Author:
- Khirnetkina Ayuna Fedorovna
otorhinolaryngologist, otoneurologist, audiologist
4.25 (Voted by: 
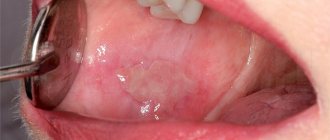
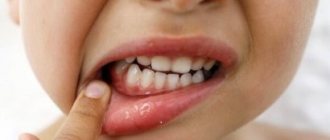
In medicine, the term paratonsillar abscess refers to the accumulation of pus in the tissues surrounding the tonsils. The term “paratonsillitis/peritonsillitis” is also distinguished when purulent has not yet formed. This is the stage before the formation of the abscess itself.
Peritonsillitis and paratonsillar abscess occupy first place among purulent processes of the pharynx and are a consequence of the spread of an acute inflammatory process from the palatine tonsils to the paratonsillar tissue and surrounding tissues, characterized by their inflammatory infiltration (edema). More often there is a one-sided process. These conditions are a complication of acute or exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis, tonsillitis, due to trauma to the pharynx by a foreign body, odontogenic process (caries, periodontitis, etc.).
Peritonsillar abscesses belong to a group of diseases that require emergency care. For diffuse purulent inflammation of the peritonsillar tissue for 2 days, when an abscess has not yet formed, the treatment is the same as for a severe form of tonsillitis (lacunary or follicular). In the absence of positive dynamics, the patient is hospitalized. In cases where an abscess has formed (usually by the 5-6th day, and with some infections and a decrease in the body’s immunity, an abscess can form, despite active treatment, earlier - on the 3-4th day from the onset of the disease) it is necessary to perform his autopsy.
How to treat peritonsillar abscess?
Treatment is carried out in two stages:
- Surgical.
- Conservative.
First of all, it is necessary to evacuate the pus from the peritonsillar space.
This can be done in the following ways:
A) Tonsillectomy - removal of the tonsils.
B) Puncture (puncture) and aspiration.
B) Opening (incision) and dividing the paratonsillar space.
After draining the pus, the patient should receive antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy.
Causes of the disease
Peritonsillitis occurs when pathogens enter the tissues around the tonsils.
The causative agents of the disease are streptococci, staphylococci, and fungi.
How do pathogenic microorganisms get into the paramygdaloid tissue? There may be several reasons for the start of the inflammatory process:
- untreated tonsillitis, when bacteria from the tonsils penetrate into nearby tissues;
- exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis, when pathogenic microflora also penetrates from the tonsils;
- dental diseases - for example, caries (infection comes from the oral cavity), although it is not necessary that the tonsils themselves become inflamed;
- injury to the tissue around the tonsils, during which infection occurs;
- infection through the bloodstream;
- chronic accumulations of infection in the body (for example, chronic sinusitis);
- diabetes;
- reduced immunity;
- smoking.
Typically, purulent inflammation acts as a complication of chronic or acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis) - this is the most common cause of the disease.
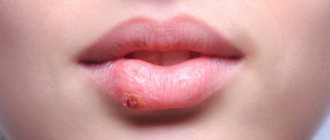
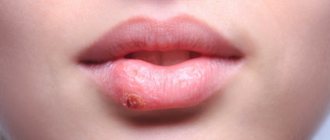
Signs and symptoms of paratonsillitis
The disease has an abrupt onset. An abscess forms a few days after an exacerbation of tonsillitis or the onset of a sore throat and is accompanied by vivid symptoms:
- acute pain in the throat, radiating to the jaw or ear;
- sensation of a “lump” in the throat;
- fever (temperature 39-40°C);
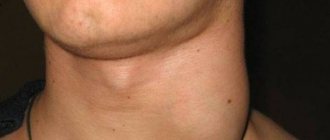
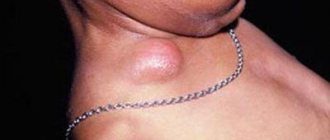
- submandibular lymph nodes are greatly enlarged;
- difficulty swallowing (even drinks);
- the appearance of a repulsive odor from the mouth;
- neck pain that gets worse with exercise;
- general weakness;
- inability to fully open the mouth;
- headache;
- speech impairment (voice as if there is a hot potato in the mouth);
- difficulty breathing (with large ulcers).
Spontaneous breakthrough of suppuration into the throat cavity is accompanied by an improvement in well-being and the appearance of an admixture of pus in the saliva.
The spread of the abscess contents into the peripharyngeal space significantly worsens the condition, so there is no need to delay operations to open the abscess. If you have even one of the symptoms listed above, schedule a consultation with an otolaryngologist today. Doctors at the Center for Operative Otolaryngology at GMS Hospital use gentle microsurgical techniques, which contributes to a speedy recovery and the absence of relapses of the disease.
Indications for autopsy
Drug therapy is possible only at the stage of paratonsillitis, when there is inflammation, but there is no abscess yet. If antibiotic therapy was not carried out in the first two to three days, the abscess will need to be opened. At the stage of purulent inflammation, conservative treatment will not give a positive result.
In 25% of cases, the abscess opens on its own without surgical intervention. At the same time, the temperature drops sharply, the pain goes away and recovery occurs. But if this does not happen, then the patient is shown opening the abscess cavity with a scalpel.
If the operation is not performed, then the purulent inflammation can go further, which poses a danger to life.
Symptoms of a throat abscess
Any form of throat abscess begins with a sharp increase in body temperature to critical values – 39-40°C. The febrile state is accompanied by a deterioration in the general condition.
Symptoms and manifestations of throat abscess:
- Children have tearfulness and anxiety, loss of appetite, restless sleep;
- In infants - impaired sucking;
- Increased pain when swallowing food and saliva;
- Impaired nasal breathing due to damage to the upper pharynx;
- Nasal voice;
- Attacks of suffocation when the abscess is localized in the middle and lower part of the pharynx;
- Impaired breathing in an upright position due to pus flowing down the wall of the larynx, closing the lumen of the trachea;
- Hoarseness of voice;
- Bubbling in the throat during sleep;
- Swelling and tenderness of the occipital and upper cervical occipital lymph nodes;
- Swelling of the neck in the area of the lower jaw.
Due to severe pain, the patient takes a forced position when his head is turned towards the affected side and slightly thrown back.
Treatment methods
The treatment tactics for paratonsillitis depend on the extent of the spread of the purulent process and the presence of complications. Peritonsillitis in the initial stage is treated conservatively, with antibiotics, decongestants, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. If drug treatment is ineffective or an abscess forms, the abscess is surgically opened and its cavity is drained. The opening of the paratonsillar abscess is carried out under local anesthesia. The otolaryngologist dissects the wall of the abscess, removes the purulent contents, and rinses the cavity with an antiseptic. An improvement in the condition is observed immediately after opening and draining the abscess.
You have questions? We will be happy to answer any questions Coordinator Tatyana
Complications
The development of a purulent inflammatory process leads to severe complications:
- Bronchopneumonia as a result of infection spreading through the upper respiratory tract;
- Congestive pneumonia due to respiratory failure;
- Brain abscess, purulent meningitis due to the spread of infection into the cranial cavity through the circulatory system;
- Cardiac arrest;
- Asphyxia (suffocation) due to blocking of the trachea by an abscess, swelling of the larynx, pouring of purulent masses into the larynx during independent opening of the formation;
- Purulent mediastinitis – spread of infection into the mediastinum;
- Phlebitis;
- Jugular vein thrombosis;
- Arrosive bleeding due to purulent fusion of blood vessels;
- Sepsis (blood poisoning).
Why is it necessary to open and drain a peritonsillar abscess?
Peritonsillar abscess is an urgent condition in otolaryngology. The proximity of vital structures (windpipe, large vessels of the head and neck) requires immediate diagnosis and treatment. In the initial stages, when an abscess has not yet formed, the pathology responds well to drug therapy. A course of antibiotic therapy, anti-inflammatory and painkillers is prescribed. If conservative treatment is ineffective, the abscess is opened surgically.
Peritonsillar abscess is dangerous due to its complications, fraught with the development of phlegmon, mediastinitis and even sepsis. The Otolaryngology Department at the GMS Clinic has everything you need to accurately diagnose and treat peritonsillar abscesses.
The opening of the abscess is carried out using modern surgical equipment. During the operation, the potential of laser and radio wave surgery is actively used, which allows the procedure to be performed in the most gentle manner, eliminating the development of surgical complications. Opening abscesses in children is performed under anesthesia, which significantly increases the comfort of the intervention.
Prevention of paratonsillitis
The following simple preventive measures will help prevent the development of peritonsillar abscess:
- strengthening the immune system;
- healthy lifestyle;
- timely treatment of acute and chronic diseases of the ENT organs (sinusitis, adenoids, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, etc.), caries;
- rejection of bad habits.
In the presence of recurrent abscesses, elective tonsillectomy is recommended.
Opening a peritonsillar abscess at the GMS clinic is a simple and safe surgical procedure that is performed in an outpatient or inpatient setting. Recovery takes 10-14 days, after which you will return to your normal life. You can make an appointment with an otolaryngologist at GMS Hospital by phone or using an online application.
Indications for opening an abscess
The possibility of developing this kind of complications can be assumed if the following symptoms are present:
- tonsillitis, the duration of which exceeds 5-6 days: during this time an abscess may form;
- severe, severe pain in the throat that is felt when swallowing or moving the head;
- temperature increase over 39 degrees;
- significant enlargement of one or two tonsils;
- signs of intoxication and fever (weakness, malaise, muscle pain, apathy and drowsiness);
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- increased heart rate and breathing.
The development of an abscess, which is accompanied by such symptoms, is a direct indication for opening the abscess.
Usually the operation is performed 4-5 days from the onset of the inflammatory process - by this time the abscess is already fully formed. To check the readiness of the cavity for removal, the doctor may prescribe a diagnostic puncture - puncturing the cavity with a thick needle in the place that protrudes the most above the tonsil. The progress of the procedure is most often monitored by endoscopic or ultrasound monitoring. If pus is found in the cavity of the syringe used for puncture, it means that an abscess has formed and is ready for removal.
The autopsy is performed on an outpatient basis, that is, to perform it, the patient does not need to go to the ENT department of a medical institution.
Causes of throat abscess
In children, the most common cause of abscess development is an infection caused by streptococcus, staphylococcus, and, less commonly, E. coli. The disease is almost always secondary to the pathology that provoked it. The infection enters the throat through the lymphatic tract, so nearby lymph nodes are always affected and inflamed.
Primary foci of infection in childhood:
- Purulent otitis;
- Mastoiditis;
- Parotitis occurring with complications;
- Rhinitis;
- Pharyngitis;
- Complications of acute infectious diseases (influenza, ARVI, measles, scarlet fever, diphtheria);
- Complications after surgery (adenotomy, tonsillectomy).
The rapid development of the inflammatory process is facilitated by reduced immunity, rickets and a history of diathesis in the child.
In adults, the formation of a pharyngeal abscess most often occurs due to tissue trauma.
Causes of throat abscess in adults:
- Damage to the throat from rough food, bone, or foreign object;
- Trauma to the mucous membrane of the throat after gastroscopy, bronchoscopy, endotracheal anesthesia;
- Complication after tonsillitis;
- Consequence of tuberculosis, syphilis;
- Presence of caries.
The rapid spread of infection is facilitated by a history of HIV infection, diabetes mellitus, malignant tumor, somatic diseases, or any process that reduces immunity in an adult. The causes of purulent inflammation in the throat cannot be strictly limited to age categories. Predisposing factors from each group can occur at any age.
Diagnostics
For the differential diagnosis of paratonsillitis, the following research methods are used:
- examination by an otolaryngologist;
- laryngoscopy;
- pharyngoscopy;
- laboratory tests (blood tests, culture for flora and sensitivity to antibiotics, etc.).
In some cases, to clarify the diagnosis, additional studies are performed - ultrasound, CT scan of the soft tissues of the head and neck.
A comprehensive examination allows you to assess the condition of the abscess and tonsil, determine treatment tactics and the scope of intervention. You can complete all the required tests at the GMS clinic in a day.
Clinical picture
ENT patients mainly complain of a sensation of a foreign body in the throat and larynx and pain, which becomes much stronger when eating. In some cases, the pain is so severe that swallowing becomes impossible. During examination of the larynx, a limited area of inflamed mucous membrane is observed, and in its center a focus of inflammation is clearly visible. As the disease develops in the arytenoid cartilage or epiglottis, their mobility sharply decreases. In the absence of timely treatment, acute laryngeal stenosis may develop.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!