Sometimes a seemingly healthy tooth, which has only recently been filled, suddenly begins to experience pain of varying intensity. This seems counterintuitive, but such situations are quite common in dental practice. Conventionally, these cases can be divided into two categories: a painful symptom immediately after treatment (within one to two days) or the appearance of discomfort months or years after the installation of the filling material.
In the first option, toothache is not always a pathology. The fact is that dissection (drilling) of organ tissue, treatment of a carious cavity with an antiseptic and installation of a cement material foreign to the enamel - all this treatment is a serious stress for the tooth. Therefore, at first, aching sensations in the tissues and a feeling of discomfort are considered normal. Another question is when the tooth under the filling hurts for more than two weeks. This state of affairs should alert a person and, at a minimum, force a telephone consultation with the treating dentist.
Often the cause of discomfort in the tooth is improper grinding of the filling during treatment, which does not correspond to the bite. To fix this, the dentist only needs to test the filling surface using carbon paper. If the fissure tubercles of the filling are too high, this will lead to an increase in the load on the treated tooth and, as a result, to injury to the soft tissues of the organ. The risk of displacement of the entire jaw bite, deformation of the tooth, or chipping of one of its walls increases.
The second variant of painful sensations in the tissues of a filled tooth appears a long time after the moment of treatment. A number of reasons may contribute to this.
What can hurt after filling?
The pain associated with the installation of a filling directly depends on the structure of the tooth. It consists of a crown, neck and root. On top, all these structures are covered with hard dental tissues that do not have nerve endings. In the crown area it is dentin and enamel, in the root area it is cement. Inside, under the hard covering in the crown area, there is a dental cavity filled with pulp - a pulp that has many nerve endings and blood vessels. The cavity is connected to root canals, also filled with pulp. In the area of the apex (apex), the root is connected to the bone tissue of the jaw using a ligament - the periodontal ligament, which has excellent innervation.
Conclusion: a tooth can only hurt if the pulp and periodontium are diseased or injured during filling.
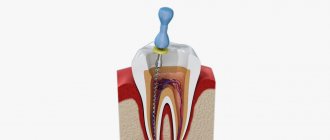
Canal cleaning and filling
The most common cause is caries - a pathological process accompanied by the destruction of hard dental tissues. This opens access to the dental cavity, root canals and periodontal tissue, inflammation or irritation of which causes severe pain.
Preparing a tooth for filling
Filling is a method of treating caries, but this process itself can cause mechanical irritation of soft tissues, accompanied by pain. Minor pain may be normal, but sometimes you cannot do without the help of a specialist.
In the superficial and middle stages of caries, the affected hard tissues are removed and a filling is placed on top, restoring the shape of the tooth. The dental cavity remains closed. This treatment is absolutely painless and does not require anesthesia. An even more effective way is to have your teeth professionally cleaned to remove plaque and tartar. Regular implementation of this procedure prevents the development of caries and allows you to keep all your teeth healthy for a long time.
Tooth preparation and depulpation
With deep caries, a hole forms in the hard tissues and an infection enters the dental cavity, causing intense pain. In such cases, before filling, preparation is carried out to remove damaged hard tissues and expand the cavity. If necessary, the old filling is also removed. Then the pulp is removed (depulping).
This is a painful procedure, but modern local anesthetics used in dentistry allow the patient to experience no pain at all. If deep caries has developed not so long ago, and the periodontal tissues are healthy, then it is possible to remove only the pulp from the dental cavity (amputation), after which a therapeutic lining is applied and a temporary filling is installed. If there is no pain, a permanent filling is placed after a few days.
In case of long-standing caries, the pulp is first completely removed from the dental cavity, and then from the root canals (extirpation). At the same time, the cost of filling increases.
It is very important to carefully remove the pulp (patients often call it the nerve) from the canal, making sure that no particles of destroyed hard tooth tissue remain in it. All this can support a long-term inflammatory process.
If a tooth hurts after canal filling, the infection can gradually reach the root apex, causing an inflammatory process in the periodontium, accompanied by fever and pain.
Pain in the tooth after installing fillings and root canal fillings
Canal filling is carried out in case of pulpitis. This disease is quite insidious and can cause complications dangerous to health. It is much more difficult to deal with than classic caries.
When treating pulpitis, the pulp is killed and removed, the canals are washed, then treated with an antiseptic and sealed. After such changes, the patient may experience mild aching pain for several days. If it does not go away longer, you need to undergo a dental examination. The problem may be related to:
- Root perforation. This happens if a pin was installed in the channels. Then the tip of the screwed element damages the walls and immediately rests against the bone tissue. If perforation occurs, treatment should be carried out as soon as possible. A self-formed perforation will not heal. But the risk of infection will remain very high. The presence of perforation can be suspected by very severe pain spreading to surrounding areas. Sometimes a person cannot understand at all what is hurting him - it feels like his whole face and jaw are being “taken away” and going numb.
- Refilling or the release of dental composition beyond the root apex. If the volume of excess is insignificant, as the painful symptoms shrink, they will fade away by themselves. If it is large, it is impossible to do without resection of the root apex. The patient’s subjective sensations with this complication are pain symptoms reminiscent of advanced neuralgia.
- Underfilling. It is observed if, when filling the canal, some parts of it were left unfilled with material. Then pathogenic microorganisms begin to actively spread in them, increasing the risk of developing an abscess and inflammation. In the early stages of the disorder, the pain is throbbing, then it becomes aching and spreads to the soft tissues. In case of underfilling, repeated endodontic treatment is indicated.
- The presence of a piece of dental instrument in the treated canal. If the roots are very tortuous, narrow and long, it is problematic to process them. It happens that the instrument used by the doctor breaks off and part of it remains in the canal. If the doctor does not notice this and puts a filling on top, the patient will experience acute pain in the coming days. It intensifies during eating and when the jaws are tightly closed. In case of this complication, it is necessary to carry out repeated endodontic therapy.
Why does a tooth hurt after filling?
If a tooth hurts under a filling, there are usually natural reasons for this - irritation and even a slight aseptic (without infection) inflammatory process. The tooth should hurt after filling. Pain appears after the anesthetic wears off and is associated with restoration of tissue sensitivity. Each patient’s pain sensitivity threshold is different: one feels almost no discomfort, while another perceives the same pain as severe.
Depending on the degree of destruction of the crown and the filling work performed, unpleasant painful sensations after the end of anesthesia can last from 5 days to several months. The doctor must warn the patient that he may be bothered by painful sensations for a certain time and how to cope with them.
There is no need to see a dentist if the pain:
- has a moderate aching character, lasts no more than 5 days and its intensity gradually decreases; during root canal treatment, pain can last from a week to a month; if the filling was traumatic, it may last even longer;
- appears or intensifies when pressing on the filling - biting on solid food;
- associated with eating irritating foods - too cold or hot, as well as sour or sweet; after the effect of irritation ends, the intensity of painful sensations decreases;
- associated with hypothermia;
- is not accompanied by swelling of the cheeks, increased body temperature and a violation of the general condition.
Pain associated with filling errors
Common mistakes: root canal perforation and foreign body entry into the root canal
Post-filling pain syndrome can also be associated with medical errors. This:
- Lack of x-ray examination at the very beginning, before filling . The tooth may have structural features: tortuous canals, the presence of additional canals, etc. Without X-rays, the doctor will not be able to properly process and seal it. This is where the answer to the question of why a tooth hurts after root canal filling lies.
- Incorrect (insufficient or excessive) drying of the prepared cavity . Drying is necessary so that the application of a special solution promotes tight adhesion of the filling material to the dentin of the dental cavity. Insufficient drying leads to disruption of this adhesion, the filling will not fit tightly to the walls, infection will penetrate into the cavity, and inflammation will begin. Overdrying is also harmful, it increases the sensitivity of tissues and post-filling pain syndrome will persist for a long time.
- Overheating of dental tissues. Most often, this complication occurs when the dentist works on old equipment. Tooth preparation is accompanied by strong heating of the bur. If you do not frequently cool the dental tissues, a burn of the pulp or dentin is possible, accompanied by severe pain. Tissue burns are also possible when filling using light-curing filling material and outdated ultraviolet lamps that have not been used for a long time. Modern halogen systems for light curing do not give rise to such complications.
- Failure to comply with preparation rules. Leads to infection, the development of pulpitis and periodontitis and associated pain, which intensifies when biting hard food, perforation may occur: the walls or bottom of the dental cavity; this complication occurs when the walls of the carious cavity are excessively prepared; the bottom of the cavity is most often perforated due to insufficient preparation of the walls, the inability to see and properly process the mouths of the root canals;
- walls of root canals - perforation is usually associated with instrumental treatment of difficult tortuous canals. To reduce pain, you will need to apply therapeutic bandages and completely re-treat the tooth.
- a fragment of a tool used to clean the canal;
To determine why a tooth hurts after filling, specialists at the YuliStom clinic first conduct diagnostics (thorough examination and x-rays) and only then treat.
What else causes toothache under a filling?
Sometimes, the tooth continues to hurt or causes discomfort. This may be caused by medical error:
- The dentist overdried the dentin, causing a burn. The tooth reacts to temperature stimuli and tapping.
- Dentin was not dried enough. An air gap with negative pressure appears between the filling and the wall, which causes pain.
- When treating deep caries, the doctor damaged the pulp chamber, pathogens penetrated into the pulp and caused inflammation - pulpitis.
- The filling was placed incorrectly; it irritates the gums, causing swelling, redness, and pain.
A broken instrument, too much or too little filling material, allergic reactions to its composition also lead to unpleasant sensations.
What to do if your tooth hurts after filling?
If a tooth begins to hurt due to a filling being placed, but its condition does not require additional dental procedures to relieve severe pain, the doctor may prescribe:
- painkillers ; most often these are drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs); Ketoprofen (Ketonal) has the best analgesic properties; in case of severe pain, it is enough to take a long-acting capsule of 150 mg - these will relieve pain for a day; instead of Ketonal, you can use the rectal suppository Diclofenac - 100 mg; both drugs are contraindicated in the presence of a gastrointestinal ulcer; in such cases, it is better to take a nimesulide tablet (Nise) - it has almost no negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract;
- physiotherapeutic procedures - to reduce pain, electrophoresis with novocaine is prescribed; for swelling, it is better to use hydrocortisone instead of novocaine; Magnetic and laser therapy are also used; the number of procedures depends on the patient’s condition;
- a one-time injection of an antibiotic solution into the periodontal tissues - for problematic traumatic treatment to prevent infectious inflammation and pain.
There are many folk recipes for relieving severe post-filling toothache:
- rinsing the mouth with a decoction of oak bark; Pour 2 tablespoons of crushed bark into a glass of water, bring to a boil, boil for 15 minutes, add boiled water to the original volume, strain and rinse your mouth several times a day; when a tooth hurts, it relieves inflammation, swelling and associated pain well;
- applying a small piece of salted (but not smoked) lard to the gum - this application is especially helpful for pain associated with tissue swelling: salt draws fluid from the tissue, swelling and pain go away;
- a reflex method of pain relief (used in folk medicine for a very long time): grate a clove of garlic on a fine grater, place it in a thin napkin, apply it to the inside of the wrist of the hand opposite the painful tooth, fix it and leave it overnight.
When you can and when you can’t tolerate pain after filling
My tooth hurts under a filling, what should I do? First of all, do not panic, but calmly understand the situation. If a tooth hurts after a filling, the nature of the pain and the appearance of some other symptoms matter.
Tooth hurts under temporary filling
The intensity of pain under the temporary filling should gradually decrease
Can a tooth hurt under a temporary filling? Of course, it can, but natural pain is not severe, and its intensity gradually decreases. The tooth hurts after filling, mainly during the day, when it is subjected to one or another impact - pressure (chewing hard food), drinking hot, cold or sour drinks.
- Possible reasons : most often, this is normal, the tooth begins to hurt for natural reasons. Painful sensations can also occur due to overheating of tissues during preparation, light-curing of fillings, problems with drying the dental cavity after preparation, or fillings that are excessive in height.
- What is the best way to relieve pain : for natural pain and pain associated with minor violations of the therapeutic process, it is enough to rinse your mouth with an infusion of chamomile flowers and take an anesthetic (Analgin, Pentalgin, Nise).
Acute pain after filling
Very often, a tooth hurts after root canal cleaning and filling. The acute nature of the pain syndrome is associated with injury or inflammation of sensitive tissues - pulp or periodontium. Much also depends on the pain sensitivity of the patient himself.
- Possible reasons : incomplete removal of pulp from the tooth cavity.
- What is the best way to relieve pain : take a painkiller and see a dentist.
Read more about the causes and methods of eliminating acute pain in the teeth in this article.
Throbbing pain after filling
If the tooth hurts severely after filling, the pain has become throbbing, then this is a sign of inflammation of the pulp - pulpitis. A sharp headache often appears.
- Possible causes : the cause of pulsating pain syndrome may be poor-quality treatment of the dental cavity and root canals, possibly perforation of the walls.
- What is the best way to relieve pain : take any painkiller orally and immediately consult a dentist.
Only a dentist can relieve throbbing pain
Aching pain after filling
When a tooth aches after a filling is placed, this is normal. How long a tooth hurts after canal filling depends on the complexity of the manipulations performed. The intensity of the pain is important: if it increases, the pain intensifies sharply when pressed, then this is a symptom of incipient inflammation. A decrease in intensity is a favorable sign.
- Possible reasons : this is natural pain in a filled tooth.
- What is the best way to relieve pain : rinse with a decoction of oak bark or an infusion of chamomile flowers. If the pain seems too severe, take a pain reliever.
Read about how to eliminate aching toothache here.
Tooth hurts after filling when pressing
If a tooth hurts after a filling when you bite it, then most often it has natural causes and goes away in five to seven days.
- Possible reasons : if after filling a tooth hurts when pressed, then most often this is a consequence of treatment and injury to dental tissues.
- How best to relieve pain : temporarily avoid chewing food on the side of the filling, rinse your mouth with light antiseptics and herbal decoctions.
Treatment
To eliminate the causes of pain, you should definitely contact your doctor. And the sooner you do this, the less likely it is to develop complications.
If your tooth hurts after having a filling installed due to caries or pulpitis, treatment will consist of drilling out the old composite, completely cleaning and disinfecting the damaged cavity, and refilling it.
With periodontitis, treatment will take longer, since repeated treatment of inflamed tooth and gum tissues with antiseptic drugs is necessary. Treatment of cysts involves exclusively surgical intervention. Recently, many clinics have begun to use a laser device for these purposes, which makes the procedure virtually painless.
In case of an allergic reaction, the only treatment is to replace the filling substance with another that does not cause harm to the body. In all other cases, only the doctor who performed the initial treatment will be able to determine why the tooth hurts after a filling and how to deal with it. All that is required on your part is an immediate response to the problem and an appointment with a specialist.
When you need to urgently go to the clinic
Occasionally, a filling can create serious problems that require immediate attention to your dentist:
- gum pain after tooth filling; if the pain does not increase, then this is a variant of the norm; but often the pain syndrome is accompanied by redness and swelling of the mucous membrane, the appearance of pus when pressing on the gums, which indicates the presence of an inflammatory process; it could be a burn to the gum tissue, an allergy to the filling material, or an infection; in any case, you need to contact a specialist;
- a toothache and a sharp rise in body temperature to high numbers or a slight increase lasts more than three days, a severe headache appears;
- the cheek on the side of the filling became swollen and pain of any nature, increasing in intensity, appeared in the tooth or periodontal tissues.
Don't put off visiting the dentist if your cheek is swollen or you have a fever!
The tooth hurts when you press on it: after depulpation (nerve removal)
The pulp is nerve fibers and vessels that provide sensitivity and nutrition to the tooth. After their removal, the tooth is considered dead, and it may seem that this is the solution to any problem, because a dead tooth is unlikely to hurt. This is wrong. A pulpless tooth can be disturbing for several reasons:
- if the dentist, while cleaning the canals, punctured the root;
- when the thin end of the endoscopic instrument breaks off and remains inside the canal;
- in case the dental canals have not been completely cleaned and an infection remains in them.
In the first two cases, the pain is quite sharp: the pulpless tooth hurts not only when pressed, but even when touched lightly. If the dentist cleans the canals poorly, pain appears after some time. In any case, a tooth without a nerve that causes discomfort is a reason for a repeat visit to the dental office.
Prevention
The risk of tooth pain after a filling is installed can be reduced if you follow all the dentist’s recommendations for oral care.
What not to do before filling
When planning a visit to the dentist, you need to:
- choose the most suitable time so that you can rest after the filling is placed;
- eat, as you will not be able to eat immediately after treatment;
- Do not drink alcoholic beverages under any circumstances, as they may have undesirable reactions with the painkillers used during treatment;
- Brush your teeth thoroughly and rinse your mouth with an antiseptic solution, such as mouthwash.
You should not plan to place a filling during any acute illness or exacerbation of some chronic disease.
What not to do after filling
It is important to adhere to the following tips:
- do not eat or drink for two hours;
- try to avoid chewing on the affected side of solid food;
- do not eat too hot or cold food for 5 – 7 days;
- avoid coloring products that can change the color of the filling material (beets, red wine, etc.);
- brush your teeth only with a new soft toothbrush twice a day;
- use an alcohol-free mouth rinse;
- do not use dental floss to remove food debris; it is better to replace them with a new product - an irrigator.
What hurts if there is no nerve?
All of the above cases can be attributed to partial filling. What if all the root canals are closed with fillings, and the nerves from them have been previously removed? Where does the pain come from if the tooth is “not alive”?
Many experts believe that there should be no pain in this case. But, since it still occurs, and in a significant number of patients, the question of the origin of pain in a tooth without nerves remains open and hotly debated.
The tooth may hurt even after the nerve is removed
In what cases can you not worry that after filling the canals under a temporary or permanent filling, pain continues?
Important! Short-term pain in a tooth where there is no nerve, even if all the work on removing nerves, cleaning and filling canals was carried out according to the protocol and without errors, is a normal phenomenon.
Table. Nature of pain after root canal filling
| How it manifests itself | Description | Cause | What to do |
| Pain during biting | After the installation of a filling, usually temporary, is completed, pain occurs several hours or days later. There are painful symptoms when biting (from pressure). | If the level of occlusion is not too high, the reason is the reaction of the peri-root tissues to the extraction of the nerve. The root canal is expanded and filling material is introduced into it. The body reacts to a stimulus. | In this case, you can do nothing. The pain lasts from 5 days to 3 weeks. Pain dynamics should be positive (gradually subsiding, until disappearance). |
| Aching pain under the filling | After the anesthesia wears off, aching pain remains under the filling. | This is also due to the body’s reaction to the removal of the nerve. The disturbed canal walls “whine.” | The pain can last from two hours to a day. If it continues longer, you should consult a doctor. |
| Jerking pain inside the canal | This type of pain is rare. It’s as if something is tugging in the tooth; the sensation may resemble the beginning of inflammation of the pulp. | It occurs exclusively as an individual reaction of the body to the expansion of the canal or to the filling material itself (its structural component). | The tooth can also “tug” from hours to days. In a maximum of a day everything should go away. |