- Causes of tooth loss
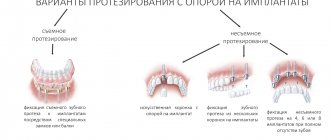
- Treatment options for complete edentulism
- — 2 implants on one jaw
- — 4 implants (all on 4)
- — 3 implants
- — 6 implants
- — 8 implants on one jaw
The absence of a tooth/teeth is called adentia.
Adentia can be partial (the absence of one or more teeth) and complete edentia (the complete absence of teeth).
In addition, adentia can be primary (when the tooth does not exist at all, its rudiment is not laid) and secondary (when the tooth was cut, but for some reason it was lost or removed). Secondary adentia is much more common.
If teeth are completely absent in the lower jaw, then they speak of complete edentulism of the lower jaw. The absence of all teeth in the upper jaw is called complete edentulism of the upper jaw.
There is also complete edentia of both jaws.
Types of prosthetics for complete absence of teeth
In dental orthopedics, there are two options for complex prosthetics for total edentia: removable and fixed.
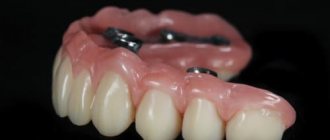
Fixed prosthetics
The Family Dentistry clinic performs daily rehabilitation operations for patients with complete absence of upper or lower teeth. We have performed more than 1,200 total jaw replacements.
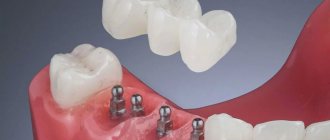
All-on-4
A protocol for complex prosthetics, involving the installation of a fixed prosthesis with 10 or 12 crowns supported by four implants:
- two are implanted in parallel in the anterior section;
- two at an angle of up to 45° in the distal.
Why is inclined implantation of two implants used? Firstly, to increase the contact area between the bone and the implant (allows you to abandon the sinus lift). Secondly, in order to eliminate the risk of damage to the mandibular nerve or maxillary sinuses.
All-on-4 technology or “All-on-4” is a predictable and well-studied method of treating complete edentia (used since 1998) without bone grafting with good results in the short, medium and long term.
3-4 hours after installation of the implants or 3-7 days (often you need to wait for the swelling of the mucous membrane to go away after surgery), a temporary prosthesis is attached to the abutments.
After complete engraftment of titanium screws into the bone tissue (on average, this takes from 3 to 6 months), fixation is carried out with a permanent orthopedic structure.
All-on-6
A technique for complete jaw prosthetics for total edentia, developed on the basis of the All-on-4 protocol and being its logical, modified continuation.
To make it possible to use the technology in the rehabilitation of patients with a complex clinical picture (severe bone tissue atrophy, periodontitis/periodontal disease, diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis), six implants are used:
- two are fixed in the frontal zone;
- four – in the distal lateral section (two each on the right and left).
The use of a larger number of implants provides more reliable support for a fixed prosthesis (a bridge structure with a length of 14 crowns can be installed) and uniform distribution of the chewing load throughout the entire arch.
Why is it impossible to refuse prosthetics if you are edentulous?
Ideally, a person should contact a dentist as soon as he notices any problems in the oral cavity. In reality, we wait until there is basically nothing left to treat - the teeth have either fallen out or are in such a deplorable state that they can only be removed.
There are many reasons for mandatory prosthetics for edentulous patients:
- Bone tissue atrophy occurs, alveolar processes decrease and disappear. The longer a person goes without teeth, the less likely he is to get even a removable denture - he simply will have nothing to cling to. In this case, they do a sinus lift - they build up bone tissue, but such an operation is expensive and beyond the means of most people.
- Disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. The inability to chew food well causes constipation, and the absorption of nutrients deteriorates. In addition, a person can ultimately only eat foods that have been pureed into a puree.
- Change in appearance. The face becomes senile - the lips fall back, the chin moves forward, and the nasolabial folds become clearly visible.
- There is a violation of diction. For many, this comes as a surprise and gives rise to complexes.
Prices for complete prosthetics
| Name | Price, rub) |
| Complete jaw prosthetics on 4 Osstem implants (South Korea) with a fixed plastic prosthesis | RUB 225,000 |
| Complete jaw prosthetics on 6 Osstem implants (South Korea) with a fixed plastic prosthesis | 275,000 rub. |
| Promotion! Jaw prosthetics on 4 Straumann (Switzerland) or Nobel (USA/Sweden) implants with a fixed plastic prosthesis | 260,000 rub. |
| Promotion! Jaw prosthetics on 6 Straumann (Switzerland) or Nobel (USA/Sweden) implants with a fixed plastic prosthesis | 320,000 rub. |
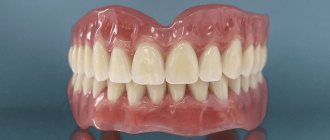
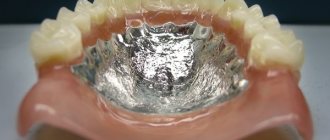
Removable prosthetics
At the Family Dentistry clinic, treatment of patients with complete absence of teeth in the upper or lower jaw is carried out only by the method of permanent prosthetics on implants. The main disadvantage of removable dentures is atrophy of the jaw bone. The longer you wear them, the more bone tissue decreases. Subsequently, when the patient decides to install a fixed prosthesis, preliminary bone grafting will be required. If you decide to wear a removable denture, we can only help you find a good dental clinic that provides removable denture services.
1 Acrylic prosthesis
2 Acry Free dentures
3 Nylon prosthesis
A classic option for restoring the integrity of the dentition with complete edentia. In demand due to its low price. But at the same time it is the most inconvenient type of complete removable denture. Pros:
- low price;
- fast production times;
- easy to repair, adaptable (increases service life).
Minuses:
- provokes injury and inflammation of the gums due to constant stress;
- takes up a lot of space in the mouth (more voluminous than its counterparts), it is difficult for the patient to get used to wearing a plastic prosthesis;
- may cause an allergic reaction as a result of the free monomer contained in acrylic reacting with saliva;
- the artificial gum is opaque, the acrylic prosthesis does not look natural;
- Acrylic absorbs food coloring pigments and requires careful care.
Acry Free thermoplastic plate prosthesis is the most durable, aesthetic and long-term solution in complete removable prosthetics. Pros:
- The Akri Free prosthesis is thin and fits more tightly to the tissues of the prosthetic bed (the patient gets used to wearing it faster);
- does not cause allergies, as it does not contain methyl methacrylate;
- thanks to the aesthetic artificial gum, it is practically indistinguishable from your own teeth;
- has no pores (unlike acrylic and nylon), does not absorb food pigments, does not cause bad breath, and is less demanding in care;
- easy and inexpensive to repair.
Minuses:
- fragile, does not always withstand increased chewing loads and breaks;
- the price is twice as high as for an acrylic prosthesis.
Made from dental nylon, which is lightweight and elastic. Typically used as a temporary solution. Pros:
- takes up less space in the mouth, weighs less, so it is comfortable to wear;
- the prosthesis is flexible, easy to remove and put on, and will not break if accidentally dropped on the floor;
- The orthopedic design is practically invisible, as it is made of translucent material with a shade close to the color of the gums.
- does not cause allergic reactions like acrylic prosthesis.
Minuses:
- due to flexibility, it does not distribute the chewing load over the entire mucosa and leads to rapid atrophy of the alveolar ridge;
- nylon cannot be polished; after 2 years, plaque and pigments accumulate on it, and its attractiveness is lost;
- Eating hot food/drinks increases the elasticity of the prosthesis; frequent adjustments are required;
- rubs the gum, causing its atrophy (abrasions and bedsores form under the denture);
- repair of a nylon removable denture is very complex and expensive, and relining in the oral cavity is impossible;
- absorbs odors, after 1-2 years it begins to smell unpleasant.
Why is fixed prosthetics better than removable prosthetics?
Preventing bone atrophy With complete removable dentures, the main part of the chewing load is transferred to the mucous membranes, so bone tissue resorption begins. Implants function like real tooth roots. The chewing load is distributed onto the artificial teeth as if they were your own. Bone loss stops.
Reliable fixation A removable denture covering the entire jaw can fall out at any time. Fixed prosthetics on implants eliminates the risk of falling out. It eliminates the constant fear that the denture will fall out of the mouth at the most inopportune moment.
Preservation of taste/heat sensitivity A complete denture covers the palate. As a result, the taste and heat receptors of the oral cavity do not work.
Full restoration of chewing function A complete removable denture restores the chewing ability of the dentition by only 20-30%.
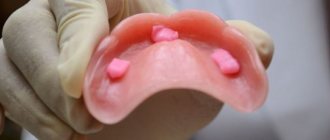
Making a complete removable denture
The production of a complete removable laminar denture is quite fast. The design itself does not have complex elements, and the patient does not require a preparatory period (except for the installation of a prosthesis supported by implants). Modern methods for manufacturing complete removable dentures imply receiving a finished structure 10–14 days after the initial visit to the clinic.
Stages of manufacturing a complete removable denture:
- Initial consultation. Photo of the jaw and choice of prosthesis.
- Taking impressions.
- Casting models.
- Making a wax base.
- Determining the relationship of the patient's jaws, correcting the prosthesis in the articulator.
- Making the final model after successful wax fitting.
- Correction and processing of the finished prosthesis.
- Installation of a complete removable denture.
Making removable dentures in the absence of teeth is usually not accompanied by major mistakes on the part of doctors, but if at the fitting stage the design gives you severe discomfort or pain, report it immediately.
Stages
1 Consultation, diagnostics
2 Preparation
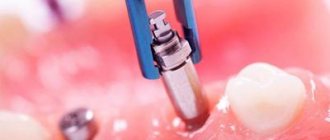
3 Surgery
4 Orthopedics
The doctor will visually examine your teeth and gums to make an initial assessment of their health. He will collect anamnesis, conduct a hardware examination (orthopantomogram + computed tomography), and make sure that there are no contraindications to prosthetics on implants.
Plaque and stone are removed, diseased teeth on the antagonist jaw (if there are teeth) are treated. The implant dentist prepares a treatment plan, incl. 3D model of the jaw for detailed planning of the operation. A date for the operation is set and a contract is concluded.
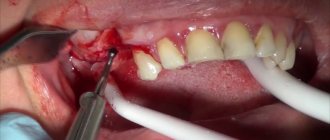
An injection of local anesthesia is administered. Four or six implants are installed depending on the technology used for prosthetics of a toothless jaw.
On days 3-7 after installation of the implants, a temporary (adaptation) prosthesis is fixed on them. At the end of the period of osseointegration of the artificial roots, a permanent prosthesis is placed.
Contraindications
Despite the fact that a person with a toothless mouth feels inferior and wants to get rid of the defect, it is not always possible to restore the dentition. Absolute contraindications to prosthetics are:
- allergy to material components;
- oncology;
- poor blood clotting;
- excessively low weight;
- severe diabetes mellitus;
- intolerance to anesthesia.
Relative contraindications include exacerbation of mental illness and viral infection. As soon as the patient recovers, full prosthetics begin.
Questions and answers
Are there any contraindications to fixed prosthetics supported by implants?
Absolute contraindications include:
- chronic heart failure, angina pectoris, arterial hypertension;
- diseases of the blood and hematopoietic system;
- oncology (cancer, sarcoma);
- pathologies of the immune system.
Relative contraindications in which surgery is postponed include:
- poor oral health;
- presence of dental diseases (gingivitis, pulpitis, periodontitis);
- malocclusion;
- diseases of the temporomandibular joint, etc.
What material do you use to install a permanent fixed prosthesis?
For total prosthetics of an edentulous upper or lower jaw supported by implants, we install a permanent bridge with crowns made of zirconium dioxide - the most durable and aesthetic material in modern dental orthopedics.
How to care for a fixed overdenture on implants?
- Be sure to purchase a new toothbrush with a soft or ultra soft hardness level. Start brushing her new teeth only after three days from the date of surgery. It is better to use a herbal paste to prevent gum inflammation.
- To clean the interdental spaces and the space between the denture and the gum (a toothbrush cannot get there), use an irrigator, but only from the 3rd week after installation of the implants. You should start with the initial speed, gradually increasing it.
- Use a mouthwash after every meal. They fight bacteria in the mouth and freshen breath.
- Visit your dentist once every six months for a preventive examination and professional oral hygiene (cleaning your teeth from plaque and tartar).
Is complete prosthetics of the upper jaw different from the treatment of an edentulous lower jaw?
The peculiarity of the upper jaw is that it receives less chewing load and is therefore inferior in density to the lower jaw. Its structure is looser and more susceptible to resorption. For her rehabilitation, the “All-on-six” method is indicated. A larger number of supports is necessary to ensure reliable fixation of the complete bridge.
For the treatment of total adentia of the lower jaw, in most clinical cases, the “All-on-4” concept is optimal, since four are quite enough to support the orthopedic structure.
It is important to know that dental implants take root faster in the lower jaw - in 2-3 months. On the top it is slower - in 5-6 months.
How does the prosthetics process work?
The entire procedure consists of the following steps:
- Examination by a dentist, development of a treatment strategy.
- Taking an impression using dental instruments and special material.
- Checking the relationship of the jaws, the comfort of using dentures depends on this.
- Taking functional tests to form an impression. Based on the result, a wax frame is produced, which the patient can check.
- Installation and correction of the prosthesis after several days of use.