If we proceed from the generally accepted canons of the formation of the dental row in a child, then by six months, maximum by 8 months, teeth should appear. However, in reality this does not always happen. Despite reaching the age of eight months, the baby does not experience teething.
Parents should not panic in such a situation, although the question of why the child has no teeth requires an immediate answer. Sometimes such a development of events is only a slight deviation from the norm, but often indicates a serious pathology.
Causes of delayed teeth emergence
A lot depends on nutrition: breastfed babies depend on the quality of breast milk. Babies who grow up on artificial formulas receive slightly more vitamins and minerals, because the formulas contain a clearly calculated amount of nutrients.
- If a child does not have a single tooth at 1 year of age, this may be a consequence of some previous disease: intestinal dysfunction, impaired metabolism, as well as insufficient calcium and vitamin D.
- Teeth may be delayed due to the special course of pregnancy; perhaps the mother suffered complications during the gestation period./li>
- Eruption after 12 months may mean that the tooth is not positioned correctly in the gum, for example, it is growing horizontally.
- Congenital absence of tooth buds in a baby. These are either hereditary disorders or a congenital pathology caused by a disruption in the normal course of pregnancy. It happens very rarely.
How can parents understand that at 12 months the baby’s teeth are simply delayed and they need to be patient, and when should they sound the alarm?
Pediatric dentists allow the first teeth to be delayed for 6 months, so if after the baby’s 1st birthday not a single baby tooth has grown, you should wait a little longer. Try to find out from your relatives about the timing and characteristics of the appearance of the first milk teeth in their childhood, perhaps this is just a family trait.
But if the teeth are already delayed by more than 6 months, and the baby’s gums do not even think of swelling, then you should contact a pediatric dentist. The specialist will conduct an examination and advise what needs to be done to help teeth appear faster.
In addition to the above reasons, the appearance of teeth after 12 months may be affected by the following:
- The teeth are located very tightly in the gums.
- There are diseases of the endocrine system, for example, hypothyroidism, due to which the activity of the endocrine glands is reduced.
- The baby suffered serious systemic diseases.
In this case, the pediatric dentist will recommend a biochemical blood test; the baby will need to have the thyroid gland examined, including an ultrasound examination. After the results are obtained, the dentist will be able to prescribe the necessary course of treatment.
Make an appointment
How many teeth should a child have before 1 year of age?
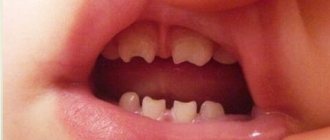
Initial signs of teething, as a rule, appear at six months of age: active salivation, inflammation of the gums, refusal to eat. During this period, the lower incisors begin to break through, which is accompanied by swelling, diathesis, tearfulness, drowsiness, runny nose, cough, fever and even vomiting, diarrhea or constipation. Symptoms disappear 3-7 days after the exacerbation.
Eight- and nine-month-old babies grow up to six teeth. As a rule, the lower incisors are already fully formed, and the upper ones are just beginning to develop. The child learns to chew and bite food independently.
At 10-11 months, as a rule, the incisors of both rows are already formed in the mouth, and adjacent teeth are also breaking through. At this time, after eating food, it is recommended to give the baby water. To avoid caries, you should not accustom him to sweets. Maintain hygiene and cleanliness of the pacifier and spoon from which you feed your baby. If a child’s lower front tooth does not grow at this age, there is no need to panic - experts define this situation as standard and not requiring intervention. To get rid of false suspicions, you can go for a medical examination. Our VTV clinic is always happy to help with any dental problem.
How to help your baby?
Initially, the dentist will take an X-ray of the baby's jaw to make sure that the baby has the rudiments of teeth inside. If there is, then eruption will happen soon. At first, the gums will swell a little and salivation will become very abundant: these are the main symptoms of the rapid appearance of teeth. You can help them a little:
- Teether toys are an excellent device for training gums; they help relieve severe itching and reduce pain.
- Mothers should learn how to gently massage their baby’s gums. It is better to massage with a clean finger lubricated with a special gel for children's gums.
- It is important to add healthy purees and healthy foods to your baby’s diet that will help the child’s body receive the necessary microelements and vitamins.
If the baby generally develops within normal limits, eats well, sleeps, is active and cheerful, then the absence of teeth at 1 year is definitely not a reason to panic. Each child develops at his own pace. In general, boys tend to lag slightly behind girls in some physiological parameters.
From this article it follows that you should not worry unnecessarily! If in any doubt, seek advice from a pediatric dentist at our Babydent
Show more tips
Over 1 year old
At one year of age, children, as a rule, already have eight full milk teeth in their mouths. This age limit is the optimal time to visit the dentist. The doctor will evaluate the condition of the oral cavity and help prevent problems.
At the age of 1.5-2 years, a child can have from 4 to 14 teeth. We must begin to accustom him to oral hygiene, showing him how cleaning is done by example. By the age of 2.5 years, children, as a rule, acquire two dozen milk teeth, which serve them until the age of 5-6 years. A visit to the dentist or orthodontist may be necessary if:
- premature development of the jaws, which is facilitated by endocrine dysfunction;
- growth retardation, often caused by rickets, digestive problems, infections and genetic inheritance;
- incorrect position of the incisors, indicating deeper bone disorders.
Until the age of six, the number of teeth remains the same - about 20. At this time, you need to continue to develop in the child a love of oral hygiene, wean him from finger sucking and nail biting.
The first replacement of baby teeth with molars begins at 6-8 years of age. By the age of 14-15, the jaws are completely renewed.
Treatment and prevention
Treatment for delayed development of primary teeth always depends on the cause of this phenomenon. The doctor needs to understand what is going wrong in the child’s body and then prescribe treatment specifically for this ailment. It is impossible to cure teeth that do not erupt, because there is always
there is a specific reason why this is not happening. It is also necessary to determine whether the child has any rudiments of teeth at all, because if they do not exist, then other measures will have to be taken.
If teeth erupt early, then parents need to worry about caries not “eating” them prematurely. But if a child does not have chewing organs at one year or 10-11 months, this can be a problem.
Prevention of teething disorders cannot exist, because when a child is born, the parents have a colossal influence on its development, but the entire basis has already been laid, so the main attention should be paid to the health, nutrition and lifestyle of the pregnant woman.
Symptoms of disorders
There are special formulas that show how to correlate the age of a child with the number of chewing organs cut through him and understand whether everything is going well, but we are not going to overload the reader by immediately getting to the point.
The concept of a norm in this case is very flexible, because in different sources we will find different terms. Some pediatricians insist that the eruption of the first teeth later than the eighth month of life is a pathology, others argue that this is quite normal, but it is impossible to separate pathology from the norm without studying a specific patient.
Even if there is a delay in dental development, if the child looks healthy and no systemic pathologies are detected, then parents can calm down and wait a little until the teeth begin to cut.
If the child is sick, then this may be a problem with his teeth. Early eruption, for example, can be both an individual characteristic of the body and evidence of incorrect functioning of the endocrine glands.
Impaired teething
Baby teeth are important for the development of a child and one cannot underestimate how much a child needs them at 10, 11 months, and a year. They allow him to eat adult food, develop and
grow correctly. The development of the facial segment directly depends on how well the chewing apparatus is developed in the child’s mouth.
Eruption disorders are considered a pathology, which includes the absence of teeth at a late age, incorrect eruption sequence, and underdevelopment during their emergence from under the gums.
To better understand what happens in a child's body and how certain factors can affect the chewing organs, it is best to first look at how teeth erupt and where they come from.
Causes of eruption disorders
As we noted earlier, the formation of teeth and their further formation occur in the early stages of pregnancy. Therefore, a common cause of pathologies are disturbances in the development of the fetus in the first 4 weeks of development or diseases suffered by the mother during pregnancy. There is probably no need to say that the first trimester is key and most important, because at this time all the systems of the future person are laid.
Diseases that can cause incorrect development of teeth include the following:
- rubella;
- congenital syphilis;
- measles and other dangerous diseases.
Bad habits of the mother and her environment negatively affect the development of the fetus: smoking (active and passive), drinking alcohol, taking medications prohibited for use by pregnant women, and so on.
There is no denying that hereditary factors and unique characteristics of the body significantly influence the eruption of baby teeth.
Development of the dental apparatus
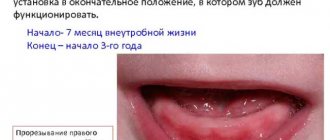
The digestive system is of central importance in human life, as well as in other creatures. Therefore, organs that belong to the digestive system are formed very early in the process of embryonic development. Already at 3-4 weeks of development, the embryo has an intestinal tube and the rudiment of a mouth, which interests us primarily. At the same time, the development of the dentition begins, the formation of the primary occlusion and the rudiments of permanent teeth.
Milk and permanent teeth are inextricably linked, because until the child grows his first permanent teeth, that is, until he is 6-7 years old, they will be replaced by temporary teeth. By the time of birth, they are well developed and ready to erupt in the near future, but the first ones - not earlier than 10-11 months.
The eruption of chewing organs is probably one of the central events in the life of the baby and his parents, because this process is associated with stress for the child. Parents are also very worried, trying to ease the fate of their baby, but what to do if the due date has come, but the teeth have not erupted?
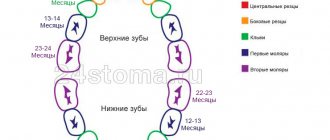
First, let's define what a “deadline” is in this case. A child’s first teeth appear at 6-8 months of life, although it is possible that they may appear later. Therefore, do not worry if there is a slight delay. The lower jaw will be filled first, followed by the upper jaw. This is necessary for the child to develop a correct bite, that is, the teeth are positioned correctly in relation to each other. You will learn more about the sequence of teething in this table:
Each organism is individual, but there are cases in which parents should pay attention to how their child’s teeth develop:
- delay in teething for more than several months, for example up to a year;
- early dental development;
- the order of eruption at 10 or 11 months is disrupted;
- tooth missing or out of shape at 10 or 11 months;
- The dentition appeared even before the baby was born.