Definition
· Poisoning occurs when consuming fluoride (F, Latin fluorum) or fluorine-containing substances in toxic concentrations.
· The toxicity of fluorine compounds depends on the degree of solubility of the compound.
· The toxic dose in children under 5 years of age is considered to be greater than 25 mg of fluoride.
· The toxic dose in people over 5 years of age is considered to be more than 5 mg fluoride/kg body weight.
· Consumption of more than 17-22 mg sodium fluoride/kg (8-10 mg fluoride/kg) causes symptoms of severe toxicity in children.
· Sodium fluoride is a commonly used compound F in caries prevention (eg, toothpaste and other dental care products). 1 mg of fluoride corresponds to 2.2 sodium fluoride.
· Swallowing too many fluoride tablets or toothpaste is common in the 1-3 year age group.
· Some insect/pest poisons are also rich in F and their consumption causes poisoning.
· Unlike children, high fluorum intake in adults is often intentional (eg, suicide attempts).
The effect of fluoride on dental and oral health
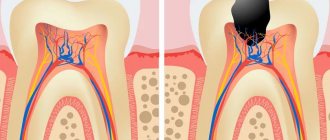
Data from numerous scientific studies leave no doubt about whether fluoride is beneficial for teeth. First of all, it protects them from caries and maintains oral health. The presence of ions of this element in saliva is critically important. The fact is that they have the ability to be embedded in the crystal lattice of hydroxyapatite, a compound that forms the basis of tooth enamel [12].
Due to this and other mechanisms of action of fluoride ion:
- prevents demineralization (loss of minerals) of enamel and strengthens it, protecting teeth from acid damage and caries [12];
- promotes remineralization of enamel, that is, helps restore the content of minerals in it and eliminate defects on its surface [12];
- suppresses the growth of pathogenic bacteria in the oral cavity [13];
- reduces acid production by pathogenic bacteria in dental plaque [14].
It was also found that in addition to systemic (internal, coming from water or food), oral health is also effectively protected by local fluoridation [12]. This is the name of a method in which fluoride is applied directly to the tooth surface, without swallowing the drug. For this purpose, fluoride-containing toothpastes , mouth rinses, and professional dental fluoride varnishes are used [12].
Etiology and pathogenesis
· Gastrointestinal genes are often dominant. These genes are caused by the formation of irritant/corrosive and systemic hydrogen fluoride in the acidic environment of the stomach, which in turn causes gastrointestinal irritation and erosion.
· Fluoride tablets contain the filler sorbitol, which causes nausea, vomiting and diarrhea without necessarily consuming toxic doses of fluoride.
· Once F is absorbed, it binds to calcium and causes hypocalcemia. It is this hypocalcemia that is the main cause of the symptoms and consequences of poisoning.
· Fluorine also acts directly cytotoxic, affecting various cellular enzyme systems.
Why is water fluoridated?
A reasonable question arose in my head after reading it. However, the answer is more than banal: those responsible for the situation either do not have information about the real danger of the substance, or deliberately turn a blind eye to the circumstances. Experts consider adding fluoride to water supplies a dangerous way to purify water. Everyone knows the expression “the less you know, the better you sleep,” but while many are silent, people are acquiring extra pounds of harmful fluoride. In the USA, the population filed lawsuits, and the government made a brilliant decision - to recognize fluoride not only as harmless to the body, but also beneficial for teeth. This is why we are so convinced that the more fluoride in the toothpaste, the whiter the teeth.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic criteria
· Ingestion of fluoride compounds in doses that cause characteristic symptoms.
· Possible mixed poisoning with another substance.
· Hypocalcemia due to any other cause.
Disease history
Signs of poisoning include nausea and abdominal pain, thirst and central nervous system depression (fatigue/lethargy). If excessive fluoride intake is suspected, the patient should answer the following questions to obtain a complete medical history:
- When did the reception take place? How much time has passed since then?
- What was accepted? In what form, and in what doses (amount of substance and concentration)?
- Consumption intention?
- Is there a danger of others using this substance by mistake?
It is worth considering that sodium fluoride is available as a medicinal product in the form of dentifrice (4 or 10 g plus solvent), dental suspension (22.6 mg/ml), toothpaste (5 mg/g) and chewing gum (0 .55 mg).
Is fluoride in toothpaste harmful?
When it comes to the benefits or harms of a microelement for the body, it is important to understand that the same substance can have positive and negative effects. It is not the substance itself that causes harm, but its excessive concentration in the body.
The harm of an excess of fluoride is manifested by metabolic disorders, deterioration of blood clotting, fluorosis, or as it is also called, speckled enamel syndrome. This is a dental disease that causes light stains to form on the teeth. Over time, they become darker, turn yellow and lead to the destruction of tooth enamel. The disease requires treatment. Typically, remineralization therapy, photophoresis, and professional bleaching are used for this.
Research
If serious poisoning is suspected, the patient is hospitalized. The following blood tests are performed in the hospital:
· Blood sugar (hypoglycemia).
· Electrolyte balance is especially important to monitor.
· Hypocalcemia is usually the most serious and pathogenic variable.
· Hypomagnesemia and hyperkalemia are also observed in poisoning.
· Fluoride poisoning can cause liver and kidney damage. ALT and creatinine should be measured.
Other studies:
· ECG and cardiac monitoring in severe cases. There may be a widened QRS complex, arrhythmia, shock, and cardiac arrest.
Is it possible to drink tap water because it is fluoridated?
Consumption of liquid, which often also contains chlorine and boron, can cause serious poisoning, and a daily habit will turn your body into a piggy bank of a substance that is almost impossible to remove.
Please note that during pregnancy you should not drink tap water. Poison in drinking water is dangerous for children. Scientists have found that fluoridation, which is used in water treatment in Russia, is one of the causes of brain damage in children. To obtain specific results, indicators such as iodine deficiency and lead exposure were taken into account. In many countries, electrochemical methods are used to purify water, that is, anodes made of graphite, ruthenium or manganese and cathodes made of iron, nickel or molybdenum. At the moment, these methods have their drawbacks, which require additional maintenance of the water supply system, which is not always possible.
In any case, drinking tap water will harm your health. There is no effective and relatively inexpensive method of water purification in Russia yet, so use bottled water from a trusted manufacturer. Carefully study the composition of the water on the packaging.
Treatment
Treatment goals: avoid the harmful effects of fluoride and eliminate existing negative symptoms. It is recommended to drink plenty of milk or calcium-rich drinks. Calcium reacts with fluoride to form poorly soluble calcium fluoride, which is not easily absorbed.
Additional recommendations and treatment regimen depending on age and fluoride dosage.
Age
|
Can fluoride accumulate in the body and can it be removed?
Initially, fluoride was never involved in the human body. We are not talking about a substance found in fresh food. The element may accumulate as a result of prolonged use.
Where can you find fluoride? For example, while brushing your teeth. You cannot completely protect yourself from the element entering the body; substances are also absorbed through the tissues of the oral cavity. Fluoride consumption harms brain tissue, being a neurotoxin, disrupting the hormonal system, being an endocrine disruptor. Of course, it is possible to remove the “chemistry”, but the process is slow. We recommend paying attention to your daily habits and avoiding fluoride products. Today there are a huge number of alternatives on the market.
Progress, complications and prognosis
Make sure fluoride medications are not available to young children.
Gradient
Typically, symptoms of fluoride poisoning occur in less than 1 hour. However, in some cases, symptoms do not appear until several hours after ingestion.
Complications
· The cause of death is usually circulatory or respiratory failure.
· Damage to the liver and kidneys occurs.
· Repeated and long-term abuse of fluoride can lead to dental or skeletal fluorosis.
Forecast
Most exposures resolve without any symptoms. Fluoride poisoning is common in young children, but the condition can be prevented by keeping tablets and the like out of the child's reach.
Ingestion of toothpaste containing F is also common in children. Poisoning is rarely life-threatening and usually does not cause complications.
Fluoride deficiency
If fluoride is supplied with food or water in insufficient quantities, a microelement deficiency develops, which is dangerous for the body; this is one of the main risk factors for the development of caries [4].
Sources of fluoride for a child's teeth are critical. The fact is that in children under 6 years of age, this microelement is involved in the formation of the enamel of permanent teeth, making them more resistant to the action of bacteria and acids in food [2]. A lack of fluoride at an early age can lead to future [5]:
- late teething;
- darkening of the enamel;
- caries.
According to some data, 2 out of 3 Russians suffer from insufficient fluoride intake from water or food [6].
“In many regions of Russia, due to the insufficient content of microelements necessary for health (fluorine) in water, dental caries in children reaches 90-100%” “Fluorides: their importance for human health in modern conditions and prospects for use”, Dr. n. Iordanishvili A.K.
Why is excess fluoride harmful?
However, an excess of this element is no less harmful. It usually occurs in regions where the population uses unfiltered fluoride-rich groundwater for drinking [7]. Another possible source is vegetables and fruits that are watered with such water.
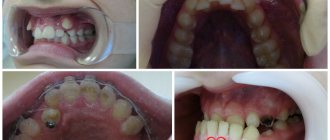
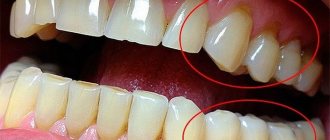
The harm of fluoride accumulation in the body is manifested in the fact that when there is an excess of it, a person gradually develops fluorosis - a disease that affects both teeth and bones. Its main symptom is stains on tooth enamel, usually white [8]. Water quality control is of great importance for the prevention of fluorosis [9].
Forms
Dentists distinguish the following forms of fluorosis:
- dashed;
- spotted;
- chalky speckled;
- erosive;
- destructive.
Let's take a closer look at each of the forms:
- Stroke is the mildest form of the disease. It is manifested by the formation of small chalky stripes on the enamel of the front teeth, which are almost invisible and can only be examined by an experienced dentist.
- Spotted is heavier than streaked. It is manifested by the formation of chalky stains on the surface of the enamel of the front teeth, which can be located on any part of the tooth enamel. The spots may be whitish or light yellowish.
- With chalky mottled disease, not only the front teeth, but almost all of the patient’s teeth are affected. The disease is manifested by the formation of pigmented spots ranging from whitish to dark brown in color.
- Erosive is one of the most difficult. With this form of the disease, small defects - erosions - form on the surface of the tooth enamel. If the patient has at least one erosion, it means that the disease is progressing and developing quite rapidly.
- Destructive is the most difficult. In this form of the disease, tooth enamel is gradually destroyed and worn away.
How and what kind of water to drink then?
Water can become both a dangerous weapon, as we have already found out, and a medicine. Today, research has established that not only water with high mineralization, but also drinking water is active water. It is important to find good bottled water, only then will it be beneficial. The question legitimately arises: “when, how much and what kind of water to drink?” We want to know how a transparent substance will help us be healthy.
Treatment and prevention of diseases must begin with cleansing the intestines. If you notice excessive consumption of fluoride, start taking mineral waters “Stelmas Mg” and “Svetla mineral”, “Izhevskaya”, “Batalinskaya”, they allow you to simultaneously cleanse the intestines, liver, kidneys, blood vessels, cells and MP; lower blood pressure, sugar, cholesterol; lose weight; strengthen the immune system and much more, i.e. normalize metabolism.
And most importantly, according to WHO, our health depends 20% on the environment, 12% on the help of doctors and 48% on yourself. Take preventive measures, help your body, analyze your habits. Your health depends on you.