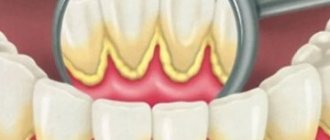
The appearance of tartar in children is based on local causes. First of all, these are shortcomings in the organization of everyday oral hygiene. In addition, it can be caused by a limited amount of solid food consumed, which acts as a natural means of cleaning the dental surface.
Another reason lies in the insufficient content of pyrophosphate in the child’s saliva. This component is responsible for counteracting tartar deposits on the tooth surface. Moreover, in the case of children, the boundaries of stone and enamel are often not obvious, and determining the beginning of deposits on the surface of the tooth is very problematic. This is explained by the strong bond between the calcium crystals that make up the deposits.
In dentistry, tartar is usually divided into two categories: subgingival and supragingival. The latter has a pale yellow or gray tint and can be easily removed from the surface of the teeth by scraping. Supragingival plaque is formed from components existing in human saliva. Such stone develops most actively in the area of the lower front teeth and in the area of the upper molars, since it is next to them that the exits of the salivary ducts are located.
Detection of subgingival stone is possible only when visiting a dental office. This type of stone is formed from substances that make up the gingival fluid. In most cases it is a dark brown or green color. It is formed mainly on the neck of the tooth or the cementum of the root. It is characterized by a high degree of adhesion to the tooth surface and the formation in some cases of full-fledged protrusions.
How does tartar form on baby teeth in children?
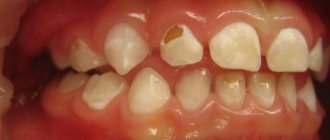
The formation of tartar in children under 3 years of age, and in adults as well, begins with the deposition of soft bacterial plaque, which undergoes progressive calcification: calcium phosphate minerals are deposited both within and between the plaque bacteria, and then again covered with a layer of plaque. Thus, a hard mineralized plaque appears on the teeth, mainly in the front part, which cannot be removed with a children’s toothbrush. The usual color of tartar in adults is brown. But in children under 3 years old it is usually green. According to dentists, the appearance of such plaque is associated with the vital activity of chromogenic microorganisms containing chlorophyll, which, as we know, is green.
What to do for preventive purposes
- The diet should be balanced with sufficient amounts of calcium, fluorine, and phosphorus.
- It is necessary to include raw hard fruits and vegetables in the diet, and reduce the amount of sugar-containing foods.
- After each meal, rinse your mouth with plain water, and in the morning and evening, thoroughly brush your teeth.
- Reduce the number of daytime snacks and, if possible, eliminate night meals.
- Visiting your dentist at least twice a year will help you identify causes that contribute to plaque formation, such as a bad bite, chewing on one side, or damage to your gums or enamel.
- It is important to choose the right toothbrush and change it every three months. Choosing age-appropriate toothpaste is also important.
- It is recommended to eliminate such bad parental habits as tasting the child’s food with his own spoon or licking the baby’s pacifier. If an adult's saliva gets into a child's mouth, it can worsen the condition of his teeth, since the composition of saliva in children and adults is different.
Examine your child's mouth frequently to spot problems early. Do not try to remove plaque yourself, as you can cause even more harm, because the child’s teeth are sensitive and the enamel is very thin. Only a doctor can answer the question of how to remove plaque from a child’s teeth. Having correctly diagnosed, he will prescribe adequate treatment.
Causes of tartar in children
Local factors play a large role in the formation of tartar in a child aged 2 years and older. First of all, this is poor oral hygiene in children. Also, the causes of tartar include insufficient consumption of solid foods. In addition, the occurrence of a large amount of tartar may be a consequence of the lack of pyrophosphate in the saliva, which retards the development of dental plaque, or the lack of a certain protein in the saliva, which slows down the growth of crystals. The presence of tartar on children's teeth is not always obvious. Calcium phosphate crystals can be closely bound to the surface of the enamel, making it often difficult for the dentist to discern where the enamel ends and the stone begins.
Causes of plaque
Tartar in most cases occurs under the influence of local factors. Some of the most striking reasons for the formation of plaque in children include non-compliance with oral hygiene rules and a lack of solid foods in the daily diet. In addition, the cause of plaque in large quantities may be the absence or deficiency of pyrophosphate in the baby’s saliva. This substance can slow down the development of various types of deposits on teeth. The appearance of tartar may also indicate an insufficient amount of a particular protein in the saliva of a small patient that can inhibit the growth of crystalline deposits.
It is not always possible to recognize the presence of tartar on a child’s teeth. This is explained by the fact that the surface of the tooth enamel and the calcium phosphate crystals are closely connected, and this, in turn, complicates the recognition of the boundary between the beginning of the tartar and the end of the enamel.
Types of tartar
In dentistry, there are only two types of tartar, which are recognized by their location on the teeth:
- supragingival
- subgingival.
Supragingival tartar is usually gray or white-yellow in color. It can be seen with the naked eye and can be easily removed by scraping. The formation of supragingival tartar occurs due to the deposition of minerals that come from saliva. In most cases, the localization of this type of stone is in the areas of the frontal teeth of the lower jaw and upper molars (buccal surfaces), where the ducts of the glands that form saliva are located.
Regarding subgingival tartar, it is more difficult to recognize. Only a dentist can do this with probing. Subgingival tartar is formed due to mineral deposits, which come mainly from the gingival fluid. Places of its localization: tooth neck, root cement, periodontal pocket. In most cases, plaque is firmly attached to the tooth surface, covering the neck and forming protrusions. Subgingival stone is dark brown and has a greenish tint.
A child has tartar – what to do?
If you have discovered tartar on your child’s teeth, then first of all, make an appointment with a pediatric dentist. Tartar removal will be performed in two steps. At the first appointment, the little patient will have a professional teeth cleaning. With its help, soft plaque and deposits on the teeth will be removed. Subgingival tartar is removed under local anesthesia using ultrasound. As a rule, after such procedures, the pediatric dentist explains to the little patient how to properly brush his teeth and care for the oral cavity, and asks his parents to supervise the procedures. The second appointment is scheduled a couple of weeks later. At the second visit to a specialist, the thoroughness of the previously removed tartar and deposits is monitored.
Tartar in children: prevention
Among the reasons listed above for the formation of tartar, the absence of pyrophosphate in the child’s saliva was noted. And to prevent the formation of plaque on your teeth, you can use special toothpastes that contain this component. This will help not only stop the process of mineralization of stone on the teeth, but also prevent the growth of a new layer. Thus, the pyrophosphate contained in the paste, in some way, replaces the natural analogue if it is not present in the child’s saliva. However, when choosing a toothpaste with this component, be sure to take into account the appropriate age category.
The toothbrush plays an important role in the formation of tartar. Choosing the right toothbrush for your child will help prevent new growths. When choosing a brush to clean children's teeth, it is necessary to give preference to artificial bristles, since bacteria and microorganisms can form in natural bristles. At the same time, do not forget that experts recommend changing brushes once every 3 months, at least.
To prevent the formation of tartar in the youngest patients who cannot yet brush their teeth on their own, you can use special wipes. They contain xylitol, which can inhibit the development of bacteria in the oral cavity. By wiping the surface of your child’s teeth with these napkins, you can also clean them of soft plaque.
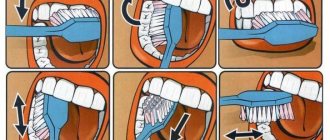
In order to maintain proper oral hygiene, it is necessary to teach your child the basic rules. According to the basic recommendations of pediatric dentists, you should first brush the teeth of the upper jaw with brush movements from top to bottom, starting in the lateral sections and smoothly moving to the front. In the same sequence, it is necessary to manipulate the toothbrush when brushing the lower teeth, moving it from bottom to top. At the same time, do not forget to pay attention to the hygiene of the mucous membranes of the tongue, cheeks, and palate, because bacteria can form on them too.
Among other things, it is worth diversifying the children's menu by adding more solid foods to it. An excellent option would be fresh carrots, apples, cabbage and others.
Note to parents
Parents should regularly monitor their child’s oral hygiene. To prevent the formation of tartar, it is worth taking your child to the pediatric dentist. This will allow pathology to be detected in time so that it does not cause the development of diseases (periodontitis, gingivitis, stomatitis, etc.) in the child’s oral cavity. In addition, the child will not have problems associated with bad breath. Visits to the dentist will allow you to timely provide the necessary care to your teeth with braces installed on them.
And remember that only a pediatric dentist who uses an individual approach and a special set of professional tools and products can remove tartar and mineralized plaque.
Tags: Cleaning
Types - place of formation and color
In dentistry, there are two types of tartar - supragingival and subgingival. They are distinguished by their location on the surface of the tooth. The first is visible to the naked eye and has a grayish or whitish-yellow color. It is easily removed by scraping. Minerals coming from saliva participate in the formation of supragingival tartar. It is most often localized in the area of the lower front teeth and the buccal surfaces of the maxillary molars, where the ducts of the salivary glands open.
Subgingival tartar can only be detected by a dentist during probing. It is formed due to minerals coming mainly from the gingival fluid. As a rule, it is dark brown in color with a greenish tint, localized on the neck of the tooth within the gingival groove, on the root cement, in the periodontal pocket. Covering the neck of the tooth, the stone is tightly attached to its surface, and often forms protrusions.
How to prevent it?
The main task of parents is not to cure the disease, but to prevent it! Therefore, certain measures should be taken to prevent mineral deposits on teeth:
- As soon as the first teeth appear, you need to teach the child to eat solid food, do not follow the lead of the little lazy person - do not chop carrots and apples;
- You should brush your teeth with a children’s brush, which is better to buy on the recommendation of a dentist;
- You need to change the brush every 2-3 months;
- Teach your child to brush their teeth correctly. The doctor will give you all the necessary recommendations at your appointment.
- purchase pastes with pyrophosphate (but strictly in accordance with the age of the baby).
But the most important rule is to bring your child once every six months for a dental examination. This will not only help get rid of tartar, but also prevent serious diseases in the future that are caused by mineral deposits: periodontitis, gingivitis, stomatitis.
Tartar removal in children
How to remove tartar from a child? If you find your child has tartar, the first thing you need to do is make an appointment at a pediatric dentist. On the first visit, the child undergoes professional teeth cleaning: soft plaque and dental deposits are removed. Removal of subgingival tartar in children is carried out using ultrasound under local anesthesia. After the procedure, the doctor explains to parents how to monitor whether the baby is brushing his teeth correctly. Before and after the procedure, the hygiene index is checked, and the rules of oral care are repeated in the presence of parents. After 1 - 2 weeks, an appointment is made to monitor the thoroughness of dental plaque removal.
Preventive actions
What to do to prevent your child from developing tartar? The answer to this question lies in prevention, the essence of which comes down to following important recommendations:
- choosing a suitable brush and paste for daily brushing of teeth: it is advisable to change the toothbrush once every three months,
- using special wipes to additionally remove plaque and food debris from the mouth - such products can be used from a very early age, even if the child is only 1 year old. Such napkins allow you to maintain baby’s oral hygiene when he does not yet know how to brush his teeth,
- the presence of a sufficient amount of solid foods in the diet,
- control over how responsibly the child approaches daily hygiene procedures,
- Regular visits to the dentist for preventive examinations and timely detection of possible diseases.
Teach Children Good Oral Hygiene
Tartar may not seem like a serious problem that requires immediate action. However, it is dental plaque that in most cases causes the development of serious inflammatory dental diseases and ultimately leads to the loss of living teeth. For this reason, it is extremely important to take a responsible approach to regular visits to the dentist and strictly ensure that the child maintains the proper level of oral hygiene.
- Epidemiology, prevention and treatment of major dental diseases in children: material, scientific and practical. Conf.: RIC TGMA, 2004.
Prevention measures
- As noted above, the absence of a substance such as pyrophosphate can lead to the formation of tartar. Therefore, some toothpastes contain this component. It stops the mineralization of tartar and prevents the process of new growth. The addition of pyrophosphate to toothpastes to some extent compensates for the lack of a natural analogue in saliva. When choosing a paste with this substance, pay attention to what age children it is recommended for.
- A properly selected children's toothbrush will also help prevent the appearance of tartar in children. It is best to prefer a brush with artificial bristles, since, unlike natural bristles, microorganisms do not form in it. Naturally, you need to remember that you should change your toothbrush every three months. In the meantime, until your child reaches the age when he can brush his teeth on his own, you can use special napkins to clean his teeth. They contain xylitol, which inhibits the growth of bacteria on teeth and gums and cleanses them well of soft plaque. Also relevant in this case are fresh hard fruits and vegetables: apples, carrots, cabbage.
- In order for oral hygiene to be as effective as possible, it is very important to teach your child how to brush their teeth properly. Among the main recommendations of dentists, we highlight the following: first, we clean the upper jaw from the outside and inside, starting from the sides, then the front teeth from top to bottom. On the lower jaw the sequence is the same, only the brush moves from bottom to top. Do not forget about the hygiene of the mucous membranes of the cheeks, palate and tongue, where a large number of bacteria are formed.
- Parents need to monitor their children's oral hygiene and regularly take them to the pediatric dentist. This will help prevent the formation of tartar, which can cause various oral diseases, for example, gingivitis in children, childhood periodontitis, and various types of stomatitis in children. In addition, your child's bad breath will also not bother you. Teeth with children's braces will need special care. Remember that food debris and soft plaque can be easily removed with a toothbrush and toothpaste. Removal of mineralized dental deposits is carried out only by a hygienist using special means and instruments.
Why do you need to remove plaque from your teeth?
Tartar can be discovered by parents themselves, or by a dentist during an oral examination. Even if the deposit is insignificant, it must be removed.
Tartar can cause:
- inflammatory lesions of the gums;
- bleeding and sore gums;
- exposure of roots and loosening of the tooth;
- carious lesion;
- constant bad breath.
Pathological processes that provoke hard deposits on teeth can lead to premature loss of baby teeth, which also has a number of negative consequences.
How to prevent the formation of tartar?
Proper hygiene and dental care is very important in preventing the formation of tartar. They must be thoroughly cleaned of food residues with special children's pastes. It is best to buy products containing pyrophosphate - it will stop the mineralization of dental plaque and prevent the growth of stone. When choosing, pay attention to the recommended age of children for whom the paste composition is developed.
Other preventive measures are:
- Using a toothbrush with artificial bristles (bacteria do not grow on it). The shelf life of this product is usually no more than three months. Special wipes with xylitol will help clean delicate enamel, as well as eating fresh apples, carrots, and cabbage.
- Proper brushing of teeth, gums, cheek surface, tongue.
- Routine visit to the dentist.
Make an appointment with a pediatric dentistry specialist in Khabarovsk “Healthy Teeth” now. We will help you quickly and inexpensively solve your child’s dental problems.
Ultrasonic toothbrushes
Recently, a new gadget has appeared on the market - an ultrasonic toothbrush. In addition to mechanical cleaning, this brush provides ultrasonic treatment of hard-to-reach areas of the tooth and gums to a depth of up to 4 mm. Ultrasonic waves destroy bacteria and effectively remove pigmentation and deposits when mineralization begins. However, such a brush cannot remove formed tartar; this can only be done by a specialist using professional equipment. In addition, the use of an ultrasonic brush is effective and safe only for people with absolutely healthy teeth.
Contraindications to ultrasonic brushes
Due to the presence of ultrasonic microvibration, the use of such brushes is not recommended for persons:
- with veneers, fillings and crowns, as their service life is reduced;
- with areas of loose and porous enamel, due to the fact that the development of the carious process accelerates due to the destruction of defective enamel;
- with gingivitis and periodontitis, due to the increased spread of infection by hematogenous route;
- with periodontal disease, as the process of bone destruction accelerates;
- having precancerous changes and cancer, due to the acceleration of the division of atypical cells.
These significant drawbacks significantly limit the use of ultrasonic brushes, since almost 95% of the adult population have certain problems. It is also not recommended to use any power brushes during pregnancy or for people with pacemakers.
After the procedure
At the end of the procedure, regardless of the method of stone removal, the dentist must grind and thoroughly polish the enamel.
Sometimes, at the request of the patient, after cleaning, the teeth are coated with a special protective composition against infection and plaque buildup.
Within 15 days after cleaning:
- Do not use bleaching abrasive pastes;
- the use of toothpastes from the “sensitive” series, based on herbs and with an anti-inflammatory effect, is indicated;
- rinses with astringent and soothing properties are recommended;
- Do not eat spicy foods or dyes;
- categorically give up smoking or at least abstain for this period.
What do dental stones lead to?
- Halitosis (bad breath) – bacteria that are part of dental plaque produce sulfurous substances that have an unpleasant odor. You can try to mask it with special sprays, chewing gums and perfumed rinses, or remove the source of its occurrence (i.e. tartar and plaque).
- Inflammation of the gums (gingivitis and periodontitis) – inflammation of the gums is of an infectious nature.
Microbial plaque and tartar release toxins and inflammatory mediators, which trigger the process of inflammation in the gums. Inflammation is first characterized by swelling and redness of the gums, bleeding, pain when brushing teeth - these symptoms are characteristic of gingivitis. If gingivitis is not treated on time, the inflammation affects not only the marginal gum, but also the bone tissue, and also leads to the destruction of the periodontal attachment. As a result, gingivitis turns into periodontitis. The latter (in addition to the preservation of all the symptoms of gingivitis) is characterized by the development of tooth mobility, suppuration from periodontal pockets, bone atrophy and exposure of tooth roots... - Caries - you need to remember that cariogenic microorganisms that are part of soft and hard dental deposits release hydrochloric acid during the digestion of food residues. This acid destroys the tooth enamel at the point of contact, after which the defect is populated by microflora and the tooth begins to rot.
- Diseases of the oral mucosa - accumulations of dental plaque reduce the local immunity of the oral mucosa, which increases the risk of developing certain diseases of the mucous membrane. We are talking about the formation of erosions and ulcers, and even necrosis of areas of the mucosa. In general, the risk of developing herpetic and aphthous stomatitis in the presence of dental plaque always increases.
- Worsening of chronic diseases - cardiovascular, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, etc. This occurs due to the absorption of toxins released by microbial plaque into the blood. Toxins are carried through the bloodstream and affect the functions of all organs and systems.
Important:
remember that the worse your hygiene, the more often you need to visit the dentist for ultrasonic teeth cleaning. Patients with good hygiene are recommended to do this only once a year, with satisfactory hygiene – once every six months. If hygiene is poor - once every 3 months, or even once a month (everything is individual here). We hope you found this article helpful!
Sources:
1. Dental education of the author of the article, 2. Based on personal experience as a periodontist, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. American Academy of Periodontology (USA), 5. “Therapeutic dentistry. Textbook" (Borovsky E.V.).
Are there any traditional methods for removing stones?
There are no home methods to remove stones in one procedure, like in clinics. Moreover, with extensive and long-fossilized formations, traditional methods will not help. Grandmother's recipes can only be used when stone formation begins, when the deposits are thick, but still loose and light. In this case, the following will help:
- cleansing teeth with radish pieces;
- It is also useful to eat a salad of grated radish with lemon every day;
- brush your teeth with fresh and already cooled coal ash;
- soften plaque with hydrogen peroxide, then brush your teeth with soda.
It should be noted that the first two methods will definitely not cause harm; they can be safely used, even if they do not help. But the last two options do not have clinical trials and proven effectiveness, and therefore may be unsafe. Therefore, you should not take such dubious and radical measures on your own when dental care is available to everyone.
Contraindications
Contraindications for hardware teeth cleaning include:
- wearing dentures and braces;
- the presence of implants in the body, including pacemakers;
- ARVI, active stage of tuberculosis, HIV infection;
- oncological diseases;
- pregnancy (or with the permission of an obstetrician-gynecologist);
- childhood, until all baby teeth are replaced.
- pregnancy.
Pregnancy is a relative contraindication to dental cleaning. Dental procedures can be performed during a satisfactory pregnancy with the permission of an obstetrician-gynecologist. If there is a threat of miscarriage or other serious conditions, it will be recommended to postpone the removal of stone deposits and the beauty of the smile.
Consequences
Many people do not consider the formation of tartar to be a problem and are in no hurry to see a dentist. If plaque has formed on the inner surface of the teeth, it is invisible during communication, and the person mistakenly believes that the problem does not exist. In fact, the appearance of stone is quite dangerous for the health of teeth and gums. Let's start with the fact that its location at the very edge of the gum can cause gum bleeding over time and contribute to the formation of a periodontal pocket in which food debris will accumulate, causing inflammatory processes in the gum.
If the stone is not removed in time, the consequences can be dire, including loss of teeth. After all, dental plaque is an excellent environment for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, in particular those that cause caries.
We must remember that the process of formation of tartar is long, so a systematic visit to the dentist will help get rid of the cause in a timely manner, avoiding complications. It is useful to carry out professional hygiene procedures at least 2-3 times a year, including the removal of dental plaque. This will help avoid such unpleasant consequences as bad breath, caries and inflammatory gum diseases.
Hardware ultrasonic cleaning.
This is the most popular and effective way to remove mineral deposits. Ultrasonic waves break up tartar and easily remove it from the enamel surface. Moreover, such cleaning has an antiseptic effect and is therefore also indicated for gum inflammation. If the stone formation is very dense, before the cleaning procedure, means are used to soften it, then ultrasonic removal of deposits is carried out. During ultrasonic cleaning in the area of the neck of the lower incisors, when the roots are exposed, there may be mild pain. Then, at the request of the patient, local anesthesia is applied.
Despite the presence of many contraindications for the use of ultrasonic toothbrushes, the use of ultrasonic cleaning when removing stone is necessary. First, the dentist will use visual guidance to avoid areas of thinned, porous enamel. Secondly, one-time professional cleaning does not have as negative an effect on fillings as twice-daily brushing.
Laser cleaning.
The newest non-contact method of removing hard dental deposits is highly effective and absolutely painless. However, the price is much more expensive than ultrasonic. Laser cleaning has the same contraindications as ultrasonic cleaning.
Air-flow
Refers to mechanical methods. A jet of air with a therapeutic abrasive mixture is supplied under pressure, which removes both soft plaque and hard deposits. The gum area may tingle during the procedure. It is less effective than ultrasonic and laser cleaning.
Manual method
Mechanical manual method of beating stones using special tools. Currently, it is outdated due to the painfulness of the procedure, the presence of complications and the emergence of more effective methods. It is used free of charge under the compulsory medical insurance policy in public hospitals or as an additional method of treatment if indicated. Due to the painfulness of the procedure, especially when removing subgingival stones, local anesthesia is performed. It is a relative contraindication for periodontitis due to high trauma.