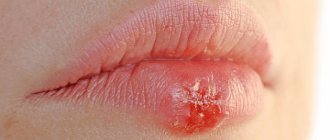
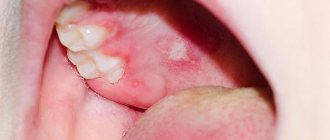
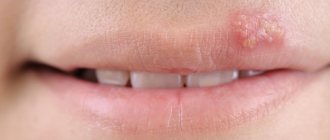
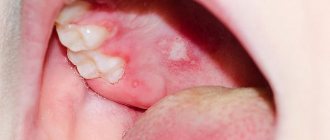
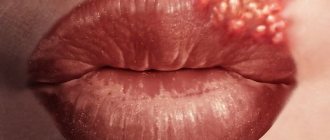
Herpes on the lips (herpes labialis) is one of the most common infectious diseases. People call herpes on the lips “cold sores” or “fever”. Cold sores are a very well-known disease. The first description of the symptoms of a “cold on the lips” was made by the Roman physician Herodotus in the 5th century BC. Chronic herpetic infection is an immunodeficiency disease with lifelong persistence of the virus in the cells of the nerve ganglia with dysfunction of both the autonomic and central nervous system, characterized by periodic exacerbations with the appearance of clinical signs (“hypertic vesicles”), localized in places that are constant for each patient - “Locus minoris” . Herpetic blisters affect the mucous membranes of the urethra, vagina, cervix, as well as the mucous membranes of the mouth, eyes, lips, genitals, skin, and when the process generalizes, the liver, brain and other organs. Herpes on the lips, although it is a disease of the body as a whole, usually gives external manifestations on the lips, less often on the nasolabial triangle (on the lips and on the wings of the nose).
Herpes on the lips is characterized by the ability to recur. Some people regard herpes on the lips as an unpleasant inevitability or a cosmetic defect, others, who experience frequent relapses of the disease, as a serious disease that can not only disrupt life plans, but also significantly reduce the quality of life and lead to depression. Most patients who have repeatedly suffered relapses of herpes on the lips wait with fear for the next relapse.
Fact About 20% of the Russian population is susceptible to herpes on the lips
So, after all, the appearance of herpes on the lips: an unpleasant inevitability or a disease worth fighting? Let's figure it out together.
The causative agent of herpes on the lips in 76% of cases is herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). There are cases of herpes on the lips caused by HSV type 2. HSV-1 and HSV-2 are close relatives and have a number of common biological properties, including the ability to persist for life in the human body. This means that after the initial infection, the virus is not completely removed from the body. Can you get cold sores or herpes labialis? Yes, sure. After all, a “cold on the lips,” being a viral disease, is very contagious. Therefore, sick people and those around them must take the necessary precautions. Patients should not only treat colds on the lips with modern, effective means, but also strictly observe all safety measures during the period of exacerbation, so as not to infect loved ones, children, and colleagues.
How can you get infected with herpes
The content of the article
The disease is caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV, Herpes simplex virus). Of the eight types of this pathogen, genital lesions are the result of two infectious agents. HSV-2 causes 80% of cases of the disease, and HSV-1 - 20%. There are also combined infections, in which both viral types are to blame.
There is a misconception that herpes on the lips and genitals are completely different diseases. In fact, both types of pathogens often “swap places” during domestic infection and oral sex. And both infections are equally dangerous.
Both types of virus are transmitted:
- For all types of sexual contact - vaginal, oral, anal, during which the virus enters the body through microdamage to the mucous membrane. You can also become infected from a partner who does not have rashes on the genitals or other manifestations of the disease. This condition is possible with strong immunity, when the virus lies low and waits in the wings. A person becomes a carrier of a herpes infection, but does not experience any health problems.
- Through common objects - washcloths, sponges, bed linen, towels. A person with a cold sore caused by the type 1 virus can become a source of genital herpes infection.
- During autoinoculation (self-infection), when the patient transfers the pathogen from the face to the genitals.
- A child becomes infected from a sick mother when the virus penetrates from the vagina into the uterus or transplacentally through the placenta. During childbirth, infection occurs as the newborn passes through the birth canal.
Statistics of hidden and overt forms of herpes
The body cannot overcome the pathogen on its own. The virus settles in the roots of the spinal cord, and the infected person continues to live with the disease throughout his life.
The pathogen can remain in the body for many years without causing symptoms. Therefore, it is impossible to know without testing for herpes whether a person is infected with the virus. According to WHO, type 1 herpes, which causes a rash on the lips and genitals, affects 67% of the world's inhabitants, and type 2 affects 11% of people. Only 20% of the disease occurs in the classical form, which is beyond doubt. In the rest, the course of the disease is latent or asymptomatic.
How often can herpes on the lips reactivate?
Relapses with type 1 HSV infection occur earlier and more often than with type 2 HSV infection. Lip herpes in 25% of adults has regular relapses 1–2 times a year, and in 5–10% of adults there can be up to six relapses per year. Relapses of the disease can occur with varying frequencies. The appearance of herpetic lesions no more than 4 times a year is regarded as a favorable prognostic sign, especially if the rashes appear in the same place and are moderately expressed. Relapses that occur more often than once every 3 months, monthly or every 2 weeks indicate a significant defect in the immune system, which requires additional examination of the patient. In some patients, a continuous course of the disease is possible, when old elements have not yet resolved, but new ones are already appearing.
The frequency of recurrence of herpes on the lips in men and women is the same.
Persistent herpes on the lips (often recurrent) leads to the development of secondary immunodeficiency, manifested in frequent colds, disruption of general condition, decreased performance, the appearance of low-grade body temperature, lymphadenopathy, and psychoasthenia. Often recurrent herpes on the lips is often the cause of neuropsychiatric disorders.
Recurrent herpes on the lips is accompanied by the risk of:
- Infection of children, sexual partners, others;
- Infection of other areas (eyes, genitals, mucous membranes);
- Long-term persistence of symptoms (up to several months) in persons with reduced immunity;
- The appearance of several lesions;
- Attachment of a secondary bacterial infection.
Primary herpes
There are three periods of illness:
- Prodromal
(precursor period), during which the temperature rises, the inguinal lymph nodes become inflamed, weakness, fatigue, and headache appear. A person experiences a condition similar to the symptoms of flu and colds. If you take an antiviral drug during this period, the disease may not develop. If the symptoms are ignored and treatment is not started on time, the second period of the disease begins. - A rash
that occurs three to four days after the onset of a flu-like condition. Common symptoms include pain, heat, swelling, itching in the genital area, anus, buttocks, pubis and perineum. Soon, numerous blisters filled with clear liquid appear on the inflamed skin and mucous membranes, reminiscent of a “cold” on the lips. The rash causes pain and itching, worse at night and leading to insomnia. - Ulcerations.
After some time, the blisters burst and ulcers (erosions) form in their place, surrounded by a focus of inflammation. Contact with stool and urine on the eroded surface increases pain and complicates tissue regeneration. - Healing,
during which the ulcers gradually heal. If the genital organs are poorly cleaned, the immune system is weak, and infection occurs, the healing process is delayed.
After the ulcers disappear, the disease goes into remission. During this period, despite the presence of the virus in the body, there are no rashes on the genitals.
Herpes on the lips. Prevention.
If you have a “cold” on your lips, follow these steps:
healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits, active sports
systematic and correct use of barrier contraception during orogenital contacts
maintaining personal hygiene
maintaining immunity (avoiding factors that reduce immunity)
treatment of caries, ENT diseases that cause a decrease in local immunity
abstaining from kissing during an active form of the disease or relapse of herpes in the intimate area
timely treatment of herpes on the lips after consultation with specialized specialists (self-medication is not acceptable!).
Briefly about the Vitagerpavac vaccine:
Compound:
— The drug is a lyophilisate for preparing a solution for intradermal administration — Contains specific inactivated antigens of herpes simplex virus types I and II grown on a continuous cell line VERO, acceptable by WHO as a substrate for the production of vaccines
Indications:
- Patients with CGI are subject to vaccination.
- Preparing women with a history of recurrent chronic herpetic infection for pregnancy.
- HIV-infected patients in stages 1-2 of the disease.
Contraindications to the use of the vaccine:
- Active stage of herpes
- Acute infectious and non-infectious diseases
- Chronic diseases in the stage of exacerbation or decompensation
- Malignant neoplasms
- Pregnancy
- Presence of active AIDS symptoms
Vaccination against herpes is carried out in institutions under the supervision of a doctor
- The vaccine is administered in the remission stage 7-10 days after the disappearance of clinical manifestations
- The vaccination course consists of 5 injections with an interval of 7-10 days
- Revaccination - after 6 months
- For complicated herpes, the 2nd and subsequent injections are administered at intervals of 10-14 days - 5 injections. Such patients are recommended to undergo 4 courses of vaccination over 1.5 - 2 years.
Where to get vaccinated Get advice
Detailed information about the Vitagerpavak vaccine and its use can be obtained from the Methodological recommendations MZ3.3.1.0002-10 “Immunization with the Vitagerpavak vaccine (herpetic culture inactivated dry) for the prevention of relapses of infection caused by herpes simplex viruses types 1 and 2”, approved by the Head of the Federal service for supervision in the field of consumer rights protection and human well-being by the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation G.G. Onishchenko. **** These recommendations came into force in 2010.
*author of the material - Alimbarova L.M. Associate Professor, Ph.D.
Recurrent herpes
In 50%-70% of people the disease becomes chronic. This is facilitated by:
- untimely or incorrect treatment;
- decreased immunity, including that caused by taking medications that suppress the immune system;
- presence of other STDs;
- strict diets, vitamin deficiencies;
- state of chronic stress.
Why do patients develop relapses, during which the disease affects the same parts of the body? There are several reasons for this:
- Having penetrated the body, the virus settles in the tissues of the genital organs. As it multiplies, it affects cells deeper and deeper until it reaches nerve cells - neurons connected to each other by processes - axons. Through them, like bridges, the pathogen reaches the cells of the spinal cord, into which it introduces its DNA.
- An infected brain cell becomes an “incubator” for viruses, which periodically return via axon bridges to the mucous membrane or skin, causing new rashes. Schematically, the process is similar to the migration of birds, constantly returning to their “native places.”
- The immune system cannot kill viruses hidden in the spinal cord, but it deals with those that have left the “shelter”. Therefore, with high immunity, relapses occur rarely or not at all. But as soon as the body “loses its vigilance” - weakens, gets sick, catches a cold, is exposed to stress - the pathogens begin to overcome the immune defense. As a result, they reach their target - the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs. Here, the increased reproduction of viral particles inside the “captured” cells begins. Cellular structures, dying, release myriads of viruses that cause inflammation, redness, swelling and the appearance of blisters. Herpes is causing another aggravation.
- Gradually, the immune system fights back the virus, and within 10 days the ulcers at the site of the rash dry out and heal. Everything returns to normal, so that at the slightest weakening of the immune system it can start again.
From the mechanism of exacerbations, it becomes clear why herpetic eruptions appear in the same places. It’s just that the virus cells return back only through the nerve cell from which they penetrated deep into the body.
Types of recurrent herpes
Depending on the number of exacerbations, several types of the disease are distinguished:
- mild, occurring up to 3 times a year;
- moderate severity, in which exacerbations occur 4-6 times a year;
- severe, accompanied by frequent exacerbations, intervals between which do not exceed a month;
- arrhythmic, in which after a period of imaginary well-being, lasting from a month to five, rashes appear. This form of herpes is characterized by a pattern - the longer the remission, the more severe the disease;
- menstrual, manifested by rashes during menstrual periods. This type of disease is severe and difficult to treat;
- subsiding, in which the manifestations of the disease constantly become weaker, and the inter-relapse periods become longer. The subsidence of the manifestations of the disease indicates the positive dynamics of treatment and the restoration of immune defense that suppresses the virus.
How to treat herpes on the lips?
How to cure herpes on the lips? How to get rid of cold lips? It should also be noted that currently there are no drugs for herpes that can remove the virus from the human body and lead to a complete cure. Therefore, treatment of colds on the lips is aimed at suppressing the virus in the body and, most importantly, restoring the immune system.
Each case of primary or recurrent herpes on the lips requires mandatory treatment in order to:
- prevent complications
- prevent relapse of the disease,
- to prevent transmission of the virus and infection of children, loved ones, sexual partners, work colleagues, etc.,
- prevent a decrease in quality of life,
- prevent further weakening of immunity.
Drug treatment comes down to 3 stages:
- suppressing an outbreak or relapse of the disease with the help of antiviral (chemo) drugs, interferons;
- restoration of the body's defenses - immunity with the help of general strengthening agents, probiotics, vitamins, interferons;
- vaccination with the antiherpetic vaccine "Vitagerpavak".
How to treat herpes on the lips?
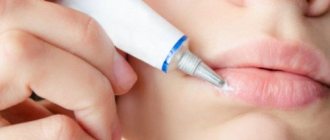
Effective antiviral chemotherapy drugs for herpes on the lips are drugs such as acyclovir, as well as its more effective second-generation derivatives: valacyclovir, Valtrex, famciclovir, penciclovir. These drugs have a comparable mechanism of action and clinical effectiveness, they help to quickly and effectively reduce the severity of symptoms, subjective sensations, and the duration of relapse, but they cannot cure the infection (completely remove the virus from the body).
Acyclovir and its analogues act only on the active herpes virus, but do not affect viruses that are in a latent state. A common disadvantage of acyclovir-containing drugs is the inability to prevent relapses of the disease and infection with a related type of virus and a negative effect on the immune system. Further suppression of the immune system leads to the emergence of resistant strains of the virus. Antiviral chemotherapy drugs are used occasionally in a short course (5-10 days) for primary herpes or for relapses of herpes.
For herpes, it is possible to use antiviral agents topically. This helps lead to a significant reduction in the time of appearance and regression of rashes due to the high bioavailability of active substances at the site of the lesion. Acyclovir (ointment, cream) and the new drug Penciclovir (1% cream Fenistil® Pencivir) have proven themselves well. The effectiveness of Fenistil® Pentsivir is 20–30% higher than acyclovir-based cream. Fenistil® Pencivir cream can be used in patients over 12 years of age. If there is resistance to acyclovir-containing drugs, antiviral drugs with a different mechanism of action (foscarnet, isoprinosine, panavir, aloferon, etc.) are used.
During pregnancy, in order to treat and prevent the recurrence of herpes on the lips and infection of the fetus, herpes medications in tablets (Acyclovir, tablets) are prescribed starting from the second trimester of pregnancy in consultation with the doctor.
The presence of side effects from the use of chemotherapy drugs contributed to the introduction of modern, effective and harmless drugs - interferon drugs - into the treatment of herpes. The ability of interferons to suppress the multiplication of a virus in the human body explains the need for their use (giaferon, viferon, genferon, etc.). The effectiveness of Giaferon is 30% higher than the effectiveness of other drugs in this group, because also contains hyaluronic acid, an independent immunomodulator. Their use as antiviral agents and immunomodulators, stopping relapses of the disease and correcting immunity, allows them to be effectively used in the treatment of pregnant women and nursing mothers, and to prevent intrauterine infection of the fetus.
How to quickly cure herpes on the lips?
If treatment using interferons and chemotherapy drugs in tablet form or for external use (ointment) is started at the first signs of the disease - during the period of precursors of relapse (itching, burning) or in the first 2-3 days of relapse, then the symptoms of herpes will be mild or may not appear completely.
Is it necessary to talk about the importance of treatment aimed at strengthening the defenses and preventing the recurrence of herpes on the lips? In cases of moderate and severe forms of the disease (relapse once every 3 months or more often), to increase the effectiveness of treatment, treatment regimens, along with antiviral drugs, include immunocorrective drugs: immunomodulators, interferons, vitamins, restoratives, immunoglobulins and probiotics. It should be noted that immunotherapy leads to deep remission, i.e. to restore immunity, allows you to shorten the duration of treatment, reduce the toxic effect of chemotherapy drugs on the body, prevent the formation of resistance to them and lead to deep remission, i.e. to restore immunity.
To increase the effectiveness of treatment of herpes virus infection, a group of virologists and infectious disease specialists led by Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. V.A. Isakov* developed a step-by-step, comprehensive method for treating and preventing recurrence of the disease using the drugs described above:
- Stage 1 of treatment – relief of the acute period of the disease (chemotherapy, interferons),
- Stage 2 – restorative therapy, immunocorrection,
- Stage 3 – specific immunoprophylaxis – vaccination with the antiherpetic vaccine Vitagerpavak,
- Stage 4 – clinical observation.
Chemotherapy drugs and interferons only suppress the virus in its active stage, but the vaccine treats, normalizing immune defense, and therefore belongs to the group of therapeutic vaccines.
It should be noted that special attention is paid to restoring the body’s immunological reactivity with the help of medication and anti-relapse treatment using general tonic agents, vitamins, interferons, probiotics, and immunoglabulins. Immunoprophylaxis at the final stage of treatment with the antiherpetic vaccine Vitagerpavak allows you to restore specific antiviral immunity, i.e. achieve suppression of the virus and normalization of immunity, leading to long-term (many years) remissions. This technique was called the “Russian method of treatment” in the West.
It is important to remember and consider that:
- Herpetic infections are a consequence of impaired immunity.
- In mild forms of the disease (exacerbation no more than once every 3 months), there is slight immunosuppression. Therefore, vaccination can be carried out immediately, without restorative treatment (7-10 days after healing of herpetic eruptions with an interval of 7-10 days, in the amount of 5 injections).
- In moderate and severe forms of the disease (recurrence once every 3 months or more often), it is necessary to eliminate severe immunosuppression by prescribing general tonic drugs, vitamins, immunomodulators, probiotics, and only then begin vaccination (10 days after healing of the rash with an interval of 10 days in the amount of 5 injections). It is necessary to carry out 4 courses of vaccination with an interval of 3 months under the cover of Giaferon (1 suppository 2 times a day rectally - 5 days).
The effectiveness of treatment is more than 86%, which is confirmed by the results of its use for 12 years and numerous studies of effectiveness conducted by leading scientists and clinicians of the Russian Federation in various fields.
The Vitagerpavak vaccine is used during the period of remission of the disease. The purpose of vaccination is to activate cellular immunity, i.e. its immunocorrection.
The use of the Vitagerpavac vaccine has a number of advantages over antiherpetic drugs, as evidenced by studies conducted in leading medical institutions in Russia.
Prof. N.S. Potekaev** and Associate Professor M.A. Samgin (Department of Skin and Venereal Diseases of the I.M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University) studied the effectiveness of the Vitagerpavak vaccine in 233 patients with recurrent herpes, including herpes on the lips . The treatment was the Vitagerpavac vaccine. It was shown that regular vaccination led to an increase in the period of remission to 1-3 years. Over time, 5 years after regular 4-year vaccination, 88 patients were examined: a positive effect was noted in 72% of patients with a recurrent form of herpes; complete cure - in 42 patients, significant improvement - in 24 patients.
In another study, the vaccine was studied in 3,000 patients with frequently recurrent forms of herpesvirus. Dynamic observation of patients over a period of 3 to 5 years showed that vaccine therapy led to a complete cessation of disease relapses in 1890 patients (63%), to a decrease in the frequency of relapses in 810 people. (27%). The lack of effect was detected in 240 (8%) patients (MD, professor, head of the department of skin and venereal diseases of the RUDN University, A.L. Tishchenko).
In a study conducted by Prof. Barinsky I.F. et al., **** at the Federal State Budgetary Institution “Research Institute of Virology named after. DI. Ivanovsky" of the Ministry of Health of Russia, Moscow, it was shown that in patients with frequently recurrent herpes, including herpes on the lips, 6 months after vaccine therapy (Vitagerpavak) a significant improvement (increase in the inter-relapse period by 3 times) was noted in 19 (31.1%) patients, improvement (increase in remission by 1.5–2 times) - in 35 patients (57.3%) and only in 7 (11.6%) patients the therapeutic effect was weak or absent. As a result of vaccination, the majority of patients (38 people) stopped treatment due to improvement. In 52% (20 patients) of them, clinical symptoms of recurrent herpes were completely absent.
Prof. Barinsky I.F. et al.,*** also conducted a comparative study of the effectiveness of the vaccine alone and in combination with the immunostimulant Giaferon in patients with frequently recurrent herpes, including herpes on the lips. The means of treating herpes were: the polyvaccine Vitagerpavak and the immunostimulant Giaferon. Patients of group 1 (28 people) were prescribed the Vitagerpavac polyvaccine in combination with an immunostimulant. Patients of group 2 (25 people) received only the vaccine. Efficacy was assessed by reducing the duration and intensity of clinical manifestations of genital herpes during relapse and increasing the duration of the interval between relapses. When using the vaccine in combination with Giaferon, a positive result was noted in more than 96% of cases, when using one vaccine - in 84% of cases. The conducted studies demonstrated the advantage of the combined method of vaccine therapy and the immunostimulant “Giaferon”. The proposed combined treatment regimen made it possible to prevent relapses of herpes, including herpes on the lips.
Dynamics of clinical parameters in patients with recurrent HH during vaccine therapy
| Clinical indicators | Before vaccine therapy | After vaccine therapy |
| Duration of remission | 2 months | 6 months in 36 (59.0%) patients |
| Relapse rate | 5–10 times a year | 2–3 times a year |
| Duration of relapse | 3–8 days | 2–3 days |
Of interest are the results of a study using the Vitagerpavac vaccine conducted by Prof. A.A. Kasparova et al. (Research Institute of Eye Diseases of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences), with the participation of patients with ophthalmoherpes caused by the herpes simplex virus. Of 114 patients with ophthalmoherpes with frequently recurrent forms, relapses of the disease completely stopped in 71 patients (63%), their frequency became significantly less frequent in 32 (27%) and did not change in only 11 people. (10 %). Analysis of the results revealed a 5-fold reduction in the frequency of relapses and a 3.2-fold reduction in the duration of relapses per 1 patient suffering from herpetic keratitis, keratoiridocyclitis and iridocyclitis. When studying the blood of patients with herpes using PCR and MFA methods, it was revealed that the use of an inactivated vaccine was accompanied by the elimination of viremia.
In the above-mentioned studies, it was also shown that vaccination was accompanied by a 3-4 times increase in specific reactions of T-cell immunity, against the background of a constant level of B-cell immunity reactions. The study of T-cell immunity reactions showed an increase in the specific T-killer activity of lymphocytes and the activity of NK cells. Vaccination contributed to the cessation of viremia both after the end of vaccination and in long-term follow-up (after 6 months). Vaccination using Vitagerpavak led to a pronounced immunocorrective effect, reducing immune disorders from degrees 3 and 2 to 1. After 6 months after vaccination, immune disorders corresponded to the 1st degree.
The above results of long-term studies of the Vitagerpavak vaccine indicate the reliable effectiveness of the vaccine in preventing relapses of herpes infections against the background of activation of cellular immunity reactions and specific desensitization.
If you are faced with the question “how to get rid of colds on the lips,” and other methods have proven to be ineffective, then you should definitely pay attention to this method of preventing relapses of the disease.
How to treat herpes on the lips using the Vitagerpavac vaccine?
The basic vaccination regimen using the Vitagerpavac vaccine: 0.2 ml of the vaccine is injected intradermally into the flexor surface of the forearm. The vaccination cycle consists of 5 injections, which are carried out at intervals of 7-10 days. For a lasting preventive effect, repeated courses of vaccination are necessary. In case of herpetic rashes, the intervals between injections should be increased to 14 days. After 6 months, revaccination is carried out (5 injections). In severe forms of the disease, revaccination is carried out after three months, 4 courses over 1.5 - 2 years.
Where can I get vaccinated?
Vaccine for the prevention of chronic herpes virus infection.
1 package – full course of treatment.
Vaccination course: 5 injections, given at intervals of 7-10 days. Store at a temperature of 2-8 ºС. The drug can be transported at a temperature of 9-18 ºС, but not more than 3 days.
To increase the effectiveness of treatment and prevent relapses of herpes on the lips in people with weakened immune systems, along with drug treatment, it is necessary to pay attention to strengthening the body's defenses. Particular attention should also be paid to the prevention of factors that contribute to decreased immunity and exacerbation of herpes infection.
Atypical forms of herpes
Sometimes genital herpes is erased. These forms of the disease account for 65% of cases of the disease:
- In women,
atypical herpes resembles inflammation of the vagina or vulva. There is pain, itching and swelling of the genital organs, profuse leucorrhoea and pain during sexual intercourse. External manifestations are limited to areas of redness or pinpoint rashes. - In men,
the atypical form of the disease is similar to inflammation of the head and foreskin (balanitis or balanoposthitis). A reddish rash appears on the mucous membrane of the penis, accompanied by pain and burning, which does not look like a herpetic rash. Inflammation of the prostate gland occurs, causing pain radiating to the anal area. Damage to the urethra leads to pain and burning when urinating, and the appearance of traces of blood in the urine.
There is a latent form of the disease in which there are no clinical manifestations, but despite this, the person remains a source of infection. But imaginary well-being does not last forever. With hypothermia, loss of strength, decreased immune defense, pregnancy, stress, severe concomitant diseases and other unpleasant conditions, the virus begins to multiply rapidly and the person becomes ill.
The disease is activated by concomitant sexually transmitted infections, especially ureaplasmosis. Due to the ability to rapidly “bloom” against a background of weakened immunity, herpes occurs in 90% of HIV patients. Therefore, if herpetic rashes appear, you need to be examined for other STDs.
Short
- Herpes simplex usually appears as a blistering rash on the face, lips, or genitals.
- It is transmitted during touching, kissing, petting, any type of sex, even when using someone else's lipstick.
- The virus can remain in the body without symptoms.
- It can become more active due to stress, weakened immunity, sunbathing, menstruation, smoking or drinking alcohol.
- During the period of exacerbation of herpes, it is better to avoid sex and close contacts. Or be sure to use a condom.
- Acyclovir is a drug with proven effectiveness that helps to quickly eliminate the symptoms of herpes. The dosage and regimen should be discussed with your doctor.
- Herpes can be dangerous for pregnant women, newborns, and people with HIV infection.
Features of the course of genital herpes during pregnancy
The number of positive (seropositive) reactions to herpes viruses 1 and 2 in pregnant women is 50-70%. Due to the increased load on the body and decreased immune defense, herpes often relapses during this period. But only 30% of women experience the classic development of the disease. Basically, the symptoms of herpes during pregnancy are limited to the appearance of areas of redness and cracks, which women mistake for irritation.
The manifestation of a herpetic infection caused by recurrence is not dangerous for the child. The woman’s body has already built up immunity to infection by producing antibodies—substances that protect her from the virus. Some of the antibodies will pass from mother to baby, protecting him from infection.
Only a relapse that occurs immediately before childbirth is dangerous. To prevent infection of the baby and rupture of inflamed tissues, women with a herpetic rash on the genitals are advised to deliver by cesarean section.
It is much worse when the infection is primary. Herpes belongs to a group of infections, infection of which for the first time during pregnancy leads to the birth of children suffering from developmental delays and congenital defects.
Herpes tests for pregnant women: interpretation and prognosis of pathologies in the fetus
To determine the degree of risk for the baby, a woman’s blood is taken for IgM and IgG antibodies, the concentration of which determines when infection occurred. The analysis is carried out using the ELISA method (immunofluorescence), which reacts to IgM and IgG antibodies to the virus. By the presence or absence of antibodies, you can find out whether a woman is infected and when the infection occurred:
- IgM antibodies
appear after 2-3 weeks. after the onset of the disease, therefore indicating a “fresh” infection or relapse of infection. These antibodies disappear after 1-2 months. after recovery. The presence of IgM in the analysis is a bad sign. - IgG class antibodies
- appear as protection against the virus after 2 weeks. field of infection, quickly increase the titer (concentration) and persist throughout life. Their detection means that the body encountered a herpes infection and managed to cope with it.
It is bad if a fourfold increase in IgG is combined with the detection of IgM. This means that antibodies are being formed right now, i.e. the woman is sick.
Infection with the herpes virus is determined in the laboratory. It is better to undergo such an examination twice - before pregnancy and during it.
Table of interpretation of results for herpes
| IgM | IgG | What does it mean | What to do | |
| — | — | The woman is healthy (seronegative) - she has never had herpes | Before pregnancy | During pregnancy |
| In order not to become infected, you need to avoid contact with people who have manifestations of herpes, incl. on the lips. Periodic antibody monitoring is recommended | ||||
| — | + | Female carrier (seropositive) | The infection occurred a long time ago and does not pose a danger to the child, no measures are needed | |
| + | — | Recent infection | It is better to plan pregnancy after acute symptoms subside and re-examination | Consult a doctor and undergo additional diagnostics to find out if everything is okay with the baby. |
| + | + | Exacerbation of infection | It is better to plan pregnancy after acute symptoms subside | Recurrent herpes is less dangerous than primary herpes, so the likelihood of complications and intrauterine infection is only 0.02% |
Fetal pathologies in children infected with herpes during pregnancy
The most dangerous thing for a child is primary infection of the mother during pregnancy, which leads to many complications.
| Gestational age at primary infection | Possible complications |
| I trimester (up to 13 weeks) | Fading pregnancy, miscarriages, severe malformations |
| II trimester (14-27 weeks) | Child infection, internal organ defects, fetal death |
| III trimester (29-40 weeks) | Intrauterine infection, death of a child after birth, premature birth, hearing, vision, and nervous system defects of the child. Subsequently - mental retardation. |
Herpes on the lips. Diagnostics
If typical symptoms are present, the diagnosis is made based on clinical data; laboratory confirmation is not required.
Laboratory confirmation is required in the following cases:
- when establishing the etiology of the disease in asymptomatic and chronic relapsing course,
- when establishing the etiology of the disease during dissemination of the process,
- when uncharacteristic rashes or atypical localization of rashes appear,
- when establishing the etiology of the infectious process in HIV-infected persons or persons with secondary immunodeficiencies of various origins.
In the above cases, the diagnosis must be established based on a combination of anamnestic, epidemiological, clinical data and laboratory research methods. The specificity of the patient’s rash is confirmed by laboratory methods: either by isolating the virus in cell culture (“gold standard” of diagnosis); or by identifying virus antigens; or by determining viral DNA in discharge from the lesion, in biological materials from the patient using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). To do this, material is taken directly from areas of rashes suspected of herpes. The state of humoral immunity in a patient is assessed by identifying specific antibodies of the IgG and IgM classes to HSV-2/-1 in the blood serum (for this diagnosis it is necessary to donate blood from a vein) using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Detection of IgM and IgG antibodies to HSV determines the duration and severity of the disease and answers the question: is a person infected with HSV?
If you have herpes on your lips, what should you do?
Consult a doctor (infectious disease specialist, dermatologist-venereologist) for advice.
Self-medication is not acceptable!
If your herpes on the lips does not go away, often recurs, and is accompanied by complications, what should you do?
It is recommended to consult a doctor for advice; confirm the specificity of rashes on the lips using laboratory methods, examine the intensity of antiherpetic immunity, the state of the immune status, and sensitivity to antiviral drugs.
Discuss on the forum
Herpes in newborns
A child becomes infected with the pathogen from the mother in utero or by passing through an infected genital tract during childbirth. In newborns, the mucous membranes of the eyes and mouth, skin, and genitals are affected. When the pathogen enters the child’s brain, meningoencephalitis occurs, causing death or severe disability.
A generalized form is possible, in which all organs and systems of the newborn are affected. The child experiences jaundice, respiratory distress, and urinary retention. Children are restless, do not latch on to the breast, and are vomiting. Death occurs from shock, bleeding, dehydration, intoxication, and organ failure.
The likelihood of infection increases with primary infection of the mother in late pregnancy.
Diagnosis of herpes
If genital herpes is suspected, after an external examination, scrapings from the affected areas, blood, and urine are taken for examination. This will allow you to differentiate the disease from other skin lesions that have similar symptoms.
For diagnostics the following is used:
- Cultural method - during the study, the contents of the vesicles are transferred to a growing chicken embryo; if it dies, the disease is confirmed. The method is reliable, but too time-consuming.
- PCR is a test that detects viral DNA in tissues. The method allows you to calculate the pathogen even from a small amount of viral material. Effective for diagnosing any form of disease, incl. hidden. The method can be used immediately after infection before symptoms of the disease appear. PCR not only detects the virus, but also determines its type.
- Methods aimed at determining antigens and antibodies to the pathogen: ELISA - immunofluorescence diagnostics, CFR (complement fixation reaction), various types of agglutination reactions. With their help, you can identify the type of pathogen, determine its quantity and duration of infection.
A complete diagnosis of herpes virus infection allows you to make the correct diagnosis in order to prescribe treatment.
Maybe I should donate blood to find out whether I am in the active phase of the disease or not?
There are antibody tests that can be used to find out whether you have already had an illness or are in the active phase of the disease. Memory antibodies that store the data that you have been ill are called IgG. And others - IgM, show that you are sick now.
But the British Herpes Virus Association and the UK National Health Service consider these tests for diagnosing both types of HSV to be unreliable and do not recommend taking them. The American CDC also does not recommend self-testing for the herpes virus. They are needed only by certain groups:
- people with frequent relapses of herpes;
- partners of people infected with the herpes simplex virus;
- people with HIV infection or at high risk of HIV infection$
- those who are tested for STIs.
You need to remember that you are almost always contagious, but to a lesser extent when there are no symptoms, to a greater extent when they are present.
Complications of herpes
The worst thing is that a herpes infection brings not only unpleasant symptoms. This virus causes many terrible complications. The most obvious ones are:
- Irritation and dryness of the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs;
- Cracks in the genitals caused by metabolic disorders in tissues caused by herpes;
- Adhesive and cicatricial deformities of the labia, vaginal opening, perineum, urethra and rectum. The complication arises due to the specific feature of herpetic rashes appearing on the same areas of the skin and mucous membranes
- Cervical erosion leading to cancer of the reproductive organs.
- Lacerations during childbirth caused by poor distensibility of inflamed perineal tissue.
- Infection of ulcers due to microbes entering tissues not protected by the mucous membrane;
- cicatricial deformities of the penis, provoked by constant inflammatory rashes and ulcerations.
- Chronic herpetic lesions of the genitourinary area, spreading to the urethra, bladder and kidneys.
- Herpetic proctitis is inflammation of the rectum.
- Erectile dysfunction and male and female infertility.
- Neurological symptoms caused by a viral infection of the nervous system. Patients complain of pain in the sacrum, lower back, and groin. With recurrent lesions on the inner surface of the thighs, hypersensitivity of the skin occurs, manifested by a burning sensation, crawling “goosebumps”, tingling.
In severe cases, with a pronounced weakening of the immune system, viremia occurs - viral infection of the blood leading to damage to the brain, liver, lungs, adrenal glands, and intestines. This condition, even with adequate treatment, is often fatal.
Treatment of genital herpes
It is difficult to cure such a dangerous disease. Treatment of genital and labial herpes is long and complex. Therapy includes:
- Prescription of antiviral agents that slow down the reproduction (replication) of viruses. To maintain the effectiveness of treatment during long-term therapy, it is necessary to constantly change the prescribed medications.
- The use of drugs based on interferons - proteins released in response to viral invasion. Scientists have found that a lack of this substance provokes exacerbations of the disease.
- The use of local antiviral ointments, gels and sprays that kill viruses that have penetrated the skin and mucous membranes.
- Prescribing symptomatic medications that combat the general symptoms of the disease - reducing pain, swelling, inflammation, lowering temperature, normalizing sleep.
- Local procedures - baths and irrigations that relieve pain and prevent the penetration of secondary infections.
- Taking immunoglobulins, immunomodulators and stimulators of cellular immunity, which improve the functioning of the immune system, activate the production of antiviral antibodies and prevent relapses.
Patients suffering from genital herpes are advised to avoid wearing synthetic underwear.
Prevention of infection consists of a thoughtful choice of sexual partners, compliance with hygiene rules, periodic examination by a gynecologist and the use of emergency measures at the first symptoms of the disease.
Where to get tested and cure herpes in St. Petersburg, prices
Doctors at the modern Diana Clinic treat herpes infections in St. Petersburg. Here you can take express tests for all infections - smears, blood, etc. Tests are performed using the best methods - PCR, ELISA, etc. The cost of visiting a doctor based on test results is 500 rubles. The price of tests depends on the type of examination. For example, the cost of taking blood from a vein is only 170 rubles.
So, is herpes a completely harmless disease? Are there those for whom it is dangerous?
In most cases, harmless. But there are rare circumstances when herpes can harm your health.
Pregnancy and childbirth
If a woman becomes infected with herpes for the first time and this happens in the last 6 weeks of pregnancy, then there is a high risk of transmitting this virus to the child during natural childbirth. If the expectant mother has had herpes before, the risk is reduced. After birth, a child can be infected both during breastfeeding and through kissing.
Herpes in babies is called neonatal, and it is more severe than in adults. The baby's immune system is too weak to adequately respond to the virus with an attack. Therefore, he quickly falls ill, and the symptoms in children are worse than in adults. In addition to the rash, you may experience fever, lethargy, lack of appetite, rashes and blisters all over your face and body. In the worst-case scenario, the child becomes worse and an ambulance needs to be called. Neonatal herpes is rare: 0.1% of newborns per year, according to US statistics.
Remember: if you know you have the herpes virus, do not kiss newborn babies or touch their face.
Presence of HIV infection
People with herpes are at higher risk of contracting HIV than those without. Especially if they have genital herpes. In cases where a person is sick with both genital herpes and HIV infection, both diseases are more severe. Therefore, it is necessary to get tested regularly for HIV and practice safe sex to stay healthy.