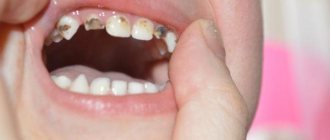
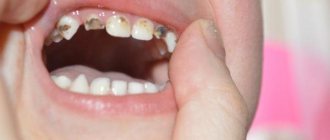
How many baby teeth do children have?
Milk teeth and even some molars begin to form at the stage of intrauterine development. Of course, a child has no visible teeth at birth - they begin to erupt only after 6 months. During this six-month period, they are hidden under the gums, but slowly develop and form, beginning to move outward.
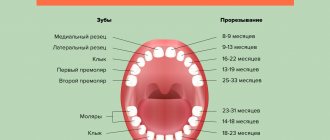
In total, a child grows 20 baby teeth:
- Central and lateral incisors – 8.
- Fangs – 4.
- First and second molars – 8.
Their main function is to form a space where molars will then grow.
How to help your baby?
The only troubles that can be explained by the appearance of teeth are mild “crankiness”, drooling and the formation of bad habits, for example, finger sucking. Appetite may decrease, the rhythm of sleep and wakefulness may be disrupted due to constant itching of the gums. Of course, these manifestations do not bother the baby for 2 years without stopping; as a rule, there are days when the child shows the greatest concern about teething. How can you make life easier for a child during this difficult period?
- Remedy No. 1
. Double the affection and care of parents. Don't be afraid to spoil your baby; Constant crying and whims spoil your character much more! - Remedy No. 2
. Using teethers. These are rubber or plastic toys that your baby can bite on. Chewing teething rings with liquid inside, which can be placed in the refrigerator and cooled, is especially soothing. A child aged 6 months and older will feel better even after chewing on a clean, cold cloth. - Remedy No. 3
. Gently massage the gums with a gauze pad. Wrap your index finger in a gauze pad soaked in cold water and gently massage your baby's gums. - Remedy No. 4
. A homeopathic medicine that must be prescribed by a pediatrician or homeopathic physician. - Remedy No. 5
. Medicinal. Pain-relieving gels containing a local anesthetic, such as lidocaine (available in pharmacies without a prescription). They cause numbness in the gums and thereby relieve pain.
Many mothers believe that while the child has few teeth and they are baby teeth, it is not necessary to brush them. However, this is not true at all! In young children, the protective properties of tooth enamel are reduced and in the presence of provoking factors (consumption of sugar-containing products, poor oral hygiene), this can lead to the development of caries.
How many teeth should a child have per year?
During this period, baby teeth begin to cut.
They begin to break out in the following sequence on the upper and lower jaws. On the top:
- 8-12 months. Central incisors.
- 9-13 months. Lateral incisors.
- 16-22 months. Fangs.
- 13-19 months. First molars.
- 25-33 months. Second molars.
In the lower jaw, this process is distributed in time somewhat differently:
- 6-10 months. Central incisors.
- 10-16 months. Lateral incisors.
- 17-23 months. Fangs.
- 14-18 months. First molars.
- 23-31 months. Second molars.
It is worth noting that these time limits are averaged and deviations up or down by 1-3 months are considered normal.
If you want to know how many teeth a child has per year is considered normal, you should refer to the chart described above. You get that at the age of 12 months there should be 6-8 of them.
Main signs and symptoms
Many parents are in a hurry to find out how their children are teething, especially those who are faced with this phenomenon for the first time. Rarely does such a process go unnoticed; most often it manifests itself with characteristic symptoms.
Experts call the following main symptoms that a child is teething:
- worsening sleep;
- increased moodiness and tearfulness of the baby;
- Bad mood;
- swollen and sore gums;
- loss of appetite, sometimes even leading to refusal of food;
- increased salivation;
- the child puts everything into his mouth, so he tries to relieve the pain;
- the formation of various redness and rashes around the mouth caused by skin contact with saliva.
In addition to the main signs indicating the appearance of teeth in children, accompanying symptoms can also be traced. Due to the increased function of the salivary glands, the following may be observed:
- runny nose;
- hoarseness of voice;
- cough without sputum production;
- indigestion in the form of diarrhea.
Often, as a child teethes, the body temperature rises. Usually it stays at around 37.5 ̊C, but it can rise to 39 ̊C.
The most severe pain is accompanied by the eruption of fangs. They have very sharp edges that cut through the gums and cause severe pain. The appearance of the upper “eye teeth” is especially painful, as they are closely connected to the facial nerve.
The approximate timing of eruption of milk jugs is presented in the table below.
| Tooth name | Baby's age |
| Central incisors | Below - at 6-9 months, above - 7-10 |
| Lateral incisors | On the upper gum – 9-11 months, on the lower gum – 11-14 |
| First molars | In the bottom row - in a year and a half, in the upper – 13-20 months |
| Fangs | In the lower dentition - 16-22 months, in the upper dentition - 17-23 |
| Second molars | Below - at 20-26, above - at 26-33 |
Please remember that this is just a rough guide to teething timing. Later dates are also acceptable, but not later than 6 months.
Changing baby teeth to molars
Around the age of 4, a child’s growth spurt begins, the jaws enlarge and the baby teeth seem to move apart, with gaps appearing between them – trema. If this does not happen and by the age of 5 the teeth are still tight, you need to show the child to the dentist, as there may not be enough space for permanent teeth.
At about 5-6 years of age, baby teeth begin to become loose and gradually fall out, which indicates that the molars are already beginning to grow underneath them. Usually this process of change lasts for 5-8 years and the final formation of the dentition occurs somewhere around 14-15 years.
This happens in the following order:
- 5-6 years – lower and upper incisors.
- 7-8 years – lower and upper lateral incisors.
- 8-10 years – upper and lower molars.
- 9-11 years – upper and lower canines.
- 11-13 years – upper and lower molars.
Milk teeth are replaced by permanent molars. Their number at the age of 14-16 years is 28. At the same time, the third molars (wisdom teeth) are already formed, but they begin to grow only after 18 years. True, not all people grow them. It all depends on individual characteristics.
Eruption of second molars
The first fundamental units of the primary occlusion are the molars. They have the largest chewing area. They are diamond-shaped from above and cube-shaped from below. Children have 8 molars - two on each side below and above. The first molar and the second molar are distinguished. In terms of ranking from the central incisors, they occupy 4th and 5th positions. Their cutting order is as follows:
- the first in the lower jaw – 13-18 months;
- the first in the upper jaw – 14-19 months;
- the latter in the lower and upper jaws erupt approximately equally - at 23-31 months.
After a year, parents should prepare to meet these “guests”: the first to climb will be the one in the top row. By the age of two, the second ones appear. The correct sequence of appearance ensures a beautiful and correct bite. Many parents like to look into their babies' mouths and check how their teeth are coming in. You shouldn’t do this and worry the baby once again. Genetics plays a large role in this process.
There is no need to interfere: nature will take care of everything itself. A photo of molars will help you find out what chewing units look like. To help the child and alleviate his condition, it is very important for parents to know what the symptoms of teething are. Since the process occurs after a year, many children can already point to the sore spot and even say what they feel.
How many teeth should a child have?
It all depends on age. The maximum number of teeth in the period from birth to 5-6 years is 20 - these are milk teeth. Then, until the age of 15-16, the molars begin to erupt, pushing out the milk teeth. Ultimately, their number grows to 28.
The latest are the third molars. They grow only after 18 years of age, but not everyone has them.
It is worth noting that the period of formation and eruption of baby teeth is very individual. In some children, all 20 teeth grow by the age of 2, while in others - by 2.5 or later. Such delays within a year are considered normal and are not a developmental anomaly.
If teeth do not start cutting in the first year of the baby’s life, you should consult a doctor to find out the reasons.
To the list of posts
Help from folk remedies
If you do not want to give your baby medications, you can use natural formulations. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of an allergic reaction in the baby. Also follow safety precautions and remember that small objects can be swallowed or choked by the baby.
- Amber beads
. These products are made from Baltic products. They have a pronounced analgesic and regenerating effect. In addition, the product can relieve fever and fever. The beads are made in such a way that they can enhance the effect of other medications. - Plant herbs
. Herbs such as chamomile and phytolacca can help alleviate the teething condition of a child. They relieve inflammation and partially relieve gum pain. Remember that they must be used in accordance with the instructions. You should not give your baby prepared formulas to drink. Simply treat the inflamed areas of the mucous membrane with the decoction.
What microelements are needed for teeth growth?
Vitamins and microelements are a necessary component for the development and normal functioning of the child and adult body. The formation of dental tissue cannot do without:
Fluorine
Strengthens enamel, makes incisors resistant to bacteria, the destructive effects of acids, and prevents caries. Fluoride is taken in tablets or drops when a deficiency is diagnosed. Enters the body with sea fish, nuts, grape juice, spinach, and most vegetables.
Toothpastes with fluoride are not approved for use by children under 4–5 years of age. Children aged 1.5–3 years swallow the tasty mass when cleaning their mouths, and an excess of the element is formed in the blood. For foolish children, choose toothpastes without fluoride to protect them from the negative consequences of hygiene procedures.
Calcium
It is the building material of infants' teeth. Without calcium, mineralization in tissues is impossible. After finishing breastfeeding, a one-year-old child should receive dairy products daily, greens and fish at least three times a week.
Vitamin K
Necessary for complete absorption of calcium and protein synthesis. Found only in natural dairy products (cottage cheese, sour cream and others).
Teething for young parents seems like an extremely difficult and nervous process. They prepare for it mentally, they are afraid of hysterics and hyperthermia.
Young and inexperienced parents do not need to worry or be negative. It is better to study the issue of dentition in infancy in order to arm yourself with knowledge and understand why the baby cries and is nervous. In this case, jaw development will be perceived as a normal physiological stage of growth, which will be experienced easily and quickly.
Permissible deviations
Don't be too alarmed if teeth erupt at intervals of several months or in the wrong order. But if the baby does not have incisors after 1 year, this is a reason to consult a specialist.
Usually, when the first tooth appears late, then all the others begin to cut late. If there is a hereditary factor, there is no need to worry.
Factors influencing deviations from the norm:
- weakened immune system;
- use of medications by the mother during pregnancy;
- sucking on a pacifier for a long time;
- lack of breastfeeding, bottle feeding;
- lack of vital elements in the diet;
- lack of necessary load on the jaws (mashed food).
Premature babies, babies with high body weight, and children on IV are at risk.
An acceptable deviation from the norm is a lag of six months. If a tooth begins to erupt with a discoloration, shape, or in the wrong direction, the baby should be shown to the dentist.
It is advisable to consult if teeth appeared too early or one of the paired incisors or molars is missing for a long time. Gaps in the dentition can be both normal and pathological.
In this video, the pediatrician talks about how many teeth should be at 2 years old and what to do if your child has deviations from the norm.