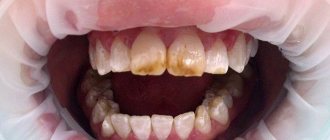
Changing the color of tooth enamel is an alarming signal that cannot be ignored. Dark spots can be associated not only with the consumption of coloring foods and drinks, but also with the development of various pathological processes. If the tooth has turned black at the root, you should contact your dentist as soon as possible. Do not wait for pain and other symptoms to appear, as they indicate extensive damage to hard tissues or inflammation of the dental nerve. It is easier to treat any disease in the early stages, so do not delay visiting a doctor.
Chromogenic components (food, drinks, other products)
The food we eat and other substances we use contain coloring agents (coffee, tea, cola, wine, tobacco, etc.) that can cause yellow, brown or bright orange spots to appear on the skin. teeth In most cases, the discoloration of teeth is generalized, which means that stains tend to form with equal success both on the entire surface of the tooth and in individual areas. If stains appear, it is better to make an appointment with an inexpensive dentist near your place of residence.
Possible reasons
Has the tooth turned black near the root? There may be several reasons for this.
- Tartar. One of the most common problems. It is a hard brown coating. It is formed from food debris and soft plaque, which harden under the influence of saliva. Violation of the rules of oral hygiene is the main cause of the appearance of tartar. Most often it forms around the neck of the tooth. It can also be subgingival - adjacent to the root and covered by the gum.
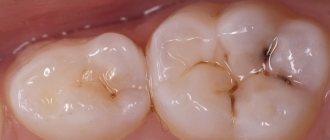
- Cervical caries. Dark spots at the root of the tooth may turn out to be carious cavities. They appear due to demineralization of enamel and destruction of dentin by pathogenic bacteria. As a rule, dental caries is preceded by tartar. The risk of developing the disease increases with insufficient oral hygiene, decreased immunity, and lack of calcium, phosphorus and vitamin D in the body.
- Dying of the pulp. Blackening of the tooth can also be a consequence of necrosis of the cells of the neurovascular bundle. Pulpitis occurs due to deep caries, burns during tooth treatment before prosthetics, or trauma. Pulp necrosis is manifested by prolonged pain when eating hot food and mechanical impact on the diseased tooth, but is often asymptomatic.
- Fluorosis. Darkening of teeth may be due to excess fluoride entering the body. This microelement is necessary for strong bones and teeth, but if the permissible concentration is exceeded, it leads to the development of fluorosis. This disease provokes destructive changes in the enamel and the formation of dark spots and stripes on the teeth.
Tooth decay
In the early stages of tooth decay, white spots or spots appear on the tooth enamel. The affected areas lose their natural shine and become dull. A thorough examination reveals the presence of damage to the enamel. If the process of tooth decay progresses, the affected area becomes brown or black, it is necessary to diagnose dental treatment. The damage is initially noticeable as a small dark spot or spots that gradually increase in size (over several months to several years) and often lead to actual tooth decay.
Conservative (medicinal) treatment of dental granuloma
This technique is used only for those cases in which the development of granuloma has not yet progressed far. The essence of conservative therapy for tooth root granuloma will be the intake and use of various drugs - antibiotics, antiseptics, drugs that have an anti-inflammatory effect. All medications are prescribed by a dentist and the treatment process takes place under the strict supervision of a specialist. This treatment option for granuloma is effective with early diagnosis of the disease and, if you strictly follow the doctor’s instructions, the granuloma will resolve within 1-2 weeks.
In some cases, conservative treatment of granuloma is complemented by root canal therapy. Working with tooth canals for root granuloma is indicated:
- For constant toothaches, the intensity of which does not subside from taking painkillers;
- Swelling of the gums, spreading to the cheek and jaw;
- Treatment of tooth canals is clearly indicated when large granulomas are detected - from five millimeters.
Prevention
You can prevent blackening of a tooth under a filling with the help of effective prophylaxis. To avoid the need for re-treatment, you should follow several rules:
Firstly, follow all the hygiene instructions of doctors - brush your teeth in a timely and regular manner, using the right toothpaste, floss, and rinses. Secondly, undergo preventive examinations in a timely manner in order to identify and treat any diseases in the early stages, before complications arise.
Try to avoid temperature changes - do not eat hot and cold food at the same time, do not drink hot drinks in the cold. Avoid traumatic effects - do not gnaw hard food (nuts, seeds) with filled teeth. Treat any infectious diseases in a timely manner, including those that are not directly related to the oral cavity.
Get rid of bad habits that disrupt the body’s activities and weaken its protective functions. Do not skimp on tooth restoration and, if the filling has darkened, replace it in a timely manner.
Additional symptoms
Typically, the appearance of secondary caries is accompanied not only by darkening, but also by a number of other symptoms that are difficult to miss. What should you pay attention to if your teeth turn black? Let's consider additional symptoms:
- change in enamel color, appearance of a black dot on the surface, darkening and other visual signs of destruction;
- bad breath, especially in the morning after waking up, is the result of the development of pathogens and tissue destruction;
- mobility of the filling, which may eventually partially crumble or fall out completely;
- pain, especially if the nerves are not removed;
- redness of the gums caused by the presence of an inflammatory process.
Even if the blackening of the filling is not accompanied by the additional symptoms described above, it is recommended to undergo a preventive examination so that a specialist can identify the causes of the problem and determine the tactics for further action.
Treatment methods for initial caries
In most cases, treatment of caries in the spot stage is carried out without drilling. For this purpose, in particular, remineralizing therapy or deep fluoridation of enamel can be used.
When the chewing surface of a molar or premolar is damaged, the doctor often suggests invasive fissure sealing, that is, sealing the enlarged natural grooves with a sealant.
If the stain has acquired a dark shade, it is sanded or prepared, then the defect is filled.
One of the modern technologies for treating caries in the spot stage is the Icon technique. When using it, the affected tooth surface is treated with a flowing material that penetrates the enamel, fills its pores and neutralizes bacteria.
Why does the enamel color change?
Blackheads occur for many reasons, of which dentists identify the main ones:
- Presence of plaque if not cleaned regularly with a toothbrush.
- Hereditary factor.
- The presence of sealed teeth treated with metal fillings.
- Smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Long-term wearing of braces.
- Poor cleaning of dental canals due to caries.
- Erasure of enamel.
- Use of tetracycline antibiotics for treatment.
How to treat granuloma on the root of a tooth
Treatment is selected by a specialist depending on several factors:
- At what stage is the inflammatory process currently?
- Has the damage affected neighboring areas?
- What conditions accompany the pathology (pinched nerve, stomatitis, multiple caries, etc.).
As a result, drug therapy or surgical intervention is chosen. The second method is more radical; it allows you to cope with the problem when the root, pulp is damaged or a crack has formed.
Conservative way
To exclude a bacterial infection (it is this that leads to suppuration), antibacterial drugs are prescribed to relieve swelling, inflammation, redness and severe pain. The diseased tooth is sanitized. It is opened, the dentist drills a hole down to the root canals to remove all the affected tissue cells. Then the medicine is placed into the formed cavity. Unfortunately, this does not provide a 100% guarantee that a relapse will not occur.
Physiotherapeutic method
You can act on the granuloma, but do not damage the soft tissue. This is done using:
- Depophoresis. In this case, a special medical composition is placed into the dental canals, which have been previously cleaned from the inside. This mixture perfectly eliminates infections and prevents re-infection.
- Laser. This is a very effective technique at the initial stage of development. A laser beam affecting the root system completely disinfects it.
Note that after all the above methods, a temporary filling is installed. This allows the doctor to then re-open and examine the condition of the tissue. If everything is fine there, then he seals the area being sanitized.
What to do if large or small spots appear on your teeth?
Any changes in the color or structure of tooth enamel are a reason to be wary and seek advice from a dentist. Only a doctor, after diagnosis, will be able to accurately answer the question: is a blackhead a symptom of caries? Or the darkening occurred for another reason.
If a stain on the front teeth occurs as a result of a bruise, the dentist will remove the affected tissue, process and fill the canals, and, if necessary, recommend installing veneers or endo-whitening (lightening the tooth from the inside).
If the cause of dark spots is poor hygiene or poor plaque removal, professional cleaning using ultrasound or laser will help solve the problem. These methods are good at removing plaque and tartar from the enamel surface and returning the teeth to their natural shade.
If food coloring is the cause of teeth staining, professional hygiene combined with a subsequent whitening procedure can help.
Unfortunately, dark spots on teeth are caries in the vast majority of cases, and the carious process at any stage requires immediate treatment.
Types and classification
Depending on the location of the defect formation, caries in the spot stage is divided into types:
- Fissure. The discolored area is located on the chewing surface of a molar or premolar.
- Contact. Changes are detected on the lateral parts of the tooth, which are in contact with each other.
- Cervical. The stain is found in the area bordering the gum.
The form of the disease can also be different. Progressive caries develops quickly and after a short time passes into the superficial stage. The intermittent form is characterized by periodic exacerbations and attenuation of the pathological process. Suspended caries spots can persist for years without moving to the next stage.
Causes and features of caries in the spot stage
According to Miller's chemical-parasitic theory, dental caries in the stain stage and at deeper stages develops with the participation of microorganisms. Bacteria contribute to the production of lactic acid and the destruction of inorganic components of enamel under its influence. The process of carious changes in the hardest tooth tissue is triggered by a certain type of bacteria, or rather by the products of their vital activity. Tooth enamel is unique in that it is, in theory, indestructible, since it does not contain constantly renewed cells. The extraordinary strength of this body tissue is also evidenced by the remains found by archaeologists with skulls in which teeth were preserved.
But microorganisms can still destroy tooth enamel. The main role in this destructive activity belongs to the bacterium Streptococcus mutans, which lives in the oral cavity and forms part of its microbiota. The mentioned microorganism is considered opportunistic, that is, activated under certain conditions. These include frequent and excessive consumption of sugar and other carbohydrates that can be fermented.
When sweet food enters the oral cavity, the number of cariogenic bacteria rapidly increases, and as a result, the balance of microflora changes in favor of pathogenic microorganisms. When sugar is fermented by these bacteria, the amount of acid increases, which leaches calcium and other minerals from the enamel. As a result of such exposure, the surface of the affected area undergoes characteristic changes.