One of the most common reasons for patients visiting dental clinics is traumatic damage to teeth and surrounding tissues. At any age, a tooth bruise can occur - a painful injury, which, despite the discomfort, at first looks quite harmless. Subsequently, it often turns out that the pain does not subside, and the bruised tooth begins to react to hot or cold. This usually means that the neurovascular bundle—the dental pulp—is damaged, and a visit to the dental office is necessary.
Even a very careful adult can get a severe bruise to a gum or tooth (for example, by not calculating the movement and hitting himself with a spoon or glass). What can we say about kids who are constantly on the move and often fall, hitting their teeth on various objects. As a result, enamel cracks, root fractures, dislocations and other injuries occur. In the ICD (International Classification of Diseases), chapter 29 is devoted to dental injuries, which describes the consequences of single or multiple mechanical impacts leading to disruption of the integrity of teeth and surrounding tissues.
Main reasons
Dental injuries can occur for various reasons, the most common of which are:
- accidental impact of the jaw on a hard object during a fall or in an accident;
- a blow to the front teeth with a glass, spoon or other utensil (sometimes such blows are so strong that they break off part of the incisor);
- a blow to the teeth with a fist or other blunt object (a professional injury that often occurs among fighters of various martial arts);
- chronic injuries associated with a person’s habits or lifestyle (tendency to bite nails, bite pens, frequent consumption of sunflower seeds, cracking pistachios and other relatively soft nuts with teeth);
- damage during the treatment of adjacent teeth (severe tooth bruising can occur both due to a dentist’s mistake, and due to the anatomical features of the patient, advanced diseases and other factors).
The likelihood of enamel fracture and other traumatic damage to dental tissue increases significantly with poor oral care and dental health. In this case, the enamel becomes more fragile, and the initial stages of caries may develop, significantly weakening the tooth. Timely treatment and proper oral health care significantly reduce the risk of injury to teeth as a result of a blow or other physical impacts.
Prevention of dental injuries
Whether the tooth can be saved during treatment or not depends on the nature of the injury and the timeliness of contacting the dentist. Often, tooth restoration is complicated by a person’s general poor health or advanced age.
Modern methods of dentistry and orthodontics are progressive. This allows you to preserve natural teeth, restoring them even after the most complex damage. If it is impossible to save the tooth, the doctor suggests replacing it with a prosthesis or implant that fully matches the functional and aesthetic characteristics of natural teeth.
Prevention of dental damage consists of following the rules of caution both at home and at work, as well as eradicating bad habits - gnawing nuts with your teeth, opening metal plugs, etc. When engaging in extreme sports, dentists recommend using a protective helmet or mouth guard.
Symptoms of a tooth bruise
Depending on how long and intensely the tooth hurts after a bruise, one can draw conclusions about the severity of the injury.
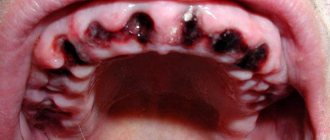
Often, immediately after the blow, it seems that the pain gradually subsides and will soon go away completely. However, over time, the discomfort only intensifies, and when pressure is applied to the tooth itself or the gum next to it, the pain can become unbearably strong. In addition to pain, the following symptoms may be observed:
- the gums in the area of the bruised tooth swell, a hematoma or edema appears;
- the tooth may acquire a reddish tint due to blood released into the pulp from ruptured vessels;
- bruising of the front teeth can lead to noticeable loosening of individual incisors (it seems to the person that the tooth does not hold well and may fall out);
- Over time, the crown may noticeably darken due to disruption of the nutrition of dental tissues and the penetration of pollutants into enamel cracks.
Any of the listed symptoms is a serious enough reason to contact a dental clinic as soon as possible. Painful sensations always indicate the presence of damage, which can eventually lead to the loss of a healthy-looking tooth.
Crown fracture
This is one of the types of transverse fractures, it is quite easy to identify. The choice of treatment depends on the size of the chipped segment and the condition of the pulp. If the dentin is not damaged, but only part of the enamel is affected, a composite filling is the solution. In case of a fracture of the front tooth, extensions or veneers can be used.
If dentin is affected, doctors use special insulating pads. In cases where a tooth breaks in half and the pulp is damaged, it is removed and the canal is filled. Next, a pin can be installed followed by the use of a filling composite in order to restore the original shape.
A fracture of the neck of the tooth is also common. There are cases when the tooth wall breaks completely, but the pulp sac is not damaged. Typically, in such situations, specialists are in no hurry to get rid of the root, since it can become a good basis for a pin. In this case, in any case, the pulp is removed.
Tooth bruise - what to do?
Please note that it is impossible to determine the severity of the injuries yourself. A complete diagnosis must include an x-ray and a professional examination in a dental office. At home, an experienced dentist can examine the damage and make certain assumptions, but even without the necessary tools, he will not be able to make an accurate diagnosis.
If it is obvious that the tooth bruise is quite serious, self-treatment is unacceptable. To ease the pain, you can apply ice or just a cold object and go to the dentist as quickly as possible. If it looks like the jaw is damaged, it is advisable to fix it with a bandage. It is advisable that someone accompany the victim, since he may lose consciousness on the road.
Diagnostics
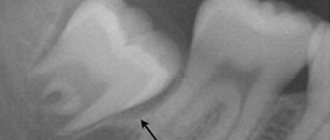
Examination of the patient first reveals a tooth dislocation, a root fracture is confirmed later by X-ray examination; It is recommended to perform a 3D computed tomography, since a regular x-ray may not detect a fracture. In addition to determining the area and direction of the fracture, the study makes it possible to determine the condition of the walls of the alveoli, periodontium, and the position of displaced fragments.
The dentist is also able to determine a root fracture using the following technique: with his right hand he slightly moves the crown of the tooth back and forth, while the finger of his left hand located on the vestibular surface (oriented towards the vestibule of the mouth) of the alveolar part of the jaw will feel the movement of part of the broken root associated with crown This method is not suitable if the fracture occurred in the apical part of the root, so an x-ray examination is required.
Treatment
Oral injuries can vary in nature and severity. No matter how painful a tooth bruise seems, treatment must be carried out in a specialized dental clinic. We at Natadent often encounter such cases. After the initial diagnosis, visual examination, interviewing the patient and collecting anamnesis, an x-ray is taken - this is the only way to clearly determine which tissues are damaged and prescribe the correct treatment.
By studying an x-ray, the doctor can determine what kind of damage the tooth has received (this could be a fracture, dislocation, crack, various deformations and other pathologies).
Only after a correct diagnosis can treatment be prescribed. If a tooth injury has caused serious damage, electrodiagnostics is prescribed - a special procedure that allows you to determine the condition of the pulp, detect hemorrhages and necrotic areas in it. If diagnostic actions show that the damage is not very serious, a set of preventive measures is prescribed, which includes:
- application of compresses;
- use of decoctions for mouth rinsing;
- exclusion from the diet of hot dishes and foods that require chewing; exclusion of this area of the dentition from the chewing process by applying a bandage or protective splint.
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs.
If a more serious tooth injury is diagnosed, treatment may include surgery to the structure of the tooth and surrounding tissue. The sequence of actions is determined by the complexity of the injury, but in most cases includes the following steps:
- ;
- Local anesthesia is performed (or general if complex and painful treatment is involved).
- If the pulp sac is damaged, even if the tooth enamel has retained its structure, the doctor drills a hole in it and removes the nerve.
- The canals and cavity are cleaned, treated and filled, as in conventional caries treatment.
;
;
A tooth bruise is a dangerous injury that can lead to undesirable consequences and complications. Even if pulp removal and filling have been performed, it is advisable that the patient undergo a course of therapeutic treatment, and after some time come for additional examination. Only after this can it be said that the consequences of the injury have been completely eliminated and there will be no complications.
Root fracture
In the event of a tooth root fracture, a specialist analyzes its position to select the appropriate treatment. The fracture can occur near the neck, at the apex, in the middle part, or at the border of the upper and middle parts. In most cases, transverse fractures occur.
Diagnosis of such damage does not cause any difficulties. First of all, a person feels pain while chewing food and biting it. During palpation, mobility of the injured element of the dentition is observed. When percussing and closing the jaw, the patient experiences discomfort and pain. And if the fracture is located near the crown, the enamel may take on a pink tint. Radiography helps to clearly establish the number of cracks, as well as their position.
Possible complications
Since bruising of a gum, tooth or other tissues in the oral cavity is always individual, it is impossible to give reliable predictions about recovery and possible complications. It usually takes several visits to the dentist to carry out the necessary examinations and procedures, after which a complete recovery can be established. If you do not approach the treatment process responsibly, you can get the following complications:
- darkening of the enamel (due to the penetration of pollutants through cracks, blood entering the pulp and disruption of the nutrition of dental tissues);
- death of pulp cells and formation of necrotic areas leading to tooth death;
- chronic inflammatory processes (pulpitis and periodontitis) leading to more serious consequences.
Very often, a tooth bruise leads to serious but hidden injuries. The victim may feel minor pain and think that everything will go away soon. However, this is not a reason to avoid qualified medical care. The sooner an examination is carried out in a dental office, the greater the likelihood that all consequences will be eliminated, complications will be avoided and the tooth will be as healthy as possible.
Types of tooth dislocations
| Variety | Description |
| Incomplete | Incomplete tooth dislocation is characterized by partial displacement of the root in the socket, rupture or stretching of part of the fibers of the periodontal ligament. The position of the tooth is disturbed: it deviates to the vestibular, oral or lateral side. Rotation around an axis is possible. The injury may be of a combined nature (with a fracture of the supra-, subgingival part of the unit, the bone of the alveolar process). |
| Full | Complete damage (traumatic extraction, avulsion) is characterized by loss of a segment from the alveolus, rupture of the fibers of the circular dental ligament, nerves, and blood vessels. The most common condition is complete dislocation of the front tooth (central incisors) of the upper jaw. |
| Hammered | Intrusion is the depression of an injured unit under the influence of a blow into the depths of the alveoli. Immersion can be complete or partial. With such an injury, the root enters the spongy jawbone. The periodontal ligament is usually completely torn. Some fibers are sometimes preserved, but they undergo stretching. Capillaries and nerve bundles also break. The bottom and walls of the cortical plate break down. At the same time, the segment can deviate to the side and rotate around its axis. If the injury is localized in the upper jaw, there is a risk of damage to the maxillary sinus. Impacted tooth dislocation has a poor prognosis. Almost all cases of injury (especially with a late start of endodontic treatment) end in resorption. |