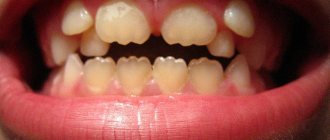
What is Priestley's plaque
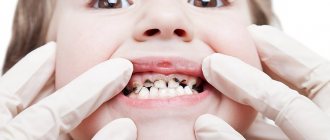
Plaque on baby teeth of a yellowish, black or brown color appears in a child when bacteria actively multiply in the oral cavity. Priestley's plaque is often seen at an early age, but can also occur in older children. When deposits appear, teeth lose their attractiveness, which can negatively affect the child’s psychological state. If symptoms of this unpleasant phenomenon develop, you should immediately contact your dentist to eliminate Priestley’s plaque in children.
Removing plaque from the Family Dentist blade
Visits are provided by pediatric dentists with a good reputation and more than 16 years of experience. Our doctors know how to adapt the baby and relieve anxiety. When communicating in a playful way, the child is not afraid of dental procedures and perceives all manipulations calmly. Our regular little patients sit in the miracle chair without fear and open their mouths to expel harmful microbes that have settled in their teeth.
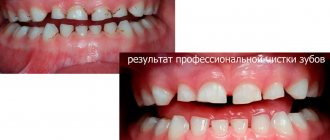
We clean plaque on the teeth of a preschool child (up to 7 years old) manually using circular brushes and a “tasty” professional paste. The procedure is comfortable and painless; usually all babies quickly get used to the buzzing of the brush and do not interfere with cleaning. Polishing paste copes well with soft deposits and pigmentation.
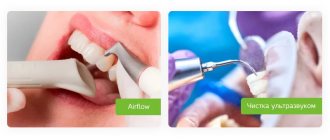
We carry out professional hygiene for children over 7 years old using the Air Flow air-polishing technology, using the latest modification of the Japanese Prophy-Mate system. A thin water-air jet containing calcium or glycine-based powder is supplied from the tip under pressure. The doctor directs the flow onto the tooth, the abrasive mixture knocks down sticky, pigmented and low-mineralized deposits, cleans the fissures and interdental spaces.
Spherical granules of polishing powder do not damage sensitive enamel and mucous membranes and provide a polishing effect. On a smooth surface, plaque forms more slowly. During the procedure, the child does not experience pain. Kids love the pleasant taste of the solution.
After cleaning with a brush or the Air Flow method, the dentist applies fluoride varnish to the teeth. Fluorides reduce sensitivity and strengthen thin enamel, inhibit bacterial activity. In Minsk, the concentration of fluoride in water is low, so fluoride varnish is safe for children.
If you notice dark or sticky deposits on your child's teeth, make an appointment with your pediatric dentist. Timely removal of plaque reduces the risk of caries and gingivitis by 70%.
Causes of black plaque in children
The main causes of black plaque on teeth are:
- Priestley plaque is the main cause of deposits. Growing up, the child gets rid of this problem, since plaque almost never settles on permanent teeth. This phenomenon does not harm health and is characterized as a purely aesthetic defect.
- Tooth decay is a serious disease that can lead to tooth loss. The carious process is accompanied by yellowing and subsequently blackening of the tooth enamel. When the first symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a dentist.
- Dysbacteriosis is a disease that leads to the appearance of dental plaque due to disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system. The causes of the disease are poor diet, long-term use of medications, chronic diseases affecting the liver or intestines.
- Oversaturation of the body with iron. Prescribing iron-containing medications to children leads to the formation of both black plaque and deposits that are dark purple or brown in color.
In addition, teeth can darken due to a lack of calcium in the body caused by some disease. In general, the exact cause will be revealed during an examination by a dentist.
Types of plaque
- White.
By the end of the day, all children have a small amount of harmless white residue. Abundant formation indicates vitamin deficiency, reduced immunity or insufficient hygiene. This type of plaque can be removed from a child’s teeth if you brush your teeth thoroughly every day. The presence of hard fruits and vegetables in the diet, such as apples and carrots, promotes mechanical cleaning. If no action is taken, the layer will harden, mineralize and turn into tartar.
- Yellow.
Indicates insufficient hygiene and poor nutrition. In children under two years of age, it can occur, for example, due to the consumption of sweet liquids from a bottle. It may also indicate the initial stage of caries. By choosing the right toothpaste and brush, as well as brushing your teeth more thoroughly, this problem can be solved.
- From light gray to green.
Gray - possible with abundant release of chlorophyll, sometimes acquires a greenish tint. Green - provoked by a fungus - chromogenic bacteria. Damages the pellicle, the natural protective film on the teeth. Only a dentist can help remove such plaque.
- Brown.
Indicates a fungal infection of the oral cavity and a disorder in the gastrointestinal tract. The result is darkening of the enamel. Iron supplements can also stain teeth brown. How to remove such plaque from a child’s teeth? Sometimes it goes away on its own after you stop taking iron-containing foods or medications. If the deposits have hardened, you will need professional teeth cleaning - ultrasound or chemical whitening. It is also necessary to adjust the child’s nutrition.
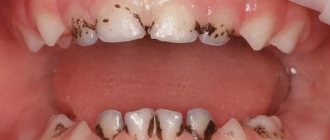
- Black.
Black plaque is the first harbinger of caries. Especially if it has a point character. In such cases, it is better not to postpone a visit to the dentist.
What does ignoring the problem lead to?
Failure to promptly contact a dentist when plaque appears on baby teeth leads to the following negative consequences:
- development of the inflammatory process;
- bleeding gums, which occurs if the child eats or brushes his teeth;
- the likelihood of developing diseases such as caries, stomatitis and periodontal disease increases;
- milk teeth with a black coating are very unaesthetic, which is fraught with the development of complexes in the child;
- deposits may be accompanied by bad breath.
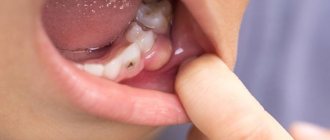
What are the types of tartar?
Dentists distinguish two types of tartar – subgingival and supragingival. They are classified according to their location on the tooth surface. Supragingival can be easily seen with the naked eye, is whitish-yellow or gray in color and is easily removed by scraping. Minerals that come from saliva take part in its formation. The predominant localization of such a stone is the area of the buccal surfaces of the upper molars, where the ducts of the salivary glands and the frontal teeth of the lower jaw emerge.
The second type of tartar can only be detected by a dentist during probing. Its formation involves minerals that come mainly from gingival fluid. Most often, it has a dark brown color and a greenish tint, and is localized in most cases on the root cement, on the neck of the tooth (near the gingival groove) and on the root cement. The stone covers the neck of the tooth and is tightly attached to its surface; it can often form protrusions.
Preventing the reappearance of black plaque on teeth
Prevention of plaque formation includes:
- Regular dental and oral care. For babies, their gums are cleaned using cotton pads and special silicone tips. When the baby turns two years old, he needs to be taught to properly brush his teeth with a brush and toothpaste, as well as to regularly rinse after meals.
- Balanced diet. Your child's diet should include fewer sugar-laden foods and more natural fruits and a variety of vegetables.
- Timely limitation of the use of pacifiers and bottles. Long-term use of these items leads to the appearance of malocclusion, the development of a certain dependence, and the formation of so-called “bottle caries.” If a child can do without a pacifier and bottle, they should be disposed of.
In addition, you should constantly monitor the state of the child’s immune system and support it with the help of vitamins, which have a beneficial effect on the health of the teeth and the whole body. If you follow these simple recommendations, your child will always delight his parents with his beautiful and healthy smile.
Reasons why tartar forms
Local factors play a major role in the formation of tartar. For starters, this is poor oral hygiene in childhood. In addition, the cause of tartar is an insufficient intake of solid foods. Also, tartar in large quantities occurs as a result of the lack of pyrophosphate in saliva - a substance that retards the development of dental plaque and the lack of protein in it, which tends to slow down the growth of crystals. Tartar on children's teeth is not always obvious. Calcium phosphate crystals can bind tightly to the surface of the enamel, making it often difficult for the dentist to determine where the stone begins and the enamel ends.
Provoking factors
The main reason why tartar forms in young children is poor oral hygiene. Even parents are not always able to thoroughly clean children’s teeth, so, as a rule, large plaque accumulates in hard-to-reach places.
The provoking factor may be:
- lack of solid food in the child’s daily diet;
- bite pathologies;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- gastrointestinal diseases.
It is not always possible to eliminate the provoking causes of tartar in a child, so dentists recommend that parents constantly monitor the quality of their teeth cleaning.
Tooth enamel: general characteristics and properties
This is the hardest and most durable tissue in our body, its thickness on the outer surface reaches almost 2 mm. It consists of many layers formed at various stages of mineralization and has a crystalline structure. The chemical composition is represented predominantly by apatites, calcium and phosphorus predominate from inorganic compounds, and proteins, lipids and carbohydrates from organic compounds.
The main function is to protect dentin from external factors: mechanical, chemical and temperature stimuli. Thanks exclusively to this tissue, teeth can fulfill their main purpose - grinding and chewing food.
Despite its extraordinary strength, enamel is permeable to water and many organic and inorganic substances contained in saliva. It has been found that the degree of permeability for much-needed connections depends on several factors. If we talk about temporary occlusion, this is:
- condition of the oral cavity;
- nutritional features;
- long-term treatment with certain medications (in particular, tetracycline antibiotics);
- features of intrauterine development.
Enamel maturation
The composition of the protective tissue covering dentin is constantly changing, which is associated with age-related characteristics. Throughout the year after teething, there is an active accumulation of calcium and phosphorus, and during this period it is extremely important to receive all the necessary elements with food or multivitamin preparations. It has been proven that a sufficient content of microelements prevents the development of caries.
The child has yellow teeth. Reasons and what to do?
There is nothing better than a dazzling smile. For people whose work involves communication, a snow-white smile is the norm. And to ensure that their teeth always look pleasing, they go to great lengths: constant visits to the dentist, whitening procedures, expensive care. But what to do with children who, from a very early age, have unattractive yellow teeth? Parents should understand that dental plaque contains a lot of pathogenic bacteria, which very often lead to inflammatory processes in the throat and oral cavity.
Very often, parents do not attach importance to this problem, believing that yellowness on baby teeth does not pose any threat to the child’s health. There is an opinion that these teeth, as a temporary phenomenon, do not require special attention from the dentist. In practice, this is not the case at all. If you do not pay attention to the yellowness of your teeth in time, then in the future quite serious dental problems in the oral cavity may arise.
Causes of yellowness
1. Heredity. It will not be surprising if parents with yellow teeth discover this problem in their child. However, the hereditary factor does not often become the determining factor; most likely, the reason will be completely different.
2. Improper oral care. If a child does not know how to brush their teeth, they will most likely have visible yellow plaque stains. It is very important for parents to teach their child how to properly use toothpaste and a brush and, if possible, control this process. Parents wipe the first teeth with a soft brush after each feeding. After the baby has already learned to hold this instrument independently, he should be taught to brush his teeth correctly. The paste and brush are selected according to age, and all manipulations must be carried out under the strict supervision of adults. Dentists recommend monitoring this process until the child turns 10 years old. Children who wear orthodontic elements in their mouths require special control and assistance. The best option for them is to have their teeth professionally cleaned at the dentist's office every month.
3. Thinned enamel. The white color of teeth is provided by enamel. If it becomes thinner, dentin, which has a yellow tint, begins to show through. This is what causes teeth to turn yellow. Thin enamel can be present from birth, in other cases the problem arises due to improper brushing of teeth, incorrectly selected toothpaste and brush, as well as from drinking a large amount of carbonated drinks. But the most common cause of thinned enamel in a baby is the pathology of the mother’s pregnancy.
4. Taking medications. You should be aware that some medications can cause yellowing of the enamel on your teeth. These include the antibiotic tetracycline or amoxicillin. Even taking these drugs by a pregnant woman will cause the baby to have yellow teeth.
5. The cause of yellow teeth in children can be developmental pathologies in the womb.
6. Acquired diseases also affect the color of tooth enamel in children. For example, children who have had jaundice develop a dark brown plaque on their teeth. If a child has digestive problems, his teeth will also have a yellowish-brown tint.
7. Mechanical damage. The impact can chip the enamel on your child's teeth, resulting in unattractive yellow stains.
Methods for dealing with yellowed teeth in children
You need to understand that the hereditary cause of yellow teeth has no cure. All you can do for your child is to visit the dentist at the Sanation clinic on time and perform teeth whitening procedures.
1. Professional cleaning involves removing tartar and plaque, followed by coating the tooth with silver or fluoride varnish.
2. Whitening can also be done in a dental office. But if you don't have enough time or money, there are a few simple tricks that can help restore the whiteness of your child's teeth. The most famous: rinsing the mouth with water and lemon juice, chewing parsley leaves.
3. Teeth whitening with ultraviolet light. This method is good for cleaning teeth that have become yellow from taking medications. Under the influence of ultraviolet light, the antibiotic dissolves and the teeth become white. But to use ultraviolet lamp cleaning, strict indications are required; they can only be determined by a doctor.
4. Exclusion from the diet of foods containing artificial colors. To avoid staining your child’s teeth, you should avoid all carbonated drinks and colorful sweets. The consumption of these products not only stains the enamel of teeth, but also very often leads to caries.
5. Mechanical cleaning. You can get rid of yellow plaque on children's teeth using a special abrasive paste and brush. But it should be noted that this manipulation can only be carried out in a doctor’s office and no more than once every 3-4 months. Brushing on your own can damage tooth enamel, which can lead to even more dental problems.
6. Cleaning with special preparations. There are a number of medicinal ointments and solutions, the use of which effectively whitens a child’s tooth enamel. These include Remodent, Gluftored, Profokar. As a rule, the correct use of these products at home does not cause any harm to the child’s health.
To prevent your child from having yellowed teeth, you need to carry out preventive measures in a timely and efficient manner:
- brush your teeth twice a day (starting with milk teeth);
- visit the dentist’s office at least once every two months for an examination;
- monitor the child’s proper and balanced diet;
- Have your teeth professionally cleaned at least once every six months.
Helpful information
Children's dentistry