The term “ dead tooth ” is used in dentistry to refer to a tooth whose pulp has been removed or has lost its vitality.
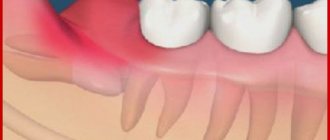
The pulp is loose connective tissue with a huge number of lymphatic, blood vessels and nerves. It is this neurovascular bundle, located in the so-called pulp chamber, that provides nutrition to the tooth, perceives various irritations, stimulates regenerative processes and acts as a biological barrier that prevents pathogenic microscopic organisms from entering the carious cavity into the periodontium.
A tooth with dead pulp quickly becomes brittle, darkens and loses its ability to regenerate.
What is a “dead” tooth?
This is what dentists call a tooth without nerve endings that no longer receives blood. Consequently, the tooth stops receiving nutrients and its work stops, the tooth dies. The disruption of blood supply is explained by damage to the pulp, the area where blood vessels and nerve endings gather into a single bundle. If the vessels and nerves do not function, then the nutrients no longer support the life of the tooth.
Method of treatment
The use of analgesics numbs the pain, but when a dead tooth appears, a trip to the dentist is inevitable. Doctors will take therapeutic measures:
- remove the remains of decomposed pulp;
- root canals are filled with gutta-percha;
- restore the front part of the tooth with a filling or crown
Restoration of the coronal part is carried out using a filling, or a filling on a pin, in case of a large volume of lost tooth tissue. If the filling is ineffective, the doctor will install a crown or inlay.
The indication for pulp removal is its extensive inflammation, which threatens decomposition processes and further development of infection.
Is it possible to cure such a tooth?
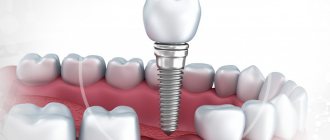
You can cure, but you cannot resurrect. The dentist will remove all affected tissues, nerves, root canals, expand them, clean them and treat them with an antiseptic, and then seal them hermetically so that infection does not enter from outside. The crown, if more than half of it is preserved, will be restored with a filling. For more severe lesions, an artificial crown will be installed. However, in case of extensive inflammation, the tooth can be removed and replaced with a prosthesis - an implant.
A “dead” tooth must be shown to a doctor, otherwise there is a risk of complications from the infection, which will develop into gumboil, osteomyelitis. A cured tooth can perform its function fully, but it can withstand the load worse, so its service life is significantly lower than that of “living” teeth.
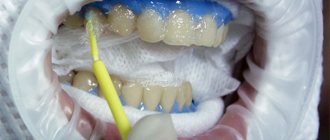
Removing the pulp of the affected tooth
Pulp removal is a complex dental procedure that requires a highly qualified doctor.
Stage 1 – local anesthesia or general anesthesia
At the first stage of treatment, local anesthesia is administered in the area of the affected tooth. In exceptional cases, the patient may require general anesthesia. The use of anesthetics allows one to avoid preliminary killing of the nerve with arsenic.
Stage 2 – x-ray
At the next stage, the doctor conducts an X-ray examination to determine the length of the root canals.
Stage 3 – pulp removal and tooth filling
All video presentations
After reviewing the x-rays, the dentist:
- gently removes pulp,
- cleans, rinses with antiseptic preparations and fills root canals,
- and then restores the natural anatomical shape of the tooth.
If all procedures are carried out competently, and the patient carefully and impeccably observes personal hygiene, then the service life of a pulpless tooth can reach several decades.
Severe toothache is a consequence of unprofessional dentists
Evidence that the dental operation was performed incorrectly is a sharp toothache accompanied by an increase in temperature. If depulpation is of poor quality, the patient may need repeated surgery. At the same time, aching, mild pain after removal of the dental nerve is considered normal.
External difference
Doctors note that a tooth devoid of pulp can often be recognized by external signs. For example, immediately after living tissue has been removed from it, it may acquire a grayish tint, which will become darker over time. In addition, such a tooth stops reacting to cold and hot. One of the disadvantages is the fact that, even if such a tooth is damaged by caries, a person may not feel the destructive processes in a timely manner, since due to the lack of nerve endings he simply will not feel pain. Such a tooth, in addition, over time begins to gradually deteriorate and crumble.
Teeth guarantee. Why is it important to read a contract in dentistry? More details
For chronic and acute inflammatory processes
In most cases, tooth extraction is accompanied by acute or chronic periodontitis, inflammation of the gum tissue, or even the formation of purulent foci. If such a process covers a large area of tissue and is accompanied by high temperature, the formation of fistulas and edema, then most likely the attending physician will prescribe enhanced antibacterial therapy to slightly reduce the severity of inflammation. And only after this will surgery be performed in the oral cavity. On the other hand, there may be a need for immediate surgical intervention if the surgeon considers such intervention urgent. There can be many criteria for this choice, and only an experienced doctor can make an adequate decision.
For what indications is it necessary to extract a tooth?
For complex tooth extractions, the dentist uses stronger painkillers, special instruments, and in some cases, it is necessary to use purely surgical methods of cutting the gum tissue and applying sutures. Of course, such manipulations require special indications, which are identified during X-ray examination and based on the general clinical picture. The need for removal occurs when:
- incorrect inclination of a growing tooth (wisdom);
- severe inflammatory process in tissues, which poses a threat to the patient’s health (abscess, phlegmon, osteomyelitis, etc.);
- the need for prosthetics;
- maxillofacial injury that cannot be treated due to the interference of hard tissues.
If some of these indications apply to you, then it makes sense to seek out a highly qualified oral surgeon. The fact is that complex tooth extraction requires the doctor to have many years of practice and extensive knowledge in this area. The network of dental clinics “LeaderStom” is known not only for its latest equipment, but also for its experienced doctors who cope with the most complex diseases.
What causes a tooth to die?
Trauma or damage to a tooth is one of the possible causes of tooth death. For example, putting something dangerous in your mouth that can cause the death of your tooth. The tooth can die quickly, over a few days, or slowly, over a period of months or years.
A tooth can also die as a result of poor oral hygiene. This can lead to cavities which, if left untreated, can slowly destroy your tooth. Cavities start with the enamel, which is the outer protective layer of your tooth. If left untreated, they can slowly eat away at the enamel and eventually reach the pulp. This leads to contamination of the cellulose, which separates the blood from the pulp and eventually causes it to die. You will likely experience severe pain as the decay reaches the cellulose.
A dead tooth can be identified during a routine dental examination, which includes an x-ray. You should always see your doctor after any tooth injury or if you have signs of a dying tooth. This way, your dentist can begin treating the tooth as soon .
Anesthesia for tooth extraction
The possibilities of conduction anesthesia can completely relieve the patient of pain. In this case, the dentist injects the drug along the nerve ending, which allows you to block all impulses emanating from the diseased organ. However, there are special cases when the use of this method is inappropriate. If the patient has a history of an allergic reaction to novocaine drugs, then the tooth extraction operation must be performed under general anesthesia in the presence of an anesthesiologist. Intravenous anesthesia is also used for patient panic attacks during dental procedures.
If there is a need to remove a diseased tooth, you should not put off this unpleasant procedure. Complications and chronic pathologies take much longer to treat and require large financial investments. You can contact the receptionist of the LeaderStom clinic and receive all the necessary information on examination, tooth extraction and the possibilities of modern prosthetics. the cause of inflammation of the tissues of the gingival hood that covers the organ; They may even remain under the gum and at the same time put pressure on the neighbor.
Most dentists tend to believe that it is more advisable to remove wisdom teeth, since they are vestigial organs and do not serve an important function. However, their removal in itself can become a serious problem.
To perform this operation, the dentist, under local anesthesia, makes an incision in the gum tissue and uses a drill to drill a hole in the bone. This allows you to remove the tooth from the socket without damaging neighboring organs and nearby soft tissues.
Stuck root
The most common complication of tooth extraction can be a stuck, broken off root. If the root tip remains in the tissue, then the dentist has to use the entire arsenal of tools to get to the fragment: sometimes the tissue is drilled out or a section of the alveolus is removed to get to the desired depth. When hard tissues are crushed, this process can take quite a long time, since the dentist faces the difficult task of removing absolutely all the scattered fragments. In some cases this may take several hours.
Reasons why the pulp dies
There are many reasons why pulp dies. Most often, it is removed when pulpitis has already developed, the nerve is inflamed, it no longer brings any benefit, but is only a cause of torment (this situation leads to the development of severe pain) and a source of infection. It is important to understand that an attempt to endure the pain from pulpitis, when a person uses various painkillers that relieve discomfort, but do not stop the destructive process, can also destroy a tooth.
Also on the list of reasons why pulp dies is injury. For example, if a person hit his jaw hard, and after that did not visit a doctor, leaving everything as it was. Against the background of such a situation, pain often persists for some time, and then gradually subside, while the tooth inside dies.
A tricky problem. What you need to know about toothbrushes and how to choose them? More details
What happens to such a tooth?
“Of course, such a tooth ceases to receive the microelements it needs, its resistance to bacteria is impaired, and over time it becomes fragile. But at the same time, it is worth understanding that such processes do not occur at lightning speed, but proceed very slowly, and such a tooth can remain in the oral cavity for many years,” notes Ilya Antonov.
Of course, certain rules of hygiene will help to preserve even a dead tooth: regular and correct brushing of teeth, the use of additional oral care products on the recommendation of a doctor, as well as preventive examinations according to the approved rules of dental medical examination.
Why is a tooth without pulp considered dead?
The main thing that changes in the condition of the tooth after depulpation is that the trophism (nutrition) of the hard tissues is lost, the tooth becomes very fragile and reacts sharply to external factors.
The absence of nerve endings affects the protective function of the tooth: in the absence of a pain reaction, a person can damage the tooth by biting something hard on it and not notice it. The pulp ceases to protect the tooth from microbes, as a result of which it becomes more susceptible to caries.
As you can see, a pulpless tooth requires additional care, as it is more vulnerable than healthy ones.