The appearance of a child’s first teeth is an important event in every family. It brings with it many troubles that are temporary. Fever, loose stools, problems with the digestive system, and anxiety are accompanying symptoms that will not harm the baby. However, every mother needs to know that everything should be within acceptable limits. It is important to monitor the child and react in time to developing deviations.
Symptoms of teething
The very first tooth appears when the child reaches 6 months. This process lasts about two years, or a little longer, depending on the child’s body. Each baby experiences teething differently. For one, everything will be easy and almost painless, for another it will be painful. Each child is unique, so parents should be attentive and monitor the well-being of the baby. When the crowns of the first teeth begin to erupt, the local immune defense reduces its functions. Therefore, pathogenic microorganisms enter the baby’s body, causing physiological stool disorders.
During this period, it is necessary to be attentive to the child’s condition and recognize in time that the appearance of loose stools is not associated with an inflammatory process caused by an infection. During the natural physiological process of teeth formation, symptoms are identified that do not cause harm to health.
Brushing our first teeth
Some parents believe that oral hygiene should be started when the baby already has several teeth; until then, there is simply nothing to brush. In fact, there are plaques on the child’s gums. These are small films that can accumulate food debris and be a source of infection. For this reason, dentists recommend starting to brush your teeth before they even appear.
It is not recommended to use a full-fledged toothbrush until the age of two. Oral hygiene can be carried out with a special children's brush, which is placed on your finger, or simply with a small piece of gauze soaked in boiled water.
The child’s mouth needs to be cleaned 1-2 times a day, and after the first teeth appear, special attention should be given to them to prevent the development of caries in the future.
Increased salivation
A natural protective property of the body that disinfects the child’s oral cavity. At a young age, children actively put various objects in their mouths that come their way. Thus, bringing various bacteria into the body, which the immune system fights, releasing large amounts of saliva. This is due to the fact that nature has the property of disinfecting wounds and injuries by wetting with saliva, which contains an antibacterial enzyme (lysozyme). Therefore, excessive salivation is not considered a pathology, but, on the contrary, protects the baby from pathogenic bacteria.
How many days does the feeling of bad health last?
The baby’s poor health when one tooth comes out can last about three days. But less often, due to a temporary weakening of the immune system, the child “catch” some virus or catch a cold. Then the symptoms will drag on indefinitely until the small organism overcomes the infection. You can't do this without a pediatrician.
Taking antiviral and immunomodulating drugs on your own is strictly prohibited. Any drug intervention for a child under 1 year of age must be strictly discussed with the doctor.
It is very important to learn to distinguish temperature and nasal congestion, which are the main symptoms of teething, from signs of a cold. So, for a cold there will be additionally:
- presence of snot in the nose. With simple congestion, which goes away after three days, they are not present;
- redness of the neck - you can check at home yourself;
- temperature rises above 38°C;
- the child began to cough.
There is nothing wrong with the fact that the baby has a cold - it is natural in this case. The pediatrician will prescribe the necessary treatment and the disease will go away in a week.
There are other circumstances in which calling a pediatrician is simply necessary, because we are talking about serious problems in the child’s health.
When should you call a doctor?
It is necessary to urgently call a doctor if:
- painful manifestations do not go away for more than three days;
- the baby “cleanses” more than five times a day;
- feces of atypical color: with a greenish tint, with dark inclusions, etc.;
- foreign inclusions in the stool, including blood;
- stool has a watery, foamy texture.
All of the above manifestations may indicate the presence of other diseases; ailments cannot be attributed to the “first tooth”.
Swelling and redness of the gums
Swelling, swelling, and an increase in the size of the baby’s gums are accompanied by discomfort (pain, itching). At this time, children try to chew on what is within walking distance, thereby trying to eliminate the unpleasant sensations that have arisen. All this is explained by the fact that an inflammatory process occurs in the area of the emerging tooth. Bone tissue forms inside the jaw, so it is necessary to push through the gum to appear on the surface. When swelling and redness are accompanied by profuse salivation, and a white bubble is also detected, this indicates that a baby tooth will soon appear.
Changes in behavior
This period is characterized by changes in the baby’s behavior. Children are capricious, sleep poorly, refuse to eat, and show apathy. This is due to the fact that the appearance of a tooth causes itching and pain, which bring great discomfort. At night, all symptoms become more active and cause concern not only for the child, but also for the parents.
Desire to gnaw
The baby has a need to chew as a result of severe itching and discomfort in the gums. The child puts toys and any other things into his mouth that can relieve the itching sensation. The harder the object, the better it eliminates itching when rubbed against the gums. This whole process is temporary, so the child is constantly looking for a new object that will help relieve unpleasant sensations. Many companies produce special teethers with various cooling effects that help babies go through this period with the least discomfort.
Symptomatic therapy
In addition to treating the main symptoms of digestive disorders and gum pain, sometimes it may be necessary to eliminate other symptoms. For example:
- If itching and rash appear on the skin, an ointment with panthenol, which is sold in any pharmacy, is ideal. Panthenol has a softening and restorative effect and quickly relieves any irritation.
- Allergies are treated with antihistamines, which have no contraindications for children under one year of age. You can consult a doctor and always keep the medicine he has prescribed at the ready.
- For nasal congestion, any children's drops with naphazoline or oxymetazoline can be used. The main thing about them is the dosage, which should be suitable for your baby’s age.
- If your baby is excessively restless, buy him a light soothing syrup with natural ingredients. Such syrups are also sold in any pharmacies.
- To prevent your child from putting everything in his mouth, buy him a teether. These toys are sold in any pharmacies and are specially adapted for pain relief and gum massage - they have special pimples on them that your baby will really like.
Increase in temperature, appearance of cold symptoms
This is due to the fact that during this period the body tries to produce the required amount of substances that can facilitate the growth of baby teeth. It is also possible that an infection or local inflammation may occur, during which the glands are activated and muconasal secretion (nasal mucus) appears, disappearing after a couple of days. The local inflammatory process provokes the body, which reacts and leads to fever and malaise. The main indicator that there is no serious illness is a temperature not higher than 38 degrees. When teething, sometimes a rash appears on the skin, nasal congestion, and a slight cough, which is caused by a large volume of salivation. A cold may occur less frequently, but this is due to a decrease in the body’s protective functions during periods of active viral infection.
Lifestyle
During treatment, it is also important to follow the following recommendations:
2
- Wash toys, teethers, pacifiers and pacifiers regularly. Prepare your best.
- Do wet cleaning, clean the crib and play area.
- Avoid contact with people with infectious diseases. Avoid crowds, especially during an epidemic.
- Massage your gums. This method makes the child’s condition easier. Before the massage, you need to wash your hands thoroughly; it is safer to resort to using soap petals.
Problems in the digestive system
One of the symptoms of the appearance of baby teeth is loose bowel movements. The stool becomes liquid because the volume of salivary fluid increases, as well as due to the penetration of bacteria that disrupt the microflora of the children's intestines. Regurgitation, flatulence, specific sounds in the stomach that last no more than three days, and bowel movements no more than four times a day are considered normal manifestations of the body. If the symptoms are of a different nature or for a long period, then you should immediately contact your pediatrician.
Important! During the teething period, the immune system weakens its protective functions due to the child's stress reaction. Due to weak immunity, there is a risk of contracting a serious infection, which is why it is worth carefully monitoring the baby and detecting a pathological abnormality in time.
What can diarrhea in a baby indicate?
Diarrhea may be accompanied by moodiness
We must learn to distinguish normal stool from any pathological changes. A timely reaction of parents to changes can save the health and even the life of the child. After all, failures can be evidence of serious illnesses. And simply diarrhea, which is a consequence of a disease, for example, a common acute respiratory viral infection, can quickly lead to dehydration.
What should you pay attention to?
If your baby has loose stools accompanied by vomiting, you should immediately call an ambulance. The following are cases when you should not delay calling an ambulance in case of diarrhea in a newborn:
- the child is not a year old, much less 6 months old, and has developed diarrhea (more than 3–5 cases);
- temperature above 38° C;
- the baby vomited more than 3 times;
- the child has signs of dehydration: sunken fontanel, no tears when crying, dry lips, sunken eye sockets.
You should contact your local doctor if you have the following signs of disturbances:
- mucus, foam in stool;
- a lot of gases coming out during defecation;
- diarrhea occurs often, because of this the baby is weak and does not gain weight;
- streaks of blood are noticeable in the stool;
- a rash appeared in the abdomen, on the cheeks, on the elbows and legs; the rashes have a rough surface;
- diarrhea developed after taking acetylsalicylic acid with an increase in temperature due to ARVI,
- even if several days have passed;
- diarrhea began after treatment with antibiotics for other diseases.
When does the first set of teeth appear?
The process of eruption of the baby’s first teeth depends on his physiological characteristics. But on average, growth begins at six months and ends at two and a half years.
Table. Stages of growth of the first set of teeth.
| Stage | Set of teeth | Approximate eruption interval |
| 1 | Central (medial) mandibular incisor | 6-8 months |
| 2 | Central (medial) maxillary incisor | 7-12 months |
| 3 | Lateral (lateral) incisor of the upper jaw | 12-13 months |
| 4 | Lateral (lateral) incisor of the lower jaw | 12-15 months |
| 5 | Maxillary small molar | 14-18 months |
| 6 | Mandibular small molar | 14-18 months |
| 7 | Maxillary canine | 15-24 months |
| 8 | Mandibular canine | 15-24 months |
| 9 | Large mandibular molar | 20-31 months |
| 10 | Maxillary large molar | 20-31 months |
The main causes of loose stool in a child
Doctors identify the main causes of diarrhea in babies, which are associated with the growth of the first teeth. Normally, all intestinal disorders should not last more than 3 days. If the child’s condition does not improve within this time frame, then it is necessary to urgently show the child to a doctor.
Table. Factors affecting the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
| Cause | Impact |
| Loss of appetite changes the amount of food consumed, but salivation continues. Saliva enters the gastrointestinal tract in large quantities, thereby increasing intestinal motility, diluting stool and causing loose stools. Due to increased salivation, diarrhea occurs up to 4 times a day. | |
| To get rid of the itching of aching gums, the baby puts various objects into his mouth that may contain bacteria. Many bacteria, penetrating into the child’s body, begin to actively multiply. Fermentation occurs in the intestines, followed by diarrhea. In such a situation, watery bowel movements are a way to cleanse the body of pathogenic microorganisms. In some cases, vomiting, chills are observed, and mucus and foam are found in the stool. | |
| When the first baby teeth appear, complementary feeding is introduced. The child is given fruit and vegetable juices, purees, meat purees, and milk, which can cause the development of diarrhea. The body is trying to adapt to new foods, but the digestion is not yet able to accept heavy food, so indigestion occurs. | |
| The body is in a stressful situation, regularly experiencing discomfort, so watery bowel movements are considered a response. |
Causes
Table 1. Causes of diarrhea during teething
| Cause | Mechanism of influence on the gastrointestinal tract |
| Excessive drooling | Large volumes of saliva produced go directly to the stomach and intestines. Saliva significantly dilutes stool, which causes the development of diarrhea. |
| Desire to chew everything | Microbes can enter the baby's body. Diarrhea is the intestines' way of getting them out and cleansing themselves as quickly as possible. |
| New foods in your baby's diet | The period described often coincides with the introduction of complementary foods. It is possible that the cause of diarrhea is indigestion, a period of adaptation. Especially “dangerous” products in this regard are: various juices (apple juice is especially “dangerous” in this case), vegetable purees or meat dishes. A child’s body may well react to meat dishes with diarrhea, because meat is a heavy food, and at first there may be problems with digesting it. Introducing whole cow's milk before the age of 1 year can also cause diarrhea. It's all about the specific milk proteins of this product. |
| Acceleration of metabolism under the influence of stress | The “exit” of a tooth is always a stressful factor: there is pain and a violation of the integrity of the tissue. It is possible that diarrhea is a response to stress. |
Signs that require medical help
Sometimes a baby may undergo internal processes that are not associated with the appearance of baby teeth. These processes are very dangerous and can cause serious harm to a small organism. Since the child constantly puts everything in his mouth to relieve anxiety associated with teeth growth, pathogenic microorganisms can enter the intestines at this time. An intestinal infection is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- frequent bowel movements in liquid form (more than 5 times a day);
- abdominal pain;
- atypical color of stool;
- blood and mucous inclusions in feces;
- the structure of the stool is watery, foamy;
- frequent vomiting;
- high temperature, more than 39 degrees.
In addition to bacteria, a virus can enter the body, then the symptoms will be similar to a cold, only a few more points will be added:
- mucous discharge from the nose;
- coughing;
- heat;
- redness of the throat;
- weakness and increased sweating.
Important! In case of intestinal and viral infections, a pediatrician is urgently called to your home. The doctor prescribes medications after making a diagnosis. You should not give medications on your own without a doctor’s examination.
Features of tests for diarrhea
It is necessary to monitor the general condition of the child
To determine the causes of stool disorders, several tests are performed. Each of them is fundamentally important, helping to create a complete picture of what is happening in the body and make the right prescriptions.
- A CBC is needed to determine the severity of inflammatory processes. If diarrhea is infectious, there will be significant changes in leukocyte counts and ESR.
- Coprogram. This examination reveals malfunctions in the enzymatic system, shows the functioning of the pancreas, helps to find out what the nature of the problem is, how severely the intestinal function is impaired. If diarrhea is in the acute stage, you won’t get the full picture. Therefore, it is necessary to first stabilize the condition, and then conduct an examination.
- A stool test for dysbacteriosis identifies bacteria living in the intestines. The resulting list of pathogenic microorganisms will help prescribe adequate therapy. After all, Staphylococcus aureus is susceptible to the effects of some drugs, and Klebsiella – to others. Timely detection of enterococci and Proteus is important. The same analysis shows whether there are beneficial bacteria. As a rule, with diarrhea they are present in minimal quantities and may be almost completely absent. This type of examination has its drawbacks. It is not done quickly: at least 5 days. And in most cases it is offered to be done at the paid services department.
- A stool/worm test is necessary to rule out helminth infection. After all, the vital activity of worms often provokes attacks of diarrhea.
- Stool culture. Such an examination gives a picture of infection with infectious diseases. The analysis takes about a week. Moreover, they can prescribe cultures for dysentery, typhoid group, staphylococci, etc.
Drug therapy for teething
During this period, the main thing is to provide the child’s body with a constant level of fluid so that there is no dehydration. The doctor prescribes medications aimed at pain relief, eliminating inflammatory processes, destroying bacteria and viruses, and maintaining the natural intestinal microflora. It is prohibited to decide on your own what medications to give, since before the age of one year you can cause great harm to the baby’s body.
Complex drugs with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects
The pediatrician selects a set of products in the form of suspensions, ointments, gels, syrups, suppositories that have antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects. Medicines are also prescribed to relieve pain and allow the child to eat. Some products can be applied at night so that the baby and parents can rest, but the therapeutic effect will still be active.
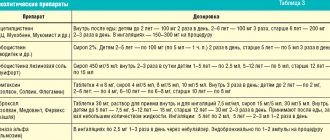
Table. Analgesics, antipyretics for the appearance of baby teeth.
| A drug | Therapeutic effect | Dosage |
| Efferalgan (syrup, suppositories) | Antipyretic, analgesic | 10-15 mg/kg, 3-4 times a day |
| Paracetamol for children (suspension) | Antipyretic, analgesic | 10-150 mg/kg, 4 times/day |
| Ibuprofen (suppositories) | Antipyretic, analgesic | 5-10 mg/kg, 3-4 times a day |
| Ibufen (suspension) | Antipyretic, analgesic | 5-10 mg/kg, 3-4 times a day |
| Nurofen (suspension, suppositories) | Antipyretic, analgesic, anti-inflammatory | 50-100 mg, 3 times a day |
| Dantinorm baby (solution) | Painkiller | 1 ml, 2-3 times/day |
| Dentokind (tablets) | Painkiller | 1 tablet, 3 times a day |
| Kamistad (gel) | Painkiller | 0.5 cm, 3 times/day |
| Dentinox (gel) | Analgesic, anti-inflammatory | 1-3 drops, 2-3 r/day |
| Cholistal (gel) | Analgesic, anti-inflammatory | 0.5 cm, 2-3 r/day |
| Kalgel (gel) | Analgesic, anti-inflammatory | 7.5 ml, no more than 6 times a day |
| Panadol for children (suspension) | Antipyretic, analgesic | 15 mg, 3-4 times/day |
Important! It is necessary to strictly observe the dosage of the drugs, as well as follow the doctor’s prescription, only in this way the treatment will be effective and will not harm the baby.
Antidiarrheal drugs
Drugs are prescribed by a doctor to eliminate loose stools, as well as to destroy pathogenic microorganisms. The dosage is prescribed by the pediatrician depending on the severity of the disease. The drugs are given ready-made, some need to be diluted with water, but you should always strictly follow the dosage regimen.
Table. Antidiarrheal drugs.
| A drug | Therapeutic effect | Dosage |
| Enterofuril (suspension) | Antimicrobial | 2.5 ml, 2-3 times/day |
| Stopdiar (suspension) | Antimicrobial | 2.5-5 ml, 2-3 r/day |
| Smecta (powder) | Adsorbent, antidiarrheal | 3-6 g/day |
| Enterosgel (powder) | Adsorbent, detoxifying | 2-5 g, 6 r/day |
| Polyphepan (powder) | Adsorbent, detoxifying | 0.5-1.5 tsp, 3-4 r/day |
| Filtrum STI (tablets) | Adsorbent, detoxifying | ? tab, 3-4 times/day |
| Polysorb (powder) | Adsorbent, detoxifying | 2.5-1 tsp, 3 r/day |
Important! Some drugs help remove both harmful and beneficial substances. Therefore, it is necessary to take medications to normalize the intestinal microflora, which are prescribed by a doctor.
Medicines for flatulence
To reduce bloating and gas in the baby, medications are taken that help relax the intestinal muscles, reduce and eliminate gas formations.
Table. Drugs that reduce gas formation and normalize intestinal microflora.
| Drugs | Therapeutic effect | Dosage |
| Espumisan baby (drops) | Reduces flatulence | Prescribed by a doctor |
| Sub-simplex (suspension) | Reduces flatulence | 0.6 ml during feeding |
| Babycalm (suspension) | Carminative, antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial | 10 drops, 3-4 r/day |
| Bobotik (drops) | Reduces flatulence | 20 mg, 4 times/day |
| Linex (capsules) | Normalizes intestinal microflora | 1 capsule, 3 r/day |
| Bifiform (solution) | Normalizes intestinal microflora | Prescribed by a doctor |
| Bifidumbacterin (powder) | Normalizes intestinal microflora | ? package, 1-2 r/day |
| Hilak forte (drops) | Normalizes intestinal microflora | 15-30 drops, 3 times a day |
| Acipol baby (drops) | Normalizes intestinal microflora | 5 drops/day |
| Biobakton (powder) | Normalizes intestinal microflora | 2.5 mg, 2 times/day |
Drugs for dehydration
An important point when dealing with loose stools in an infant is to take medications that maintain normal water levels in the body.
Table. Preparations for dehydration.
| A drug | Therapeutic effect | Dosage |
| Rehydron (powder) | Correction of electrolyte and fluid imbalances | Prescribed by a doctor |
| Glucosan (powder) | Correction of electrolyte and fluid imbalances, elimination of acidosis | 10 ml/kg, 1 r/day |
| Hydrovit (powder) | Correction of electrolyte and fluid imbalances, elimination of acidosis | 3-5 sachets, 1 r/day |
| Reosolan (powder) | Correction of electrolyte and fluid imbalances, elimination of acidosis | 40-50 ml/kg, 1 r/day |
| Citraglucosolan (powder) | Correction of electrolyte and fluid imbalances | Prescribed by a doctor |
Medicines for allergic reactions
Sometimes, with an intestinal disorder, the baby develops a rash (urticaria), itching and redness of the skin. Your doctor may then prescribe medications to relieve symptoms of an allergic reaction.
Table. Antihistamines.
| A drug | Therapeutic effect | Dosage |
| Suprastin (solution) | Antihistamine, antiemetic | Prescribed by a doctor |
| Fenistil (drops) | Antihistamine | Prescribed by a doctor |
| Fenkoral (powder) | Antihistamine | 5 mg, 2-3 times/day |
| Tavegil (syrup) | Antihistamine | 2-2.5 ml, 2 times/day |
Dehydration therapy
The key element in the treatment of diarrhea will be dehydration therapy. At home, powders can be used to prepare salt solutions. For example, “Regidron” and others. They contain the required amount of ions that restore the fluid level in your child’s body.
One packet of Regidron is diluted per liter of water and drunk throughout the day. Preferably warm.
Natural remedies
The use of medicinal herbs has a beneficial effect on the baby’s body. Using natural ingredients, you can prepare teas that have an anti-inflammatory and restorative effect. At the same time, the manifestation of side effects is minimal. However, you should know that the use of natural remedies is an auxiliary action in the main therapeutic treatment.
Natural remedies that can be used during baby teething include:
- medicinal herbs (chamomile, St. John's wort, sage, mint, chicory, motherwort, black tea). Infusions are prepared from herbs, which are used to treat the oral cavity, make enemas, and also take orally. Such herbs have anti-inflammatory, antiseptic effects;
- massage the gums with a small amount of honey. Honey is a natural antiseptic, it has an anti-inflammatory effect, and at the same time enriches the body with vitamins;
- berries (blueberries, bird cherry). Dry berries are poured with boiling water, and the resulting infusion is given to the child. The infusion has an antiseptic and antidiarrheal effect;
- rice broth. Has a strengthening effect, soothes irritated intestines, reduces gas formation;
- banana. The fruit must be kept in the refrigerator and then offered to the baby. A cold banana perfectly soothes itchy gums, and also, when entering the child’s body, saturates it with vitamins.
Important! Traditional medicine is used only after consultation with a doctor, since many natural remedies have a high percentage of allergens.
How to help your baby?
Intestinal disorders and fever cause a lot of trouble. But itching and swollen gums cause particular discomfort to the child. There are now many remedies available to relieve teething symptoms in children.
- teethers with cooling gel
- dentinox gel
- kamstad gel baby
- dentinorm drops
- Traumeel C ointment
- fenistil drops
- Kalgel
Experienced mothers know that drugs from the pharmacy are not the only help in eliminating the baby’s pain. When a baby is teething, caring parents advise:
- massage your gums with your finger
- wipe your gums with ice wrapped in cloth
- apply a weak soda solution (1 tsp per 200 ml of water) to swollen gums
- chew on a soft, damp terry towel
- invite the baby to chew on a cracker, an apple, a carrot, making sure that the child does not choke
Teething is an important and integral process in your baby’s growing up process. And you can make it as painless and comfortable as possible. Calmness, affection and a sensitive understanding of what your child needs will help you overcome all the difficulties of this period.
Traditional methods
These include herbs. Those that have minimal allergic effects can be prescribed to the baby. The most popular is chamomile. A tablespoon of dry herb is brewed with a glass of boiling water, infused for fifteen minutes and given to the child one teaspoon of the strained solution up to five times a day before meals.
Chamomile has powerful anti-inflammatory properties and plays the role of a mild anesthetic. When bacteria enter the intestines, chamomile acts in its lumen, exhibiting its bactericidal effect, and to some extent is a natural replacement for antibacterial agents.
In addition to chamomile, the following herbs can be used:
- blueberry;
- St. John's wort;
- sage;
- bird cherry;
- mint, etc.
Herbs are by their nature strong allergens, even those that are recognized as suitable for children. The connection of any folk remedy to the main therapy must be discussed with the treating pediatrician, otherwise the consequences can be serious.
Compliance with diet and drinking regime
During the teething period, it is necessary to properly water and feed the baby, since dehydration and lack of nutrients are dangerous to the life and development of the baby. The main rule is little by little, but often. In this way, the body constantly receives vital nutrients.
Dehydration can be noticed by some symptoms:
- dry skin;
- peeling;
- pale skin tone;
- lethargic state;
- urine is rarely excreted;
- change in the color and odor of urine;
- There is an odor of acetone in the mouth.
Depending on the degree of dehydration, the doctor prescribes drugs to regulate the water-salt balance in the body, which are administered orally at home or in the hospital under a drip.
Complementary foods should be used very carefully so as not to provoke new attacks of diarrhea. During this period, you can give a little:
- fruits (banana, pear, peach);
- cereals (rice);
- boiled cow's milk (with caution);
- jelly from fruits and berries.
Fresh juices and fermented milk products are temporarily excluded from the diet, and vegetables are given only boiled in the form of puree.
Mom needs to eat nuts, which will have a strengthening effect through breast milk. Breast milk should be fed more frequently to avoid dehydration. If the child refuses, then in addition to the food, give boiled water using a teaspoon.
How to identify diarrhea that requires medical attention?
Listed above are symptoms that require immediate response. As a rule, these signs indicate the development of the disease. After all, disorders associated with stool almost always indicate that one or another disease is beginning. Even otitis media in infants makes itself felt precisely through diarrhea. However, it is impossible to determine from the diarrhea what exactly happened.
Additional diagnostic tools are needed to know whether bronchitis or sinusitis is the cause of loose stools. Below are some common situations that signal the development of certain diseases.
A combination of diarrhea and fever (stool may contain mucus and blood)
Both the number of bowel movements and the frequency matter
Most likely, this is the penetration of an infection into the intestines; it can be either bacterial or viral. Symptoms may indicate that food poisoning has begun. A parasitic infection manifests itself in a similar way. In particular, giardiasis often produces exactly these symptoms.