Use of anesthesia during abortion
Nowadays, memories sound like a terrible fairy tale that in the Soviet Union, in most cases, abortions were carried out with purely symbolic anesthesia.
Today, one of the tasks of a doctor performing such an operation is to select a high-quality and effective anesthesia, such that the woman feels a minimum of pain. It is selected depending on many parameters. First of all, the type of termination of pregnancy, duration, state of health of the woman, individual contraindications and intolerance to certain drugs are taken into account.
In most cases, one of three types of pain relief is used:
- general anesthesia,
- sedation,
- local anesthesia.
Is lidocaine dangerous during pregnancy?
According to the instructions for the drug, Lidocaine is contraindicated for use while waiting for the baby. However, cases where this drug was used for anesthesia in pregnant women are not so rare. Is the medication really suitable for use during pregnancy?
Lidocaine during early pregnancy
The first trimester of gestation (before the 12th week of pregnancy) is the most dangerous in terms of the use of any medications. The child’s body is just beginning to develop, so chemical compounds can cause irreparable harm to it. The most dangerous period is from 2 to 8 weeks of gestation, because the drug can have a teratogenic effect (provoke deformities, as well as dysfunction of organs and systems). Another danger lies in the threat of increased uterine tone. As a result, there is a threat of spontaneous pregnancy loss. Therefore, the use of lidocaine in the first trimester of pregnancy is strictly prohibited. The only exceptions may be urgent interventions.
Lidocaine during pregnancy in the second trimester
The second trimester of pregnancy is the safest for many interventions. Regarding the use of medications, restrictions on many of them are also becoming less stringent. This is due to the fact that the baby has already formed by this period, so negative effects on his body are practically excluded. Another factor is a decrease in the uterine sensitivity to external influences. The most common reason for using lidocaine during this period is the need for dental intervention. The severe pain that a pregnant woman may experience during treatment or tooth extraction can cause much more harm to the pregnancy than the anesthesia administered. During this period, it is also recommended to carry out other planned interventions, the duration of which does not allow the end of pregnancy.
Lidocaine during pregnancy in the third trimester
The final weeks of waiting for the baby again call into question the possibility of using Lidocaine. During this period, the woman’s body experiences maximum physiological stress. The result of using the drug may be premature onset of labor. At the same time, it is worth taking into account a possible reaction to the drug from the woman’s body - a drop in blood pressure and oxygen starvation of the expectant mother can lead to a slowdown in the baby’s heartbeat and asphyxia. The doctor must constantly monitor the woman’s condition and respond to the slightest changes. If the problem can be postponed for a while, it is better to return to it after the birth of the baby (especially if we are talking not about health, but about aesthetic beauty).
Lidocaine for toothache during pregnancy
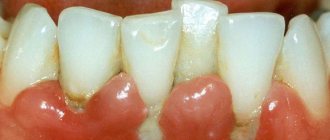
Oral health is difficult to underestimate. The pain that occurs at the site of inflammation causes significant discomfort to the woman. No less dangerous is the infection that has accumulated in the affected area. In this case, you should under no circumstances hesitate to contact the dentist. Even if a woman does not experience acute pain, it is strongly recommended to visit a doctor if she has the following conditions:
- Periodically occurring or constant pain in the teeth (even of mild intensity).
- Bleeding gums.
- Increased sensitivity of teeth, manifested in pain when eating hot or cold food (or drinks).
A timely consultation with a dentist will help you adjust your oral care, thereby preventing the need for more radical intervention, incl. and with the use of anesthesia. During pregnancy the following treatment is allowed:
- Caries (resolution of hard dental tissues).
- Stomatitis (inflammation of the mucous tissue lining the oral cavity).
- Gingivitis (inflammation of the marginal surface of the gum).
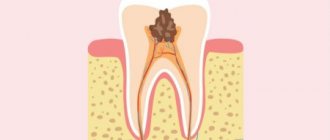
- Pulpitis (inflammation of the internal tissues of the tooth).
Tooth extraction is allowed only if the latter are painful. An exception is wisdom teeth, because... their extraction is often accompanied by a complicated recovery period. So that tooth pain does not come as a shock and surprise to you, be sure to sanitize your oral cavity at the stage of pregnancy planning.
In dental practice, when treating pregnant patients, Lidocaine is used (if the doctor chose this drug) in the form of a spray (from 1 to 3 doses), as well as in the form of injections. It is worth considering that the area that needs to be numbed with the spray should be small, and the anesthesia time will last about 5 minutes. The medicine can be used no earlier than 16 weeks of gestation. The use of lidocaine during pregnancy for dental treatment in the form of “conduction” anesthesia is strictly not recommended. The dose of the drug is calculated based on the body weight of the pregnant woman. The maximum permissible dosage for an adult is 4.5 mg/kg.
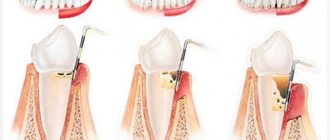
Procedure for tooth extraction:
- anesthesia;
- detachment of the gums from the dental crown;
- grasping the crown with special forceps;
- gentle movements back and forth to loosen;
- removal of the lower or upper tooth;
- treatment of the wound, suturing if necessary.
After the operation, it is necessary to monitor the patient’s condition for at least half an hour - periodically check blood pressure and pulse rate. Then give the necessary recommendations and release. It is advisable that she does not drive on this day, and that she has someone accompanying her.
If the tooth is open, removal may be avoided. Prescribe rinsing with solutions to liquefy and remove pus. If the channels are more or less passable, this can help relieve pain for a while. The pain occurs due to the pressure formed by the pus due to inflammation on the surrounding tissue. Once the outflow is created, the pain will subside almost immediately.
But, as mentioned above, only a doctor, after carefully weighing all factors, decides to remove or postpone. Therefore, in any case, you need to contact a specialist. If you take any independent actions, they can worsen the situation even further. It is better not to take risks due to fear of visiting the dentist.
How does lidocaine affect pregnancy and the fetus?
Lidocaine cannot be considered an absolutely safe drug, but panic after a single use of the drug (not earlier than the second trimester) should not be caused either. The main concerns associated with the use of Lidocaine are based on its ability to easily penetrate the placental barrier, and therefore into the baby’s body.
- The use of anesthesia in the first weeks of pregnancy can cause congenital deformities. The use of lidocaine even externally during early pregnancy is strictly not recommended.
- At later stages, it is necessary to be extremely careful if there is a tendency to arterial hypotension. A dangerous decrease in a woman’s blood pressure can lead to oxygen starvation of the baby.
- Exceeding the permissible dosage can lead to the development of bradycardia in a child.
- Using the product after 28 weeks of gestation may cause premature birth. In the last months of pregnancy, a woman’s abdominal organs experience maximum pressure from the uterus, and blood flow may be disrupted. Pressure in the epigastric area often provokes tightness of the thoracic region, and the pregnant woman may experience shortness of breath. The use of Lidocaine can cause difficulty breathing, decreased blood pressure, and muscle spasms. The listed phenomena can seriously disrupt the course of pregnancy and lead to its completion ahead of schedule.
Is it possible for pregnant women to have x-rays and anesthesia?
When treating pregnant women, only local anesthesia is allowed. Modern drugs for such anesthesia are effective and safe for health. But during pregnancy, the choice of anesthetic and calculation of its dose is performed individually for each woman, depending on her age and stage of pregnancy. The issue of the admissibility of radiography for diagnostic purposes in pregnant women is still debated in the medical community. The latest generation of X-ray machines have a minimal radiation dose, but gynecologists still advise refraining from such examination at least in the first trimester. Computer diagnostics for pregnant women is allowed at any stage.
Please note: the “Smile” chain of clinics is equipped with innovative radiographic and computer equipment for high-precision diagnostics. The minimal dose of radiation allows even pregnant women to be examined.
Contraindications to the use of Lidocaine (spray, injection) during pregnancy
Before using any drug, the doctor should check with the woman for possible contraindications. For Lidocaine, this list is as follows:
- Individual hypersensitivity reaction.
- Low blood pressure.
- Pathologies of the liver and/or kidneys.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Lidocaine during pregnancy - reviews of the drug
Despite the restrictions on the use of Lidocaine during pregnancy, many doctors still use this drug for anesthesia during various medical procedures. The experience of most women who have already given birth is based on a single administration of the drug. No negative phenomena were noted, the children were born on time and without developmental deviations. A number of women noted that the drug was prescribed as part of an antibacterial “cocktail” in the second half of pregnancy. There were also no significant negative consequences noted.
To summarize, it is worth noting that despite the warnings of the drug manufacturers, the drug still finds use in such a category of patients as pregnant women. It is difficult to answer for sure whether Lidocaine is harmful during pregnancy. While there are potential risks from exposure of the drug to the baby in the womb, there is no statistical data regarding a higher number of complicated pregnancies after a single use of Lidocaine. The drug is a drug of last resort, so you should not use it unless absolutely necessary, especially since the modern pharmaceutical market can offer safer alternatives (for example, Ultracaine).
Introduction
Migraine is a common primary form of headache (TH), which manifests itself in the form of repeated attacks, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, photo- and phonophobia.
The prevalence of migraine, according to various estimates, ranges from 2.6% to 21.7%, and the average rate is 14.7% [1]. In Russia, the prevalence of migraine reaches 20.8%, which is approximately more than 30 million people [2]. The prevalence of migraine in women is more than 2 times higher than that in men, and the highest prevalence of migraine within the female population occurs during reproductive age [3]. For this reason, issues of tactics for managing patients with migraine during pregnancy are of high relevance. Issues of pregnancy planning, as well as rules for taking medications for pain relief and approaches to preventive treatment of migraine during pregnancy are discussed very often.
Purpose of Kamistad gel
Dentists recommend using Kamistad for diseases such as:
- stomatitis of any etiology;
- gingivitis;
- cheilitis (inflammation of the lips);
- erythema of the lips.
Dental gel can also be used in the following cases:
- in case of injury to the oral mucosa (from the use of dentures, after operations);
- with irritation from wearing braces;
- during teething
;
- during orthodontic and dental procedures.
Kamistad gel is an immediate local anesthesia; the drug effectively eliminates inflammation, regenerating the tissue of the lips and oral mucosa.
Comparison with other drugs
The properties of the drug “Kalgel” are very similar to Kamistad; it also contains lidocaine and a chemical antiseptic. The only difference between the Kalgel gel is that its anesthetic effect is weaker and can only be used by children from 5 months. However, “Kalgel” can be used even for ulcerative stomatitis; it also provokes less salivation, which is very good if it is necessary to numb the teeth of a one-year-old baby.
Cholisal gel has a wider spectrum of action than Kamistad, it relieves pain, relieves inflammation, and destroys pathogenic microorganisms. However, the anise oil included in the composition provokes strong salivation, so it is not recommended for use in infancy.
The article was written by a dentist with 12 years of experience!
Why is this composition so good?
The gel quickly relieves pain and effectively relieves inflammation due to the content of antiseptics and anesthetics in the composition. Chamomile extract acts as an antiseptic, which has an anti-inflammatory and healing effect. Anesthetics (lidocaine and polidocanol) relieve itching, cool, soothe the mucous membrane, and also block pain impulses from the first seconds of applying the gel.
special instructions
What do dentists recommend to their patients when they prescribe Kamistad?
Before use, you should always wash your hands thoroughly to avoid introducing infection into the oral cavity. Under no circumstances should the gel get into your eyes.
Benzalkonium chloride (antiseptic), which is part of the gel, can cause the formation of black pigment plaque on tooth enamel. Chromatogenic staining of enamel is a temporary and non-hazardous defect, but it does not go away on its own and must be removed in the dental office with professional teeth cleaning.
.