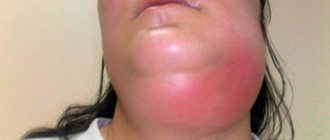
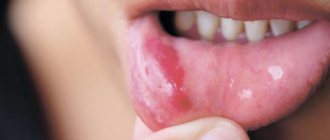
Photo: phlegmon of the submandibular region
Phlegmon of the submandibular region is a diffuse purulent-inflammatory lesion of the subcutaneous tissue and muscles in the area of the lower jaw. This disease is characterized by the intensive spread of the pathological process, which from the very beginning has a diffuse course.
In dental practice, it is customary to distinguish between several types of phlegmon. These can be odontological, adenophlegmon and osteophlegmon. According to statistics, the ratio of abscesses and phlegmons in the maxillofacial area is 4:1.
Causes and pathogenesis of abscesses and phlegmons
Most purulent lesions of the maxillofacial area are odontogenic in nature. This means that the disease is formed due to the spread of infection from the inflamed root or periodontium. In such cases, streptococci and staphylococci from the primary lesion penetrate through the lymphatic vessels into the deep layers of the soft tissues of the face.
The state of immunity is of great importance in the development of the purulent process. A decrease in the body's protective abilities is a powerful predisposing factor for tissue suppuration.
Reasons for formation
Due to their development, there are two types of perimaxillary abscesses:
- Odontogenic. The cause of development is damaged dental elements.
- Non-odontogenic. Not caused by the condition of the dentofacial apparatus.
The most common causes of anomalies are dental diseases:
- Advanced carious lesions of units, pulpitis.
- Deep periodontal pockets.
- Periodontitis.
- Pericoronitis.
- Infected and impacted molars and premolars.
- Root cyst.
The development of a lesion can be triggered by penetration of infection under the periosteum from a diseased unit.
Reasons for the development of non-odontogenic foci of pus:
- Traumatic lesions of the jaws, elements or soft membranes of the oral cavity with infection.
- Nasopharyngeal and ear infections.
- Complications of unqualified dental treatment.
- Spread of infection to the jaw from other organs and systems.
The development of an abscess depends critically on the general health and immunity of the patient.
Clinical picture of the disease
In the initial stages, abscesses and phlegmons adjacent to the lower jaw are manifested by compaction and progressive swelling of the soft tissues of the face. The skin over the purulent focus is often hyperemic. The key symptom of suppuration is fluctuation - the feeling of fluid in a confined space.
The course of phlegmon is accompanied by general intoxication, in which the patient presents the following complaints:
malaise and feeling of chronic fatigue; increase in body temperature; fatigue and joint pain.
Abscesses, as a rule, do not cause such symptoms due to the limited nature of the pathological process.
Abscess, phlegmon of the maxillofacial area in children is characterized by an acute and severe course of the disease. Diffuse purulent lesions of soft tissues are formed as a result of the imperfection of the children's immune system.
Symptoms of a tooth abscess
The inflammatory process in the tissues of the tooth and gums occurs in stages and is accompanied by different symptoms:
- At the beginning of development, discomfort appears, slight swelling, gum bleeding is possible when brushing teeth, and pain is sensitive when pressed.
- In later stages, swelling increases, and a reaction to hot and cold foods appears. There is prolonged pain and an unpleasant odor. In addition to local changes, the abscess is accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, increased body temperature, and general malaise.
A bitter aftertaste is noticeable in the mouth, and a change in the shade of the tooth body is possible. It is important to remember: the symptoms of gum abscess can manifest themselves in different ways - everyone has their own pain sensitivity threshold and perceives signals subjectively. Therefore, you should not wait for acute conditions; a reasonable step is to visit a dental clinic at the first incomprehensible sensation.
Diagnosis of the disease
Establishing a diagnosis for acute odontogenic infections includes the following measures:
Collection of medical history. The doctor finds out the patient’s complaints and the general condition of the patient. External examination of the maxillofacial area and palpation of regional lymph nodes. Most inflammatory and purulent processes cause enlargement and pain of the lymph nodes. Instrumental examination of the oral cavity, during which the doctor detects chronic foci of odontogenic infection. X-ray in frontal and lateral projection. Laboratory blood test, in which there is an increase in SOE, leukocytes and a decrease in the concentration of red blood cells and hemoglobin.
Abscess of the maxillary
The formation of an abscess is preceded by toothache, as in periodontitis. Biting on the affected area increases the pain. Next comes dense swelling with the formation of a painful compaction. An abscess developing under the mucous membrane is characterized by bright hyperemia and protrusion of the affected area. Facial asymmetry is sometimes noted.
In the absence of therapy, the patient’s general condition worsens: body temperature rises, refusal of food is observed. After spontaneous opening of the abscess, the pain subsides, the contours of the face take on normal shape, and general health stabilizes. But due to favorable conditions for microorganisms in the oral cavity, the process becomes chronic, so its spontaneous opening does not indicate a cure.
With short-term weakening of the immune system, perimaxillary abscesses worsen. Chronic suppuration from the fistulous tracts is possible; it is accompanied by an unpleasant odor from the mouth and ingestion of purulent masses. The body becomes sensitized by decay products, and allergic diseases worsen.
Abscesses of the floor of the mouth are characterized by hyperemia in the sublingual zone with rapid formation of infiltrate. Conversation and eating become sharply painful, and hypersalivation is noted. The mobility of the tongue decreases, it rises slightly upward so as not to come into contact with the forming abscess. As the swelling increases, the general condition worsens. Upon spontaneous opening, the pus spreads to the peripharyngeal region and neck, which leads to the appearance of secondary purulent foci.
Palate abscess most often occurs as a complication of periodontitis of the upper second incisor, canine and second premolar. During the formation of an abscess, hyperemia and soreness of the hard palate are observed; after the bulging, the pain becomes more intense, eating becomes difficult. Upon spontaneous opening, the purulent contents spread to the entire area of the hard palate with the development of osteomyelitis of the palatine plate.
If a cheek abscess occurs, then depending on the location and depth, swelling and redness may be more pronounced on the outside or on the oral mucosa. The soreness of the lesion is moderate; when the facial muscles work, the pain intensifies. The general condition is practically not affected, but an abscess of the cheek is dangerous if it spreads to neighboring parts of the face even before opening the abscess.
A tongue abscess begins with pain in the thickness of the tongue, the tongue increases in volume and becomes inactive. Speech, chewing and swallowing food are severely difficult and painful. Sometimes with an abscess there may be a feeling of suffocation.
General principles of treatment of the disease
The doctor who treats phlegmon of the maxillofacial area is an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
Each doctor, when starting to treat an odontogenic process in the maxillofacial area, is guided in his actions by the following principles:
The tooth that caused the development of phlegmon is removed. Timely diagnosis is very important due to the characteristics of this area, from where the infection can spread, causing severe consequences (in particular, mediastinitis). It is necessary to eliminate the spread of the infection, that is, promptly open the lesion and eliminate the inflammatory exudate, relieve tissue tension. The rate of subsidence of inflammation depends on the quality of evacuation of all decay products from the wound, that is, careful postoperative treatment of the wound is necessary. Comprehensive treatment of pathology using all means and methods available in this medical institution. Friendly management of the patient with colleagues from other areas, timely appointment of consultations with all specialists for combined lesions. Visible external changes often occur, which are not always pleasant for the patient, which is especially painful in the face area. Therefore, there is an urgent need to organize work with patients by a medical psychologist in the early stages after surgery, especially if there is a significant visible defect. Correct stage-by-stage treatment, organization of medical rehabilitation, referral to the appropriate department with complete information about the patient. Fully informing relatives and the patient about the violation of significant functions of the maxillofacial area, if any. Upon leaving the hospital, the patient should have clear further recommendations, especially if it is necessary to continue treatment on an outpatient basis.
Stages of development of gum abscess
| Disease stage | Description |
| Initial | The beginning of inflammation. If the immune system is functioning well, the process may stop on its own. Symptoms are absent or mild. If the immune defense is insufficient, bone or soft tissue begins to melt. Hyperemia of the mucous membrane and discomfort appear. |
| Subacute | The inflammatory process intensifies. Pus accumulates in the pathological area (near the root, inside the periodontal pocket, near the gingival papilla). The pain intensifies. The tooth reacts to irritation. |
| Acute | Progression leads to abscess formation: a cavity with pus forms in the central zone of infiltration. The clinical picture is clearly expressed: the pain is constant, sharp, swelling appears. A lump appears on the surface of the gum, inside of which there is purulent exudate. Inflammation spreads to the submandibular lymph nodes. |
| Chronic | The abscess on the gum spontaneously opens and the contents of the cavity come out. Signs of acute inflammation subside. |
Complications of abscesses and phlegmon
Purulent lesions of the maxillofacial area can be complicated by the following pathologies:
Sepsis is a serious condition of the body that is caused by the penetration of a bacterial infection into the circulatory system. Treatment of such a complication is difficult due to the development of body resistance to antibiotic therapy. Sepsis is often the cause of death. Mediastenitis in the form of purulent inflammation of the tissue of the mediastinum, where the heart, lungs and bronchi are located. Meningitis . Inflammatory damage to the meninges develops as a result of the spread of purulent infection through the lymphatic and blood vessels of the head.
Pathogenesis of the disease
Perimaxillary purulent pathologies are mainly observed in patients aged 20-30 years. Experts associate this with the high intensity of the carious process and difficult eruption of wisdom teeth.
In the human body there is a dynamic balance between beneficial and pathological microorganisms of the oral cavity. Activation of pathogenic microflora and the development of a purulent-inflammatory process occurs with a decrease in the level of local and general immunity.
Further spread of infection from the primary focus occurs in the following ways:
- Contact method. Until recently, doctors considered gradual inflammation of the soft and hard tissues of the oral cavity to be the key mechanism for the formation of perimandibular abscesses and phlegmon. But in practice, diffuse suppuration of the muscle spaces develops within a matter of hours, and for the contact method of spread it takes 2-4 days.
- Hemetogenous and lymphogenous. Modern medical research has shown that most cellulitis and abscesses are the result of the spread of pathogens through the lymphatic and blood vessels.
Boundaries of the submandibular region
Submandibular phlegmon is localized within the following boundaries:
| Borders | Facial tissue |
| external | inner part of the lower jaw bone |
| Front and rear | digastric |
| top | deep fascia of the neck |
| lower | superficial layer of cervical fascia |
Location of the maxillary spaces
Forecast and prevention of the disease
The prognosis of odontogenic abscesses and phlegmons is usually favorable. A positive treatment result is observed with timely indication of full surgical care. In such cases, the patient must be hospitalized in a specialized medical hospital.
Lethal outcomes from purulent lesions of the soft tissues of the maxillofacial area are associated with late presentation of the patient and systemic suppression of his immunity.
Prevention of the disease is achieved in the following ways:
sanitation of the oral cavity, during which the dentist treats all carious, pulpitic and periodontitis teeth; strict adherence by patients to the rules of personal hygiene and regular brushing of teeth; undergoing regular preventive examinations at the dentist, at least twice a year; timely consultation with a doctor if symptoms of dental diseases are detected. Every person should remember that the cost of prevention is much lower than the cost of treatment. And in some cases, sanitation of the oral cavity can prevent the development of severe complications, which are accompanied by high mortality in patients.
Causes of dental inflammation
The main causes of tooth gum abscess and pulp infection:
- Advanced caries affecting the root apex. Suppuration develops against the background of periodontitis.
- Untreated gingivitis and periodontitis (gum disease). They often develop as post-traumatic complications: pathogenic microflora accumulates in periodontal pockets.
- Weakening of the immune system after illness (flu, sore throat, etc.).
- Iatrogenic factors - bacteria entered after the use of unsterile instruments during treatment, injections, or incorrect tooth extraction.
The development of the inflammatory process may be preceded by damage to the oral mucosa and the formation of boils.