Removing a tooth is the last thing a dentist will suggest. Due to a number of subjective and objective reasons, it is impossible to maintain the dentition in ideal condition until old age.
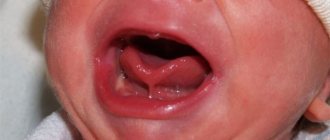
Dental defects are the loss of one or more dental units, leading to a violation of the integrity of the dentition, deviation in the development of physiological occlusion, and an abnormal arrangement of individual teeth.
Reasons contributing to the development of dental defects
Dental defects arise due to:
- untimely treatment of caries;
- inflammatory processes in the oral cavity;
- presence of malocclusion;
- genetic conditioning;
- diseases leading to changes in metabolic processes;
- damage to the jaw apparatus;
- various neoplasms.
Classification of anomalies of the dentofacial system
Bite defects develop for various reasons and cannot be ignored. This problem concerns not only aesthetics, but also general health. The pathological arrangement of teeth affects the functionality of the jaw. Due to poor quality of chewing food, various problems with the digestive organs arise.
Modern orthodontics offers effective treatment methods for children and adults with defects in the dental system. But, first of all, you need to make a correct diagnosis and determine the degree of complexity of the anomaly, which will allow the specialist to choose the right treatment in each specific case.
Let's start with the main thing - the classification of anomalies of the dental system, displayed in the diagnosis. We propose to consider the division of anomalies according to etiological and morphological characteristics (Kalvelis classification , orthodontics
).
Types of anomalies:
1. Anomalies in the number of teeth - supernumerary teeth, partial or complete hypodontia.
2. Anomaly of shape and size – ugly shape, spiky, oversized teeth.
3. Defects in the structure of hard dental tissues.
4. Premature or delayed teething in children.
5. Anomalies in the position of individual teeth in a row: distal, palatoglossal, mesial, labiobuccal, etc.
6. Diastema (disproportionately large spaces between teeth).
7. Crowding of teeth in a row.
8. Anomalies in the shape of the dentition (asymmetrical arrangement, V-shaped, etc.).
9. Sagittal malocclusion.
10. Vertical malocclusion (deep, open).
11. Transverse malocclusion (narrowed rows, disturbed relationship of lateral teeth, etc.).
Anomalies of the dental system can be genetic, congenital or acquired. For example, intrusion is quite common in orthodontics.
, in which partial or complete immersion of the tooth crown into the alveolar process occurs, and the root moves into the jaw bone. This anomaly is acquired in nature and occurs as a result of tooth trauma due to a strong blow or fall.
Hypoplasia and hyperplasia
These are rare congenital pathologies. With hypoplasia, the enamel is underdeveloped or absent altogether. With hyperplasia, its quantity, on the contrary, is excessive. Such disorders arise due to metabolic failure, general pathologies of fetal development, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as health problems that arise in women during pregnancy. Usually the problem of hyper- and hypoplasia is solved in childhood by removing “extra” or replenishing missing hard tissues. Sometimes those who had congenital hypoplasia may require more frequent remodeling therapy in adulthood.
Diagnosis of anomalies of the dentofacial apparatus
In modern orthodontics, various diagnostic methods are used, allowing specialists to make accurate diagnoses and select an effective treatment protocol. One of the diagnostic stages for malocclusion pathologies is the calculation of TRG.
TRG - teleroentgenogram involves taking an x-ray in the lateral and direct view, which clearly displays the soft tissues and bone structures of the skull.
How to calculate TRG orthodontics
: The interpretation of the TRG image is carried out by a diagnostician. The conclusion indicates the exact dimensions of the jaws, the angle of inclination of the teeth, the type of growth of the facial skeleton and other important details, on which the correctness of the diagnosis and the choice of treatment method largely depend.
In modern dental centers, TRG diagnostics are carried out using digital equipment. The images are interpreted using special computer programs that show the most accurate research results.
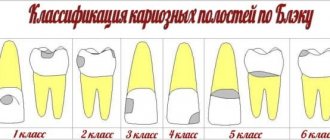
Erosion
Looks like areas of damaged enamel with a changed shade. In the affected areas, during erosion, hard tissues soften, gradually collapse, and a cavity is formed that reaches the dentin. At this stage, the tooth begins to hurt, react to any irritants, and the defect itself becomes clearly visible. Erosion has several possible causes:
- frequent consumption of sour or sweet foods;
- brushing teeth with hard brushes or pastes with an abrasive effect;
- low calcium content in hard tissues (due to metabolic disorders, pregnancy, certain diseases).
Erosion looks like a spot with a smooth, non-shiny surface. It is treated by performing remineralization and tooth restoration. It is important to find and eliminate the cause of the defect. If this is not done, erosion will appear in new places.
What are mouth guards in orthodontics?
Mouth guards are special designs used to correct malocclusion and dental defects. Unlike braces, they are outwardly invisible and do not interfere with diction.
Features and advantages of mouth guards:
- have a transparent plastic or silicone base;
- you can remove it yourself and carry out thorough hygienic care;
- soft structure that does not injure the oral cavity and does not damage tooth enamel;
- aesthetic designs ensure a tight fit to the teeth;
- do not create discomfort for the patient;
- do not require restrictions on food intake.
The only disadvantages of orthodontic aligners include their higher cost compared to braces, as well as a longer treatment period.
Indications for wearing mouth guards:
- slight curvature of teeth;
- rotation, crooked teeth;
- large gaps between crowns;
- elongation or shortening of dental alveoli;
- abnormal position of the upper canines;
- crossbite (effectively handled by McNamara mouthguard
).
Orthodontics
considers other indications for wearing a mouthguard. Such designs have an undeniable mass of advantages, are easy to maintain and completely invisible to others. They are made in dental laboratories individually for each patient using a dental impression. Installing the aligners takes only a few minutes.
Orthodontic aligners are also used to consolidate the results after wearing braces.
Dental defects
Treatment of dental defects
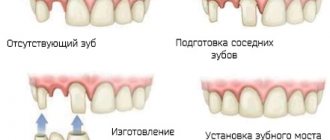
Correction of dental defects is carried out using prosthetics.
Thanks to modern materials, high aesthetic results can be achieved. To treat included dental defects, bridges are used, and defects on one or both sides are replaced using removable clasp prosthetics. The first stage of treatment for dental defects will be an examination of the patient, after which the orthopedic surgeon will select the optimal method of prosthetics. After selecting a personal design, the oral cavity is sanitized. This procedure involves the elimination of roots and teeth that cannot be cured, the removal of dental plaque and the treatment of caries. Preparation of the supporting teeth involves grinding and preparation, after which an impression of the jaw is made. Based on the impression, crowns are made in the laboratory for the abutment tooth, the color of which is selected individually for each patient. After fitting, the final design is developed, which is fixed in the oral cavity using a cement mixture.
Dental prosthetics with fixed dentures corrects damage of varying severity. Minor damage can be restored using inlays, crowns and veneers. Significant defects in the dentition can be corrected using bridges on implants, using metal-free ceramics and metal-ceramic crowns. Fixed structures are characterized by durability, convenience and practicality, and also guarantee an aesthetic appearance.
Removable prosthetics
Edentia and significant dentition defects require the use of removable dentures, which are made from acrylic plastics using injection molding followed by cold or hot polymerization. Thanks to modern techniques, dentures have a warranty period and high wear resistance, which allows them to be replaced and repaired much less frequently. The shape, color and size of future structures are selected personally for each patient based on the characteristics of the structure of the dentofacial apparatus.
Partially removable prosthetics
Treatment of dental defects can be carried out using partially removable prosthetics, which is performed in the following cases:
- renewal of the main chewing teeth;
- absence of teeth over a significant extent;
- if the patient refuses to grind adjacent teeth;
- impossibility of installing bridge structures;
- presence of tooth wear and deep bite.
Nylon designs
With the help of nylon structures, large defects and minor flaws in the dentition can be healed. They do not change their shape and structure in conditions of high moisture and under the influence of aggressive chemical substances, and also have strength, flexibility and the ability to withstand mechanical loads. Nylon dentures are suitable for people with incompatibility with other prosthetic components and materials. They are attached with alveolar clasps and match the color of the gums, making the design invisible to others and does not harm healthy teeth and gum tissue.
Ceramic dentures
Ceramic dental structures are widely used to restore front teeth. They are elastic and lightweight, capable of imitating the translucency and shape of natural enamel. Ceramic dentures can hide defects of varying severity, which is why they are used in cases of tooth decay. Experts recommend ceramics because it does not injure the oral mucosa and gum tissue, is harmless to bones, is not susceptible to microorganisms, and does not enter into various reactions. Proper hygienic care and proper operation of structures affects the external condition. Proper manufacturing is important so that dentures do not cause the sensation of a foreign particle in the mouth.
Thanks to various technologies, the availability of dentures makes it possible to restore the dentition, defects of which not only disrupt the appearance, speech and chewing functions, but also lead to repeated deformations. Therefore, choosing a qualified specialist is very important, since incorrect prosthetics can provoke serious consequences and even loss of supporting teeth.
Diagnostics
To successfully treat patients, a thorough examination must be performed. When initial signs appear, patients should consult a dentist. He will examine the oral cavity, assess the condition of the gums and chewing organs. If necessary, the patient will be referred for additional studies. According to indications, instrumental diagnostics are prescribed. If consultation with an endocrinologist, therapist, or gastroenterologist is needed, the patient is referred to these specialists. Consulting an orthodontist is important for drawing up a correction and prosthetic plan.
As a rule, the pathology has a specific severity, so it is diagnosed during a visual initial examination. Establishing provoking factors most often requires additional diagnostic procedures. In order to make a final diagnosis, as well as determine therapeutic methods, doctors may refer the patient for radiography. It will allow you to obtain complete information and create the correct treatment plan.
Pigmentation
If this defect appears, the color of the tooth changes. It may turn brown, gray or almost black, pink or red, yellow. The shade depends on what dye is applied to the crown. For example, if it is tea or coffee, the color will be brown, and if it is nicotine tar, it will be yellow or grayish. If the color of the crown changes unevenly and clearly visible pigmented areas appear, this indicates enamel defects. It absorbs dyes better where there is demineralization and the structure of the fabric is damaged. Pigmentation itself is not dangerous, but it can be associated with other dental health problems. It often appears in the presence of chips, poor hygiene, and some concomitant diseases. To restore pigmented areas, professional teeth cleaning and remineralization are performed. Sometimes whitening, restoration of crowns or installation of veneers may be required.
Necrosis
This is the death of hard tissue cells, due to which multiple defects appear on the surface of the crowns, as well as on the tooth root. The structure of the cells changes, and destruction can affect not only dentin, but also the pulp. Necrosis is rare and is usually not directly related to the condition of the teeth. It can be caused by severe toxin poisoning, hormonal imbalance, or severe systemic diseases. Treatment at the dentist is symptomatic: restoration of hard tissues, remineralization, prosthetics for complete tooth destruction. The main therapy must be related to the disease that caused the necrosis, and dental treatment only complements it.
You have questions?
We will call you back within 30 seconds
+7