Increased sensitivity of teeth (hyperesthesia) is a short-term occurrence of pain under the influence of temperature, chemical or mechanical irritating factors. Usually occurs when drinking cold water, sour, sweet, salty, or touching with a toothbrush. The intensity of pain varies from mild to unbearable.
According to WHO, every second person in the world suffers from hypersensitivity. In Russia it is about the same: 45–65% of adults aged 20–55 years. More often women make complaints.
A little anatomy
A tooth consists of a crown and root part, connected by a neck. The coronal part is covered with enamel, the root part is covered with cement. Beneath the enamel and cement there is dentin, a hard tissue. Inside there is soft tissue - the pulp; blood vessels and nerves pass through it.
Dentin is not sensitive, but consists of many tubules in which fluid circulates. The irritant causes fluid movement, which is detected by the nerve endings of the pulp. A person feels their reaction as pain.
Complications
High reactivity of hard tissue structures of teeth can affect the general condition of a person. Diseases of the psyche and gastrointestinal tract may worsen. Soreness often disrupts the usual diet.
One of the most obvious and severe consequences of hypersensitivity is pulpitis - an inflammatory process that affects the neurovascular tissue inside the tooth. Constant exposure to irritants on the pulp can lead to aggravation of the process, as well as a deterioration in the general condition of the body. Treatment of such a complication is multi-stage and labor-intensive: the pulp is removed, endodontic treatment is carried out, and the coronal part is restored.
It happens that excessive sensitivity is only one symptom of pathology, for example, a harbinger of a wedge-shaped defect. Therefore, it is important to immediately make an appointment with a specialist with this problem in order to determine the provoking factors of the disease and avoid complications. Dentists at the West Dental clinic will help you with this and select fast and high-quality treatment.
Tooth sensitivity: causes
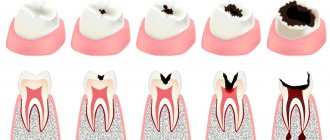
- Demineralization of enamel. It becomes more loose due to the leaching of calcium, phosphorus, and other trace elements.
- Thinning of enamel. As a result of increased abrasion due to malocclusion and the occurrence of wedge-shaped defects.
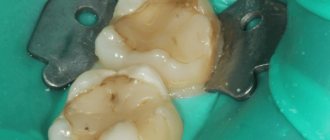
- Untreated caries or violation of the marginal seal of the filling.
- Exposure of roots as a result of injury, metabolic-dystrophic process or inflammation of the gums.
- Changes in the pH of saliva due to the consumption of certain drinks, foods, and medications. A pH of less than 5.5 is considered dangerous.
- Some diseases accompanied by gastroesophageal reflux and endocrine disorders.
- Vitamin deficiency, exposure to radiation, work in hazardous industries, living in a region with an unfavorable environmental situation.
- Smoking.
More often than not, several reasons are discovered at once. The enamel becomes thinner, loses strength, and cannot protect dentin from irritants. The result is pain.
Mechanisms of pain
Dental hyperesthesia is a problem of global importance, because it is observed in more than half of the entire adult population of the planet. Statistics also point to the fact that the disease is more common in women than in men. However, despite the widespread prevalence of the disease, it is still not entirely clear how the pain reaction to direct external stimuli occurs. There are three theories about this:
- Nervous reflex. Its essence lies in the fact that the basis of the problem is disturbances in ion exchange processes in dental tissues, as a result of which the dentin receptor apparatus exhibits increased sensitivity.
- Receptor. It is assumed that pain occurs as a result of a direct reaction of the nerve endings of dentin to irritation and subsequent transmission of a signal to the pulp of a particular tooth.
- Hydrodynamic. Accepted by domestic doctors as the most likely. According to the opinion, pain occurs as a result of activation of mechanical receptors of nerve fibers. This occurs due to disturbances in the circulation of dentinal fluid in the tubules, which in turn is caused by various external factors.
In addition, enamel hyperesthesia specifically in women may be a consequence of a lack of hormones in the blood, namely estrogens.
Provoking factors
Hyperesthesia does not appear immediately. There are several factors that you need to pay attention to in order to eliminate them in time. Don't wait for discomfort to appear. It is better to initially develop healthy habits that will help you maintain your health so that you never experience acute dental pain. Sensitivity increases when any of the factors listed below are present.
- Insufficient oral hygiene. Soft plaque is an accumulation of microbes that eat food microparticles stuck in crevices, releasing organic acids that dissolve enamel minerals. Externally, the dental unit looks intact, but the density of the enamel is significantly reduced. Its demineralization occurs. The first alarm bell is increased sensitivity, then caries develops.
- Consumption of certain foods. Juices, wine, sweet soda, fruits, candies, and other sweets contain phosphoric and other acids that negatively affect the strength of enamel.
- Constant use of aggressive whitening pastes containing abrasive and chemical components.
- Ultrasonic cleaning. Under a dense coating, the enamel becomes thinner and becomes loose. After professional cleaning, it is exposed, its sensitivity increases sharply. Usually, dentists, taking this point into account, use strengthening pastes at the end of the procedure for the preventive treatment of tooth sensitivity.
Classification
Clinical studies have resulted in the most complete structuring of dental hyperesthesia (ICD K03.8), based on which the doctor will determine the causes of the pathology and will be able to differentiate it from other diseases. And most importantly, the specialist will be able to make a true diagnosis and formulate the correct treatment tactics. The classification allows us to systematize the factors influencing the occurrence of the disease.
By location:
- Limited - a limited number of units are affected (1-3). Teeth ground for orthopedic structures, or affected by cervical caries.
- Generalized - most of the dentition is affected, sometimes the entire tooth row. The reasons are erosion, gum recession, high abrasion.
By origin:
- due to a decrease in the volume of solid tissue structures.
- volumes of hard tissues do not affect. Associated with periodontal diseases, pathologies of the endocrine, nervous and gastrointestinal systems. Visually, the integrity of the enamel is not compromised.
According to the severity of the pathology:
I—response to temperature;
II - pain when interacting with sweet, sour and bitter foods;
III - pain is caused by all irritants, as well as hygienic cleaning.
The strength of pain reactions depends on the characteristics of the body.
Types of hypersensitivity
If sensitivity is increased on one or more teeth, it is called limited. If for everyone - generalized.
Table 1. Types of hyperesthesia
| № | View | Reaction |
| 1. | Light | for cold, hot |
| 2. | Average | as with 1st degree plus for sour, sweet, salty |
| 3. | Expressed | as in grade 2 plus mechanical irritants (when brushing teeth, eating) |
What is dental hyperesthesia
Let's say you drank hot coffee and started eating ice cream. I immediately felt a “ache” in my teeth. The feeling is not pleasant. This is how hard dental tissues reacted to a sharp change in temperature, showing excessive sensitivity. Dentists call this phenomenon hyperesthesia. A similar reaction can occur to other chemical, mechanical and temperature irritants: spicy, sweet, sour, exposure to cold, brushing teeth, chewing. The pain can be sharp or nagging, long-lasting or short-lived.
Dental hyperesthesia is a painful reaction of teeth to chemical, temperature and physical stimuli. Pain can be localized in one or several dental units, or spread to all elements of the dentition (generalized hyperesthesia). It has been proven that emerging sensitivity (in the absence of caries) precedes non-carious lesions of the dental element (elements) and is an early diagnostic symptom of this clinical situation. The pathology is mainly observed in people aged 30 to 60 years.
Sensitivity of teeth. Stages of treatment
- Eliminate the cause of hyperesthesia: get rid of plaque, deposits, stones, caries, wedge-shaped defects.
- Carry out professional oral hygiene.
- Strengthen the enamel with calcium and fluoride.
- Teach the patient how to use a toothbrush and floss correctly.
- Choose suitable dental care products: toothpaste, mouthwash.
Table 2. Tooth sensitivity: causes and how to treat
| № | Cause | What to do |
| 1. | Soft coating. | Careful hygiene with home remedies. |
| 2. | Hard coating. | Professional hygiene in dentistry. |
| 3. | Caries in the white spot stage. | Deep fluoridation, remineralization. |
| 4. | Caries, pulpitis, periodontitis. | Dental treatment. |
| 5. | Exposure of the cervical part, wedge-shaped defect. | |
| 6. | Malocclusion. | Orthodontic therapy. |
Summary
- If hypersensitivity occurs, avoid drinks and foods containing acids (fruits and fruit juices, wine, etc.).
- If you have previously used whitening toothpastes, stop using them, because... with a high probability, hypersensitivity is caused precisely by their use.
- Consult your dentist about the cause of sensitivity - it may be caused by caries or exposed tooth necks. Remember that caries in the form of a white spot is a reversible form of caries, and if you undergo remineralization therapy on time, you will not only get rid of increased sensitivity, but also prevent the destruction of this area of enamel.
- If there are dental deposits, they must be removed, followed by a course of remineralization and/or deep fluoridation.
- Maintain proper oral hygiene - cariogenic microflora in the cavity, feeding on food debris, produces acids that wash calcium from the enamel and lead to the appearance of both hypersensitivity and dental caries. Check out the link above for comprehensive hygiene tips, as well as videos on proper brushing and flossing techniques.
Sources:
1. Higher professional education of the author in dentistry, 2. Personal experience as a dental therapist, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. The European Academy of Paediatric Dentistry (USA), 5. “Therapeutic dentistry. Textbook" (Borovsky E.).
Elimination of tooth sensitivity
Using ultrasound, the doctor removes soft and hard deposits from the teeth. After removing plaque, teeth become more sensitive for a short time, so remineralization or deep fluoridation is immediately carried out. During remineralization, the enamel is treated with active compounds of calcium and phosphates. Deep fluoridation – coating with sodium fluoride. Both procedures significantly strengthen the enamel's resistance to irritants.
The doctor uses agents that reduce the movement of fluid in the dentinal tubules. It “seals” them using desensitizers or reduces their volume through remineralization. Protecting exposed dentin reduces the force of transmission of the irritant impulse from the enamel to the nerve.
Diagnostics
When examined by a specialist, it is important to conduct a thorough differential diagnosis in order to distinguish hypersensitivity from other diseases with similar symptoms:
- pulpitis;
- caries;
- cracked tooth or filling material.
In case of dental hyperesthesia, differential diagnosis consists of a visual and instrumental examination; an X-ray and electroodontodiagnosis (EDD) may be necessary.
A characteristic feature of high enamel reactivity is quickly subsiding acute pain. To identify it, a specialist needs to check the condition of the pulp using X-rays or using EDI. If a preliminary diagnosis of hypersensitivity is made, the doctor performs diagnostic tests to determine the degree of reaction of dental tissues to irritants. Afterwards, the specialist draws up an individual detailed plan for the treatment and prevention of dental hyperesthesia.
Basic points of proper hygiene
Use a synthetic, medium-hard or soft brush. Change it every three months.
The toothpaste should be suitable for very sensitive teeth. Typically, such products contain hydroxyapatite, strontium chloride, fluorides, potassium nitrate, or a combination of calcium carbonate and arginine.
Take enough paste. For children under 3 years old - the size of a grain of rice, from 3 to 14 years old - the size of a pea, for adults you need to squeeze out about one centimeter.
Brush your teeth for 2 minutes: 30 seconds on each surface, top and bottom. Monitor time using an hourglass or mobile phone timer. Electric toothbrushes emit a short beep every 30 seconds and a long beep every 2 minutes from the start of brushing.
Cleaning sequence
- Using sweeping movements, clean the outer and then the inner surfaces of the bottom row. Move from molars to incisors. Then do the same on the top row. Hold the brush at a 45-degree angle and do not use a sawing motion. This leads to damage to the enamel.
- Brush chewing surfaces with small circular movements.
- Close your jaws and walk along your gums in a circular motion.
- Brush your tongue using a leisurely four to five strokes from root to tip.
- Treat the interdental spaces with dental floss.
- Rinse your mouth.
It is more effective to clean with an electric brush or irrigator. The quality of hygiene increases 3–4 times. Hyperesthesia can be dealt with faster.
Is it possible to strengthen sensitive teeth at home?
Yes. If you can’t get to the dentist, you can try to help yourself. There are several remedies that can solve the problem of hyperesthesia at home.
Table 3. Popular products for home use
| № | Name | Mechanism of action | Age category |
| 1. | ROCS Medical Minerals, GC Tooth Mousse | Remineralizing gels | Adults and children |
| 2. | Colgate Duraphat 2800 ppm | Fluoridating paste | 10–15 years |
| 3. | Colgate Duraphat 5000 ppm | From 16 years old | |
| 4. | ELMEX junior | Fluoridating paste | 6–12 years |
| 5. | ELMEX | From 13 years old | |
| 6. | LACALUT Extra Sensitive | Paste that reduces tooth sensitivity | For adults |
| 7. | Colgate Sensitive Pro-Relief | ||
| 8. | PRESIDENT Sensitive | ||
| 9. | LACALUT Sensitive, 300 ml | Rinse for sensitive enamel | From 15 years old |
Disturbance of sensations
General information
Sensation and perception are closely related.
Both one and the other are the so-called sensory reflection of objective reality, existing independently of consciousness and due to its influence on the senses: this is their unity. A sensation is a reflection of a separate sensory quality or impression of the environment. Sensations and perceptions, therefore, are united and different, and constitute the sensory-perceptual level of mental reflection. At the sensory-perceptual level we are talking about those images that arise from the direct impact of objects and phenomena on the senses. Sensations are a reflection in the consciousness of objects and phenomena acting on the senses at the moment. Sensation disturbances occur in the following psychopathological diseases:
- Hyperesthesia. Impaired sensitivity, which is expressed in super-strong perception of light, sound, smell. Characteristic of conditions after previous somatic diseases, traumatic brain injury. Patients may perceive the rustling of leaves in the wind as like rattling iron, and natural light as very bright.
- Hyposthesia. Decreased overall sensitivity to sensory stimuli. The surroundings are perceived as faded, dull, indistinguishable. This phenomenon is typical of depressive disorders.
- Anesthesia . Loss of tactile sensitivity, or functional loss of the ability to perceive taste, smell, or individual objects, is typical of dissociative disorders.
- Senestopathies . Unusual complex sensations of the body with the experience of displacement, transfusion, overflow. Patients report tickling moving inside the brain, fluid pouring from the throat to the genitals, stretching and compression of the esophagus, and other unusual sensations.
- Paresthesia . Feeling of tingling, burning, crawling. A common case of somatoform mental disorders and somatic diseases. Paresthesias are caused by the peculiarities of blood supply and innervation, which makes them different from senestopathies. Heaviness under the right hypochondrium has long been familiar to me, and occurs after fatty foods, but sometimes it spreads to pressure above the right collarbone and into the right shoulder joint.
- Phantom syndrome. Occurs in patients with the absence of any limb. The patient represses the absence of a limb and seems to feel pain or movement.
Sensation disorders
Impaired sensation may be associated with damage to the peripheral and central parts of the analyzers and pathways of the central nervous system. The sensation of pain usually indicates irritation of pain receptors by the painful process, and may also represent damage to the nerve trunks (phantom pain). In mental illness, sensations can be formed in the brain regardless of the information coming from the analyzers. This is the nature of psychogenic hysterical pain, which is based on the mechanism of self-hypnosis.
depressive syndrome are very diverse (pain in the heart, pain in the abdomen, headaches, etc.). All these disorders cause lengthy and unsuccessful examinations and treatment by a therapist or even a surgeon. Features of the mental state largely determine the threshold of sensitivity, examples of changes in which in mental disorders are symptoms of general hyperesthesia , the phenomenon of hysterical anesthesia.
Hyperesthesia is characterized by a general decrease in the threshold of sensitivity, which is perceived by the patient as an emotionally unpleasant feeling with a hint of irritation. This leads to a sharp increase in susceptibility to even extremely weak or indifferent stimuli. Patients complain that they cannot fall asleep because “the alarm clock is ticking right in the ear,” “the starched sheet rattles like a tram,” “the moon is shining straight into the eyes.” Dissatisfaction is caused by phenomena that were simply not noticed by the patient before, for example:
- sounds of dripping water;
- the beat of your own heart.
This disease is one of the characteristic manifestations of asthenic syndrome , as part of which it is observed in many mental and somatic diseases. Hyperesthesia acts as the main disorder in the mildest neurotic diseases, for example, neurasthenia.
Hypoesthesia is manifested by a decrease in sensitivity, manifested by an unpleasant feeling of change, dullness, and grayness of the surrounding world. Patients note that they cease to distinguish shades of color and the taste of food; sounds seem muffled to them, uninteresting, coming as if from afar. Hypoesthesia is characteristic of depression. With this syndrome, it reflects the general pessimistic background of the patients’ mood, suppression of desires and a general decrease in interest in life.
Hysterical anesthesia is a functional disorder that occurs in individuals with demonstrative character traits immediately after the effects of psychotrauma. With hysteria, both loss of skin (pain, tactile) sensitivity, as well as loss of hearing or vision are possible. The patient is absolutely sure that there is a gross sensitivity disorder.
Areas of cutaneous anesthesia do not always correspond to typical areas of innervation. Instead of the smooth transition characteristic of polyneuropathy from a healthy area of skin to the insensitive distal part of the limb, a sharp border is possible. An important sign of the functional hysterical nature of the disorder is the presence of unconditioned reflexes, for example, the “gaze tracking” reflex (while vision is preserved, the eyes are fixed on objects and cannot move simultaneously with turns of the head).
With hysterical cutaneous anesthesia, an atypical persistence of the reaction to cold objects in the absence of pain sensitivity is possible. With hysterical neurosis, anesthesia can be observed for a relatively long time, but more often it occurs in a demonstrative personality as a transient reaction to a specific traumatic event. In addition to a general decrease or increase in sensitivity, a manifestation of a mental disorder is the occurrence of atypical or pathologically perverted sensations. Paresthesia is a common neurological symptom observed with damage to peripheral nerve trunks (for example, with alcoholic polyneuropathy). It is expressed in a feeling of numbness, tingling, and “crawling” that is familiar to many.
Paresthesia is often associated with a transient disruption of the blood supply to the organ, for example:
- while sleeping in an awkward position;
- during strenuous walking;
- in patients with Raynaud's disease.
Senestopathies are a symptom of mental disorders, manifested by extremely diverse, always extremely subjective, unusual sensations in the body, the vague, undifferentiated nature of which causes serious difficulties for patients when trying to accurately describe the feeling they are experiencing. For each patient, it is completely unique, not similar to the sensations of other patients.
Algorithm of actions for hyperesthesia
- Adjust your diet. Avoid completely or significantly reduce the consumption of foods and drinks containing acids and sugar. Especially fruit and berry juices, wine, candies. Eat more green vegetables, fiber-rich foods, and whole grains.
- Change your toothpaste. Never use bleach. Choose from those labeled "Sensitive".
- Check if you are practicing proper oral hygiene. If it's wrong, correct it.
- Make an appointment with your dentist to find out the type of tooth sensitivity, find out the cause and get treatment.
- Visit the dentist twice a year, even if nothing hurts.
How to cure hyperesthesia?
The method of treating the disease directly depends on the causes of its occurrence. For example, if there is caries, it is necessary to prepare the tooth and install fillings. If the problem is exposed tooth roots, surgical intervention may be necessary: the gums will be raised to a physiologically normal level.
Another option to combat the problem is the fluoridation procedure: an additional protective layer will significantly reduce the unhealthy reaction of the enamel to irritants. Sometimes sensitivity occurs as a side effect of bite problems. In this case, the patient may be offered orthodontic therapy.
Author:
Treatment of hyperesthesia in the “Family Doctor”
If hyperesthesia occurs, make an appointment with a dentist by calling the contact center in Moscow +7 (495) 775 75 66 or using the online appointment form. Our clinic has been operating for more than 26 years. Experienced doctors help patients cope with pressing problems, including hypersensitivity.
The doctor will find out the cause of tooth sensitivity and provide effective treatment. In most cases, it is enough to select suitable oral care products and carry out proper hygiene procedures. In more complex situations, full treatment is used, and if necessary, surgical treatment.
The clinic takes a gentle approach to patients. All procedures are accompanied by adequate pain relief, which eliminates the occurrence of discomfort and pain. Increased sensitivity of teeth is not just a feature of them. This is the beginning of a disease that must be cured. And it's better to do it as quickly as possible.
Hypersthesia in children
Dental hyperesthesia in children, in most cases, is associated with non-carious lesions of the enamel:
- Thinning of enamel prisms, resulting from microcracks and defects;
- Bite pathology leading to abrasion of hard tissue structures;
- Traumatization of teeth;
- Treatment not carried out in a timely manner, leading to exposure of the root parts of baby teeth;
- Abuse of soda and sugar-containing products;
- Adolescence (10-14 years) during the eruption of several permanent teeth with still immature enamel.
At the appointment, the dentist will examine the child and diagnose the pathology. He will tell you in detail about preventive measures (remineralizing therapy, fluoride pastes) and treatment.