Thrush or candidiasis is a well-known disease, the development of which occurs due to the activity of yeast fungi called “Candida”. These microorganisms are opportunistic, therefore they exist peacefully in the body of almost all inhabitants of the Earth.
However, a temporary drop in immunity or another unfavorable factor can cause activation of fungal microflora, triggering the development of corresponding ailments. One of these is the already summarized candidiasis. Read more about its course in infants, the danger of the pathology for their body and the principles of its treatment below.
The mechanism of development and features of candidiasis in infants
Candidiasis manifests itself as a white coating
As noted earlier, no one is immune from thrush or, scientifically, candidiasis. This state of affairs is not difficult to explain, because the provocateurs of this pathology can exist quite peacefully in the body of any person.
Why? All because of their conditional pathogenicity. If the human body is in good shape and is able to organize its high-quality defense, then the activation of Candida fungi will not occur. But as soon as it gives the slightest glitch, the unfavorable microflora is activated, begins to actively multiply and literally “eat” healthy tissue.
Fungal microorganisms can and often do live in all parts of the human body. The largest accumulation of candida microflora can be found in:
- oral cavity;
- intestines;
- genital area.
As a rule, the activation of fungi in one area entails the unfavorable activity of their “brothers” in another part of the body. In infants, candidiasis is an inflammatory disease that develops either in the mouth, or in the groin area, or both.
Many parents are interested in “Where could their child, seemingly born quite recently, pick up fungal microflora?” In fact, anywhere. Often, Candida fungi are transmitted to children at birth and live in their bodies for the rest of their lives.
Naturally, only with the activation of unfavorable microflora does the development of pathology and its accompanying manifestations take place.
Candidiasis in children: consequences
Like any sexual disease, candidiasis in a girl is fraught with disruptions to the reproductive system, which begins during intrauterine development. Before puberty, girls have very delicate genital mucosa, so even a mild form of infection can lead to fusion (synechia) of the labia and vagina.
Thus, parents should carefully monitor the general health of the girl and her external genitalia, and later, when the child is able to take care of herself, explain how to take care of herself.
Thrush in children: symptoms and types
Symptoms depend on the form and type of candidiasis:
- candidiasis (without symptoms and harm to the health of the carrier);
- acute and chronic forms;
- recurrent and persistent (complicated) forms;
- secondary candidiasis, which develops with non-fungal lesions of the genital organs.
Vulvovaginal candidiasis (thrush, vulvar candidiasis) in children and adolescents is manifested by the following symptoms:
- itching and burning in the perineum (constant or worsening in warmth, in a hot bath, when walking and wearing the wrong underwear (too tight, synthetic, etc.);
- pain and burning when urinating.
As a result of constantly appearing signs, the child may develop a fear of taking a bath or urinating, as well as before sexual intercourse (in sexually active adolescents), up to severe nervous disorders.
In the acute form of thrush in children, the following occurs:
- hyperemia and swelling of the external genitalia and vagina;
- discharge (cheesy or creamy) with a sharp sour odor;
- in some cases, a grayish-whitish coating is observed on the walls of the vagina.
In the chronic form of thrush in children, the following occurs:
- less pronounced symptoms (itching, burning, redness, etc.), which may intensify before menstruation (in menstruating girls);
- less intense swelling and mild or completely absent plaque;
- changes in the skin of the labia and around the vagina.
If you notice symptoms of thrush in your child, you should urgently consult a doctor to undergo a course of treatment and prevent it from becoming chronic or recurrent.
Symptoms of pathology
Candidiasis in infants
The development of thrush in newborns and very young children is more than pronounced. In general, the pathology occurs in three stages, at each of which specific symptoms are observed.
If we consider each stage of candidiasis in more detail, we should highlight:
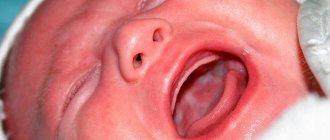
- Absence of discomfort in a sick child at the first stage of the disease. It is indirectly indicated only by redness in the mouth, a slight cheesy coating on the tongue and the appearance of a sour odor from the baby’s mouth.
- A more pronounced manifestation of the noted symptoms in the second stage of the disease, also supplemented by the formation of small erosions in the oral cavity and pain in the child. The latter, by the way, are expressed in the constant crying of the baby, which cannot be calmed down.
- The most severe manifestation of pathology is at the last – third stage. Symptoms at this stage of thrush are the most pronounced and severe. It often manifests itself in damage to the entire oral cavity, which results in the appearance of large areas covered with a cheesy coating. Often additional signs of the disease are fever, abnormal bowel movements and insomnia in infants.
Perhaps the most obvious signs of candidiasis in a small child are:
- strong sour odor from the mouth;
- the appearance of a cheesy coating in the oral cavity;
- temperature rise to 38 degrees Celsius.
Having discovered at least one of the noted manifestations in their child, parents must show it to the pediatrician.
At a minimum, before starting treatment, it is important to confirm with a specialist the fact of thrush and receive basic recommendations for combating the pathology. It is better not to self-medicate candidiasis in infants, for example, due to its considerable danger.
What to do if your child is not eating well due to oral thrush
Thrush in a child's mouth does not always cause pain and tears. And small white spots on the mucous membrane are easy to miss. Can thrush go away on its own or will it develop into something more serious, how to feed and treat a child with thrush, says allergist-immunologist Tatyana Nikolaevna Dzyaduk.
— Tatyana Nikolaevna, what is candidiasis in a child’s mouth?
— Candidiasis in an infant is a fungal disease of the oral cavity caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida (candida). Of all age groups of children, it occurs most often in infants.
— How is thrush transmitted from mother to child?
— Candida fungi enter the baby’s body when passing through the birth canal, from the nipple of the mammary gland, or from the hands of the mother and staff. True, several cases of a child becoming infected with thrush in the womb have been described due to a violation of the integrity of the membranes. Unfortunately, the intrauterine process leads to stillbirth or miscarriage.
Candida in single quantities is a normal resident of the microflora of the skin and mucous membranes, including the oral mucosa. But when actively multiplying, it causes a disease, which in newborns and infants up to one year is due to the immaturity of the immune system.
— Why does candidiasis more often affect the oral mucosa in children?
— Candida fungi attach well to the epithelium of the oral and vaginal mucosa, which is why candidiasis occurs more often on these organs. The most common fungal infections in young children are oral candidiasis and skin candidiasis in the diaper area and skin folds (diaper rash).
— How is thrush in children related to intestinal infections and acute respiratory infections?
— You can talk about oral thrush after taking antibiotics - this is a risk factor for the disease, but not a necessary condition.
| Dysbacteriosis (changed ratio of bacteria and fungi on the skin and mucous membranes) will lead to thrush if you give your child antibiotics: they will only kill bacteria. Space will be freed up for mushrooms, and they will begin to reproduce more actively. | Regurgitation itself does not in any way affect the presence or absence of thrush. But if the cause of regurgitation is gastroesophageal reflux disease, then its treatment can lead to candidiasis esophagitis - this is a lesion of the esophagus, and not the oral cavity. | Intestinal infections and acute respiratory diseases do not affect the development of oral thrush unless treated with antibiotics. |
— Can formula or breast milk cause oral thrush in a newborn?
— According to statistics, formula-fed children suffer from thrush somewhat more often than breastfed children. This may be due to the fact that breast milk contains substances that inhibit the growth of fungus.
The fungus can enter the baby's body from the mother's breast. Therefore, laboratory detection of fungal cells in breast milk or culture of breast milk is pointless; this will not affect the treatment tactics or the outcome of the disease. But the mother needs to be checked for candidiasis of the nipples during breastfeeding and, if necessary, undergo external treatment, since the presence of candidiasis of the skin of the nipple increases the risk of oral candidiasis in the child.
Principles of therapy
Antifungal drugs
Getting rid of thrush in a baby is quite simple, naturally – with timely and high-quality treatment.
Despite their possible pathogenicity, Candida fungi have little resistance to basic therapy methods and die almost completely within a relatively short period of time. All this helps to improve the child’s condition, the absence of complications and direct recovery from pathology.
Treatment of infants for candidiasis is primitive, but it should be organized together with a professional pediatrician. The general principles of therapy largely depend on the age of the sick child.
Treatment plan
How to treat vulvar candidiasis (thrush) in children of school age, and not only?
Basically, treatment involves eliminating the pathogen and stopping its reproduction, which will therefore eliminate the symptoms. Only a good specialist can treat the disease correctly and effectively, who can prescribe:
- antifungal drugs and antiseptics (topically);
- antibiotics;
- ointments and medicinal baths;
- therapy to restore and strengthen the immune system;
- therapy to restore the microflora of the reproductive system.
Which course of treatment will be chosen and prescribed depends on the specific case and the reasons that led to vulvovaginal candidiasis in a teenage girl and a smaller child.
Repeated appointment
At the follow-up appointment, the doctor assesses the child’s condition and checks how effectively the chosen regimen works. If no positive dynamics are observed, then repeated diagnostics and selection of new methods for treating thrush in the child are prescribed.
Control reception
The control reception is an important point. The doctor prescribes it to see how the child recovers after a full course of treatment, to see if there are any relapses or suspicions of them. It is also possible to prescribe physiotherapy and rehabilitation (for example, if a long course of antibiotics has been prescribed). A follow-up appointment is usually scheduled after 21–30 days or later.
Treatment result
The disease can be cured, but the timing of treatment is individual and depends on the stage and causes of thrush in young children or teenage girls. All details of treatment are discussed individually at a doctor’s appointment. If there is a suspicion that the parents are infected, then both parents are treated.
Prevention
Thrush in children is a fairly common occurrence, especially under “favorable” conditions for the disease. To protect the child, it is necessary to take preventive measures:
- carry out proper personal hygiene of the child in accordance with age;
- wear the correct underwear;
- normalize nutrition (moderate or limited consumption of sweets, starchy foods and fast foods, more fruits, vegetables, etc.);
- Strengthen your immune system by taking vitamins and exercising.
Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene at home and in public places will also help avoid the occurrence of vulvar candidiasis and other unpleasant diseases in a teenage girl or young child.