Drugs
- Entrop
- Enterofuril
- Entoban
- Enterospasmil
- Enterosgel
- Enterolax
- Enterokind
- Enterol
- Enterogermina
- Enkorat
Alexey Portnov, medical editor Last edited: 06/24/2018
x
All iLive content is reviewed by medical experts to ensure it is as accurate and factual as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable sites, academic research institutions and, where possible, proven medical studies. Please note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to such studies.
If you believe that any of our content is inaccurate, out of date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
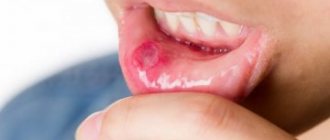
Stomatitis, not complicated by temperature or intoxication, especially in the initial stage, can be cured with the help of local applications with special gels. In this case, ointments are not so effective, since the fat base does not allow rapid absorption of the main medicinal components into the mucous membrane. The gel form is more effective, the gel is better absorbed and its active ingredients penetrate well into the source of inflammation, stopping it. Gel for stomatitis can be intended for anesthesia, but most often it also includes anti-inflammatory components, so this remedy rightfully belongs to the category of combined topical preparations. The gel is selected by the doctor according to the type of inflammation, its severity, and the location of aphthae (ulcers).
Let's consider the most effective gel forms of medications that help reduce the intensity of symptoms of stomatitis:
- Stomatitis caused by a virus often manifests itself not only in the oral cavity, but also on the lips. In such cases, external agents are prescribed in the form of ointments, and the internal cavity is treated with applications of an effective interferon gel - Viferon. The drug is applied to slightly dried inflamed areas, three times a day for a week. Viferon gel has an excellent effect on the inflammatory process, regardless of the patient’s age and has no contraindications.
- Bacterial stomatitis, antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity for any type of inflammation are well controlled by Elugel. Elugel is a chlorhexidine-based product that can be used as a medicine and also as a local prophylactic drug. A wide spectrum of bactericidal action allows Elugel to be used to neutralize almost all types of bacteria and fungi. The gel is applied to damaged areas of the oral cavity 3-4 times a day, the greatest effect is achieved if the patient carries out parallel rinsing with Eludil solution. Please note that Elugel must be absorbed into the mucous membrane and does not require rinsing; solutions are usually used 2-3 hours after applying the gel applications.
- The initial stages of stomatitis are well treated with Cholisal-gel, which helps to anesthetize the inflammation and begin to neutralize it. Before applying Cholisal, the mouth should be rinsed with Miramistin solution; the procedure should be repeated 4 times a day for 7-10 days. Cholisal will also help to numb the resulting ulcers; the pain subsides literally 2-3 minutes after applying the gel, which is absorbed into the deep layers of mucosal tissue.
- After relief of acute symptoms, it is necessary to help the regeneration of mucosal tissue. Actovegin-gel comes to the rescue, which activates the process of restoration and healing of the oral cavity.
- Kamistad gel, which contains lidocaine and chamomile extract, has a good anesthetic effect. Kamistad is used not only as an anesthetic, but also as an antibacterial agent. By providing a local anti-inflammatory effect on the mucous membrane, Kamistad gel is able to alleviate the symptoms of stomatitis within a week and activate the healing process of the wound surface. Since the gel contains a large percentage of lidocaine, the product is used only as directed by a doctor.
- Herpetic stomatitis can be treated locally with Viru-Merz-Serol gel, which effectively relieves itching, pain and burning in the oral mucosa. The course of applying the gel is 5 days and should be stopped after the first vesicular formations appear.
- Antiseptic gel "Instillagel" contains two effective components - lidocaine and chlorhexidine. Simultaneous analgesia and antibacterial action provide fairly rapid neutralization of uncomfortable symptoms.
- Metrogyl Denta contains metronidazole and chlorhexidine. This combination of antibiotic and antiseptic provides rapid relief of the first signs of inflammation in the oral cavity, however, unlike Cholisal, Metrogyl Denta is not able to overcome the mucous membrane and is not absorbed into the deep layers of tissue. This gel for stomatitis is prescribed as a surface antibacterial agent that works in the initial stage of the process.
- Mundizal gel effectively fights inflammation and relieves pain in the oral cavity. This remedy can be used to treat stomatitis in both adults and children. The gel is able to be quickly absorbed and affect the deep layers of mucosal tissue, while simultaneously attaching to the surface of the oral cavity. Choline salicylate has an anesthetic surface effect, and tsetalkonium chloride, which is part of Mundizal gel, has an antimicrobial effect.
- Kalgel can help treat stomatitis in young children, which is also used during teething as a local antimicrobial and analgesic. Cetylpyridinium chloride has an antiseptic effect, and lidocaine relieves pain symptoms, however, these components can cause an allergic reaction, so independent use of Calgel is undesirable.
[1], [2], [3], [4], [5], [6]
Cholisal gel for teething
Using the drug when the first baby teeth appear in babies is quite dangerous, since the active work of the salivary glands will cause saliva flowing from the child’s mouth to irritate the delicate skin. In addition, excess saliva can lead to more tragic consequences, as the baby may choke.
However, at an older age, the use of a gel to anesthetize the process and relieve inflammation is quite justified.
Before applying the drug, it is recommended to dry the gum area with a swab and lightly apply the product. Usually, the procedure is repeated 3-4 times a day, but for children of the younger age group, experts advise using special products that are produced in the form of:
- candles;
- syrups;
- tablets.
The appearance of wisdom teeth is also a rather painful process, however, the use of Cholisal gel in these cases is recommended if the following is not observed:
- discharge of purulent masses;
- swelling of the cheeks or gums;
- pain when swallowing;
- difficulty opening and closing the mouth;
- temperature rise;
- unpleasant smell
since, if such symptoms appear, you should immediately contact your dentist.
Metrogyl denta for stomatitis
In order to quickly cure stomatitis, you need to start therapeutic actions as early as possible. Metrogyl denta for stomatitis is an effective drug that helps stop a spreading infection at an early stage. Metrogyl gel adheres well to the mucous membrane without being absorbed into the deep layers of tissue, thereby capturing and limiting foci of inflammation. In addition to its antimicrobial effect, the drug relieves burning and itching well, the effect lasts up to 12 hours, after which the gel can be applied again.
Metrogil denta for stomatitis has the following advantages and positive characteristics:
What is aphthous stomatitis
Aphthous stomatitis is one of the manifestations of the disease, which can be recognized by its characteristic signs. Initially, slight redness appears on the mucous membrane, then swelling, accompanied by burning or pain. Afterwards, aphthae form - round or oval white sores with a red halo. In addition to painful sensations, a person begins to worry about increased salivation and bad breath. Sometimes the temperature rises. The aphthous form of stomatitis can be triggered by various reasons: infections, allergies, gastrointestinal diseases, vitamin deficiency, injuries, insufficient oral hygiene, etc.
Kamistad for stomatitis
Kamistad dental gel consists of an anesthetic - lidocaine, a plant component - chamomile tincture, cinnamon oil, benzalkonium chloride, ethanol, formic acid and auxiliary ingredients.
Such a rich combination of active ingredients together with the gel form makes Kamistad a very popular drug in the treatment of many diseases of the oral cavity - eruption of wisdom teeth in adults, mechanical irritation of the gums when wearing dentures, stomatitis and gingivitis.
- Lidocaine provides local anesthesia.
- Chamomile has a local anti-inflammatory effect and also helps in the process of tissue epithelization.
- benzalkonium chloride has antiseptic properties.
Kamistad for stomatitis is effective in the initial stage of the inflammatory process as a local anesthetic and anti-inflammatory agent. Not only honest manufacturers, but also dental practitioners note the rather moderate effect of Kamistad on inflammation, however, it can be used as the drug of choice when canceling another treatment method.
Advantages of the gel for stomatitis:
- Short anesthetic effect.
- Convenient gel form, which is fixed on the tissues of the mucous membrane.
- Ease of use.
- Good ability to distribute in the inflamed area.
- Possibility of using the gel for up to 2 weeks.
Disadvantages of Kamistad:
- Weak anti-inflammatory effect.
- Lack of components with antiviral effects.
- It should not be applied to the ulcerated mucosal surface, as benzalkonium chloride will irritate it and interfere with the regeneration process.
- It is not recommended for use in the treatment of pregnant women and during lactation.
- The gel is used with caution in the treatment of stomatitis in children. In this sense, various sources, as well as manufacturers, do not have a common opinion. There are recommendations for the use of Kamistad when cutting baby teeth; at the same time, there is information about the inadmissibility of applying the gel to children under 12 years of age. Obviously, infants will react to oral numbness with hypersalivation, which can lead to the ingestion of microbial-contaminated saliva. Consequently, Kamistad is used only as prescribed by a doctor, who determines the appropriateness and potential effectiveness of this drug.
How does Kamistad use for stomatitis? The gel is squeezed out into a small strip (up to 0.5 cm) and applied to the slightly dried surface of the mucous membrane and gums using a gauze swab. Application with a finger is not recommended even after antiseptic treatment of the hand; it is more convenient to use a special spatula or a cotton swab. The application regimen is from 3 to 6 times a day, depending on the type and stage of development of stomatitis.
Oral care during stomatitis treatment
Local treatment of stomatitis in adults plays an important role in the success of therapy. It is necessary to follow a gentle and low-allergenic diet. Food should be warm and soft, not irritating the mucous membranes. During treatment, you should exclude hard, spicy, sour, and sweet foods from your diet. After every meal you need to rinse your mouth. For this purpose, special remedies for stomatitis (solutions or infusions) can be used, which the doctor will recommend. They have an antiseptic effect and protect the oral cavity from the development of pathogenic bacteria.
An important aspect in the treatment of stomatitis in adults is pain relief, since aphthae and ulcers can cause significant discomfort, interfering with normal eating and talking. In this case, local painkillers such as Cholisal® have worked well. This gel has a local analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect for stomatitis in adults. The antiseptic included in the composition protects the oral cavity from bacteria. The analgesic effect of the gel against stomatitis occurs within 2-3 minutes and lasts from 2 to 8 hours. Such remedies for stomatitis in adults, in combination with the main therapy prescribed by the doctor, help cope with unpleasant sensations in the mouth and speed up the healing process.
Attention!
To make information easier to understand, these instructions for use of the drug “Gel for Stomatitis” have been translated and presented in a special form based on the official instructions for medical use of the drug. Before use, read the leaflet included directly with the medication.
The description is provided for informational purposes and is not a guide to self-medication. The need to use this drug, the prescription of the treatment regimen, methods and doses of the drug are determined solely by the attending physician. Self-medication is dangerous for your health.
How and how to treat stomatitis in children?
It just so happened that stomatitis “loved” the children more. This is very unpleasant, but not so scary, because competent and timely treatment with safe means will allow you to quickly get rid of the disease. To do this, the doctor must determine the cause of its appearance and the type, of which there are several. Only on the basis of the information received is a decision made on further prescription of the necessary drugs.
What medications are needed
In the case of herpetic origin of the disease, modern dentistry cannot do without the use of antiviral agents:
- Viferon suppositories or ointment. The frequency of their use is no more than three times a day, and treatment should not last longer than a week.
- Acyclovir. It is prescribed for injection, oral and/or topical use. The ointment is applied to the affected areas twice a day. If we talk about tablets, then an infant is given half the adult dose. Injections are given in consultation with the doctor.
- Oxolinic ointment. It is applied to the area of the rash up to three times a day.
For stomatitis caused by the action of fungi, the drug “Futsis” in tablet form shows good results. The daily dose, which is not recommended to be increased independently, is calculated using the formula “child’s weight/10 mg.” Nystatin tablets are also quite effective; they need to be dissolved in warm water until a paste is obtained, which is then applied to the required areas.
Types of stomatitis in children
Depending on the cause that caused the inflammation of the oral mucosa, the following types of stomatitis are distinguished.
Viral.
This type of stomatitis occurs most often. The virus is transmitted by airborne droplets, through toys, dishes, and household items. At first, the disease is often confused with a cold: the child becomes lethargic, the temperature may rise, a runny nose and cough may appear. Moreover, viral stomatitis often occurs against the background of various acute respiratory viral infections, for example, influenza, measles, chickenpox. Around the second day, aphthae begin to appear on the gums, inside of the cheeks, tongue or lips - small round ulcers of a light yellow hue with a bright red border. That is why such stomatitis is also called aphthous or ulcerative.
Bacterial.
This stomatitis often accompanies tonsillitis, sinusitis, and pneumonia. It can be recognized by the formation of a thick yellow crust on the lips, which tightens the red border, preventing the child from opening his mouth wide. Bacterial stomatitis often occurs as a result of decreased immunity and may be accompanied by an increase in temperature.
Traumatic.
Such stomatitis is caused by mechanical injuries to the oral mucosa, for example, biting the inside of the cheek or lips, burns from hot food, the habit of gnawing hard objects, etc.
Candida.
This stomatitis most often occurs in infants. The cause of its appearance is a fungus of the genus Candida. The fact is that breast milk, which remains in the baby’s mouth, is a favorable environment for the proliferation of this microorganism. Such stomatitis can be suspected by a persistent white cheesy coating in the oral cavity, under which red irritated tissue is hidden.
Release form, composition and packaging
◊ Dental gel
in the form of a colorless, transparent, homogeneous mass with the smell of anise oil.
| 1 g | |
| Choline salicylate | 87.1 mg |
| cetalkonium chloride | 0.1 mg |
Excipients: hyaetellose – 20 mg, methyl parahydroxybenzoate – 1.5 mg, propyl parahydroxybenzoate – 0.8 mg, glycerol – 50 mg, anise seed oil – 1.61 mg, ethanol 96% – 390 mg, water – up to 1000 mg.
pharmachologic effect
When applied topically, choline salicylate
quickly absorbed by the oral mucosa, providing local analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects. It inhibits the activity of COX, the functions of macrophages and neutrophils, the production of interleukin-1 and inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins. It also has antimicrobial and antifungal effects in acidic and alkaline environments.
Cetalkonium chloride
– antiseptic, acts on bacteria, fungi and viruses.
The gel ethanol-containing adhesive base ensures rapid development of the effect and retains the active substances on the mucous membrane for a long time.
The analgesic effect occurs within 2-3 minutes, while its duration is 2-8 hours.
Disease Gingivitis With caution
The drug should be used in children under 1 year of age.