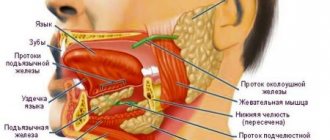
Pathogenesis of neck pain on the left side
Pain can be caused by a variety of reasons. A symptom often indicates the presence of pathology and its progression or exacerbation. As a rule, pain in the left neck appears due to:
- osteochondrosis in this part of the spinal column;
- infectious processes (colds, etc.) that provoke inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck;
- injuries to the muscles or ligaments of the neck;
- pinched nerves with subsequent inflammation;
- muscle spasms, which are provoked by high levels of stress, hypothermia, drafts, etc.
How often a person will experience neck pain depends on age and the specifics of their lifestyle and work. If you have a sedentary job, don't like walking, and don't exercise even minimally, you'll most likely experience discomfort in your neck more often.
Why does the left side of my head hurt?
Physiological reasons
Under certain circumstances, pain in half the head can occur in a healthy person. Features of the pain syndrome are episodic in nature, rapid disappearance after rest or taking an analgesic. The symptom is observed in the following cases:
- Intense physical activity
. A combination with darkening of the eyes, dizziness, shortness of breath, palpitations and tingling in the heart area is possible. - Stressful situations
. The left or right half of the head hurts due to the release of stress hormones, causing vasoconstriction and increased blood pressure. There is pronounced emotional stress. - Mental fatigue
. Pain is caused by significant mental stress, as well as the need for prolonged concentration and tension when staying in one position, for example, when preparing for an exam or working at a computer. - Bad habits
. The symptom sometimes appears with the abuse of tonic drinks (coffee, strong tea, energy drinks), smoking and drinking alcohol. The cause is changes in vascular tone and the entry of toxic substances into the body.
Cluster headache
It develops in people of a certain type - it affects mainly tall men with an athletic build, ambitious but indecisive. The pain syndrome develops acutely, reaches a peak within a few minutes, lasts from 15 minutes to 3 hours. The pain most often occurs in the left side of the head. It is most strongly expressed in the orbit, burning, stabbing, unbearable, reminiscent of a “rupture” or “squeezing out” of the eye. Cluster headache is accompanied by autonomic disorders. It decreases with movement, so patients rush around and punch the wall.
Migraine
During a migraine, the left side of the head hurts somewhat less frequently than the right side. The pain is pressing, throbbing, with the epicenter in the temple, forehead or eye. Sometimes painful sensations arise in the back of the head, and from there spread to the entire half of the head. A typical sign of pathology is the periodic change of the affected side. Manifestations vary slightly depending on the type of migraine:
- Simple migraine.
Diagnosed in 80% of cases. There is no aura. A prodrome in the form of drowsiness, worsening mood, and decreased performance is possible. Hemicrania is combined with nausea and vomiting, and intensifies with movements and exposure to auditory and sound stimuli. Lasts from 4 hours to 2-3 days. - Migraine with aura.
The attack itself proceeds in the same way as with a simple migraine. The difference lies in the presence of an aura - visual disturbances, transient sensitivity disorders, ringing in the ears, the appearance of unusual smells or sounds, and deterioration of speech. Migraine in children is often preceded by “Alice syndrome” - visual distortion of objects, visual hallucinations. Lasts from several hours to 4 days. - Ocular migraine.
Typically there is loss of certain areas of the visual field, the presence of paracentral or central scotomas, and flickering before the eyes. The headache is throbbing, occurs in the forehead, moves to the orbit. The duration of visual disturbances is 10-20 minutes, the duration of an attack of cephalgia is 30-120 minutes. - Vestibular migraine.
Manifests with a prodrome, which is subsequently joined by dizziness, sometimes in combination with other variants of the aura. Then half of the patients develop pain in the left or right side of the head, lasting no more than 3 days. Dizziness stops with the onset of hemicrania, persists throughout the entire painful attack or becomes its only manifestation (painless paroxysms).
If the symptom persists for more than 3 days or a series of continuous paroxysms during this time, they speak of migraine status. The pain is very intense, wave-like. Pallor, adynamia, severe weakness, inability to take food and medications due to repeated vomiting, and increasing dehydration are observed. The condition is serious.
Pain in the left side of the head
Paroxysmal hemicrania
Unilateral pain is paroxysmal, very severe. It can be aching, pulsating, burning, boring, stabbing or reminiscent of a fist blow. It is localized mainly in the temple or orbit, less often in the area of the forehead, back of the head or crown of the head. Associated with damage to the trigeminal nerve. An attack of paroxysmal hemicrania lasts from 5 to 45 minutes; during the period of exacerbation, from 1 to 40 episodes can be observed per day. It is supplemented by vegetative symptoms, drooping eyelids, constriction of the pupil, and photophobia.
Vertebrobasilar insufficiency
Left-sided or right-sided headache is observed in the spondylogenic form of vertebrobasilar insufficiency. Develops suddenly with movement. From the neck and back of the head it spreads to the forehead, temple and eye socket, and radiates into the arm. A clear connection is revealed between the intensity of cephalalgia and the position of the cervical spine. The pain syndrome is complemented by unilateral hearing loss, noise in the ear, dizziness, visual disturbances, cerebellar disorders and autonomic reactions.
Hypnic headache
It is observed in people over 50 years of age and is chronic. It always develops during sleep, in 40% of cases it occurs only in the left or right half, in other cases it spreads to the entire head. An attack of hypnic headache forces the patient to wake up. On average, it lasts 30-60 minutes, repeats from once a week to several paroxysms throughout the night. The painful sensations are dull, moderately expressed, less often intense. Mild nausea and increased sensitivity to sounds and bright light may occur.
Cerebral tumors
Local pain in the left side of the head becomes an early symptom of tumors on the left side. Deep, bursting, quite intense, often occurring in the form of paroxysms. As neoplasia progresses, hemicrania is complemented by increasing focal symptoms. Then there are cerebral manifestations caused by edema and intracranial hypertension. The pain becomes diffuse, bilateral, accompanied by dizziness, nausea, and vomiting.
Arachnoiditis
The left half of the head may hurt with limited arachnoiditis, which developed in the long-term period after a head injury, inflammatory and infectious diseases. Symptoms increase gradually. The pain is bursting, more disturbing in the morning, combined with emotional instability, fatigue, irritability, and sleep disturbances. Subsequently, focal symptoms may develop, the process may spread with diffuse headaches and liquorodynamic crises.
Other reasons
Pain in the left side of the head is provoked by certain rheumatic and otolaryngological pathologies and diseases of the spine. The cause of the symptom is:
- Horton's disease.
The pain is one- or two-sided, dull, throbbing, with an epicenter in the temple area, intensifying at night, growing over several weeks. Fever, anorexia, myalgia, arthralgia, thickening and tenderness of the temporal and parietal arteries are noted. - Sinusitis.
Left-sided hemicrania accompanies unilateral frontal sinusitis and sinusitis with damage to the left paranasal sinus. Pulsating, bursting, localized in the eyebrow and forehead area, radiating to the temple. Complemented by general hyperthermia, intoxication, nasal discharge. - Mastoiditis.
Develops against the background of purulent otitis media. Accompanied by intense pain in the ear and behind the ear, which spreads to the crown, temple, orbit and upper jaw, sometimes covering the entire half of the head. Febrile temperature, intoxication, and profuse suppuration from the ear are observed. - Spine pathologies
. Unilateral compression of blood vessels and nerves due to osteochondrosis, protrusion, hernia and some other diseases of the cervical spine causes pain in the left half of the head. It is accompanied by pain in the neck, and sometimes by numbness and weakness of the upper limb.
Types of neck pain
To identify the causes of pain in the left neck and prescribe treatment, you need to pay attention to the nature of the pain, the frequency of its manifestation, as well as the conditions under which the pain intensifies. All this will help to more accurately determine the cause and undergo exactly those diagnostic measures that are needed in your case to confirm the disease.
Pain in left front
In this case, problems may be associated with inflammation of the pharynx, tonsils, and vocal cords, which leads to pain in the left side of the neck in front. If the process is bilateral, the same sensations will appear on the other side. In this situation, a person has symptoms associated with inflammation - sore throat, cough, fever, etc.
Pain in the left back of the neck
If pain appears in the left neck, the cause may lie in osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. The nature of the pain can be cutting, shooting, aching, but in any case, such a symptom will provide constant discomfort. The same sensations are provoked by a hernia in the cervical spine. Often the problem lies in spinal stenosis, which leads to a narrowing of the spinal canal. Most often, this disease affects the upper parts of the spine and can lead to compression of the spinal cord, nerve endings and subsequent disruption of the functioning of the upper extremities, numbness and severe pain.
Pain on the left side
The neck hurts on the left side for the same reasons as in the front and back. That is, pain syndrome can develop from hypothermia and muscle strain, as well as due to the development of osteochondrosis and other diseases of the spinal column in the neck. Often a person receives neck injuries in this area; the pain can even be caused by turning the head too sharply.
Left and goes to the head
In this case, the problem may be the development of osteochondrosis, injury to neck structures, as well as circulatory disorders. If you feel pain that radiates to the back of your head, it is worth measuring your blood pressure, since a common cause of pain is its increase. With atherosclerosis of the vertebral artery, the symptoms are more or less identical. If the pain in the left neck is acute, the cause may lie in occipital neuralgia. In this case, very strong, even unbearable pain will “rise” from the neck to the head, temples, and eyes.
On the left side under the jaw
In this case, muscles may ache, but most often the problem is that the tonsils are inflamed, the person has developed pharyngitis or laryngitis, and there are also problems with the thyroid gland, inflammation of which is called thyroiditis
.
Reasons why the left side of the head hurts
Headache on the left side can be caused by various reasons. It does not necessarily occur in diseases - painful sensations can also appear in healthy people due to stress or fatigue. Doctors at the Clinical Institute of the Brain advise you to go for an examination if the pain continues for more than 2-3 days in a row or bothers you too often. It is impossible to determine the exact cause at home or during a simple examination, but the doctor will need information about how the pain began, how long it lasts, in what area it occurs and with what intensity.
Physiological reasons
Even a healthy person, without any disorders or chronic diseases, can have a headache in the left area. If this symptom occurs once, is not very intense and goes away quickly, including after taking painkillers, there is no reason for concern. However, it is important to understand what can trigger a headache attack on the left side of the head in order to avoid such manifestations.
- Intense physical activity is the reason for accelerating blood circulation and activating the central nervous system. As a result, symptoms such as headache, dizziness and dark circles before the eyes, shortness of breath and tingling in the heart area may appear. To relieve them, a good rest is often enough; if the left side of your head hurts badly, you should take a painkiller tablet.
- Stress is one of the most common headaches. They arise as a result of increased concentrations of the hormones adrenaline, cortisol, angiotensin and others. They provoke vasoconstriction and increased blood pressure. To relieve pain, it is recommended to rest and resolve stressful situations, otherwise dangerous consequences are possible: chronic headaches, increased risks of stroke.
- Prolonged mental stress, including working at a monitor without breaks, can cause severe pain in the left area of the head. Constant concentration and tension, especially in a sitting position, is dangerous to health. Doctors recommend taking breaks of at least 5-10 minutes every hour and doing a light warm-up.
- Abuse of tonic drinks, which include tea and coffee, is one of the reasons why a healthy person may have a headache. They contain substances such as caffeine and tannin. These are plant components that cause a constriction of the blood vessels that supply the brain. This effect is often accompanied by an increase in blood pressure.
- Alcoholic drinks in large quantities are not a cure for headaches, but the cause that causes them. Ethyl alcohol first dilates blood vessels, and then provokes their sharp narrowing. Jumps in blood pressure are accompanied by pain, weakness and impaired heart function.
- Smoking is a source of nicotine, as well as hot vapors of other harmful compounds. This habit provokes the development of atherosclerosis, in which the lumen of the arteries narrows and they cannot supply enough oxygen to the brain. In addition, smokers often suffer from high blood pressure.
Most of the factors that cause pain in the left hemisphere of the head in a healthy person are related to habits and lifestyle. Doctors recommend completely giving up bad habits and spending time relaxing and walking in the fresh air. As a result, you can notice a significant improvement in your well-being and get rid of headaches.
Pathological conditions in which the left side of the head hurts
Pain on the left side of the head requires examination if it occurs frequently and is of high intensity. There are a number of reasons that can cause this symptom. These diseases can progress, so at the initial stage it is important to determine their cause and select an effective treatment regimen.
Migraine
An acute headache that occurs for no apparent reason and is highly intense is a migraine. During the examination, no functional impairment is observed, but it is known that this type of pain on the left side of the head is vascular in nature. Symptoms last from 4 hours to 3 days, and a migraine aura appears before the attack begins. It includes typical symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased sensitivity to light, smells, auditory and tactile stimuli;
- numbness or tingling sensation on the skin of the face and hands;
- decreased visual acuity.
Statistically, women are more likely to suffer from migraines. Despite the fact that its primary cause has not been discovered, each patient has his own factors that can trigger another attack. This could be certain smells, foods, alcoholic drinks, extreme fatigue or stressful situations. You can relieve symptoms with painkillers, but they are not effective enough for migraines.
Tension headaches
Tension headaches are often symmetrical, but can also occur only on the left side. This is a complex of symptoms that develops due to stress, chronic fatigue, and muscle tension in the neck. One of the reasons why pain in the left head can occur on an ongoing basis is injuries in the cervical spine. The patient is concerned about characteristic manifestations:
- compressive pain that covers the temple and back of the head, spreading to the area behind the eyes;
- muscle tension in the neck and shoulder girdle;
- Symptoms increase towards the end of the day.
To get rid of pain in the head on the left, it is recommended to monitor your posture. Massage therapy can also help, but should be performed by an experienced professional, especially if there has been previous injury in the area.
Cluster headaches
Cluster headaches are considered the most intense and can significantly affect the patient's daily life. They arise in one part of the head or spread over its entire surface, often affecting the area behind the eyes, forehead and temple. Additional signs also appear:
- nasal congestion, difficulty breathing;
- ptosis - drooping of the eyelid;
- increased sensitivity to light in one eye, watery eyes;
- redness of the facial skin, increased sweating.
Cluster headaches are one of the rarest types. Their exact cause is unknown, but they often occur at regular intervals, in spring or autumn. The attack lasts for 5-10 minutes, and then the pain becomes less acute and persists for up to 3 hours. A characteristic sign of cluster pain is that it begins every day, at a certain time, for 1–3 months.
Diseases of the cervical spine
Pain in the left hemisphere of the head can be caused by diseases of the cervical spine. Here pass important vessels and nerves that carry blood and impulses to the brain. Their compression or inflammation leads to acute headaches, including unilateral ones.
- Osteochondrosis is a chronic disease in which degenerative changes occur in the cartilage layer between the vertebrae. They become less durable and elastic, and therefore lose their ability to absorb shock during movement. The space between adjacent vertebrae narrows, which leads to compression of blood vessels and nerves. Soreness manifests itself after a long stay in a sitting position or after exercise.
- Displacement of the vertebrae is a dangerous condition that leads to acute pain, inflammation of the nerves and compression of blood vessels. Most often this condition is associated with injuries, falls, or increased stress on the neck area, but in some patients the displacement can also occur in a calm state. In this case, congenital instability of the vertebrae and weakness of the neck muscles are important.
- Protrusion - protrusion of the intervertebral disc, the initial stage of a hernia. The process is accompanied by acute pain in the neck and one part of the head; any movement is difficult. The diagnosis can be made based on analysis of x-rays. The pain in the left hemisphere of the head goes away if the integrity of the spinal column is restored and the compression of blood vessels and nerves is relieved.
Chronic neck diseases require timely treatment as they can progress. The Clinical Institute of the Brain has all the conditions for a full diagnosis, as well as treatment and recovery from injuries, osteochondrosis, vertebral displacement and intervertebral hernias.
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a chronic vascular disease that occurs when fat metabolism is impaired. Some products, including cholesterol, are not excreted, but accumulate in the blood and settle on the walls of the arteries. The vessels become fragile, insufficiently elastic, and cannot fully narrow or expand in response to increases and decreases in pressure. There are a large number of factors that can lead to the development of atherosclerosis, including:
- frequent consumption of fatty foods of animal origin (the main source of cholesterol);
- disruption of the secretion of enzymes that are involved in fat metabolism;
- liver diseases;
- overweight and sedentary lifestyle;
- smoking and alcohol abuse.
With atherosclerosis, a headache may occur on the left or right due to impaired blood supply to the brain. Painful sensations are often associated with increased blood pressure. The inability of the blood vessels to dilate and compensate for this condition leads to acute pain, dizziness, nausea and other alarming symptoms.
Traumatic brain injuries
Pain in the left hemisphere of the head can appear even long after injury. Concussions, bruises, open and closed craniocerebral injuries cause disruption of the blood supply to certain areas of the brain. Even in patients whose nervous activity is completely restored, pain may be felt after exercise and due to changes in weather. Injuries often trigger chronic migraines. The pain can be relieved with painkillers, and the doctor will help you choose the most suitable option.
Stroke
An acute headache on the left side of the head is one of the first signs of a stroke. In this condition, a sudden disruption of cerebral circulation occurs, resulting in areas of ischemia. The process can be determined at home, but it is important not to miss its first manifestations:
- acute headache, often one-sided;
- increase or decrease in blood pressure;
- pain in the heart area;
- asymmetry of movements of facial muscles and limbs;
- loss of consciousness.
The most common type is ischemic stroke. It occurs when there is an acute disturbance of cerebral circulation due to vascular disease or blockage. Atherosclerosis, stress and other factors can lead to an attack. Hemorrhagic stroke is less common, but is more life-threatening. It is accompanied by rupture of the vessel and the release of blood into the brain. It can accumulate in the brain ventricles or meninges, thereby provoking the appearance of areas of necrosis. Help for a stroke can only be obtained in a hospital, in an inpatient setting. Doctors at the Clinical Institute of the Brain emphasize that the highest probability of a favorable outcome remains if you seek help in the first 2 hours.
Neoplasms in the brain
Tumors and cysts can cause acute headaches, including unilateral ones. Neoplasms disrupt the processes of cerebral circulation, compress blood vessels and nerve tissue. The pain is chronic and always appears in the same area, but can spread to the entire surface of the head. The diagnosis is made based on CT or MRI data, and treatment tactics are selected individually. Early diagnosis of lumps is important because over time they can grow in size and cause more dangerous symptoms.
Colds
Colds and flu are common infectious diseases that appear more often during the cold season and in the off-season. The virus infects the upper respiratory tract and causes a persistent increase in temperature. Headache is also considered one of the characteristic symptoms. It is associated with pressure changes, high temperature, and also with the accumulation of exudate in the nasal sinuses. It decreases after rest and taking antipyretic drugs.
Arterial hypertension
Increased blood pressure is one of the main causes of headaches in the left area of the head. With hypertension, it is one-sided, pulsating, and can spread to the temple area or the back of the head. At home, you can measure your blood pressure using a tonometer. Normally, the result is about 120/80 mmHg; hypertension can be considered when the result is 140/90 mmHg. and more. An attack of hypertension may also be accompanied by additional symptoms:
- tinnitus, temporary deterioration in hearing and vision;
- rapid heartbeat;
- redness of the facial skin;
- painful sensations and discomfort behind the sternum.
Attacks of hypertension are often triggered by intense physical activity, stress and nervous tension. They appear more often in hot weather and in poorly ventilated areas. The pressure increases due to the need to increase the supply of oxygen to the cells. To normalize blood pressure, it is recommended to ventilate the room and take medicine.
Causes of neck pain on the left side
It becomes clear that the area around the neck on the left can hurt for many reasons. It is worth learning more about each disease and determining the symptoms in order to roughly understand what triggered the development of pain and discomfort in the neck.
Osteoarthrosis and osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis manifests itself in the fact that the cartilage tissue of the spinal column gradually begins to deteriorate. The intervertebral discs become thinner, the distance between them decreases, and nerve roots are pinched. Osteoarthritis also affects the joints of the spinal column.
Neck muscle damage
One of the most common cases of neck pain is damage to muscle tissue. If you hit yourself or simply overstrain your muscles by being in a not very comfortable position for a long time, or get too cold, inflammation may begin, accompanied by pain and sometimes fever.
Diagnostics
A neurologist is involved in determining the nature of the disease that provokes pain in the left half of the head. According to indications, a rheumatologist, oncologist, and otolaryngologist are involved. Primary cephalgia (migraine, cluster and hypnic headache, paroxysmal hemicrania) are diagnosed based on clinical symptoms, auxiliary methods are prescribed to exclude organic pathology.
In other cases, when establishing a diagnosis, they rely on both objective data and the results of imaging and laboratory techniques. The examination program includes the following procedures:
- Echoencephalography.
It is produced to measure intracranial pressure and helps to exclude conditions accompanied by intracranial hypertension. Despite the possibility of detecting volumetric processes, in the early stages of tumors it may not be informative due to the small size of the formations. - Assessment of cerebral blood flow
. Includes duplex scanning, ultrasound examination of the vessels of the head and neck. As part of differential diagnosis, it allows you to detect hemodynamic disorders characteristic of atherosclerosis and other diseases. Recommended for patients with vertebrobasilar insufficiency to clarify the nature and structure of the stenosis. - Radiography
. Standard photographs of the cervical spine reveal signs of hernia, osteochondrosis and other diseases of the spinal column. To confirm extravasal compression of the vertebral artery, radiographs with functional tests are taken. For sinusitis, an X-ray of the paranasal sinuses is performed, and for mastoiditis, an X-ray of the temporal bone is performed. - Tomography
. MRI of the brain is prescribed for suspected tumors and arachnoiditis. In angiography mode, it provides comprehensive information about the condition of the main arteries. If a vertebrogenic etiology of pain is suspected, MRI and CT of the cervical spine are performed. For sinusitis, an MRI of the sinuses is sometimes performed.
Consultation with a neurologist
Diagnosis of the disease
To understand what to do and how to treat if the neck on the left is very painful, first of all, the doctor needs to understand what caused the pain syndrome. It is not enough to relieve the condition by taking painkillers; you need to identify what the pain indicates and eliminate its cause. To determine the exact reasons you may need:
- x-ray
; - Ultrasound;
- MRI
; - general blood test, etc.
Based on the results of the diagnosis, the doctor will tell you why the neck hurts in the lower left and how to cope with this phenomenon in order not only to feel better, but also to eliminate the root cause.
How to treat pain on the left side of the neck
Most often, treatment is needed in the presence of pathologies of the musculoskeletal system in the cervical region. Treatment of pain may include the use of lidocaine and novocaine, injections of which are otherwise called “blockade”. This is necessary when the pain intensifies to unbearable. In other cases, various medications, physiotherapy and medical procedures are prescribed that relieve pain and inflammation and are selected individually.
Medicines
A nagging pain on the left side of the neck requires timely treatment, since otherwise the state of health will only worsen. Most likely, for pathologies of the structures of the musculoskeletal system, you will be prescribed:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which should reduce pain and stop inflammation;
- muscle relaxants to relieve muscle spasms;
- chondroprotectors that will stop degenerative processes in the joints;
- drugs to normalize blood circulation;
- Antidepressants, which will reduce anxiety and nervousness, will create a favorable basis for treatment.
Sometimes, when shooting pain appears on the left side of the neck, you need to use hormonal medications, as well as warming ointments that are applied to the collar area. If you have pain in the neck, do not delay visiting a specialist, make an appointment with a doctor.