- Classic comprehensive hygiene in 3 stages (ultrasound + air-flo + polishing) - 3,500 - 4,600 rub
- Periodontal cleaning of one segment (light) - 2,600 rub.
- Periodontal cleaning of one segment (medium degree) - 3,000 rub.
- Periodontal cleaning of one segment (severe) - 4,000 rub.
- Periodontal cleaning in the area of one tooth - 580 rub.
- Removal of a periodontal tooth during periodontal cleaning - 650 rub.
- Vektor therapy (Vector therapy) - 1st visit (90 min.) - 8,818 rub
- Vektor therapy (Vector therapy) - repeat visit (90 min.) - 7,334 rub
- Vektor therapy (Vector therapy) -1 tooth (20 min.) — 305 rub
Do your gums hurt? This means that you are developing an inflammatory process in your gums or have a painful tooth. When the cause of pain is in the tooth, the pain is local and does not spread to surrounding tissues. If your gums hurt, the cause may be periodontitis. Thus, the gum itself can be the cause of pain or it can serve as a symptom of another process.
When it comes to gum disease, the pain spreads to all or most of the teeth. This picture is especially characteristic of the development of gingivitis and periodontitis.
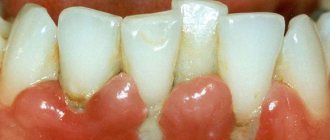
If you notice that the gums around a tooth or several teeth are swollen, red in color and bleeding, then we are most likely talking about gingivitis. If gingivitis is not cured, the process will go further and periodontitis will develop. If it seems to you that the gums near the tooth are swollen, then you need to promptly contact a periodontist for treatment, which must be carried out responsibly, since periodontitis can develop even if periodontitis is not treated well enough.
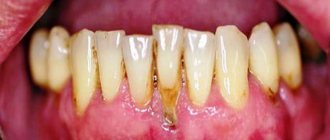
With periodontitis, the symptoms of gingivitis appear in a much more intense form, in addition, periodontal pockets begin to fester, and the necks of the teeth become exposed.
The initial stage of inflammation (gingivitis) - pain is felt in all gums. Further, when inflammation develops into periodontitis, pustules appear on the gums, and the pain intensifies around one/part of the teeth. The localization of the pain is explained by a periodontal abscess in the area of one of the periodontal pockets, in this case you may notice how the gums around a specific tooth are swollen. The main reason for the development of diseases of this nature is poor oral hygiene. The soft plaque covering the teeth tends to harden over time into a dense growth on the teeth, forming tartar. It is in the stone that pathogenic bacteria live comfortably, which provoke inflammatory processes in the gums and the appearance of pain. Therefore, it is necessary to both treat the gums and get rid of stone deposits, as well as eliminate carious areas of the tooth.
Saying goodbye to gum pain
If your gums are sore and swollen, what should you do first? No, don’t use a plot from your mother’s best friend’s neighbor’s great-grandmother. All “spells” for dental problems are in the hands of the dentist, and only he knows how to correctly “spell” gums from pain and bleeding.
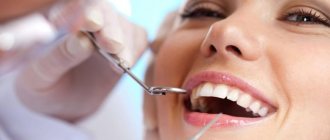
Inflammatory processes occurring in the teeth and gums in the case of periodontitis and gingivitis are provoked, as already mentioned, by bacteria colonizing tartar. So, if you notice that your gums are swollen, what should you do with your right mind? That's right - remove stone deposits from teeth. Unfortunately, no toothbrush can “overpower” tartar plaque, so you need to go to the clinic for professional teeth cleaning. Only when the teeth are cleared of all deposits will therapeutic treatment be prescribed, including antibiotics, if the complexity of the case requires it.
Don’t ask about advanced inflammation: this is only a matter for the dentist. You can treat inflammation yourself only in the initial stages; it includes rinsing the teeth with a chlorhexidine solution and treating with cholisal gel.
The course is usually designed for 10 days. Procedures must be carried out after meals in the morning and evening. Such rinses are quite effective when the case is not advanced.
If your gums hurt not because of mild inflammation, but because of the development of severe and moderate periodontitis, then the treatment process will be different.
Periodontitis is the development of an inflammatory process at the apex of the tooth root, which leads to a periodontal abscess - the formation of a dental cyst - a sac of pus that can burst and leave a fistula opening. Under such circumstances, pain in the gums can be caused by caries or pulpitis. How to treat gums with periodontitis? Treatment in this case will consist of:
- removal of carious areas of dental tissue;
- nerve removal;
- treatment of root canals with medicinal paste and temporary filling;
- removal of stones;
- anti-inflammatory therapy of a general or local nature.
Why does the gum move away from the tooth?
- The use of too hard brushes, incorrectly fitted dentures and high fillings - all this leads to the fact that the gum moves away from the tooth, exposing the neck.
- Another reason is insufficient hygiene procedures, due to which bacteria causing gingivitis spread in the oral cavity. Often the first symptoms of the disease are bleeding, itching, pain when brushing, and bad breath. Ignoring these problems causes the gums to recede from the teeth. Gingivitis, like a number of other periodontal diseases, can be triggered by a general decrease in immunity, a number of chronic diseases, impaired hematopoiesis in the body, a lack of vitamins and endocrine diseases.
- Another common cause is periodontitis. Plaque that accumulates on the surface of the enamel forms tartar. Initially, gingivitis develops, and then pathogenic microflora destroys other periodontal tissues. Smokers have a high predisposition to this disease.
- An incorrect bite can also cause the gum to become inflamed and pull away from the tooth.
- Hormonal changes are also one of the reasons. Periodontal problems may appear during pregnancy, puberty, and other hormonal changes.
- Chronic diseases of the hematopoietic, endocrine system.
- A genetic predisposition is also possible.
My gums hurt and are swollen, what should I do?
If you start to feel pain in your gums, you shouldn’t hope that maybe it will go away on its own; hurry up and see a doctor. It is he who will understand the reason that caused the development of inflammation. Determines the degree of the inflammatory process. Once diagnosed, treatment is very effective and you will soon feel healthy again.
For prevention purposes, we recommend choosing the right brush and toothpaste according to the condition of your teeth and gums. For example, sensitive gums are further damaged by hard bristles, so it is better to choose a brush with soft bristles. It is necessary to practice oral hygiene at least 2 times a day – in the evening and in the morning.
If you follow the recommendations described above, both your teeth and gums will not cause you any discomfort.
Why does the gum between my teeth hurt?
You may need the help of a dentist not only when your teeth hurt, but also if there is pain between your teeth. Gum diseases can cause a lot of trouble, including negatively affecting dental health and the general condition of the body. Therefore, the specialists of the “Dentist and Me” clinic advise that if painful sensations in the gums occur, not to self-medicate, but to go to an appointment with a specialist.
Pain between teeth: causes
There are many reasons why your gums may hurt. Starting from basic non-compliance with hygiene rules and ending with such serious diseases as stomatitis and gingivitis. Let's figure out why the gums between the teeth most often hurt.
- Mechanical damage. If you scratched your gums with food or a toothpick, or injured them during dental procedures, then there is no need to worry. In this case, it is enough to rinse the mouth with antiseptic solutions, observe all the necessary hygiene measures, and the gums will soon heal.
- Gingivitis. One of the most common gum diseases that occurs due to poor cleaning of teeth from plaque is called gingivitis. The accumulated plaque turns into tartar and becomes a source of infection, which causes inflammation and pain in the gums between the teeth. The gums become loose and painful when pressed, and swelling develops. If you have symptoms of incipient gingivitis, you should immediately consult a doctor, who will prescribe the necessary rinses and medications, remove tartar and give further recommendations. Remember that advanced gingivitis can lead to periodontitis, a disease that can lead to tooth loss.
- Stomatitis. If your gums between your teeth not only hurt, but ulcers appear on it and your temperature rises, it’s most likely stomatitis. He must be treated under the supervision of a dentist.
- Periodontitis. Not only gum disease can cause pain, but also problems with the teeth themselves. If a tooth begins to decay inside, for the time being it may not bother you, but gradually such inflammation will begin to affect other tissues, coming out. If you don’t want your tooth to completely decay, you should tell a specialist about the problem and get competent treatment.
- Lack of vitamin C. The exotic word “scurvy” refers to a fairly common disease that occurs due to a lack of vitamin C in the body. Even if you are not a polar explorer, bleeding, loose and painful gums will tell you that you urgently need to make up for the lack of this vitamin and rinse your mouth with a decoction of oak bark.
Make an appointment by calling +7 (8342) 308-088 or using the form below.
Make an appointment
Possible consequences
The most common complications of tooth trauma include gum inflammation. Due to severe mechanical damage, soft tissues become injured and inflamed, which slows down the recovery process. The following negative factors can aggravate the problem:
- decreased immunity,
- lack of vitamins D and group B,
- trauma to the oral mucosa,
- damage to the gums by hard brushes, dental floss or orthodontic appliances.
Inflammation of the gums can be local and generalized. In any case, you should consult a specialist.
Treatment of gum inflammation after tooth trauma
Dentists draw up a treatment plan taking into account the clinical picture, diagnosis and diseases suffered by the patient. To eliminate gum inflammation, experts most often prescribe:
- treatment of soft tissues with anti-inflammatory gels,
- rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions,
- professional teeth cleaning.
If there are signs of a bacterial infection, your doctor may prescribe antibacterial medications. They must be taken strictly as prescribed by a specialist. It is also important to use suitable toothbrushes and other personal hygiene products.
Causes of tooth bruises
According to statistics, closed dental injuries are most often encountered by children, adult men and professional athletes. You can get a serious injury:
- when falling or getting hit in the jaw,
- during an accident,
- in a fight
- in training.
The main causes of mechanical damage also include some bad habits:
- bite your nails,
- bite the threads,
- open bottles with teeth
- crack nuts and seeds,
- hold hard objects in your mouth.
This causes damage to the enamel, increasing the risk of serious tooth injury. Bruises are accompanied by aching pain, unpleasant sensations when closing the jaws and loosening of the injured dental unit.
When to see a doctor?
You need to make an appointment with a dentist if you have the following symptoms:
- redness and bleeding of the gums,
- mild or intense pain,
- suppuration of soft tissues,
- bad breath,
- discomfort when eating and brushing teeth.
The listed signs indicate gum inflammation. There is no need to wait for them to disappear and put off visiting a doctor. Ignoring warning signs can lead to soft tissue infection, increased tooth mobility, and tooth loss.
Possible diseases
Constant pain in the gums is one of the main symptoms of the following oral diseases.
- Gingivitis. Acute or chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane. Develops due to the accumulation of plaque. Soft deposits mineralize and turn into tartar, which cannot be removed with a regular brush. Pain occurs in the gums between the teeth.
- Periodontitis. Periodontal inflammation, in which the dentogingival joints are destroyed. Develops due to advanced gingivitis. The risk group includes patients with a hereditary predisposition to the disease.
- Stomatitis. An inflammatory process accompanied by the formation of blisters or ulcers. They cause burning and pain in the mouth when eating and brushing teeth. Stomatitis can be triggered by injuries, burns, as well as pathogens - herpes simplex virus, Candida fungi.
Treatment of teeth and gums
A dentist can determine why the gums between the teeth hurt based on diagnostic results - a visual examination. The treatment regimen is developed individually for each patient. This may include:
- antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity,
- professional teeth cleaning,
- treatment of periodontal pockets,
- treatment of caries and other diseases.
To prevent the situation from worsening, patients need to follow a diet for several weeks after treatment, use hygiene products and rinses recommended by the doctor, and avoid physical activity and stress.
Treatment of injuries to teeth and gums in children
Has the tooth been hit (bruised, dislocated) or has become loose? Be sure to see a dental surgeon. It doesn’t matter at all that the tooth looks intact. A root may be broken or a nerve damaged. Such a tooth can be saved.- Is a temporary (baby) tooth knocked out? We are not talking about saving it and installing it back. After all, the jaw contains the germ of a permanent tooth and the main thing is not to injure it. It is necessary to close any access of infection to the permanent tooth germ, so a doctor’s examination is necessary.
- The tooth’s growth has not yet finished – is it possible to restore it? Don't believe the myths that immature teeth cannot be restored! Special restoration techniques do not affect the further growth and formation of the tooth. On the contrary, tightness and the absence of infection ensure full growth and formation of the tooth. We have many years of experience of the best domestic and foreign traumatologists, serious and reliable research on our side.
Diagnosis of tooth trauma
Often, one medical examination is not enough to understand how damaged the tooth, its roots, the tissue surrounding the tooth, or the germ of a permanent tooth are, if we are talking about a primary bite. A computed tomography scan or a targeted image of an injured tooth will allow you to make a correct diagnosis in time and begin saving the injured tooth. Medfodent Plus specialists are armed with the best methods for treating dental trauma. Together with you, we will do everything possible to keep the injured tooth healthy!
Gum injury, treatment
The gums are part of the oral mucosa. The gums consist of very delicate and vulnerable tissues, and therefore are often injured, especially in children who, for research purposes, often carry into their mouths any objects that come into their hands.
A child can injure the oral mucosa if he falls, hits a hard object, or hits his own teeth due to injury.
Injury to the oral mucosa can also occur as a result of the child’s bad habits: biting the cheek, the inside and outside of the lips, etc.
Discomfort or pain in the gum area can also occur after treatment, when treatment is carried out in a very inconvenient and hard-to-reach place, or when the tooth is severely damaged and caries is at or even below the level of the gum. In this case, in order to properly treat the tooth, the dentist is forced to push back the gum mucosa and isolate it from the tooth tissue.
The oral mucosa is saturated with blood vessels, and therefore injury may be accompanied by swelling and bleeding. However, as a rule, the mucous membrane heals quickly without serious consequences. Of course, injury to the oral mucosa and gums is a reason for an urgent visit to a pediatric dental clinic. A specialist - a pediatric dentist or a dental surgeon - will assess the severity of the injury, treat the wound surface with disinfectant solutions that will not cause additional harm to the delicate mucous membrane, and also discuss some home procedures: rinsing, treatment with a special dental paste, and, if indicated, oral medications, incl. h. painkillers and inflammation relievers.
Treatment of tooth or gum injury
If a child suffers a tooth injury, it is worth taking him to a pediatric dental clinic as quickly as possible (unless the child requires more urgent care that requires hospitalization). The choice of a clinic in this case should be based on the willingness of the attending physician to work with the injury and save the teeth (tooth) that can be saved. Often an injury requires medical observation for quite a long time, following recommendations such as a gentle diet, rest and immobilization for the injured tooth.