What is thrush
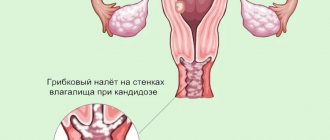
Thrush (or candidiasis) is a type of stomatitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane in the mouth) caused by a yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida. It is this fungus that causes the disease, usually transmitted through contact with an infected person.
The fungus is not a “guest” in the body: like other microorganisms, it always lives on the mucous membranes of the intestines, genitals, and mouth, but in small quantities. However, such a normal state is possible only with a “friendly” balance of “good” and “harmful” bacteria representing the microflora of the human body. This balance of equilibrium can be disrupted upon contact with a patient with thrush: in this case, a fungal infection from the outside enters the body of a healthy person and begins to multiply quickly there, disrupting the natural microflora.
This is possible when the immune system is weakened, when the number of “good” bacteria sharply decreases, and they are unable to fight the growing number of “harmful aliens.”
The occurrence of thrush in the mouth in children over the age of one year is explained by the fact that when they come into contact with each other, they pass toys and objects that they take in turn in their mouths, and among them there is often at least one child infected with candidiasis. And since the child’s immunity is still in the development stage, its internal protection is weakened, so infection occurs very quickly.
Is stomatitis contagious?
Infectious variants of the disease are quite easily transmitted from sick children to healthy ones. Most often, the infection spreads through airborne droplets from saliva during normal talking, coughing or sneezing.
The herpes virus can pass from an infected mother to the child during childbirth or during breastfeeding in the event of an exacerbation of herpetic inflammation.
We must remember that some forms of infectious stomatitis may well be transmitted through shared objects. This is especially true for cutlery, toys and personal care products. Therefore, if a child gets stomatitis, it is necessary to take measures aimed at preventing the possibility of its transmission to healthy children.
- If there is another child in the family, then it is worth protecting him from communication with the sick baby for at least a few days.
- It is imperative to provide the patient with individual household items that can be processed separately from the belongings of the rest of the family.
- If a case of stomatitis is detected in a kindergarten, it is recommended to disinfect all toys that healthy children may come into contact with.
Symptoms of thrush in the mouth of a baby
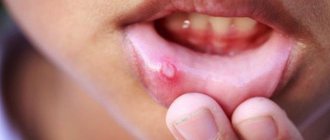
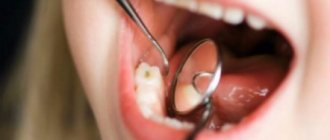
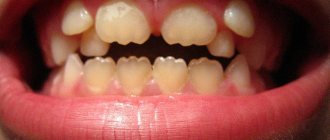
What does thrush look like in a baby? When a fungal infection enters the child’s oral mucosa, its proliferation leads to inflammation in the mouth area. Therefore, quite quickly you will be able to notice small crumbs of white “cereal”, reminiscent of cottage cheese, on the child’s cheeks, palate, gums and tongue. An inexperienced mother may well assume that this is the remains of milk or formula after regurgitation. But checking whether this is so is quite simple: take dry sterile gauze or a bandage and very carefully try to remove the white coating. If these are really leftover food, they will be easily removed; if it is thrush, it will be more difficult to erase the curdled coating. And after removing it, you will notice inflamed redness in the oral cavity. If your baby has thrush, his appetite and sleep will most likely worsen, and he will become restless and moody.
Clinical manifestations
Stomatitis in children is characterized by a gradual onset of the disease. Clinical signs of the disease do not appear immediately after infection. The incubation period is typical for this pathology; it lasts from two days to three weeks.
Symptoms of herpetic stomatitis in children appear starting from the prodromal period.
Each period has its own clinic:
- Latent – lasts up to two weeks. The child's sleep is disturbed and he refuses to eat. The baby becomes restless and whiny. He has increased salivation, possible nausea and vomiting. The lymph nodes are enlarged and painful on palpation.
- The height of the disease - at this time rashes appear on the skin and mucous membranes. They are located on the soft, hard palate, gums, cheeks, lips and tongue. They are group or single, up to three millimeters in size. They are thin-walled bubbles filled with a clear liquid. Their formation lasts up to four days. The vesicles quickly open, then erosions and painful aphthae form. They are shallow ulcers covered with a white coating. The mucous membrane in the mouth is swollen and bleeding. The child develops a high temperature of up to 40 degrees. A runny nose, cough, and conjunctivitis occur.
- Fading - aphthae, erosions gradually heal and epithelialize. These formations heal without scarring. Often there is a wavy course of the disease. The periods of appearance of rashes alternate with rises in temperature.
The illness usually lasts up to two weeks. In children under one year of age, generalization of the process is possible. The development of sepsis, damage to all internal organs and meninges is likely.
Causes of oral thrush in newborns
How can Candida fungi get into a baby’s body?
- infection can occur during the mother’s pregnancy if she suffers from genital candidiasis on the eve of childbirth: during the birth process, a fungal infection enters the placenta and amniotic fluid, and then into the newborn’s body;
- a baby can also become infected from a nursing mother if her nipples are affected by a fungal infection;
- when a child is bottle-fed or sucks on a pacifier, it, as well as bottles and nipples, must be treated in a sterilizer or boiled water before giving it to the newborn; unsterile nipples can cause bacteria to enter the oral cavity;
- the fungus can live not only on the mucous membrane, but also on the skin of the hands, from where it can easily migrate to the skin of the child if he is cared for by a person affected by thrush;
- The fungus can also be found in pet hair, dust, raw vegetables, meat or milk, so after contact with all these “transmitters” of bacteria, you must wash your hands thoroughly before touching the newborn;
- treatment with antibiotics can also disrupt the natural balance of the body's microflora; as a result of antibiotic therapy, candidiasis occurs in mother and baby who did not take medications containing “beneficial” bacteria along with antibiotics;
- candidiasis can occur if the mother has not learned how to properly attach the baby to the breast during feeding; the child may swallow too much air when sucking and, as a result, often burp; under such circumstances, most of the dairy food can remain in the child’s mouth, giving rise to fermentation processes and promoting the proliferation of fungi.
- thrush often develops in premature babies because their immune defenses are still too weak;
- candidiasis during artificial feeding can affect the baby due to the fact that he does not receive substances from mother’s milk that suppress the growth of fungal microflora;
- if the mucous membranes in the child’s mouth often dry out due to too dry air in the room or thirst, then such situations can contribute to the development of thrush;
- if the child’s immunity is reduced due to illness, poor sleep, lack of vitamins, then this can also cause fungi to multiply;
- candidiasis can also have a chronic form: in this case, it is often caused by serious illnesses in the child - diabetes, leukemia, HIV.
Pathogen dossier
What are the causative agents of the disease? Candida fungi are present almost everywhere: in the air, on the surface of any objects, including food, which means they can be transmitted by air, through food, or by contact. They are also present in limited quantities in the human body. With a decrease in immunity, hormonal changes, long-term use of antibiotics or dysbacteriosis, our body ceases to restrain their reproduction, which causes inflammatory processes on the skin and mucous membranes. Candida feed on sugar, releasing toxins that help reduce the body's immune properties. The main cause of thrush in children is the Candida albicans (white) strain. Of the variety of known varieties of fungi of this genus, the most dangerous strains are Candida lusitanlae, Candida glabrata and Candida krusei, which are resistant to some antifungal drugs.
Dangers of candidiasis for a newborn
Candidiasis can occur in simple and complex forms. And depending on the degree, it contains certain dangers:
- in severe forms of thrush, the fungus can reduce immunity and disrupt the gastrointestinal tract;
- candidiasis in a girl can spread to the vaginal mucosa, creating the risk of a pathology called synergy - fusion of the labia or vaginal mucosa;
- a mild form of thrush, in which it is enough to treat the plaque, usually does not pose any danger;
- with moderate thrush, inflammation forms under the white coating, which begins to bleed during treatment; this form brings additional discomfort and pain to the child; in the absence of proper treatment, the disease can become more severe;
- in severe cases of the disease, the fungal infection spreads throughout the entire oral cavity; in addition to pain and discomfort, the child may have a fever; Difficulties with swallowing can lead to the baby refusing not only food, but also water, which leads to rapid dehydration; this condition is life-threatening for the child, so its treatment is sometimes carried out in a hospital;
- thrush can occur not only in the acute, but also in the chronic stage: in such cases, exacerbation is characterized by the appearance of plaque on the mucous membranes and dry mouth; as a result of the infection spreading to the skin, small ulcers appear in the corners of the child’s mouth, and dense lymph nodes become noticeable to the touch under the jaw; reddish inflammations acquire a brownish tint and become painful, their area increases.
Is research necessary?
Usually, thrush in the mouth of a baby does not require additional research, since it is not difficult for an experienced specialist to diagnose it based on obvious signs. But sometimes, in case of serious lesions, additional studies may be prescribed:
- microscopic: in this case, the doctor will take scrapings from the oral mucosa to examine the yeast-like fungal cells more carefully;
- bacteriological: during such a study, a scraping is also taken and then bacteria are cultured to understand how large the volume of fungal colonies is and how amenable to treatment they are with antifungal drugs; in addition, bacteriological testing helps determine which drug is the most effective in treatment, because some of them may not have an effect in the treatment of thrush;
- serological: this study requires a blood test, in the serum of which antibodies to fungal infection are examined.
How to treat oral thrush in infants
Treatment of oral thrush in an infant is not a complicated process, but it requires the systematic implementation of certain procedures several times a day until the child recovers. If you find a mild degree of thrush in your baby, but at the moment you cannot call a doctor (for example, on a day off), then you can use traditional methods of eliminating thrush. If the degree of damage to the mucous membrane has already reached serious forms, it is better not to risk it and call an ambulance.
Traditional methods for eliminating thrush:
- using a soda solution: prepare a solution (dissolve 1 teaspoon of soda in a glass of warm boiled water), then wrap a sterile bandage around your finger, moisten the winding in the solution and very carefully wipe the areas of fungal infections; Do not rub them under any circumstances, because under the plaque there may be bleeding plaques, through which you risk allowing bacteria to enter the baby’s body; such light rubbing can be done 4 times a day until you have the opportunity to visit a doctor;
- use of honey solution: prepare a solution (dissolve 1 tsp honey in 2 tsp warm boiled water); however, please note that it is unacceptable to use a honey solution if a child is allergic to bee products; if the child tolerates honey well, then treatment with the solution can be carried out similarly to treatment with soda; You can also treat your baby’s pacifiers and toys, which he likes to put in his mouth, with any of these solutions;
- for candidiasis of the nipples, treat them with any of the above solutions;
- You can use other natural antiseptics for rinsing and treating the oral cavity - for example, herbal infusions; you can prepare a decoction of chamomile, green tea, calendula, taking 1 tsp. dry herbs for 1 cup of boiling water; Sage, elecampane, yarrow, burdock, and oak bark also have antiseptic properties, but it is also necessary to understand that any of the herbal preparations can cause an allergic reaction;
- sometimes the contents of aloe vera stems are used as antiseptics, lubricating the affected areas with this juice;
- Among the natural oils that can be used to lubricate the oral cavity, rosehip, flax or peach oils can be used after rinsing or treating plaque.
Types and forms of the disease
In order to prescribe the correct treatment, it is necessary to find out what type of stomatitis the baby has developed. To do this, you need to show the child to a doctor: he will examine the oral cavity, assess the condition of the mucous membranes, the number and size of ulcers and erosions. In uncomplicated cases, a visual examination is sufficient to diagnose the pathology, but sometimes the doctor may prescribe additional tests, for example, bacterial culture on nutrient media. This is necessary for selecting treatment tactics and prescribing treatment.
Table. Types of stomatitis and their manifestations.
| Type of disease | Cause of occurrence | Symptoms and signs |
| Fungal | Infection with single-celled microscopic microorganisms – fungi. In 80% of cases, the causative agent of infection is a fungus of the Candida family. | A cheesy coating on the surface of the gums and tongue, which has a dense consistency, bad breath, and an increase in temperature within the subfebrile range. |
| Aphthous (another name is ulcerative) | Systemic diseases that have a chronic course and have a negative effect on the activity of the immune system. | The formation of aphthae - round ulcers covered with a cloudy white film layer. Aphthae are always painful, and their number can reach up to 30 pieces. |
| Catarrhal | Poor oral hygiene and non-compliance with sanitary standards for the treatment of toys and premises. | Redness of the mucous membrane, swelling of soft tissues, increased production of saliva. |
| Bacterial | Gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms (mainly staphylococcus, chlamydia, streptococcus, klebsiella). | Yellow plaque, fever, signs of inflammation in the mucous membranes, pain during feeding. |
| Viral | Viruses of the herpes family (herpetic stomatitis) and viruses of the Vesiculorus genus (vesicular stomatitis). | Hyperemia of the mucous membranes, high temperature, increased salivation, blisters filled with cloudy liquid, which break through after 2-3 days. |
Note! There is another type of stomatitis - the allergic form. Allergic stomatitis develops as a result of interaction with irritating substances. These may be flavors and dyes included in children's toothpastes, or products used to treat toys and other items (antiseptics). This form of the disease is treated by an allergist.
Allergic stomatitis
Self-medication precautions
When choosing methods for self-treatment of oral thrush in a baby, you need to understand that sometimes such procedures may not correct the situation, but on the contrary, harm the child.
For example, improper use of soda solution when treating the oral mucosa can cause additional injuries. Therefore, carefully prepare the soda solution, not exceeding its concentration more than 1-2%, because a stronger concentration leads to a burn to the mucous membrane.
You can complicate the situation with candidiasis by using a honey solution. After all, beekeeping products are one of the most powerful allergens, so when using them you need to be absolutely sure that there is no allergic reaction.
In addition, when using herbal infusions, do not use several herbs at the same time. In this case, if an allergy suddenly arises, you will know which plant caused it.
Similar folk recipes can be used when treating an older child, but it is better not to experiment with the baby’s health. If the situation is urgent and you cannot see a doctor today, it’s better to play it safe and call an ambulance. At your appointment at the clinic, your doctor will prescribe medications to combat the fungal infection. When treated with medications, you can avoid additional risks, and candidiasis will go away faster.
Treatment of thrush with medications
If the treatment is prescribed correctly, then after a couple of days the child will feel much better even with a severe form of the disease. However, this does not mean that taking the drug should be stopped - it is necessary to complete the full course of treatment until all symptoms of candidiasis are eliminated.
Thrush that is not completely treated is at risk of returning during the next vaccinations or during the baby’s teething period. During such periods, do not use the previously prescribed medication yourself and under no circumstances increase the dosage of the medications. After all, an increased dose of an antiseptic can provoke the opposite effect - the occurrence of bacterial stomatitis due to the proliferation of pathogenic microflora. Independent and uncontrolled use of medications is always risky because beneficial bacteria living on the surface of the mucous membranes may die, and their place will quickly be taken by pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, wait for a doctor’s appointment, who will accurately determine the required dosage of the drug.
In addition, in parallel with drug treatment, do not forget about treating your baby’s nipples, bottles and toys: they can be regularly boiled and kept in a soda solution. When breastfeeding, do not forget to wash your nipples before each time your baby latches on.
Treatment of stomatitis in infants
When the first symptoms of stomatitis appear in a baby, it is important not to experiment with “folk methods”, but to show the child to a pediatrician as soon as possible. This way, it will be possible to make an accurate diagnosis in time, determine the cause of stomatitis and prevent the occurrence of complications.
Treatment of stomatitis in infants includes:
- Diet: the child should not be given acidic juices, fruit purees and other foods that can irritate the inflamed mucous membranes
- Thoroughly wash nipples, rattles, and boil bottles before each feeding
- Treatment with local drugs: you can use antiseptic rinses to reduce the number of infectious pathogens and relieve inflammation
- Protecting your child from fatigue, hypothermia or overheating
- At high temperatures - take antipyretic drugs that are suitable for age (in the form of syrup, rectal suppositories)7.
In young children, secondary infections are often associated with stomatitis. Therefore, it is extremely important to monitor the condition of a sick child: regularly measure the temperature, visit a pediatrician and take tests as prescribed. Advanced stomatitis weakens the child's immune system, making the little patient especially vulnerable to infectious diseases: tonsillitis, pharyngitis, ARVI.
To prevent your baby from getting thrush
To prevent thrush from reaching the baby’s mucous membranes, special precautions must be taken:
- Regularly care for your child’s mucous membranes, monitor their condition when the baby is sick, and especially when he suffers from infectious diseases;
- If your child is prescribed antibacterial drugs, be sure to remember to use special means to protect the microflora;
- If candidiasis occurs during pregnancy in an expectant mother, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor and undergo treatment. In addition, on the eve of birth, maternity hospitals carry out special prophylaxis for newborns with an increased risk of candidiasis. Thrush is especially susceptible to infants whose mothers suffer from chronic candidiasis and those who have foci of infection already in the immediate vicinity of birth. Mothers with inflammatory gynecological diseases or difficult childbirth can also transmit the risk of fungal infection to the newborn.