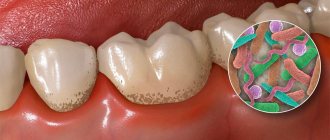
Recession represents pathological changes, loss of tissue. As a result of gum recession, the neck and parts of the tooth root are exposed, and the problem causes not only aesthetic discomfort.
In addition to the fact that receding gums spoil the beauty of a smile, many patients note serious discomfort when chewing, increased sensitivity and some pain in the area of the affected teeth. As a result, the disease affects the quality of life. In addition, prolapse can be a symptom of other periodontal diseases and related ailments, inattention to which can be fraught with even more serious consequences.
This disease can occur in people of all ages, but mature and elderly patients are more susceptible to it. It is important to recognize recession in a timely manner and consult a doctor for effective treatment; fortunately, modern methods in many cases allow you to forget about the pathology for a long time.
Recession classification
Receding gums are classified according to their causes into the following types:
- Traumatic - appears as a result of mechanical damage to the mucous membranes. As a rule, the injury is associated with a hard toothbrush and improper brushing technique, which leads to systematic damage. Other common causes of injury include incorrectly installed orthopedic structures - veneers, crowns, etc. Sometimes injury is associated with protruding edges of fillings and elements of braces. It is important to understand that bite defects are also a common cause of recessions: improper distribution of chewing load leads to changes in tissues. Injuries can also be associated with direct pressure on the gums of the teeth. And finally, another group of injuries includes burns, for example, those associated with unsuccessful home bleaching.
- Symptomatic - in this case, the prolapse is associated with some pathological process and serves as its symptom. Usually we are talking about diseases of the gums and periodontal tissues: gingivitis, periodontitis or periodontal disease. They affect mucous membranes and soft tissues, disrupting their trophism. The situation is aggravated by dental deposits in the places where the gums adhere to the tooth; as a result, the tissue simply peels off from the surface of the tooth and the tissue level drops. More rare pathologies manifested by gum recession include other diseases, for example, diabetes mellitus, leukemia.
- Physiological - it develops as a result of a general metabolic disorder, including metabolic disorders in periodontal tissues. In this case, we are talking about the natural processes of aging. However, sometimes receding gums develop at a young age due to the individual structural characteristics of the dental system. The most striking example is a shortened labial frenulum, which leads to tissue tension.
Based on the severity of a recession, it is also classified into three categories:
- light: tissue loss up to 3 mm;
- average: 3−5 mm;
- heavy: more than 6 mm.
Based on the localization of the pathological process, recessions are divided into localized and generalized. In the first case, receding gums are associated with trauma and spread to one or more closely spaced teeth. As a rule, the outer side of the teeth is affected, and the defect is noticeable when smiling.
In the generalized form, the pathology covers the entire dentition on one or both sides. It is more often observed in elderly patients, as well as in people with periodontitis and periodontal disease.
Ask a Question
Why does a recession occur?
The development of a recession can be due to a variety of reasons:
- Plaque and hard deposits. As a result of the formation of deposits, the gum epithelium is displaced.
- Specific structure of the alveolar process of teeth. Sometimes, in the presence of a massive root system, thinning of the layer of cortical bone tissue occurs. This leads to insufficient blood supply to the tissues, the formation of a gap-like defect between the tooth and the gum, and receding gums.
- Improper oral care. Brushing your teeth can damage your gums. This occurs when choosing too hard bristles or improper brushing techniques. With regular damage, the condition worsens, leading to gum recession.
- Injuries. For example, a dislocated tooth.
- Orthodontic treatment. It involves putting pressure on the dentition, displacing the teeth, which in some cases can lead to thinning of the gum tissue. In addition, non-removable structures make hygiene difficult and can directly put pressure on soft tissues.
- Exposure to arsenic. The use of arsenic pastes during endodontic treatment can cause gum loss if the drug gets on the gums.
- Gingivitis or periodontitis. Inflammatory diseases of the gums and periodontal tissues, especially those that last for a long time.
- Short frenulum of the lips.
It should be noted that there are predisposing factors that, in combination with other causes, are most likely to lead to periodontal prolapse. These include a thin gum biotype, as well as the vestibular location of the teeth or anomalies in their position, close attachment of the frenulum of the lips and tongue.
By themselves, these features do not always lead to pathology, but they increase the likelihood of recession, for example, when exposed to bacteria and viruses, injuries, etc.
Why can a tooth hurt due to gum problems?
Picture of the process: an area of inflamed gum appears in the interdental spaces due to the fact that the contacts between the teeth are not very correct and food between the teeth slips onto the gum, injuring the gum. As a result, a pathological periodontal pocket is formed. Food gets stuck under the gum and penetrates close to the unprotected tooth root. The tooth begins to react to sweets and sours. And even if you clean the area under the gum from food debris, the pain may persist because the gum itself hurts. Patients often confuse that their gums or teeth hurt.
Dentists say in such cases that the contact points between the teeth are broken.
Symptoms of receding gums
The condition in which the gums recede may be accompanied by other symptoms. Depending on the extent of the pathological process, recession is observed in a limited area, one side or the entire jaw. As a result, the neck of the tooth may be exposed, and with severe loss, part of the root.
This cannot but be accompanied by increased sensitivity of the teeth - increased susceptibility to hot and cold, sour, sweet foods and even mechanical stress. This symptom leads to difficulties while eating.
It is important to understand that some symptoms may indicate concomitant pathologies. So, if recession is observed against the background of whitish, pale gums, we can talk about periodontal disease. Bleeding and red gums often develop with periodontitis and gingivitis.
What will happen if left untreated?
Lack of timely treatment for gum recession can be fraught with more than just aesthetic problems. If there is a gap between the gum and the tooth, food debris and plaque get into it, and this can cause an inflammatory process. As the tissues become thinner and sagging, the following consequences of recession may appear:
- Hyperesthesia, or increased tooth sensitivity, difficulty chewing.
- High risks of caries development, and in the least protected and more vulnerable areas - in the area of the exposed necks of the teeth. At the same time, carious lesions in this area proceed faster and are more quickly complicated by pulpitis and periodontitis due to a thinner layer of enamel.
- Increased risk of developing a non-carious lesion - a wedge-shaped defect.
- High risks of inflammation, swelling of the gums, and the formation of periodontal pockets.
- An increase in the amount of plaque at the roots, which further aggravates the condition.
Complications can result in serious consequences such as loosening and loss of teeth.
Diagnostic methods
If the gum is moving away from the tooth, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible: in the early stages, recession is faster and easier to treat. Diagnosis involves collecting anamnesis, analysis of symptoms and complaints, examination and instrumental examination if necessary. During the examination, the doctor will assess the width and nature of the gum damage. A periodontal probe can be used for diagnosis - it is inserted into the periodontal pocket to assess the depth of the lesion.
An assessment of the degree of gum damage is calculated by calculating the recession index using the following formula: the number of affected teeth is divided by the total number of teeth and multiplied by 100%. This is how the severity of the disease is determined: less than 25% is a mild recession, 26-50% is moderate, and from 50% is severe.
For diagnostics, a microscope is used, and binocular magnifying glasses are used. The thoroughness of diagnostic measures allows you to accurately select an effective treatment method. In addition, before starting treatment, it is very important to find out the causes of the disease: to determine whether recession is an independent disease or a symptom of another pathology.
Therefore, differential diagnosis with other periodontal diseases in which the gums rise is necessary. To do this, the doctor may prescribe a targeted or panoramic X-ray to assess the condition of bone tissue and detect hidden concomitant diseases.
Associated symptoms
The clinical picture depends on the degree of periodontitis. In mild forms of the disease, the gums do not move, but bleed and are bright red. Signs of progressive pathology are:
- bad breath,
- severe pain,
- tooth mobility,
- swelling and swelling of soft tissues,
- receding and receding gums,
- increased sensitivity of enamel,
- formation of periodontal pockets,
- accumulation of pus between the gum and crown.
If the gum has moved away from the tooth, treatment must be carried out immediately. The problem cannot be ignored, since displacement of the gingival margin increases the risk of infection of the jaw bone tissue, periostitis and other complications. If you don't see a doctor in time, you can lose your teeth.
Features of treatment of gum recession
There are conservative and surgical methods, with the help of which it is possible to cope with the problem relatively quickly. The development of a treatment program is always individual and takes into account the severity, causes of prolapse, prevalence of pathology and other conditions.
The first step is always professional teeth cleaning. It is necessary to remove soft and hard dental plaque. Sometimes subgingival tartar is removed, which already makes it possible to reduce the depth of periodontal pockets, and in combination with other methods, cope with the problem completely or achieve a significant improvement.
Drug treatment can solve several problems at once:
- eliminate or prevent gum inflammation;
- strengthen gums;
- improve blood circulation;
- speed up recovery processes;
- activate the growth of mucosal cells and gum tissue.
For this, vitamin therapy, anti-inflammatory drugs and local antibiotics, self-absorbing membranes, etc. can be used. The doctor may prescribe medicinal baths, rinsing with certain solutions or application of drugs to the gums, including at home.
Preparations that activate recovery processes are also widely used: products based on hyaluronic acid, regenerating gels with growth factors. The launch of natural regeneration processes allows you to literally “grow” the gum in the place where it subsides.
Another conservative method is the use of the patient's own blood plasma enriched with platelets. This method is called plasma lifting, or APRF technology. Injections into the gums can be used, as well as special membranes that are placed under the gums, but as part of a surgical intervention. This allows you to quickly restore tissue and improve cell nutrition.
As for other surgical treatments for receding gums, the most common are:
- Flap surgery - gum recession is closed with a gum flap, which the doctor takes from the patient's own tissue located nearby. Intervention is performed when the gum defect is minor and there is a sufficient amount of surrounding tissue that can be used.
- Transplantation of a graft from the hard palate/tuberculum of the upper jaw. In this case, part of the gum or a flap of connective tissue is taken from the donor sites and planted in the defect area. Can be used for all types of recession.
- Combined method: the movement of gum tissue is combined with the collection of tissue from the hard palate. The combination of approaches makes it possible to obtain high aesthetic results and close deep recessions. However, if gum loss is more than 5 mm, multiple interventions may be required.
Closure of gum recession is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. The choice of type of operation is determined by the condition of periodontal tissues and diagnostic results. All surgical methods are often combined with curettage - cleaning the space under the gum and removing subgingival deposits, and are also supplemented with growth activators.
The gum has moved away from the tooth: treatment
If the gum has moved away from the tooth, treatment will largely depend on the severity of the inflammation. For example, if a patient seeks help at a fairly early stage of inflammation (when the depth of periodontal pockets does not yet reach 3 mm and there is no tooth mobility), significant success can be achieved in the treatment of periodontitis and the process can be completely stopped. Advanced cases of gum inflammation will require much more complex treatment and serious financial costs. Next we list the main stages of treatment.
1) Consultation and x-ray diagnostics –
It is necessary to begin treatment with a consultation with a periodontist and a panoramic photograph of the teeth, which will allow you to create an optimal treatment plan taking into account the condition of your teeth and gums. The image will allow you to determine the amount of destruction of bone tissue around each tooth, the location and depth of periodontal pockets, and will help guide the patient in the need for splinting of mobile teeth, the need for prosthetic replacement of missing teeth, and make the correct diagnosis.
An example of a panoramic image of a patient with periodontitis –
Looking closely at the image, you may notice that the level of bone tissue (the bone looks in the image as fine-mesh looped tissue and normally should reach the necks of the teeth) is reduced in different teeth by 1/4 to 4/5 of the length of their roots. The patient has decayed teeth that need to be removed, as well as carious teeth that require treatment (24stoma.ru). The level of bone tissue is most reduced in the front teeth of the upper and lower jaw, which in this case was the result of not only inflammation of the gums, but also the absence of the chewing group of teeth.
To treat gums, it is best to contact not ordinary dental therapists or hygienists, but periodontists. These are the dentists who specialize in gum treatment. The first and most important stage of treatment will be ultrasonic teeth cleaning. Next, a course of anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out, which in most cases can be successfully carried out at home.
2) Removal of dental plaque –
First of all, it is necessary to remove the cause of inflammation - microbial plaque and dental deposits. They are removed from the teeth using an ultrasonic scaler (Fig. 15), usually over several visits. It is simply impossible to remove all dental deposits in just 1 visit in a patient with periodontitis, because... It takes a lot of time to remove subgingival dental plaque, which is localized in periodontal pockets below the gum level.
It is subgingival dental plaque that poses the main danger for further progression of inflammation, so sometimes it is necessary to prescribe the patient even 3-5 times. Learn that without professional cleaning, all other stages (for example, anti-inflammatory therapy, splinting) will be completely meaningless.
Most dentists and hygienists won't bother with finding and removing subgingival calculus...as experience has shown. Therefore, it is very important to find a competent specialist. Anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed immediately after 1 session of removing tartar, and within the first 24 hours you will be able to notice changes in the appearance of the gums. In parallel with the reduction in gum swelling, their volume will also decrease, which will allow you to see new portions of dental plaque and remove them during subsequent visits.
Removing dental plaque with ultrasound: video
You can see in the following photos what happens when subgingival tartar is removed poorly. The first photograph shows that the gums are visually in good condition, although a periodontal probe revealed the presence of a periodontal pocket about 5 mm deep. The second photograph was taken after the gums were detached from the teeth, and it shows a very large amount of destruction of bone tissue, which arose due to the presence of small subgingival tartar on the surface of the tooth root.
3) Anti-inflammatory therapy –
The course of anti-inflammatory therapy usually lasts 10 days. In most cases, it is carried out by the patient himself at home, after doctor’s prescriptions and patient education. However, if the patient has deep periodontal pockets with purulent discharge, the doctor may additionally prescribe washing the periodontal pockets, which is done using a syringe and antiseptic solutions. In some cases, antibiotic therapy may also be prescribed for periodontitis.
Anti-inflammatory treatment regimen - usually a complex is prescribed, consisting of an antiseptic mouth rinse and application of gel to the gums. The procedures are carried out 2 times a day (morning and evening, after meals and subsequent oral hygiene), for 10 days. Most often, a complex of the following drugs is prescribed:
- rinsing with Chlorhexidine (instructions)
- “Cholisal-gel” applications (instructions)
In patients with periodontitis, the correct choice of treatment agents is very important. For example, a standard 0.05% solution of chlorhexidine, sold in pharmacies for 40 rubles, is advisable to use only for superficial inflammation of the gums (gingivitis), but for periodontitis it is better to use a 0.2-0.25% concentration of this antiseptic. It is a big plus when such a solution contains not only a good concentration of chlorhexidine, but also other active ingredients (for example, aluminum lactate for bleeding gums or extracts of medicinal plants).
Antiseptic mouth rinse is carried out after breakfast and oral hygiene, rinse your mouth for 1 minute. After this, the gums need to be dried with a dry gauze pad to remove excess saliva, and an anti-inflammatory gel should be applied to the gum edge. The gel is applied in front of a mirror using a finger, and usually only on the front side of the teeth. After such treatment, it is not recommended to eat for 2-3 hours, and also not to drink for 30 minutes. There are a lot of remedies for treating gums, and we hope that our next articles will help you understand their diversity -
→ The best antiseptics for mouth rinsing, → Rating of the best gels for treating gums.
4) Oral hygiene training –
If you have not yet forgotten the beginning of the article, then remember that the cause of periodontitis and destruction of the dental-gingival attachment is unsatisfactory oral hygiene, which leads to the accumulation of microbial plaque and tartar on the teeth. Therefore, in addition to the basic treatment that we described above, it is very important to constantly maintain high-quality oral hygiene.
Good hygiene doesn't mean just brushing your teeth twice a day, that's not enough. Good oral hygiene includes brushing your teeth after every meal, not snacking on cookies or candy between meals, and regularly using dental floss. You can read about absolutely all the recommendations in the article at the link above. Below, you can watch the video on how to properly use a toothbrush and dental floss.
How to use dental floss and brush correctly -
In the presence of periodontal pockets and mobile gingival margins, it is important to carry out hygiene below the gum level. This can be done using special devices - home irrigators. Special attachments allow you to rinse at home not only areas of the oral cavity that are difficult to reach for hygiene, but also periodontal pockets below the level of the gingival margin. Irrigators can use both ordinary boiled water and special medicinal solutions.
Home care and postoperative period
After treating gum recession, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics, rinses, topical gels, and other topical treatments to prevent complications and speed up the healing process. It is also important to prefer gentle, soft food at a comfortable temperature, and perform regular hygiene according to the recommendations of a specialist.
The dentist will recommend replacing your hard toothbrush with a soft one, and as healing progresses, you will likely need a toothbrush with medium-hard bristles. In addition, the doctor will definitely show the correct cleaning movements and tell you what pressure will be optimal. In many cases, such measures are sufficient to eliminate the causes of exposed tooth necks, as well as maintain treatment results.
Prevention of receding gums
To prevent gum recession, your doctor may recommend the following measures:
- Timely, regular visits to the dentist: it is important not only to undergo an examination, but also to carry out professional hygiene twice a year. This will prevent the accumulation of plaque and the formation of hard deposits.
- Timely correction of bite, treatment of inflammatory gum diseases, replacement of fillings, careful selection of orthopedic structures.
- Individual selection of oral hygiene products, especially in the presence of periodontal tissue diseases.
- Using dental floss and irrigator. It will not only improve the quality of hygiene and help remove food particles from the interdental spaces, but will also serve as a kind of gum massager, stimulate blood circulation and maintain the health of the mucous membranes. It is important to consult a doctor about the advisability of use, however, modern irrigators provide mild modes of exposure.
- Avoiding mucosal injuries: avoiding uncomfortable orthopedic structures, using special wax when wearing braces.
- Quitting smoking: this bad habit impairs the blood supply to the tissues of the oral cavity and contributes to the formation of a large amount of plaque on the teeth.
You can learn more about treatment and prevention, as well as get quality help if you have gum recession, from the doctors at the STOMA clinics. Experienced periodontists are highly qualified and have a whole arsenal of modern treatment methods: we are ready to offer comprehensive assistance in diagnosis and treatment. You can make an appointment by phone or through a special form on the website.
HOW TO STOP GUM RECESSION?
If you suspect you have gum recession, contact your dentist for an examination and appropriate treatment.
There are various treatment options for gum recession:
Cleaning and polishing the surface of tooth roots
If you have gum recession, your dentist may recommend a procedure to clean and plan the surface of the roots of your teeth. This procedure consists of two stages and is carried out by a dentist. In the first stage, the doctor removes plaque and tartar in the area of the gum line (above and below it). Then the surface of the tooth roots is polished, so that the gums can “attach” to the teeth again. Treatment may be performed under local anesthesia and may require several visits.
The procedure for cleaning and polishing the surface of the roots of teeth is quite effective. After this, you will need to visit your dentist regularly. He will check the condition of your gums and will be able to spot possible problems in time. To protect your gums, be sure to practice good oral hygiene.
Gum operations
For more severe cases of gum recession, your dentist may recommend surgical procedures. These include the following:
- Gum flap surgery: If non-surgical treatments have not been effective, your dentist may suggest flap surgery. During this operation, incisions are made on the damaged gum, then the resulting flap is raised, allowing access to the roots of the tooth. They are cleaned and polished. After this, the gum is reattached to the surface of the tooth.
- Regeneration: This surgical procedure helps regenerate damaged jaw and gum tissue. First, the area above and below the gum line is cleaned to remove bacteria and plaque. A material that stimulates tissue regeneration—a membrane, a tissue-stimulating protein, or a graft—is then attached. This triggers bone and tissue growth in the damaged area. The gum is then securely attached to the root of the tooth.
Gum transplantation
If you have lost gum tissue, your dentist may recommend a gum tissue graft. A section of gum is taken from the upper palate and sewn to the damaged area of the gum so that it covers the roots of the tooth.