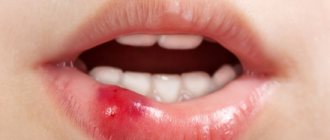
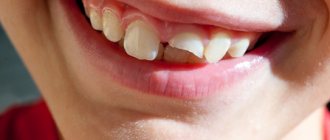
Dental injuries are a common problem in dentistry. Tooth dislocation is an injury that results in damage to the ligamentous apparatus and the tooth being displaced in its socket (photo below).
Tooth dislocation is accompanied by:
- severe pain
- bleeding
- soft tissue swelling
- appearance of tooth mobility
- change in enamel color
The causes of such injury may be:
- mechanical damage (due to impact from a fall, for example);
- biting hard food, hard objects in food;
- bad habits (crunching nuts in the shell, opening bottles with your teeth, etc.);
The diagnosis of tooth trauma (including tooth dislocation) is made based on symptoms and x-ray examination. The doctor not only determines the clinical picture, but also assesses the condition of the bone tissue at the site of dental injury. Tooth dislocation has its own types (complete, incomplete, impacted) and treatment features.
Tooth dislocation: photos and symptoms
Any injury has its own clinical picture. Tooth dislocation, photos of which can be viewed on dental websites, is also characterized by specific symptoms. During the examination, the dentist looks for signs to diagnose a luxated tooth.
The doctor also determines what type of tooth dislocation the resulting tooth is. The symptoms of each are slightly different. After analyzing the x-ray, treatment is usually prescribed.
Causes of dislocations
Dislocation always occurs under the influence of a directed force, the source of which is:
- a blow to the tooth during a game, a fall, a fight, an accident, an industrial accident;
- the load acting on the tooth when chewing bones, unshelled nuts, or opening beer bottles with the teeth;
- incorrect tooth extraction technique;
- pressure on a moving tooth when biting hard food.
When dislocation occurs, the position of the tooth root in relation to the walls of the socket changes, periodontal fibers are completely or partially torn, and the neurovascular bundle is damaged; often a dislocation is combined with a fracture of the tooth crown or maxillofacial injuries. Based on the nature of tooth displacement, incomplete, complete and impacted dislocations are distinguished.
Types of tooth dislocations. Complete, incomplete and impacted tooth dislocation - what are the differences?
To determine what type of dislocation - complete, incomplete or impacted - the injury belongs to, you should pay attention to their differences in symptoms.
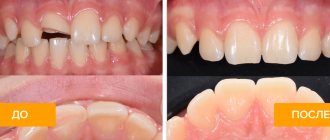
- Complete tooth luxation (photo below) is characterized by the tooth falling out of its socket. And if he is held in it, then only due to soft tissues.
- Incomplete tooth luxation is characterized by partial displacement of the root in the alveolus. Upon examination, it is noticeable that the tooth is tilted either towards the tongue, or back, or towards the cheek, or towards the lip.
- Impacted tooth dislocation is a rare type of such injury. With it, several teeth often suffer at once, which seem to go deep into the alveoli. An impacted tooth dislocation is visually recognized by a decrease in the height of its visible part (photo below). This injury leads to destruction of the jaw bone.
Complete tooth luxation, incomplete tooth luxation and impacted tooth luxation differ not only in symptoms, but also in the methods used in their treatment.
Tooth dislocation: treatment
You need to contact the clinic for professional help immediately, without delaying the visit for a couple of days. Such a pause will bring additional suffering and the risk of increasing complications and losing a tooth after dislocation.
If trouble occurs in a child, you need to remember: dislocation of a baby tooth is always accompanied by additional tissue damage and subsequently the pathology will interfere with the adequate formation of the molar. By the age of 4-6 years, the rudiments of a permanent unit are formed; their injury can lead to unpredictable results.
Impacted, complete and incomplete tooth dislocation What treatment is needed?
Experts note that in most cases, injured teeth can be saved. The main thing is to see a dentist in time.
If an impacted tooth luxation is diagnosed, treatment is not always required, since the tooth often returns to its previous position on its own. But sometimes the damage is so severe that this does not happen. If just such an impacted tooth dislocation occurs, treatment is prescribed as for incomplete dislocation. Tactics for impacted dislocation can be different, it all depends on the degree of damage to the bone tissue and the severity of the injury.
If a tooth is completely dislocated, treatment should begin immediately. It is advisable to insert the fallen tooth into the hole and get to the dentist as quickly as possible. The tooth must be placed in milk or held behind the cheek. If the replantation of a tooth after a complete dislocation is done within 2 hours, then the tooth will be completely engrafted without any consequences.
Treatment for incomplete tooth dislocation consists of repositioning the tooth to its previous position, fixing it with a splint; if the pulp dies, the canal is treated and filled.
If you still can’t save the tooth, you can get prosthetics or implantation.
Restoration of teeth after injury by our experienced endodontists:
- extended warranty
- saving 79% of teeth with injuries of various origins
- painless restoration of tooth integrity on the day of treatment
- treatment using modern equipment under magnification and a microscope (fillings last 10-15 years or longer)
- high-quality diagnosis, not treatment by eye
- quality treatment at prices in the residential area of Yasenevo
Causes of dental damage in children
The increase in injury cases is primarily due to the growing popularity of team, contact and other sports. For example, hockey, wrestling, boxing, football and others. Also, the cause of dental damage in children of different ages can be accidental falls during active games on the street or school. No less common are injuries sustained in everyday life, fights, road accidents and other cases where there is a high probability of being hit by a hard object.
The risk of tooth damage increases if a child has orthodontic pathologies. For example, in patients with a distal bite (with protrusion of the upper jaw), injuries occur 5 times more often than in those with an orthognathic (normal) bite.
Also, dental damage often occurs in children with visual impairments, problems with the musculoskeletal system and various neuropsychiatric diseases.
Diagnosis and treatment
At the initial appointment, the dentist examines the growth cavity, assesses changes in the dentition, the condition of the gums, and identifies the likelihood of additional displacement of the injured unit. Using X-rays, the condition of the root and the possible consequences of injury for other units are determined. Using the EDI apparatus, the condition of the pulp is checked and tissue necrosis is detected.
The treatment plan is drawn up according to the type of dislocation.
1. For minor bruises, no therapeutic measures are carried out. Cold compresses and temporary exclusion of hard foods from the diet are recommended.
In case of significant injury, local anesthesia and disinfection of the damaged area are performed. If the pulp tissue is bruised, depulpation is performed and the canals are filled. If the neurovascular fibers are damaged and the enamel has darkened, then bleaching is performed.
To speed up healing, anti-inflammatory measures and physical therapy are prescribed.
2. In case of incomplete dislocation, reduction is performed using several methods:
• If the root is intact, the tooth is returned to its correct position manually using medical instruments.
• If there are healthy adjacent units, a metal splint is installed in the form of a bracket.
• A dentogingival splint made of plastic and wire is installed. The structure is made using casts of the patient’s jaws.
• If there are stable adjacent units, secure the dislocated tooth with a wire ligature.
3. In case of complete dislocation, the following therapeutic measures are carried out:
– cut the gum in the area of injury;
– filling the canal;
– return the tooth to its designated place;
– fixed using devices for a certain time.
The procedure is carried out immediately or after a certain period. The healing of the injured tooth as a result of therapy occurs after 30 days.
4. When diagnosing an impacted dislocation in children during the period of mixed dentition, no therapeutic measures are carried out for the first few days. The tooth can return to its original position on its own.
In case of severe injury, a combined reposition is prescribed, followed by the application of a splint to the injured unit.
In case of pulp injury, the damaged tissue is removed, after which the canal is sealed.
Possible complications
Tooth repositioning can cause various inflammations in the oral cavity. To prevent them, the treating dentist prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs.
After the dislocated tooth is returned to its place, its root may be reabsorbed.
If a child knocks out a baby tooth, what should you do?
In the case of baby teeth, we are not talking about restoring them or putting them back. It is not necessary to look for the knocked-out fragment. But it is necessary to take care of the molar tooth germ, which is located in the gum. You cannot injure it or allow it to get infected, so a visit to the dentist is mandatory.
If the baby accidentally knocks out a molar, it must be found and returned to the socket as quickly as possible. In this case, the tooth should be washed in saline solution or plain water, and also held by the crown part so as not to cause an infection.
The best and most predictable option is to return the tooth to the socket within the first 15 minutes. This increases the chance of its recovery to 90%. If you are afraid to insert a tooth yourself, then you should see a doctor as soon as possible.
In this case, the tooth must be transported in a suitable environment - saline solution, milk, water.
Memo for parents. Actions for trauma to temporary and permanent teeth in children
• In summer, the physical activity of children and adolescents is especially high - jumping, running, cycling, skateboarding and roller skating, playing outdoors and visiting rope parks sometimes lead to falls and injury to temporary and permanent teeth.
• Unfortunately, many parents do not immediately seek dental treatment for children due to injury, but only after the development of inflammatory complications or in order to eliminate aesthetic problems. Often, some injuries to the children's dental system are completely ignored by adults.
• There is a misconception that an injured temporary tooth will still be replaced by a permanent one, so it is not necessary to show the child to a pediatric dentist. Meanwhile, if a temporary tooth is injured, not only its root can be damaged, but also the germ of the permanent tooth. This subsequently leads to the development of complications such as underdevelopment of permanent tooth enamel (enamel hypoplasia), disruption of its formation, and even death of the permanent tooth germ. In the latter case, the absence of a tooth in the dentition can lead to malocclusion and the need for orthodontic treatment.
• Dear parents! Experienced pediatric dentists at the Jasmine Clinic have prepared for you a memo on the sequence of actions in case of trauma to the dental system in children and adolescents.
• Immediately after the injury occurs, it is necessary to reassure the child and not show your confusion and excitement. Set your child up in a positive way, convincing him that you know how to act correctly in such a situation.
• Try to get an appointment with a pediatric dentist as soon as possible. Call your loved ones or friends who will urgently begin searching for a qualified pediatric dentist, followed by making an appointment as soon as possible.
In such a clinical situation, the doctor will try to make a diagnosis as quickly as possible and begin measures to save the injured tooth. If the damage is serious, you need to inquire about the availability of not only a therapist, but also a surgeon in the clinic, since tooth extraction and/or suturing of soft tissue may be required.
• Ask the child whether his general condition has changed after the injury - whether there has been any memory impairment (does he remember what preceded the fall or hit an object and what happened after that), whether dizziness, flickering of “spots” before the eyes occurred, nausea, vomiting, headache. Chipping and dislocation of teeth can be accompanied by a concussion, therefore, if there is a change in the general condition, a mandatory examination by a neurologist is necessary, along with actions to save the injured or dislocated tooth.
• Examine the child's oral cavity to understand what happened to the teeth during an impact or fall. After all, even minor injuries such as chipped enamel or a bruised tooth do not go away without consequences. It is very important to see your dentist on time! Pay attention to the preservation of the soft tissues of the lips adjacent to the injured tooth, bleeding of the dentogingival groove of the injured tooth, and its displacement outside the dentition. The cause of tooth injury is usually a blow to it. And, nevertheless, injuries are different: tooth bruise, tooth dislocation (complete or incomplete), tooth fracture (at the level of enamel, dentin, dental pulp or longitudinal tooth fractures), tooth root fracture, tooth germ injury and combined injuries. The simplest of the above types of injuries can be identified immediately by a number of symptoms. If it is a tooth bruise: the child may experience pain, especially in the first hours after the injury, which intensifies when biting. If this is a dislocation of a tooth, then significant pain, which intensifies when biting, is combined with its mobility. Diagnoses of “tooth fracture”, “tooth root fracture”, “tooth germ injury” can only be made by a dentist after an X-ray examination.
• If a tooth or part of it is missing, try to find it as quickly as possible, enlisting the help of others.
• If you find a tooth or its fragment, get to the nearest pharmacy as quickly as possible, buy a test container, saline solution and miramistin. You can use milk instead of saline solution.
• Place the tooth or its fragment in a container with saline solution or milk.
• Treat the child's oral cavity with miramistin.
• If a child, in addition to a dental injury, has suffered a bruise with damage to soft tissues (hematoma, bitten wound of the lips), buy a briquette with frozen meat or minced meat at the nearest grocery store, wrap it in a napkin and apply it every 2-3 minutes with the same breaks to the skin in projections of damage. Under the influence of low temperature, the vessels will contract, bleeding, swelling and pain will decrease.
• If a tooth is dislocated (complete or incomplete), it is important to consult a dentist as soon as possible - within 1 hour! This will give you a good chance of saving your child’s tooth. There are cases when informed parents bring in their hands a child’s tooth that has fallen out due to an injury. If the condition of the bone tissue at the root of the tooth allows, then an experienced dentist, after X-ray examinations and special preparation of the oral cavity, will be able to put the tooth back into the socket and splint it, that is, strengthen it to the neighboring teeth. A successful manipulation, with full compliance with all the recommendations of the dentist, allows you to save the injured tooth for a long period.
• If you consult a doctor within the next 2 hours after injury, the tooth also has a chance of being saved. With each subsequent hour, these chances decrease significantly. When contacting 6 hours after injury, the likelihood of saving the tooth after its reposition is very low. A permanent tooth that has been completely dislocated from its socket can and must be returned to its place as quickly as possible, but not on your own! This should be done by a doctor.
• Primary teeth cannot be repositioned. If, as a result of a fall in 2-3 year old children, the front temporary tooth has penetrated deep and disappeared under the gum, after 2-3 weeks it may come out on its own. But an urgent consultation and examination by a dentist, as well as systematic monitoring of a child’s injured tooth, are strictly necessary!
• A high-quality diagnosis before dental treatment in case of injury to the dentoalveolar system is the first thing a dentist does. The standard set of studies is a targeted (using a radiovisiograph) or panoramic (orthopantomograph) image, 3D diagnostics depending on the nature and severity of the injury, as well as electroodontodiagnostics (EDD) to check the viability of the dental pulp. To exclude a fracture of the root of an injured tooth and to identify the integrity of the adjacent bone tissue, targeted radiovisiographic images are necessary, and for sufficient information in case of chipped teeth, not one image is needed, but several, taken in different projections. Splintered fractures of the crowns of the anterior teeth can be accompanied by the penetration of small fragments into the soft tissues - the adjacent areas of the lips. To exclude this complication, an X-ray examination of soft tissues - lips - is also performed.
• For 2 weeks after treatment, it is necessary to follow a gentle diet (purees, soups, cereals) with the exception of hard foods.
• To prevent inflammatory complications, high-quality systematic oral hygiene using a soft toothbrush, as well as toothpaste and herbal rinse is important.
• A patient with dental trauma should be under dynamic observation and examined by a dentist after 2 weeks, 1, 3,6.9 and 12 months, and then 3 times a year.
• As a rule, children with malocclusion are susceptible to injury because protruding teeth are damaged when they are hit or fall. Early detection and timely treatment of malocclusion pathology is the prevention of traumatic dental injuries in children.
Dear parents! The pediatric dentists at the Jasmine Clinic are always ready to respond to a call for help and choose the best restorative treatment option for your child if an injury suddenly occurs. Let our little patients receive only pleasant emotions and a charge of vivacity, being in constant motion, surrounded by our common care and attention!
Classification and symptoms
Teeth dislocations are divided into the following types:
1. Bruise. The tooth does not move from its position, acquires slight mobility and damage to the attachment apparatus. A bruise is indicated by discomfort when chewing, palpating, etc.
2. Incomplete dislocation. Occurs due to tearing of dental tissues and injury to the alveolar walls. The crown of the tooth moves in the opposite direction to the root. Signs include pain when chewing, displacement and mobility of the unit. Bleeding gum pockets may occur.
3. Complete dislocation. Occurs when there is a complete rupture of the dental tissues in the area of the tooth that falls out. A bleeding hole indicates an injury.
4. Impacted dislocation. Trauma to periodontal tissues, possible destruction of the jaw bone. The gums swell, bleed, and the dislocated tooth becomes noticeably shorter. The patient feels significant pain that prevents the jaws from closing.
Prevention of dental injuries
There are typical situations in which children injure their teeth. For example, a quarter of front tooth injuries between the ages of 1 and 3 years occur in the bathtub when a child slips and hits the edge of the bathtub, so try not to leave your baby unattended in the bathtub. Pay attention to protecting your teeth with a mouthguard when your child plays sports, especially hard and contact sports (hockey, various types of wrestling, basketball), rollerblading or skateboarding. Contact your orthodontist in a timely manner, because... a large percentage of injuries to permanent teeth are associated with their incorrect position, i.e. existing bite pathology, which means an additional risk.
At the same time, you should not blame yourself for not looking after your child and causing dental injury. Children are restless, they love to explore the world and take risks, and we cannot always protect them from such accidents.
make an appointment with a pediatric dentist online or by phone: +7(812)3310000
Classification of injuries
Conventionally, all traumatic injuries to primary teeth can be classified into:
- bruises;
- traumatic dystopia;
- loss of unit;
- crown or root fracture;
- combined damage.
Injury
More often than other types of injuries to baby teeth, bruises occur in children. This is a rough mechanical effect that does not damage the integrity of the unit. It can cause bleeding into the pulp zone.
Symptoms of a bruise include:
- toothache, especially when pressing on the coronal part;
- slight mobility;
- The gums are most often not inflamed.
The baby cries, complains of pain, and does not allow adults to examine his mouth. It is important for parents to remain calm and not panic. The severity of the lesion can be judged by the results of electroodontodiagnosis. It allows you to study the condition of the pulp tissues. If they are severely affected, removal may be necessary.
To speed up the regeneration process, you need to provide the damaged tooth with complete rest. For this, the patient is recommended to follow a gentle diet. He should not eat anything solid, chew foreign objects, touch the dentition with his hands, and, especially, check which canines, molars and incisors are more loose than others.
If there are indications for anti-inflammatory therapy, the child is prescribed tablets for oral administration or gels for topical application. Dental lotions and rinses can also be used. It is important that parents control the treatment process and do not allow the little fidget to swallow medications.
Traumatic dystopia
With this injury, the connection between the tooth and the socket in which it is located is disrupted. Due to rupture or overstretching of the supporting ligaments, it begins to loosen. Because of this, a change in its usual location is observed - it sinks deeper into the bone or, conversely, begins to rise above its “neighbors,” tilts to one side, and rotates around its own axis.
With severe dystopia, the bite changes, and difficulties arise with chewing food. There is often bleeding from the gums. The soft tissues of the oral cavity, damaged as a result of trauma to a baby tooth, become swollen and inflamed. To avoid unpleasant sensations, the child begins to chew food only on one side of the jaw and refuses to eat solid foods. It can go so far that he deliberately does not close his teeth, because he is afraid that pain will arise.
Decayed primary teeth cannot be fixed with splints; they are usually removed. The only exception is impacted dislocation. With this diagnosis, the unit is most often left untouched, since over time it can become more firmly established and return to its original position.
It is important to understand that severe trauma can lead to the destruction of not only the baby tooth, but also the permanent root located underneath it. Deformation of the entire dentition cannot be ruled out. Therefore, consultations with a dentist and orthodontist are mandatory.
Complete dislocation
Injury to a baby tooth that cannot be treated conservatively. When it is received, the fang, incisor or molar simply falls out. If the permanent shift is still far away, the doctor can make a temporary prosthesis for the little fidget.
Some parents are surprised by this doctor's decision. A denture is needed to avoid unwanted changes in the bite. If there are still several years before the permanent replacement erupts, the place reserved for the fallen tooth will be taken by its neighbors. Because of this, in the future the permanent tooth will not have room for full growth.
Crown fracture
The split may extend along the edge or through the entire coronal portion. The child complains of pain when eating cold and hot food. The sharp edge can scratch his cheeks and tongue.
After the examination, the doctor grinds off the sharp protrusions (if possible) and coats the tooth with fluoride varnish or other effective remineralizing composition. If necessary, the existing defect is closed with a filling.
If a large part of the tooth is missing, the nerve is first removed and a pin is installed. Only after this a new crown part is formed from the filling material.
Root fracture
Dangerous injury to the mammary unit. Most often it affects the incisors. The child complains of severe pain, loosening of the tooth, and swelling of the gums. He cannot eat or drink normally.
To finally clarify the situation, the patient undergoes an urgent x-ray. From the pictures, the doctor can determine whether the root is broken. If the preliminary diagnosis is confirmed, the tooth is removed.
Combined lesions
They are characterized by the presence of several types of violations at once. For example, a baby has both a dislocation and a fracture. Therapy for this problem is selected individually, based on the characteristics of the clinical situation.
If possible, the doctor preserves the tooth to avoid unwanted changes in the bite. But in severe situations, it is most often necessary to resort to removal surgery.
Causes of dental injuries
Damage to baby teeth can be caused by any strong force applied to the jaw. For example, if a child was running and accidentally fell with his cheek on some object (chair, curb, step), this may well lead to a bruise or fracture of a tooth. Acute injuries also occur from blows to the face when children fight or play sports like boxing and karate.
Based on the nature of the acquisition, the reasons are divided into household, sports and travel. They are sudden and very painful. There are also chronic injuries that occur due to long-term bad habits. Biting nails, felt-tip pens, ballpoint pens, threads while sewing, or cutlery thins the enamel. Thin, fragile enamel and caries of baby teeth become the main factors of toothache in a child.
What to do if a child has a dental injury
- If the injury is combined with a fall or a strong blow, you should immediately visit the emergency room and make sure that the child does not have a concussion or fractures, including facial bones - jaw, nose, etc.
- If other injuries are excluded or you are sure that it was the tooth that was damaged, you can immediately go to an urgent appointment with the dentist. If you have a tooth injury, we will see you immediately, since the speed of action often determines whether the tooth can be saved.
- The dentist numbs the area of the injury, determines the type of injury and prescribes treatment. In some cases it starts immediately, sometimes you need to wait a little. Treatment of a tooth injury can last up to a month.
It is important to correctly diagnose and treat an injured tooth to prevent complications. Meet our tooth fairies and check prices.
Treatment
Tooth restoration after a fracture occurs in several stages:
- returning the tooth to its socket followed by fixation,
- grinding off sharp edges,
- restoration of the upper part of the crown with composite materials.
If it is impossible to restore a tooth, the patient is offered prosthetics.
Stages of treatment for bruises :
- Isolation of the tooth from stress for 2-4 weeks.
- A course of anti-inflammatory drugs, the use of gels and ointments to prevent inflammation.
- Radiography and electroodontodiagnostics to assess the condition of the pulp.
- Depulpation of the tooth, installation of crowns or veneers in case of extensive internal damage and serious visual defect.
- Physiotherapy.
Tooth luxation is treated by repositioning or replanting the damaged tooth. In some cases, orthodontic treatment may be prescribed. If the damage is severe, the tooth will have to be removed.
The ability to restore the normal functioning of a tooth always depends on the type of injury received, the timing of seeking help, as well as the patient’s age and general health. The sooner a person seeks help, the greater the likelihood that the tooth can be restored.