Mechanical damage to a tooth due to injury without violating its integrity is called a bruise. This type of injury is common in children and adults, especially athletes. According to statistics, among all injuries to primary teeth, bruises account for 2.5%; bruises of permanent teeth account for 1.5% of the total number of traumatic injuries in the permanent dentition.
Even if the tooth looks unchanged after a bruise, it is necessary to visit a dentist to prevent the development of complications associated with the injury.
What it is
One of the most common dental injuries, mostly occurring in childhood, is bruising. Of course, this kind of damage cannot be ruled out in adults, especially those leading an active lifestyle and involved in traumatic sports.
A tooth bruise is a closed injury caused by strong mechanical impact with a hard object. In this case, the integrity of the bone tissue and the anatomical position are not damaged, but the periodontal tissues suffer, sometimes severe rupture occurs, followed by bleeding.
If the blow was so powerful that the neurovascular bundle was damaged, the tooth may become stained or darkened due to hemorrhage into the dentinal tubules and pulp tissue. Occasionally, with a bruise, numbness is one of the accompanying signs, as well as external damage to the facial area in the injured area, as well as the appearance of swelling and bruising. In any case, most often all these damages are reversible and can be treated if you consult a dentist in a timely manner.
Providing first aid for broken, knocked out and dislocated teeth
One of the most common injuries is a fracture. The types of fracture are as follows:
- Chipping of the enamel of a tooth crown.
- Partial tooth destruction without exposing the pulp.
- Chipped crown exposing dental pulp.
- Tooth root injury.
Additionally, the mouth and gums, the jaw itself and the bone nearby can be damaged. If this happens, the first thing you need to do is calm down - the accompanying injuries create additional stress, which significantly interferes with the doctors and the victim himself. In addition, you should try to find broken fragments and leave them in the water until you see a doctor. The situation does not require an urgent visit to the dentist, so you can make an appointment a little later, for example the next day, but try not to involve the damaged tooth until it is restored.
As for diagnosis, everything is simple - the doctor will first conduct an examination. To detect the risk of root injury, the victim is sent for x-rays and electroodontometry. In this way, the condition of the pulp (tooth pulp) is checked. The goal of treatment is to restore the crown of the tooth. If the fracture led to pulpitis, the patient will be treated with subsequent restoration of the pulp. If an x-ray shows that there has been root trauma, complete extraction of the tooth and subsequent placement of a post is often recommended.
The second most common injury is dislocation. This is a partial or complete loss of connection between the tooth and the socket. Dislocation occurs:
- Partial. The tooth moves greatly or slightly, but does not fall out completely.
- Full. The tooth falls out.
- Impacted, in which the dental crown is driven into the gum.
If a temporary tooth has been completely dislocated (falls out of its socket), do not under any circumstances try to return it to its place - you may damage the new permanent one or its rudiment. And in order to look for and insert a molar into place, you will have only 20 minutes. If you manage to do this, the chance of re-engraftment becomes much greater. What is the procedure? As soon as you have discovered the lost tooth, take it with clean hands (it is also advisable to wash it) by the white part, without touching the root, and return it to the hole, orienting parallel to the neighboring teeth. When you return the lost item to its place, bite on a gauze pad or a piece of cloth, such as a scarf.
There are situations when the tooth cannot be inserted back, for example, if the victim is unconscious or the socket is severely damaged. In this case, place the found tooth in milk or saline solution. You cannot put it in water or any other liquid; you can hold it in the victim’s mouth, but there is a risk of swallowing.
Unlike a fracture, in a situation with complete dislocation, it is necessary to urgently visit a specialist for examination and subsequent treatment.
For partial dislocation, the procedure is slightly shorter. It is important to try not to spit (or do it as little as possible) and under no circumstances take out the tooth. If it prevents your mouth from closing, carefully insert it back in with clean hands, focusing on the adjacent teeth. To hold it in place, bite down on gauze or any other piece of tissue.
In the case of an impacted dislocation, first aid is practically useless; the only option is an emergency visit to the dentist.
Panoramic radiography
How are dislocations identified and treated? The doctor first examines and records the complete absence or displacement of a tooth. Next, the victim is sent for an X-ray and radiovisiographic examination, where the location and condition of the alveoli are clarified. In case of incomplete dislocation, the patient is recommended treatment aimed at preserving the tooth and fixing it with the help of special mouthguards and other structures. In addition, medications are recommended to prevent inflammation and infection in the socket, for example antibacterial ones.
If, after complete dislocation, the tooth does not take root, the specialist is forced to resort to prosthetics and implantation. In case of impacted displacement, you can either remove the affected tooth and replace it with an implant, or perform immobilization using local anesthesia.
A knocked out tooth is a dislocated or broken crown due to a mechanical injury. For example, a blow to the jaw caused the victim to completely dislocate or chip the dentin, exposing the pulp. Depending on the injury detected, you can provide first aid as described above. That is, if a tooth falls out, find it, try to put it back in, or place it in saline before visiting a doctor.
Causes
Like any other injury, a tooth bruise can have a wide variety of causes. This could be an accidental hit in the jaw with a ball or other sports equipment, an unfortunate fall, a strong blow in a fight, or the consequence of a road accident or riding a bicycle. All these reasons have one thing in common - a strong blow of a mechanical nature.
Children and athletes are the most vulnerable to such injuries. It is these two categories of patients with a similar diagnosis that are the most frequent visitors to dental clinics. However, household injuries, as a result of which a person accidentally or recklessly hits a tooth, can cause a bruise. In this case, the most unprotected and weakest anterior and lateral incisors on the upper jaw most often suffer due to the anatomical structure and overhang of the upper jaw over the lower jaw.
Diagnosis and treatment of tooth fracture
A coronal fracture is diagnosed during an examination by a dentist. To confirm or exclude a root fracture, targeted radiography is prescribed. Electroodontometry may be indicated to assess the condition of the pulp.
Treatment of a fracture of the coronal part is a complete restoration of the tooth crown using composite materials, a permanent crown and a stump inlay. In case of complications, treatment of pulpitis is carried out with further restoration of the tooth.
For tooth root fractures, treatment options may include:
- endodontic root treatment;
- tooth extraction followed by replacement.
Symptoms
The symptoms accompanying a tooth bruise are easy to recognize. If a person bruises a tooth, it hurts quite noticeably, and over time the pain only intensifies, especially with pressure on the damaged area and chewing food. The following symptoms are also present:
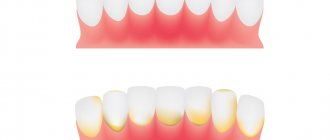
- When the neurovascular connection is ruptured, hemorrhage occurs into the pulp tissue, due to which the enamel quickly turns pink;
- The crown may darken;
- When bruised, the tooth becomes loose, although its mobility is relatively small;
- At the site of impact on the soft tissues of the gums, swelling, hyperemia, deformation of individual areas of the mucous membrane, and the formation of hematomas may occur;
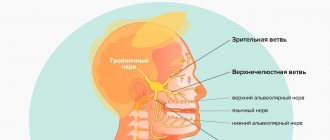
- If there is a very strong impact, ligament rupture, joint damage, or even a fracture of the alveolar process of the jaw may occur where the striking object hits the jaw. In this case, it will be difficult and painful for the patient to open and close the jaw. Such damage can only be diagnosed with an x-ray.
Clinical picture
First of all, the doctor conducts a visual examination of the bruised area to identify hidden injuries that cannot be identified by a person without medical education. For example, symptoms of dislocations or fractures may not appear immediately. Professional consultation allows you to begin timely treatment, if required.
To recognize a jaw bruise, it is important to pay attention to the following symptoms:
- severe pain in the place where the blow fell, intensifying when pressed;
- visual signs (eg, swelling, redness, abrasions, bruises);
- limitation of jaw mobility when yawning, talking, chewing;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- general weakness.
Jaw bruises are less dangerous than more severe injuries, so recovery is usually quick.
The doctor may order an x-ray or computed tomography to establish an accurate diagnosis. These studies will assess the condition of the internal tissues of the affected area.
Consequences
Not a single injury for a person passes without a trace. Even if you managed to avoid obvious complications at the time of treatment, there is always a possibility of their occurrence in the future. For a tooth bruise, the consequences are also no exception. One of the most common complications is the gradual death of pulp tissue if the pulp was damaged by an impact, but during treatment, identifying its viability gave positive results. With necrosis, the nerve endings in the tooth cavity are damaged, which inevitably leads to inflammation.
Another most common consequence of a bruise is staining of the enamel. Most often, it occurs in a short time after injury, since fluid from damaged vessels enters the dentinal tubules and stains the walls. In addition, the enamel may simply darken due to a lack of nutrients supplied through damaged fibers and tissues.
More serious complications that arise over time are also possible. This may be the development of a cyst, periodontitis, or a stop in root development in children in both milk and permanent teeth.
The likelihood of tooth loss after injury: what doctors say
Can a tooth fall out after a blow? This situation is rare, but it cannot be excluded if the supporting ligaments and periodontal tissues are severely damaged, and the person does not seek dental care for a long time.
More often, after a blow, the tooth hurts and only wobbles a little, and the gums around it are red and swollen. But even in this case, you cannot relax. According to doctors, against this background traumatic gingivitis and periodontitis can develop. These diseases, with inadequate treatment and careless attitude to oral hygiene, progress and become generalized (spread to the entire range). Advanced periodontitis is also fraught with loosening and loss of moving elements.
Diagnostics
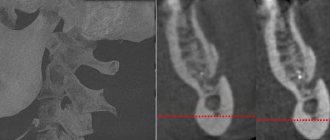
What action should you take if you or your child gets a tooth bruise? First of all, you need to contact a dental clinic as soon as possible. Using an X-ray, as well as after palpation and a thorough visual examination, the doctor will determine the extent of the damage resulting from the bruise, and will also draw up a detailed plan for further treatment.
When a tooth is bruised, diagnosis must certainly include, in addition to identifying obvious symptoms, an x-ray examination to exclude possible internal injuries, such as a fracture of the root or alveolar process. In addition, damage to the periodontal area, if present, will be visible in the image.
Also, over the course of several days, the doctor must monitor the condition of the pulp using electroodontodiagnosis. It helps to identify even the initial stages of necrosis and remove damaged tissues in time before they begin to become inflamed.
Diagnosis and treatment of tooth dislocation
Using an x-ray and available clinical data, the type of injury received is revealed. In addition, it is possible to conduct a radiovisiographic study to study the condition of the alveolar bone and the position of the tooth. Treatment is prescribed according to the specific type of injury.
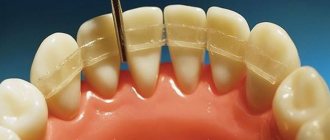
In case of incomplete dislocation, therapy is indicated to preserve the tooth. It is repositioned with fixation using mouthguards, wire splinting structures or splints. It is also recommended to take medications to prevent infection and the development of the inflammatory process. A repeat examination by a dentist is carried out a month later.
Endodontic treatment is indicated in case of pulp death.
In case of complete dislocation, prosthetics are necessary. Sometimes replantation is performed: the damaged tooth is returned to the socket, splints or splinting structures are used for healing.
Treatment of impacted dislocations involves several options:
- tooth extraction and its replacement with a prosthesis;
- tooth extraction with its replantation;
- immediate reposition of the tooth with its subsequent immobilization;
- long-term reduction.
Treatment
In some cases, if the impact is not very strong, no treatment other than monitoring the condition of the damaged area is required. It is necessary to provide the affected tooth with long-term rest, apply cold compresses to reduce the bruise and relieve swelling. Solid food is completely excluded from the patient's diet for several days. Among other things, the doctor must observe the injured tooth for two to three months to avoid complications.
In children with baby teeth, it is possible to grind off the enamel on the cutting edge to remove the load from the damaged area; this action is not carried out on permanent teeth.
To eliminate the consequences resulting from a severe bruise, treatment should consist of a number of procedures:
- first of all, the damaged area is numbed with an anesthetic;
- if there is damage to the pulp sac, the doctor performs trephination, depulpation and thorough treatment of the dental cavity with disinfectants, after which the canals are sealed;
- if the neurovascular bundle has been damaged and the enamel has darkened or become stained, it is recommended to bleach permanent teeth using hydroperite, which will return the enamel to a more or less natural color;
- if necessary, the doctor can prescribe, in addition to complete rest, anti-inflammatory drugs and physiotherapy to help quickly eliminate the consequences of the injury.
Even if there is no severe pain after a blow to the jaw, it is recommended to visit a dentist to identify possible hidden injuries. This will help you maintain the health of your teeth for many years to come.
What treatment measures do doctors usually prescribe?
In the absence of serious damage
Teeth hurt after a blow: what to do? If, as a result of the examination, it becomes clear that the injury did not bring any serious consequences, then the patient is prescribed the following therapeutic treatment:
- painkillers and syrups for pain relief: read about the best of them in the feature article on the website,
- cold compresses to relieve swelling and resolve bruises,
- treatment of inflamed gums with antiseptic solutions and anti-inflammatory ointments: you can rinse your mouth with Chlorhexidine and Miramistin, use topical gels, for example, Cholisal,
- gentle diet: the bruised element of the row should be at rest, which is why during the rehabilitation period (on average it takes up to 3-4 weeks) it is not recommended to eat hard and hard food, or chew on the side of the jaw that has been subjected to mechanical stress. You should not eat cold or hot, as this can cause pain and have an irritating effect. It is better to eat soft and pureed foods, ground in a blender, as well as liquid foods at a neutral temperature,
- physiotherapy: for rapid healing of damaged tissues, laser and magnetic therapy, UHF (ultra high frequency) therapy are usually prescribed. The course consists of 10 procedures of 5 minutes each.
On a note! For 2-3 months after a bruise or blow, it is recommended to carry out dynamic observation even in cases where no serious damage has been identified. During the process[1] of observation, the doctor can adjust treatment tactics and decide on the use of non-invasive and invasive methods. Subsequently, adults should visit the dentist 2 times a year and children 3-4 times a year for preventive examinations.
For pulpitis and periodontitis
How to save a tooth after an impact? If the injury leads to damage to the pulp, the development of pulpitis and periodontitis, then specialists perform trepanation of the crown, that is, they open it. Doctors gain access to the root canals, remove the nerve if necessary, carry out treatment, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic treatment, and filling. All procedures are performed under local anesthesia.
When changing shade
If a tooth has darkened after an impact, the patient is offered intracanal bleaching, which allows the element of the row to be restored to its former whiteness. However, the procedure is performed only on pulpless units, that is, when the nerve has been removed from them. What to do if the pulp was saved? You can hide the defect and restore the aesthetics of the anterior incisors and canines with composite restorations, veneers and lumineers, crowns made of ceramics and zirconium dioxide.
A change in the shade of the crown often occurs due to incomplete rupture of the pulp, which causes a hematoma to form in the tissue. According to some studies, the crown acquires its natural color after the hematoma resolves, so in the first days after the injury, patients are often simply prescribed dynamic observation.
With mobility of the bruised unit
How to ensure complete rest and strengthen a tooth after an impact if it begins to wobble? For this purpose, doctors may install temporary immobilization and splinting devices for you. The splints will fix the movable unit in a stable position, unite it with healthy ones, help the correct distribution of the chewing load and allow therapeutic treatment until damaged or torn ligaments are restored. They need to be worn from several weeks to several months. During the period of immobilization, it is very important to follow a gentle diet and give up solid food.
On a note! If a row of milk units is bruised, splints are not placed, and rest is provided to the moving element using mouth guards, which temporarily separate the bite and prevent direct contact with the antagonist teeth. To reduce the load on the bruised element, children also undergo grinding of the cutting edge of the antagonist crown.
For increased tissue sensitivity
Often after a bruise, increased sensitivity of hard tissues occurs. They begin to react to food temperature and mechanical stress, and then experts recommend a course of fluoridation or remineralization of the enamel. In the process, products with minerals are applied to hard tissues, promoting strengthening and increasing resistance to caries and any external factors.
When chips and cracks form
Often, a blow or bruise to the incisors and fangs leads to the formation of cracks and chips on them, and to the destruction of hard tissues. In these cases, to restore the aesthetics, original form and functionality of the damaged elements, patients undergo artistic restorations with composite materials, and microprostheses (veneers and lumineers) are installed. If the destruction is extensive, then prosthetic crowns are prescribed.
Complications after injury
Usually bruises do not affect the health of the teeth in any way, but sometimes they lead to complications. Among the most common are a strong change in the color of the enamel against the background of hemorrhage that appears in the pulp chamber. Over time, a damaged tooth may become gray or brown, this is due to a slowdown in metabolic processes occurring in the tissues.
If the pulp dies, a disease such as pulpitis may develop. If you ignore the first symptoms, the risk of developing periodontitis becomes very high. As a result, a post-traumatic odontogenic cyst may appear, which is localized on the upper part of the tooth root.
If a child whose molars have already emerged is injured, the development of the roots of permanent units may be disrupted. If the injury is in a very young patient, it can cause a disruption in the formation of the rudiments of future permanent teeth. In the absence of timely intervention, they may die.