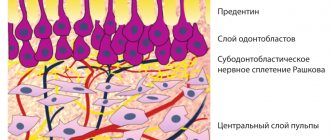
Compomer materials are used for restoration and filling of chewing and anterior teeth. Compomers are composite reflective materials for filling, for the manufacture of which glass ionomers and composites are used. Such glaciosites include an organic base in the form of carboxyl modified groups and methacrylate resin. Aluminosilicate glass is used as a filler for mixtures.
Properties of compomers
Compomers combine the positive properties of glass ionomers and aluminosilicate glass. In fact, it is a combination in the form of photopolymerizable composites and glass ionomer polymers, characterized by color fastness, high aesthetics and ease of application. Biological compatibility is good, as is adhesion to dentin tissue. The composition includes fluorine, which has protective and preventive functions.
Properties:
- single-component composition;
- chemical adhesion;
- the total shrinkage of the mass is small;
- high aesthetics;
- cumulative effect due to fluoride content;
- biological compatibility;
- solubility in natural oral fluids is low;
- the surface is polished after installation;
- the level of expansion is close to that of tooth tissue;
- Curing requires two steps - exposure to light and absorption of natural oral fluids.
Principles of caring for fillings
In order for the filling to serve for a long time and efficiently, it is necessary:
- Regularly treat all areas of caries;
- Carefully observe oral hygiene;
- Review your diet, exclude those that destroy enamel - sweets, lemonades, carbonated drinks, unnatural juices, ketchups and sauces;
- Avoid temperature changes while eating;
- The lack of calcium in the body must be replenished with cottage cheese, natural dairy products and calcium carbonate tablets.
Kinds
All compomers are divided into three large groups - packable, medium creamy, liquid-flowing. The materials being packed are quite viscous; they are rubbed into the surface with a tool. The content of organic components is high, but the hardness is insufficient. Used only for those teeth where chewing loads are the lowest.
Medium-consistency ones have a cream-like composition. They are universal and are used to fill various types of cavities. They have good characteristics, strength, durability.
Liquid materials are recommended for use in situations where the use of packaging materials is severely limited. They are easy to apply, harden quickly, and have good characteristics.
Materials are also divided into fixing, restorative, and insulating mixtures. Special materials are produced for the treatment of temporary units, fissure filling, and others.
The materials include:
- acrylic resins that provide polishability, such indicators as viscosity, strength, resistance to mechanical loads;
- polymerization initiators (ethyl 4-dimethylaminobenzoate, camphorquinone);
- thickeners in the form of silicone dioxide;
- aluminum glass (strontium-aluminium-sodium-fluoro-phosphorosilicate glass);
- strontium fluoride, providing fluoride therapy, protective, preventive effects;
- iron oxide, titanium dioxide for coloring the mixture and giving the required, lasting shade.
Overview characteristics
Compomers get their name from the combination of restorative materials such as composites and glass ionomers.
This type of material is polymerized through double curing. Initially, methacrylate resins are activated under the influence of ultraviolet rays. Subsequently, under the influence of oral fluid, glass ionomer components are bound directly inside the filling.
It is important to know! During the second stage of curing, the installed filling can increase in volume by up to 3%. This compensates for the process of possible shrinkage of the material.
Initially, it was assumed that the combination of composite materials and glass ionomer cements would absorb the best positive qualities of these compounds. But, as practice has shown, these expectations were not met. Therefore, to ensure high strength, glaciosites are used in tandem with adhesives.
Basic properties of compomers
- One-component.
- Chemical type of adhesion (due to the presence of GIC).
- Acceptable aesthetic qualities inherited from composites.
- Small total shrinkage.
- Relatively high strength.
- Accumulative effect on fluoride (absorption from dental care products and release into tooth tissue).
- Low solubility in oral fluid.
- Thermal expansion similar to that of dentin.
- Good polishability.
Curing (polymerization) of compomers occurs in two stages. First, acrylic resins are polymerized under the influence of light irradiation. Then, as oral fluid is absorbed, the glass ionomer fillers begin to harden.
During the second stage, dentin and enamel are enriched with fluoride ions. At the same time, due to the absorption of liquid, the filling material increases in volume, which partially compensates for the shrinkage that occurred during the 1st stage.
Compound
Compomers contain many chemicals that provide different properties of the material and distinguish them from each other. The main components of glaciosites are:
- acrylic resins (UDMA, dimethacrylate, triethylene glycol-dimethacrylate, trimethacrylate) – acting as a matrix (binder), providing strength, viscosity, polishability and other physical and mechanical properties;
- camphorquinone, ethyl 4-dimethylaminobenzoate – polymerization initiators;
- strontium-aluminium-sodium-fluoro-phosphorosilicate glass>;
- silicone dioxide - thickener;
- strontium fluoride – a source of fluoride ions for fluoride therapy;
- titanium dioxide and iron oxide are coloring pigments.
According to their intended purpose, there are restoration, fixing and isolating compounds, materials for the treatment of baby teeth, restoration of the cervical area (with a color to match the gum), for filling fissures, etc.
Indications
The use of the first compomers was limited by insufficient strength and wear resistance.
Over time, manufacturers have improved the quality of the drug by reducing the particle size of the filler and modifying the composite monomers by forming cross-links.
This made it possible to increase the strength and wear resistance of the material, and expand the scope of its application. Currently, compomer indications are determined by the specific brand and grade.
Generally speaking, without reference to the brand or mark, compomers can be used in the following cases:
- Filling cavities of class 1-5 in temporary teeth, provided that the tooth cavity is well isolated from saliva, blood and oral fluid.
- Filling small (not exceeding 2/3 of the distance between the cusps) class 1 and 2 cavities in permanent teeth.
- Restoration of defects in the cervical area exposed during tooth preparation.
- Filling areas of enamel erosion.
- Restoration of cervical defects of non-carious origin (erosions, wedge-shaped defects).
- Filling traumatic injuries as a temporary measure.
- Use as protective gaskets.
- Filling small cavities of classes 1 and 2 in permanent teeth after minimally invasive preparation (preferably using packable compomers).
- Temporary filling of permanent teeth.
- Treatment of cavities of any class in teeth covered with a crown.
- Fixation of orthodontic and orthopedic structures.
Contraindications
- Allergy to meth and acrylate plastics or adhesive components.
- Class 1 and 2 cavities with dimensions exceeding 2/3 of the intertubercular distance.
- Restoration of the tooth stump.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
- fluoride release continues for about 300 days;
- The material is elastic, easy to use;
- shrinkage is low, and the material does not crack;
- special disinfection before filling is not required, nor is the use of additional etching components.
The material is universal, used for treatment and restoration due to its properties. But, despite the multiple advantages, compomers have a number of disadvantages:
- color changes over time due to absorption of oral fluids;
- aesthetics are lower than that of composite materials;
- marginal fit is insufficient;
- bending strength and elasticity are lower than those of analogues based on pure composites;
- only mechanical retention, that is, there is no chemical connection with dentin tissues.
Indications for use
Indications:
- restoration, filling cavities due to caries;
- restoration of temporary (baby) teeth;
- treatment of enamel erosion;
- elimination of wedge-shaped defects;
- treatment of class 5 cavities;
- filling small cavities of classes 1-2 for permanent teeth;
- restoration for traumatic lesions;
- fixation of orthopedic and orthodontic structures;
- treatment of dentin under crowns;
- use in the form of gaskets with protective properties.
Contraindications
The use of materials has a number of contraindications:
- allergic reactions to components of dental glue, actylate and methacrylate plastics included in compomers;
- cavities of class 1, 2, the dimensions of which exceed two-thirds of the distance between the tubercles;
- restoration of the stump of the unit is required.
Manufacturers
Compomer filling materials are available from many brands, including Dentsply, Voco, Vivadent, DMG, 3M, Espe and Kerr.
Dentsply offers restorative universal materials from the manufacturer Dyract Extra 3rd generation. They are used for filling cavities of various types for units at any position in the row. The filling material contains fluoride; the materials have a cariesstatic effect. The product has a creamy consistency, which allows you to quickly apply the material, filling cavities. The advantages include abrasion resistance, properties comparable to composites, and a good range of shades.
VOCO offers Glasiosite materials - a condensable, easy-to-use, universal material with radiopaque properties, used to fill cavities of four classes - 1-3, 5. The product is suitable for restoration, including aesthetic, sealing of existing fissures, treatment of the frontal part of the row. The advantages of Glasiosite materials include:
- conducting fluoride therapy;
- stability, transparency of the shade;
- surface polishability after polymerization;
- abrasion resistance;
- strong bond with dentin tissues, thanks to self-etching special glue.
Twinkie Star is a material used to restore time series units. The eight-color compound with a slight glitter effect contains fluorine and is durable and abrasion-resistant. Thanks to its interesting glitter effect, the composition has an excellent motivating effect for the treatment of caries and other problems in children.
The cost of using the product depends on the chosen option, for example, a set of 40 compules produced by Dyract Extra costs approximately 8.5 thousand rubles. A set from Twinkie Star for treating children with colored sparkles - about 7 thousand rubles for a similar volume. Installation for one cavity also depends on the material and complexity of treatment; on average, the cost is 1-2.5 thousand rubles, excluding other measures aimed at eliminating the problem.
Types of cements
Dental cements and other filling compounds are used in the treatment of permanent and primary teeth in the form of fillings, linings, obturation materials and sealants.
They are classified according to their basis, and can be of the following types:
- Mineral cements. They are made on the basis of phosphoric acid, which is why they are called “phosphates”. These include zinc phosphate, silicate and silicophosphate compounds.
- Polymer cements. They use organic acid as a base, usually polyacrylic acid. This group includes polycarboxylate and glass ionomer cements.
- Oil-based formulations. The main material of this group is zinc oxide-eugenol cement.
- Water-based materials (water-based dentin).
Phosphates
Phosphates in pediatric dentistry are used as a permanent filling material or to form insulating linings.
The powder consists of 70-90% zinc oxide. It requires liquid to mix it.
The mixture hardens in 3-9 minutes at room temperature, but this time can be increased if you use a cooled plate when kneading.
The substance has the following advantages:
- fast hardening;
- good strength characteristics;
- plastic;
- low level of shrinkage.
However, such a substance has low aesthetic appeal, wears off quickly and can break, and irritates the pulp. The product does not provide an antibacterial effect, although many manufacturers have begun to add silver to the composition.
Phenolates
Zinc oxide eugenol cement is produced in the form of a white powder containing oxides of magnesium and zinc.
To mix the solution, a liquid containing eugenol with cottonseed oil (or olive) is required. Depending on the type of material, it takes 5 minutes or about 24 hours to harden.
The advantages are:
- acceptable level of acidity (pH 6.6-8.0);
- no impact on the pulp;
- antiseptic and bactericidal properties;
- slight anesthetic effect;
- good ductility and ease of use;
- radiopacity.
Disadvantages include solubility under the influence of saliva, insufficient mechanical strength, and the ability to disrupt the polymerization of composites, therefore it is not used as a base.
Polycarboxylates
Polycarboxylate cement is a powder containing calcium salts, magnesium and zinc oxide. It also sometimes contains colored pigments.
The substance is used for filling both temporary and permanent teeth. The main characteristic is good adhesion to enamel and dentin.
At room temperature, the mixture hardens in 2-3 minutes, at 37 degrees this time increases to 6-9 minutes.
The product has the following advantages:
- high adhesion to dentin and tooth enamel;
- practically does not irritate the pulp;
- complete biological compatibility with tissues;
- antibacterial effect;
- radiopacity.
However, this product has disadvantages. It is not durable enough, there are difficulties in use due to the short working time. Aesthetic unattractiveness and the presence of shrinkage are also noted.
There is also difficulty in removing excess cement. If the procedure is carried out too late, the composition will be difficult to separate from the enamel. Cleaning too early will damage the edge seal.
Acrylates
Such cement compositions are two-component. They are presented in the form of liquid and powder, two pastes. The powder contains quartz or borosilicate glass.
The mass hardens in 6-7 minutes, and the total working time is 10-11 minutes. This cement is characterized by high strength and resistance to the oral environment.
However, it is difficult to work with; the material irritates the pulp. Excess is difficult to remove.
Composites
The most common materials for filling teeth are light-curing composites. They freeze under the influence of light of the appropriate frequency. In appearance they are most compatible with the shade and structure of tooth enamel. They are distinguished by excellent strength, can be polished well and are almost invisible on the teeth. Due to their high height, these fillings are ideal for installation on the front teeth.
Plastic materials
Chemically cured plastics are used as filling materials. Such fillings harden fairly quickly, do not cause irritation to the oral cavity, and are resistant to chemical reagents.
Carbondent, acrylic oxide or polymethylsiloxane are used for manufacturing. The materials are resistant to abrasion, but due to subsidence, chemical toxicity and changes in the original shade in dentistry, plastic is used mainly for installing temporary fillings.
Metal fillings
To create metal fillings, alloys based on copper, silver, mercury and other metals are used. Since such materials do not serve an aesthetic function, dentists usually use them when filling molars. They are highly wear-resistant and affordable.
Almagams
Inexpensive and durable, almagam material consists of zinc, tin, silver and mercury, which gives it a dark color. Most often, almagama is used as a filling to treat chewing teeth. Advantages include durability, ductility, ease of installation and low cost. Disadvantages - unsightly appearance, long hardening, release of mercury vapor, increased thermal conductivity and shrinkage of the material.
Gold alloy
Fillings made from precious metals or their analogues are not particularly popular in dentistry. Most patients today prefer naturalness and authenticity. If the patient chooses a gold alloy as a filling material, then you should pay attention to some features: durability, excellent strength, but rather high cost.
Compomers
Good restoration materials for making fillings are compomers - composite-ionomer compositions. Compomers perfectly combine the best qualities of glass ionomers and composites, which provides the material with excellent chemical adhesion, biocompatibility, ease of installation, preservation of the original color and aesthetics.
This is interesting: What is tooth depulpation, depulpation (pulp removal) of a tooth during prosthetics
Due to the low release of fluoride and insufficient strength, filling teeth with compomers is advisable in cases where it is necessary to achieve maximum aesthetics.
Experts' opinions
Today, experts advise using high-quality composite materials for the treatment of permanent teeth in children. Photopolymers are used if the patient sits quietly in the doctor’s chair and gives him the opportunity to thoroughly clean the aching tooth.
You should not place such fillings if the carious process is advanced and hygienic care is insufficient. In this case, the photopolymer will be fixed to the weak enamel.
When installed correctly, the composite will last a long time. The product ensures the aesthetics of the tooth and has excellent adhesion. Minimal preparation is required to apply the composite.
If primary molars are subject to repair, then cement filling materials are suitable . They are not strong enough to be placed on chewing teeth. They are best used for temporary fillings.
Price
Compomer compositions, despite some negative aspects, are widely used in dentistry. This is due to the fact that they have high strength, low shrinkage, and, importantly, prevent the re-development of carious cavities. In addition, they can be used for the restoration of frontal teeth.
The pricing of compomer cements is influenced by their release form and the brand name of the company.
So the cost of restoration material from the manufacturer Ionosit-Baseliner (DMG) will range from 600 to 800 rubles.
The average price for a Twinky Star set is approximately 5500-7000 rubles. For most types of material, the cost will be within 7,000 rubles.
Reviews
Filling with compomers differs little from treatment with composite materials. In both cases, light-curing pastes are used.
If you have had your child have MagicFil or Twinky Star colored fillings, please tell us about his or her reaction to the procedure. You can leave a review at the bottom of this page.
Sources:
- https://zubovv.ru/detskaya-stomatologia/d-zubi/plombirovochnyih-materialov.html
- https://www.vash-dentist.ru/detskaya-stomatologia/d-zubi/plombirovochnyie-materialyi.html
- https://berezkadent.ru/service/terapiya/lechenie-kariesa/plombirovanie-zubov/
- https://zubovv.ru/lechenie/zubyi/plombyi/kompomernyih-materialov.html
- https://www.vash-dentist.ru/lechenie/zubyi/plombyi/kompomernyih-materialov.html
- https://dentazone.ru/preparaty-oborudovanie/materialy/kompomery.html
- https://my-ort.ru/novosti/kompomery/
- https://uvr.spb.ru/healing/plomby.html