What is stomatitis
Stomatitis is a group of dental diseases that have similar manifestations. The disease looks like inflammation of the oral mucosa, localized on the inside of the cheeks, on the palate, gums, lips, and tip of the tongue. In rare cases, lesions are diagnosed in the pharynx, on the tonsils - such formations are the most difficult to notice.
Typically, stomatitis develops as an independent disease as a result of a sharp drop in immunity, chronic infection, or allergies. The disease is contagious only in rare forms, but if left untreated, it quickly spreads through the mucous membranes of the oral cavity - it can provoke a sharp rise in temperature, causing weakness and prolonged malaise.
Stomatitis also manifests itself as a complication or symptom of other diseases - influenza, gastritis, diabetes, bronchial asthma, HIV infection.
Where can I buy
The online store “Russian Roots” offers ready-made products and ingredients for their preparation, used in folk medicine for the treatment of stomatitis. Courier delivery of goods is available in Moscow and the Moscow region. Orders to other regions are sent by mail. You can buy goods in Moscow at any of our herbal pharmacies. Call us or order products in the online store!
Attention! All materials published on our website are protected by copyright. When re-publishing, attribution and a link to the original source are required.
Stomatitis: symptoms
Since stomatitis is an inflammatory process, the manifestations of the disease are standard. Dentists identify signs of stomatitis:
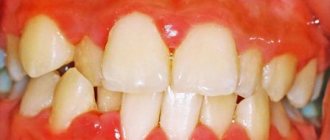
- redness, formation of a hyperemic area in the oral cavity;
- swelling, swelling of the affected area;
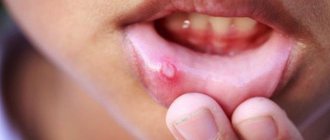
- the appearance of erosions, ulcers, aphthae;
- itching, burning at the site of ulcer formation;
- gray or yellowish coating along the edges of the canker sores;
- pain when talking, opening the mouth, or touching the mucous membranes of the mouth;
- bleeding due to accidental damage to plaque;
- local temperature increase.
Patients also note an unpleasant taste in the mouth, a putrid odor, and loss of appetite.
Treatment methods for oral inflammation
- Elimination of irritating factors - correction of braces, getting rid of bad habits, treatment of the underlying disease.
- Removal of foci of chronic infection - sanitation of caries and professional teeth cleaning.
- Rinsing with antiseptics - for inflammation of the oral cavity, chlorhexidine, miramistin, Lugol's solution, iodinol, chamomile and eucalyptus decoctions, and soda solution are used.
- Elimination of pathogenic microflora - antibiotics (only for bacterial inflammation of the oral cavity), antiviral or antifungal agents.
- Drug therapy - multivitamins, drugs to enhance immunity.
- Local treatment - anti-inflammatory ointments, gels and toothpastes to strengthen the gums.
- Surgical treatment is only used in severe cases of gum recession, periodontitis/periodontal disease and biopsy-proven neoplasms.
We strongly do not recommend diagnosing yourself or self-medicating. If you are concerned about inflammation in the mouth or other dental problems, please contact us for a consultation in the Primorsky district at st. Gakkelevskaya, 20, building 1 (metro station "Staraya Derevnya", "Komendantsky Prospekt") and in the Petrogradsky district - Kamennoostrovskaya Ave. 16 (metro station "Petrogradskaya", "Gorkovskaya", "Chkalovskaya").
Stomatitis: causes
A variety of factors and diseases contribute to the development of stomatitis in adults. For ease of diagnosis, doctors combined the causes of stomatitis into four groups, highlighting the main problem conditions:
- Mechanical injury. Ulcers appear as a result of some irritating factor. Damage can be caused by eating hard foods, poorly installed dentures, tartar buildup, and sharp edges of chipped crowns. Pathogenic microflora enters the damaged area, causing inflammation and active formation of ulcers.
- Chemical or thermal burn. Aggressive chemical agents can be food (citrus fruits), medications, nicotine, incorrectly selected toothpastes or mouth rinses. Thermal burn occurs when consuming excessively hot food or drinks.
- Poor oral hygiene. Failure to comply with regular hygiene procedures, tartar, and plaque provoke the active proliferation of bacterial microflora, which leads to inflammation of the oral mucosa.
- Chronic diseases. In adults, stomatitis develops as a reaction to problems of the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system, due to anemia, endocrine pathologies, and HIV infections.
In addition to the listed categories, the causes of stomatitis can also be internal problems:
- vitamin deficiency, micronutrient deficiency - unbalanced diet, metabolic disorders in the body;
- allergies - of any origin;
- heredity - the individual reaction of the immune system to deteriorating health;
- a general decline in immunity - as a result of serious illnesses.
Unfavorable factors become catalysts for the development of pathology, and external circumstances aggravate the course of the disease.
The variety of causes points to an important point: there is no obvious causative agent of stomatitis. In order for an ulcer to localize, several circumstances must coincide - decreased immunity for any reason, an abundance of pathogenic microflora in the oral cavity, a traumatic agent.
Inflammation of the oral cavity due to coronavirus
Covid-19 deals a serious blow to the immune system. In this case, against the background of catarrhal phenomena, changes in taste and general weakness, blisters, red spots and cracks may appear on the swollen tongue (“Covid tongue”). In weakened patients (elderly, children and people with severe chronic diseases), fungal stomatitis often develops and painful ulcers appear on the oral mucosa. The use of antibiotics in severe cases of coronavirus infection only worsens the course of candidiasis.
80% of patients experience inflammation of the oral cavity after suffering from coronavirus. Most often, the salivary glands become enlarged. Persistent dry mouth appears. Even several months after recovery, a white coating is present on the tongue and aphthous stomatitis can develop.
If signs of coronavirus infection appear, call a doctor from the First Family Clinic of St. Petersburg to your home to take a PCR test. The procedure takes a few seconds and is completely painless. If there are no symptoms of ARVI (fever, runny nose, cough), you can go to the clinic to donate blood for antibodies.
Types of stomatitis in adults
Effective treatment of stomatitis in adults begins with the diagnosis of pathology. Identifying the provoking factor is one of the main tasks of the dentist. The situation is aggravated by the fact that many reasons are similar - they overlap each other, distorting the clinical picture. For this reason, only experienced doctors treat stomatitis in adult patients.
There are a variety of classifications of stomatitis:
- according to the course - acute periodic, chronic, recurrent;
- by external manifestation - redness, aphthae, erosion;
- by localization - on the lip, on the tongue, on the palate, in the throat.
When diagnosing and selecting a treatment plan, dentists try to take into account the versatility of the disease - the form, causes, degree of damage to the mucous membranes, stage of the disease, and other classification parameters. Based on these factors, it is customary to identify the most popular types of stomatitis in adults:
- aphthous;
- ulcerative;
- herpetic;
- candida;
- prosthetic;
- allergic;
- ray.
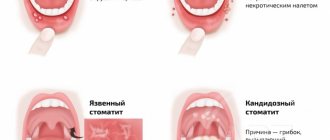
Aphthous stomatitis
Aphthous stomatitis is characterized by the appearance of round ulcerative formations covered with necrotic plaque. This is the most common variant of the disease - it occurs in 65-70% of dental patients.
The causes of aphthae formation are viral and bacterial diseases. Localization of ulcers is on almost any mucous tissue of the oral cavity.
Initially, the patient is faced with the fibrinous form, when local blood circulation is disrupted. If left untreated, the disease turns into a necrotic form, accompanied by tissue death, or into a scarring form - the mucosal tissue changes structure.
Ulcerative stomatitis
Ulcerative stomatitis is characterized by the formation of deep, painful ulcers in the mouth. They usually arise due to:
- poor hygiene - a large amount of plaque on the teeth, tartar;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract - metabolic disorders;
- chemical burns - abuse of especially spicy foods.
Lesions affect the deep layers of tissue, so treatment of ulcerative viral or bacterial stomatitis in adults is carried out only by a dentist according to a carefully developed plan.
A separate type of ulcerative stomatitis is ulcerative-necrotizing gingivitis, Vincent's stomatitis. The cause of the disease is the active proliferation of pathogenic microflora, the influence of spindle bacillus and Vincent's spirochete. The disease is observed against the background of a sharp decrease in immunity and is characterized by reactive development. Patients complain of swelling of the gums, suppuration, pain, putrid breath, and loss of appetite. Without treatment, tissue necrosis progresses and tooth roots are exposed.
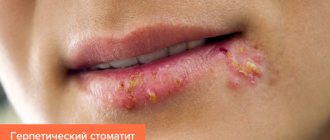
Herpes (herpetic) stomatitis
Viral herpetic stomatitis is a contagious variant of the disease provoked by the herpes virus. Transmitted through hygiene items, through negligence, by airborne droplets.
Externally it differs from other types, since the lesions look like fluid-filled blisters before turning into ulcers.
During treatment, the doctor conducts complex therapy, including taking medications.
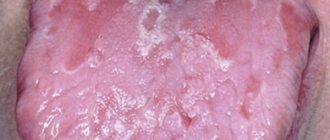
Candidal stomatitis
The cause of candidal stomatitis is a fungus that causes the appearance of a cheesy coating on the oral mucosa. Underneath the plaque is a swollen, inflamed area. When the formations are removed, the tissue surfaces begin to bleed.
The causes of the disease are decreased immunity and poor hygiene. Treatment requires careful selection of drugs so as not to aggravate the situation.
Prosthetic stomatitis
The pathology is typical only for adult patients, as it is a consequence of improper prosthetics, individual intolerance to the crown material, and poor quality of care for the orthopedic product.
The disease manifests itself as inflammation of the soft tissues around the prosthetic structure, turning into ulcers and erosion.
Allergic stomatitis
A distinctive feature of the disease is dryness and itching in the mouth. This is how increased sensitivity to allergens manifests itself. At the site of the inflamed areas, aphthae and ulcers quickly form. In severe cases, an ulcerative-necrotic form may develop.
Pathology happens:
- acute - single manifestation;
- chronic - with constant relapses and complications.
Treatment requires an integrated approach.
Radiation stomatitis
The reason for the appearance is the patient undergoing radiation therapy or chemotherapy and, as a result, a decrease in immunity. It occurs acutely - with inflammation and ulcers. Requires careful attention from the doctor during treatment to avoid worsening the situation.
How to get rid of stomatitis?
Stomatitis is perhaps the most common and unpleasant disease of the oral cavity. When an infection enters the body, ulcers form in the mouth. They cause discomfort and can subsequently lead to serious complications. How to treat stomatitis ?
Treatment of any infectious diseases first of all involves going to the doctor. Antibacterial therapy should be carried out under medical supervision. Bacterial disease most often goes away in 1-2 weeks. If the stage is not advanced, it can be treated independently. How to treat stomatitis at home :
- Rinse your mouth with soda solution. Add 1 spoon of soda to a glass of warm water. You can also use boric acid (1 teaspoon per 150 ml of water) or hydrogen peroxide (1 teaspoon per half a glass of water).
- Chamomile decoction. Heals wounds quickly.
- Sea buckthorn oil has an antibacterial effect. You can use antiseptics: chlorhexidine or miramistin.
- Anesthetic dental gels will help relieve severe pain. They should contain lidocaine.
Soda solution can also be used to treat stomatitis in infants .
Wipe the mouth and tongue with moistened gauze. If signs of stomatitis (bacterial) do not disappear, you should consult a doctor.
In case of aphthous form of the disease, you should urgently go to the clinic. How to determine:
- multiple large and deep ulcers;
- grayish coating in the center;
- red rim around the wound.
This type of stomatitis should not be treated at home. It is forbidden to cauterize ulcers with alcohol, iodine, or brilliant green. An advanced disease can lead to suppuration and tissue death.
How to get rid of stomatitis in children?
Basic methods of local therapy:
- Treating the oral cavity with baking soda. For preparation you will need 1 tablespoon per glass of boiled water. Apply 3-6 times a day.
- Rinse with Blue solution. Or 2% boric acid.
- Use of antifungal agents. This includes medicated creams and ointments. For example, Clotrimazole, Pimafucin, Nystatin, Candide.
Symptoms of stomatitis in children and treatment can be determined by a doctor. Treatment is carried out in accordance with the doctor's prescriptions. If the dosage is not followed correctly or the course is interrupted, side effects may occur.
You should not self-medicate, as this can harm the baby.
Only a pediatric dentist will prescribe the correct therapy. He can also advise treating stomatitis in children at home .
Types of stomatitis
Depending on the depth of tissue damage and the cause of inflammation, experts distinguish the following types of stomatitis:
- catarrhal;
- aphthous;
- candida;
- ulcerative;
- herpetic;
- traumatic;
- allergic.
The catarrhal form of stomatitis is the mildest and rarely causes complications. But treatment is still required, mainly local. The most severe course is ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis, which often causes bacterial complications.
The candida type occurs more often in young children.
Each type of disease has its own characteristics, causes of development and symptoms. It is difficult to determine the shape yourself.
Sometimes even specialists do not have enough clinical picture to make an accurate diagnosis. Additional laboratory tests are often required to determine why stomatitis occurs in the mouth and whether it is associated with other diseases.
Literature:
- Fungal, viral and traumatic stomatitis in a therapeutic dentistry clinic. Tutorial. Edited by Dr.Med.Sc. K.G. Karakova - Stavropol. Publishing and information, 2013. – 100 p.
- Pankrusheva T.A., Maravina I.N., Chekmareva M.S. Research on the development of the composition and technology of tablets for the treatment of stomatitis // Scientific result. Medicine and pharmacy. – T.4, No. 1, 2022, pp. 78-88.
- Tilis S.Yu. Stomatitis. Nurse, 2010, No. 2.
- Glukhmanyuk D.S., Malinovsky V.A. Aphthous stomatitis. Proceedings of the scientific and practical conference “Modern problems of pharmacology, cosmetology and aromology.” International Humanitarian University, Odessa Medical Institute, 2015. (Current problems of pharmacology, cosmetology and aromology: Materials of the scientific and practical conference dedicated to the 160th birthday of a prominent Ukrainian pathologist, endocrinologist, immunologist , microbiologist, professor Volodymyr Valerianovich Pidvysotsky and Pharmacist Day. m. Odessa, June 15, 2022 – Odessa: International Humanitarian University, 2015. – 48 p.)
- Volkova, M.N. Diseases of the oral mucosa: educational and methodological manual / M.N. Volkova, Yu.P. Chernyavsky, N.A. Sakharuk, Yu.R. Elenskaya. – Vitebsk: VSMU, 2016. – 236 p.
- Therapeutic dentistry: textbook: in 3 hours / ed. G.M. Barera. - M. : GEOTAR-Media, 2005. - Part 3. - 288 p.
- Galizina O.A. Main aspects of the occurrence, clinical manifestations, treatment and prevention of chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Russian Dental Journal, 2014, No. 6, pp. 39-43.
- Instructions for the medical use of the drug Metrogyl Denta® Dental gel // Registration number P N015982/01 // State Register of the Russian Federation. – URL: https://grls.rosminzdrav.ru/Grls_View_v2.aspx?routingGuid=9bc9a05c-d28b-…
- Dental gel for gums Metrogyl Denta® in the treatment of periodontal diseases and oral mucosa. Practical medicine, No. 1(33), March, 2009, pp. 105-106.
- Strakhova S.Yu., Drobotko L.N. Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis (lecture). RMZh, No. 29 from December 27, 2006, p. 2096
Why does the disease occur?
Stomatitis can be an independent disease or a symptom of systemic diseases. Immunodeficiency, pemphigus, streptoderma - all these are pathologies that create conditions for its development. Mechanical damage, which is possible if there are sharp dental crowns or low-quality dentures in the mouth, also lead to irritation of the mucous membranes.
Dentists agree that the disease occurs due to:
- failure to comply with oral hygiene rules;
- habits of chewing hard foreign objects;
- improper installation of braces, dental bridges, crowns;
- long-term use of certain medications;
- smoking;
- using drugs by placing them under the tongue or “behind the lip”;
- unbalanced nutrition, progressive vitamin deficiency;
- malignant tumors located in the mouth;
- prolonged stress;
- hormonal disorders.
Today it has been proven that the need to use drugs to treat stomatitis often arises in people who are accustomed to using toothpaste that contains sodium lauryl sulfate. This is a compound that promotes the formation of thick foam during hygiene measures. It has been established that sodium lauryl sulfate “pulls” moisture from the mucous membranes of the mouth , as a result of which they become more sensitive to negative external influences. Therefore, when purchasing a hygiene product, it is important to study its composition.
Diagnostic methods
Dentists, pediatricians and pediatric infectious disease specialists treat inflammatory diseases of the mouth in children. During the appointment, the doctor will examine your complaints, review your medical history to identify risk factors, and conduct a physical examination.
As a rule, a general and instrumental examination of the mouth is sufficient to make a preliminary diagnosis, since different forms of stomatitis manifest themselves as peculiar ulcers. Additional research may be required to clarify the nature of the disease.
Why treatment is necessary
If a person ignores the presence of stomatitis for a long time, the disease develops into a form that is difficult to treat, for example, gangrenous or ulcerative. Then not only soft tissues, but also jaw bones are included in the destructive process, and this is very dangerous.
Also, if you refuse treatment, complications such as:
- severe bleeding gums;
- formation of scars on the mucous membranes;
- destruction of periodontal joints;
- addition of secondary infections.
Canker sores should not be underestimated. They pose a threat to the entire body. In rare cases, they lead to disruption of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory organs.