24-48 hours or without it for a period of up to 7 days. On the second visit, a pulp mummification mixture based on resorcinol-formalin is placed into the canals. At the last visit, a permanent filling is installed;
- modern. It takes place in 1 – 2 visits. If the child can sit quietly for a long time at the doctor and the roots of the tooth are formed, extraction is performed. The nerve is removed either on the first visit or after applying the paste. Next, the canals are carefully processed, infected tissue is removed, an anti-inflammatory paste (for example, zinc eugenol) is applied and closed with a filling. The composition will gradually dissolve along with the roots when changing teeth;
- partial vital amputation. The doctor removes the upper portion of the nerve and applies an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory medication that seals the remaining living pulp.
When treating teeth with immature roots, a different approach is chosen. This is due to several reasons:
- the apex of the roots has not yet closed and there is a risk of infection of the permanent tooth germ;
- the roots are short and the channels are wide;
- trauma to the upper zone of the root can lead to disturbances in its formation;
- It is impossible to remove the entire pulp and perform a complete canal treatment.
Most often, they choose amputation of the pulp by any method or biological treatment, when the tooth is cleaned of the affected tissue and a paste with calcium hydroxide is applied for several days. After this, a filling is installed.
Services
What are measles canals?
Despite their size, teeth have a rather complex structure. They consist of a visible part - the crown, which rises above the gum, and an internal part - the root, which is located in the gum. In this case, inside the tooth there is a so-called pulp - a bundle of blood vessels and nerves that fills the root canal of the tooth. Thus, the root canals of teeth are a small cavity inside the tooth in which venous and arterial vessels and nerve fibers are located. Root canal treatment is precisely the treatment of the internal cavities of teeth, most often the area occupied by nerve endings, or pulp.
Why treat dental root canals?
Diseases such as caries, pulpitis and periodontitis can lead to root canal diseases. Typically, when treating such dental diseases, a cavity is formed in the root canals. Any open cavity in the teeth can lead to serious consequences. This is primarily due to the fact that food particles can get into the voids, which will begin to rot over time. With rotting, microbes are formed, and after them, infections. Infections, in turn, lead to serious inflammation, which must be eliminated again so that they do not cause abscesses. The resulting cavity must be closed with filling substances.
How are dental root canals treated?
Root canal treatment involves removing the nerve bundle from the pulp chamber and further filling the canal.
The procedure seems simple, but there are some peculiarities. Immediately before treatment, anesthesia is necessary, as the procedure can be quite painful. After the anesthesia has taken effect, it is necessary to get to the pulp chamber, for which the tooth is drilled with a drill.
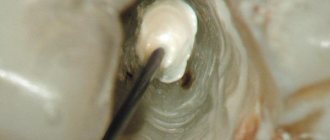
When the pulp chamber has become accessible with a special tool - a pulp extractor - the bundle of nerve endings is removed, freeing the cavity from the inflamed pulp. It would seem that immediately after this you can fill it.
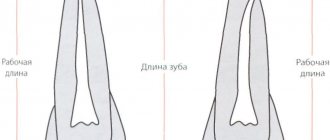
However, the resulting cavity is so thin that it is technically impossible to fill it. To do this, it is increased in size using special tools of different diameters, resembling small files.
After increasing the size of the root canal cavity, they must be treated with anesthetics to prevent infection, and filled with a special material - gutta-percha.
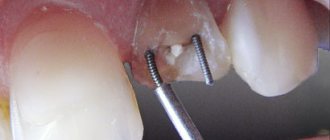
In some cases, after filling with gutta-percha, pins are installed into the root canal cavity for more reliable fixation of subsequently installed crowns.
Recommendations after the procedure
For some time after the root canal treatment procedure, pain may occur, most often associated with mechanical impact on the tooth - for example, during eating.
This is quite normal. The effect of anesthesia ends, the body begins to respond to artificial intervention. To avoid discomfort, you can take painkillers of varying strengths depending on the severity of the pain. If there is swelling after the procedure, you can apply ice to the outside of the cheek on the side of the treated tooth.
If the pain does not go away within several days or, even worse, intensifies, you should immediately consult a doctor to avoid even greater complications.
Tomsk dentistry Dentarus employs experienced therapists who carry out similar procedures every day. By contacting them, you will receive a careful approach and effective treatment at an affordable price. Do not delay going to the doctor, as it is always easier and cheaper to treat in the initial stages. Sign up for a free examination with a doctor right now.
Still have questions?
Write to us and we will be happy to answer you!
Return to list of services
Is it possible not to treat pulpitis if the teeth are baby?
There is a common opinion that it is not necessary to treat baby teeth, because they will soon fall out. This is the biggest mistake parents make. Untreated pulpitis leads to irreparable consequences and even affects permanent teeth:
- purulent abscess, periodontitis, life-threatening condition;
- deep infection affecting the germ of a permanent tooth;
- malocclusion due to early tooth extraction due to untimely treatment;
- pain interferes with normal chewing of food, uneven load on the teeth leads to accelerated destruction of other elements.
Possible complications
If treatment for periodontitis in primary teeth is not started in a timely manner, the following consequences may occur:
- With an extensive inflammatory process, when more than one chewing element is affected, the rudiment of a permanent unit of the dentition can be severely damaged or completely destroyed.
- Considering the form of the disease, the process of resorption of the baby tooth root may accelerate. Or, on the contrary, a slowdown, which will provoke incorrect and untimely development and eruption of permanent chewing elements.
- Periostitis or osteomyelitis will develop.
Prevention
The main method of preventing dental and oral diseases is regular visits to the dentist and treatment of caries in the early stages. It is important to teach a child hygiene and the rules of brushing teeth from the first years of life. Parents should control the diet, which should contain all the necessary substances, limit sweets and allow only water to drink at night.
Doctors at the VIMONTALE clinic treat pulpitis of primary teeth in children of any age. Specialists not only master modern painless techniques, but also know how to find contact with a child, know how to reduce anxiety and win the favor of the youngest patients.
Expert of the article you are reading:
Lozinskaya Alla Nikolaevna
Pediatric dentist, general dentist.
You may also be interested in:
Children's orthodontist Dental treatment for children Correction of bite in children Features of the treatment of childhood caries Removal of baby teeth Prevention of childhood caries Silvering of teeth in children
Show more
What materials are used
Many parents are interested in what is currently used to fill children’s teeth. Not so long ago, the choice of materials used to fill children's teeth was not as diverse as it is today. At one time, dentists more often resorted to using amalgam, but this composition cannot be called completely safe and harmless to the body, especially when it comes to a child. Later they began to use glass ionomer cement, but it also has its disadvantages. For example, it takes quite a long time for the material to harden, which is not always convenient if there is a baby in the dental chair.
On a note! Often, special pastes are used to fill the root canals of baby teeth. Such compositions are not able to provide perfect tightness if used to fill a vertical cavity. In addition, after some time they dissolve, and therefore are not intended for permanent filling.
This is how a child’s teeth are filled with reflective composites.
To date, the situation has changed a little, and today pediatric dentists increasingly prefer fillings made of light-curing composite, as well as compositions that are a combination of a hybrid composite and glass ionomer cement. These materials are characterized by increased strength, are easy to polish and have a high degree of adhesion.
Our patients
Patient recommendations
Akhmedkhanov Said Rashidovich
Dental surgeon, general dentist, implantologist, orthopedic dentist, dental therapist.
Make an appointment 8 (499) 520-98-70
Make an appointment
Recommendations from patient Alekseeva O.V.
Akhmedkhanov Said Rashidovich
Dental surgeon, general dentist, implantologist, orthopedic dentist, dental therapist.
Make an appointment 8 (499) 520-98-70
Make an appointment
Recommendations from patient Zolotareva S.V.
Akhmedkhanov Said Rashidovich
Dental surgeon, general dentist, implantologist, orthopedic dentist, dental therapist.
Make an appointment 8 (499) 520-98-70
Make an appointment
Recommendations from patient Vera
Akhmedkhanov Said Rashidovich
Dental surgeon, general dentist, implantologist, orthopedic dentist, dental therapist.
Make an appointment 8 (499) 520-98-70
Make an appointment
Recommendations from patient Mikhail Ivanovich
Akhmedkhanov Said Rashidovich
Dental surgeon, general dentist, implantologist, orthopedic dentist, dental therapist.
Make an appointment 8 (499) 520-98-70
Make an appointment
Collapse
Reviews
Does your child have problems with their baby teeth? Do as our patients do - come to us for an appointment, and your baby’s teeth will be like new. At the Natadent clinic, treatment is quick, stress-free and without consequences for the child’s body.