Normal condition of tonsils
Tonsils are collections of lymphoid tissue located in the nasopharynx and oral cavity. Tonsils perform protective and hematopoietic functions, participate in the development of immunity - they are the first line defense mechanism against inhaled foreign pathogens. The full immunological role of the tonsils still remains unclear.
Together with other lymphoid formations of the nasopharynx, the tonsils form the pharyngeal lymphatic ring
The tonsils serve as a local immune organ, a kind of barrier against bacteria and viruses that enter the pharynx during the acts of breathing and swallowing.
Tonsils are divided into:
- paired: palatine - in the recess between the soft palate and the tongue (first and second tonsils).
- tubal - in the area of the pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube (fifth and sixth tonsils)
- pharyngeal (nasopharyngeal) - in the area of the fornix and the back of the pharyngeal wall (third tonsil, Luschka’s tonsil). Pathological enlargement of this particular tonsil is called adenoids
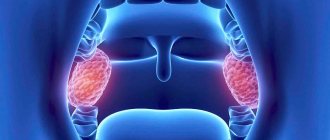
Palatine tonsils - a focus of inflammation in chronic tonsillitis
In the upper respiratory tract of a person there are a number of formations representing an accumulation of lymphoid tissue, the so-called lymphoepithelial organs - tonsils. There is a whole lymphopharyngeal ring consisting of 7 tonsils. These are unpaired pharyngeal (adenoids), lingual, laryngeal tonsils, and paired palatine and tubal tonsils. Like any organ in our body, the tonsils can be subject to inflammatory diseases.
Acute inflammation of the tonsils is a sore throat. Chronic tonsillitis refers to a long-term inflammatory process in the palatine tonsils. In most cases, tonsillitis is an exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis. The palatine tonsils (tonsils) are essentially the same mucous membrane only folded into an accordion; they are dotted inside with passages - crypts, which open on the pharyngeal surface of the palatine tonsils with lacunae.
Due to the anatomical features and location of the palatine tonsils, which are located at the crossroads of the digestive and respiratory systems, they are most often, of all other lymphoepithelial formations, susceptible to the inflammatory process, which consists of degenerative processes, as a result of which, in chronic tonsillitis, the palatine tonsils are a constant source of infection and the cause of endointoxication.
Why do we get chronic tonsillitis?
The main causes of the development of chronic tonsillitis are inflammation of the tonsils and ongoing tonsil reactions, which can be caused by long-term exposure to an infectious factor.
In the photo - lymphopharyngeal ring
During the development of chronic tonsillitis, the overall level of the body’s immunity is of no small importance.
Methods for treating inflammation of the tonsils
Chronic tonsillitis is usually treated using conservative and surgical methods, which are used only as a last resort.
The following types of therapy are used:
- antibiotic therapy prescribed by otolaryngologists taking into account the sensitivity of bacteria; treating the throat with antiseptic solutions (“Octenisept”, “Miramistin” and others); antihistamines to relieve swelling of the mucous membrane; immunomodulators to stimulate the immune system; painkillers.
The patient must strictly follow a diet. Exclude solid foods, cold or hot dishes and drinks, alcohol, soda.
Types of chronic tonsillitis
There are several classifications of chronic tonsillitis. The issue of classification of chronic tonsillitis is closely related to the clinical manifestations of this disease. The most widely used classification is that there are only two forms: compensated and decompensated.
- The compensated form is characterized by a course without complications, rare sore throats, often the only complaint can be only plugs in the throat, the protective role of the tonsils works by holding back harmful bacteria, and their further penetration, due to this, no special manifestations of the disease are observed.
- Decompensated form This form of chronic tonsillitis is characterized by frequent sore throats at least once a year, the occurrence of local complications, such as peritonsillar abscess, and diseases of other organs and systems of the body, such as glomerulonephritis, rheumatism.
Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis
The main manifestation of chronic tonsillitis is tonsillitis; as a rule, all patients suffering from this disease at least once have had tonsillitis. Sore throat is a fairly serious disease that affects all systems of the body and carries the risk of a number of serious complications, so the choice of treatment tactics for chronic tonsillitis should be related to the frequency of tonsillitis. The main symptoms of the disease can be identified:
| Smell from the mouth | One of the most common symptoms disturbing the patient is bad breath. This symptom is due to the fact that the area of the epithelium of the palatine tonsil is quite large; during inflammation, pathological secretions accumulate in the crypts of the tonsils in the form of caseous (curdled) masses. Caseous masses are evacuated through the lacunae into the pharyngeal cavity, causing bad breath. |
| Sore throat, ear | One of the main symptoms of chronic tonsillitis is pain in the throat, often a feeling of a lump in the throat. Also, the symptoms of chronic tonsillitis can be expressed by headache, unpleasant sensations in the ear, mild pain in it, which is caused by irritation of the nerve endings in the parenchyma of the palatine tonsil and irradiation of pain along the nerve fiber to the ear. |
| Enlarged lymph nodes | You can often observe an enlargement of the lymph nodes located under the jaw, and the cervical lymph nodes also enlarge. When palpating the lymph nodes, mild pain occurs. |
Quite a large number of patients do not immediately detect the symptoms of chronic tonsillitis and delay contacting an ENT doctor, which often leads to decompensation of the disease and longer treatment in the future.
Methods for washing tonsils: which one to choose?
Washing the tonsils is, of course, not a surgical operation, but it should be performed by an otolaryngologist. In no case should you try to do this yourself or with the help of relatives, since if done incorrectly, you can not only not eliminate the symptoms of chronic tonsillitis, but also “drive” the disease deeper - then it will be difficult for the doctor to cope with the consequences. In addition, you can unknowingly injure the palate and the tonsils themselves.
The two most common methods of washing the lacunae of the palatine tonsils today are with a syringe and a device that combines the effects of ultrasound and vacuum. Which method is preferable?
Flushing with a syringe. In a regular district clinic, the patient will most likely be offered to rinse the tonsils with a syringe. A cannula is attached to it (a special brass rod with a replaceable tip). The patient is required to sit for a while with his mouth open to gain access to the infected tonsils.
Before starting the procedure, the surface of the larynx is treated with an anesthetic (lidocaine) - this will reduce the discomfort. In general, the procedure is considered painless and lasts about 10 minutes. During its implementation, liquid is pumped out from the cavities of the tonsils, purulent plugs, small pieces of stuck food, pathogenic microbes and the remains of their vital activity are cleansed. At the same time, the surface of the pharynx and lacunae are irrigated with special solutions that help stop inflammatory processes.
Washing the tonsils using the vacuum method. Recently, the second method of washing the tonsils has been increasingly used - with a vacuum apparatus called “Tonsilor”. It works like a kind of micro-vacuum cleaner, sucking out the pathogenic contents of the lacunae, freeing and cleaning them. Rinsing the tonsils with Tonsilor uses ultrasound, which effectively extinguishes inflammation, has analgesic properties, and helps the fluid actively penetrate into the tissue.
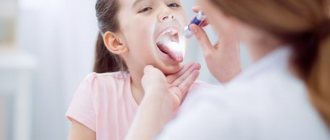
How to identify chronic tonsillitis
Diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis does not present any particular difficulties for an experienced otolaryngologist. The patient's medical history and complaints are of utmost importance in diagnosis; as a rule, the history includes previous sore throats and complaints of frequent pain and discomfort in the throat.
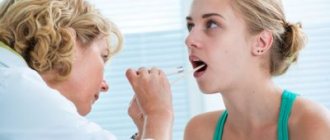
Examination of the throat for chronic tonsillitis
During mesopharyngoscopy (examination of the pharynx) for chronic tonsillitis, the following signs are present: hyperemia and roller-like thickening of the edges of the palatine arches; cicatricial adhesions between the tonsils and palatine arches; loosened or scarred and hardened tonsils; caseous-purulent plugs or liquid pus in the lacunae of the tonsils.
How is the tonsil rinsing procedure performed?
No special preparation is required before performing this procedure. Washing on this device occurs in several stages:
- first, the tonsils are treated with lidocaine; a vacuum attachment is fixed to the surface of the formation; the device creates negative pressure; the nozzle pulls out purulent plugs and removes them into a special container; the lacunae are washed with an antiseptic solution. Ultrasound injects a drug into the tonsil.
The procedure relieves inflammation, activates tissue regeneration, and removes swelling.
Complications of chronic tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis has serious complications; they are divided into two groups: local and general. All complications, as a rule, occur during an exacerbation of the process occurring in the form of a sore throat and represent the consequences of untimely treatment of chronic tonsillitis.
With chronic tonsillitis, in the upper respiratory tract of a person, more precisely in the palatine tonsils, there is a focus of chronic inflammation; the problem of focal infection is very acute in modern medicine. Currently, there are about fifty different metatonsillar diseases, which are the result of chronic inflammation in the palatine tonsils. Let's take a closer look at what this can most often threaten.
Peritonsillar abscess
This is the most common local complication. The fact is that between the palatine tonsil and the muscles of the pharynx to which it is attached there is fiber, the so-called paratonsillar fiber. With severe inflammation, the infection can enter this tissue through the hematogenous route, causing its infiltration and purulent melting, and an abscess is formed. Peritonsillar abscess is a very serious disease that requires immediate surgical treatment, usually in a hospital setting, since there is a threat of the purulent process spreading through the cellular spaces of the neck into the mediastinum, which can be fatal.
Diseases of the heart, joints and kidneys
An important role in the inflammatory process in chronic tonsillitis is played by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, which often parasitizes the palatine tonsils. The fact is that immune complexes that form in the body as a response to the aggression of this antigen can also attack healthy tissue in the joints, heart and kidneys, which, if not treated in a timely manner, can even lead to disability.
Weakness and decreased ability to work
The parenchyma of the palatine tonsils is densely penetrated by blood and lymphatic vessels, and in the thickness of the organ there are many nerve endings that connect to important autonomic centers. In chronic tonsillitis, inflammatory products enter the circulatory and lymphatic systems, and constant endotoxification occurs. All these factors plus pathological impulses from irritated nerve endings lead to decreased tone, bad mood, and apathy.
Regular colds
With chronic tonsillitis, the body spends a lot of effort to contain inflammation in the tonsils, the immune system is under constant stress, which leads to its significant weakening. Added to this is the not always correct work-rest regime, nutrition, and environmental conditions, as a result of which a person with chronic tonsillitis may literally not “get out” of a cold.
Inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system
The palatine tonsils are anatomically located in the pharynx, close to such organs as the trachea, larynx, and paranasal sinuses. With chronic tonsillitis, microbial contamination of the entire area of the respiratory mucosa occurs, which contributes to the development of diseases such as sinusitis, bronchitis, and laryngitis.
Stomach and intestinal problems
The palatine tonsils are located at the crossroads of the digestive and respiratory systems. Due to certain anatomical features, they represent a rather large conglomerate of the mucous membrane. In chronic tonsillitis, this entire area of the mucosa is involved in the inflammatory process and secretes a pathological secretion in the form of a liquid fraction and caseous masses. This pathological content is evacuated into the pharynx through lacunae and then swallowed with saliva, which often causes disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Location and structure of the tonsils
On their own, a person can only see the palatine tonsils and the pharyngeal tonsil if it increases in size. The rest can only be examined by a specialist using tools.
- Palatine tonsils. These tonsils are located between the palatine arches in the tonsillar niches. The tonsils are surfaces covered with stratified epithelium facing the pharynx. On the other side they are connected to the wall of the pharynx. Each tonsil has deep fissures - lacunae, which branch to form a network. Epithelium and microbial waste are rejected into it.
- Pharyngeal (nasopharyngeal) tonsil (adenoids). Located on the back wall of the nasopharynx. At high magnification, it can hang behind the tongue and become visually observable. Typically, problems with this tonsil occur in children: it interferes with normal breathing, contributes to hearing impairment and the development of otitis media.
- Tubal tonsils. These two small tonsils are located at the mouth of the auditory tube in the nasal cavity. Their increase can lead to hearing impairment and otitis media.
- Lingual tonsil. Located at the base of the tongue, it has a lumpy, rough surface. Inflammation of this formation leads to pain during eating and talking.
Surgical treatment of chronic tonsillitis
The whole variety of methods for treating chronic tonsillitis is divided into two large groups: surgical methods and conservative ones. Let us dwell in detail on surgical treatment. A radical surgical method is tonsillectomy - removal of the organ along with the capsule should not be confused with tonsillotomy, which is often done in childhood.
Video: tonsillectomy - removal of tonsils
With tonsillotomy, unlike tonsillectomy, not the entire organ is removed, but only a fragment of the hypertrophied parenchyma of the pharyngeal surface of the tonsil. It is necessary to resort to tonsillectomy in extreme cases; for this there must be compelling indications, such as a complicated advanced form of the disease, despite the fact that all possible methods of conservative treatment have been exhausted. Despite these “canons” that have been established for many years, removal of tonsils is often resorted to due to the lack of availability of conservative treatment, and sometimes due to the banal lack of a competent specialist dealing with this issue.
The function of the palatine tonsils is extremely important - it is an element of the pharynx, after the removal of these organs, areas of the pharynx that were covered by these formations begin to be subject to irritation by air and food masses, is this good or bad? Apparently this is bad, since nature, as a result of a long process of evolution, did not give us a single extra organ.
Preparation of an ozonized solution for a session of deep vacuum ultrasonic sanitation of the palatine tonsils
Often, tonsils are removed from patients who have not even had a history of sore throat, and whose only complaint was caseous plugs in the throat and bad breath. The long-term result of operations to remove palatine tonsils is often severe sore throat and the development of atrophic pharyngitis, which is difficult to treat.
Conservative methods of treating chronic tonsillitis include various methods of washing the tonsils. Comprehensive information about this manipulation is presented in the article washing the tonsils.
Symptoms
How to independently recognize chronic tonsillitis? Symptoms and treatment in adults and children can only be correctly determined by an ENT doctor. Below are characteristic signs - if you find them in yourself, consult a doctor.
The disease is characterized by symptoms such as:
- Headache.
- Feeling of something foreign in the throat, as if something was stuck in the throat. In fact, this is nothing more than large accumulations of caseous masses, that is, plugs in the thickness of the palatine tonsils.
- Increased fatigue, weakness, decreased performance. All this is due to the so-called tonsillogenic intoxication, or in other words, intoxication syndrome.
- Aching pain in the joints and muscles (with severe illness).
- Aching pain in the heart, with interruptions in heart function - extrasystole (with severe illness).
- Pain in the lower back, in the kidney area (with severe disease).
- Bad mood, and in some cases increased body temperature, and for a long time.
- Persistent skin rashes, provided that there was no previous skin pathology.
All these symptoms appear due to the entry of waste products of microorganisms into the blood from the palatine tonsils, i.e. staphylococcal and streptococcal infections, poisoning the entire body.
Bad breath appears due to the accumulation of organic substances and the decomposition of bacterial infection in the lacunae (recesses of the tonsils) and crypts (their canals). Tonsils become a source of bacterial infection, which can spread throughout almost the entire body and cause inflammation of the joints, myocardium, kidneys, paranasal sinuses, prostatitis, cystitis, acne and other diseases.
If the tonsils do not cope with their function as an immune organ, then even slight overwork, stress, or mild hypothermia can significantly reduce the immune defense and open the way for microbes and exacerbation of the disease.
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis without surgery
Despite the wide market of medical services, there are not so many effective conservative methods of treating chronic tonsillitis. The fact is that in modern otorhinolaryngology it is customary to divide the mucous membrane into fragments, there are doctors who deal only with diseases of the nose - rhinologists, there are specialists who deal only with the treatment of the throat. In fact, the entire area of the mucous membrane lining the upper respiratory tract is one organ.
Session of deep vacuum ultrasonic sanitation of palatine tonsils with ozonated solution
We are forced to obtain oxygen from the air, and the air is not sterile; the respiratory organs, like no other system of our body, experience a colossal biological load and are constantly in contact with microbes. The anatomical structure of the upper respiratory tract is the product of a long period of evolution. The upper respiratory tract is a complex mechanism created by nature with one purpose: to be a protective barrier. Moreover, many ENT diseases (adenoids, vasomotor rhinitis, sinusitis, chronic pharyngitis), which are classified as different and treated in different ways, are essentially one disease in different stages of development, so to speak, a “machine” in different stages of breakdown.
Video: treatment of chronic tonsillitis
So, the essence of many inflammatory ENT diseases, including chronic tonsillitis, is a degenerative process in the mucous membrane, caused by the microbes that we breathe, as a result of the weakening of the protective properties of the mucous membrane. It follows from this that when doing treatment you need to influence the entire area of the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract, you just need to take into account some anatomical features - such as the structure of the palatine tonsils, and taking these features into account, locally enhance the therapeutic effect. Since the palatine tonsils are essentially the same mucous membrane only folded into an accordion, washing the tonsils should be an integral part of the treatment process.
Conducting a photodynamic therapy session on the pharynx area for chronic tonsillitis
The lack of effective methods for treating chronic tonsillitis is also due to the fact that there are a number of dogmas in modern medicine. One of them is that the most common way to fight germs today is with antibiotics. Antibiotics, unfortunately, do not penetrate well into the upper layers of the degenerative mucous membrane; moreover, they do not restore it. With chronic inflammation, the regeneration of the mucous membrane is disrupted and microerosions form on it. Figuratively speaking, the mucous membrane becomes like a “sieve,” which is the most important basis for the inflammatory process.
Stimulation of reflexogenic zones in chronic tonsillitis
Taking into account the above, the main task of treating chronic tonsillitis is to influence all parts of the pathogenesis of the disease, therefore the following methods are used in our clinic:
| Cleansing tonsils with ozonized solution | In our clinic, we wash the palatine tonsils using the tonsillor apparatus with an ozonated solution, which is by far the most effective way to cleanse the entire thickness of the tonsils from pathological contents. |
| Sanitation of mucous membranes with mineral salts | In our clinic, we irrigate the entire mucous membrane with a solution of individually selected mineral salts, which sanitize the mucous membrane and restore it, which cannot be achieved with modern antibiotics. We also activate mucosal regeneration using photodynamic therapy. Lymph stasis plays an important role in the pathogenesis of inflammation, including chronic tonsillitis. Activation of lymph flow in the area of inflammation plays an important role: this is how the “soldiers” of our immunity - lymphocytes - move along with lymph. |
| Stimulation of reflexogenic zones | With the help of injections into the reflexogenic zone of the neck, ozone causes a spasm of the subcutaneous lymphatic vessels, which activates the lymph flow in the pharynx, leading to rapid stabilization of the immune system. The integrated approach we use affects all parts of the pathogenesis of chronic tonsillitis, which allows it to be treated conservatively, avoiding surgical treatment. |
When should you wash your tonsils?
The fact is that pathogenic microorganisms and dead leukocytes not only accumulate inside the tonsils, but they also cannot leave their location, since inside the tonsils there are many voids and tortuous “passages”. If you influence them with the same drug, then sooner or later addiction occurs - microorganisms (streptococci and staphylococci) become resistant, adapt to the antibiotic, and it is no longer powerless to cope with them. This is where a special procedure comes to the rescue - washing the tonsils.
Washing the tonsils is prescribed to a person who has long suffered from chronic tonsillitis with constant exacerbations, who feels constant weakness, soreness in the throat, in the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes.