Intrapulpal anesthesia allows you to quickly relieve pain using various methods. Most often, the drug is delivered to the affected area using a bur, but if necessary, the doctor can use the method of opening the caries hole and treating the surface. The drug is administered in a minimal amount, this is done gradually. When administered, the patient may feel pain, but it quickly passes and the effect lasts for several hours.
Description
Intrapulpal anesthesia is an additional type of anesthesia that is used in the treatment of pulpitis. The procedure involves injecting an anesthetic into the pulp area.
The manipulation is performed using a dental carpule syringe with a thin needle up to 1 cm. Such a needle makes it possible to adjust the angle of inclination. These are mandatory conditions for anatomical defects of the unit.
Most dentists prefer the injector brand IS - 01 - 1, domestically produced.
The composition of the drug is lidocaine 2% and derivatives.
For dental canals with low traffic, needle-free injectors are used.
Before the procedure, auxiliary blockade with histamines or analgesics is mandatory. The blockade is carried out 60 minutes before the treatment procedure.
Anesthetics for anesthesia
For spinal anesthesia, agents with various properties are used. Each of these drugs gives a different effect in terms of duration of exposure. Patients with allergic diseases should not worry: there are a lot of options for administered medications, and the doctor will definitely replace a drug that is unsuitable for the individual body with one with a similar effect. Here are some of the medications that are used for spinal anesthesia: Narolin, Novocaine, Mezaton, Fraxiparine, Lidocaine, Bupivacaine and many others.
"Mezaton"
For your information, the table below shows the active ingredients used in spinal anesthesia drugs, their dosages and the duration of action of each of them. Thanks to this table, the patient can determine whether he is allergic to a particular drug and whether the dosage is appropriate for him.
| Medicine | Concentration of solutions, (%) | Maximum dose, (mg) | Duration of action (minutes) |
| Procaine hydrochloride | 0.25 or 0.5 | 500 | 40-60 |
| Lidocaine | 2-5 (hyperbaric solution) | 15-100 | 60-90 |
| Tetracaine hydrochloride | 0.5 (hypobaric, isobaric or hyperbaric solution) | 5-20 | from 180 (hyperbaric solution) to 270 (hypobaric solution) |
| Bupivacaine hydrochloride | 0.5 (isobaric or hyperbaric solution | 10-20 | 90-150 |
| Artikain | 5 (hyperbaric solution) | 100-150 | up to 120 |
Operating principle
The composition is delivered to the destination area through a carious cavity or a hole drilled with a bur. The latter option is preferable, since the diameter of the hole will be equal to the needle. This will prevent the substance from leaking into your mouth.
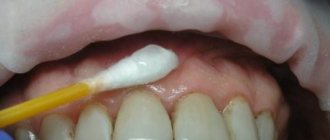
There is pain when the composition is introduced. The dentist minimizes discomfort by applying a cotton swab with anesthetic or dripping the substance directly into the cavity from a needle.
The substance is administered slowly, with a volume of up to 0.3 ml. As the fluid penetrates inside, the doctor feels resistance. This indicates the correctness of the manipulation and the delivery of the medicine.
Since the immersion area is small, it is advisable to use a needle with a curved tip.
The effect occurs half a minute after the injection and lasts up to half an hour. The specified time is sufficient for dental intervention.
Intrapulpal anesthesia under pressure involves applying a cotton swab with dicaine or other anesthetic composition to the exposed areas of the pulp or the upper part of its arch. Then the cavity is sealed for a certain time.
This action is called “druk-anesthesia”. This is an application option, as a result of which the drug is absorbed by mucous membranes and bone tissue.
Some dental surgeons classify manipulation as an intraosseous method of pain relief.
Infiltration anesthesia: application
Indications
- Treatment of pathological conditions of teeth and gums (caries, pulpitis, etc.);
- Removal of teeth of varying complexity;
- Implantation operations;
- Prosthetics;
- Opening the abscess and draining it;
- Removal of tumors on the oral mucosa;
- Surgical dental intervention in the oral cavity.
Contraindications
- Identification of the patient’s individual intolerance to the components of painkillers;
- A pronounced inflammatory process in the oral cavity (anesthesia may not give the desired result);
- The patient has a mental illness;
- Neoplasm of malignant nature.
Indications for use
The use of pain relief under pressure is only suitable for the treatment of early stages of pulpitis with carious lesions of teeth.
Anesthesia has the goal of relieving pain of varying intensity.
Application of the technique is shown:
- As a psychological impact on the client.
- In order to prevent an increase in pain.
- To prevent fainting due to the influence of the vagus nerve on the vascular system.
- For preparation of a cavity below the location of the filling in case of carious lesions in the middle part of the dental unit.
- When performing dental operations in case of superficial localization of the pulp.
The technique is prescribed for:
- deep carious lesions in acute form;
- open pulp horn;
- the need to form a cavity vault with further use of injection anesthesia.
Cons and pros
The list of advantages of using intrapulpal anesthesia includes:
- Delivery of medicine to the destination area.
- Instant results.
- No pain during dental procedures. After treatment, the pain impulse is slightly suppressed by the residual concentration of the drug in the tissues.
- Lack of resorptive effect.
It is also worth noting the disadvantages of the technology:
- Fear and psychological discomfort in the patient at the time of injection.
- Pain at the time of needle insertion or during perforation.
- Limited application of the technique due to the inaccessibility of individual areas.
- There is a possibility of intravascular penetration of the composition.
Features of tooth preparation
The technique of local anesthesia practically does not depend on the degree of progression and localization of the inflammatory process.
Algorithm for preparing for treatment:
- Clean the affected area from food debris and saliva.
- Smoothing the edges with a bur.
- Opening the working area.
- Removing the soft parts of dentin from the walls and base of the cavity.
- Treating the space with an antiseptic, drying.
After performing the above procedures, the dentist chooses the optimal method of anesthesia.
Pros and cons of infiltration anesthesia
| Pros: | Minuses: |
|
|
Let's sum it up
Spinal anesthesia is an extremely safe method of pain relief. If the patient is faced with a choice between spinal and general anesthesia, then it is worth giving preference to the first - firstly, it does not require long preparation, and secondly, the recovery period after such anesthesia is short and, moreover, quite comfortable. There is no need to be afraid of this type of anesthesia - after a few hours, sensitivity is completely restored, and the patient can forget about any discomfort.
Possible side effects of spinal anesthesia
First of all, it should be noted that the number of side effects with this type of anesthesia is much less than after general anesthesia. Therefore, the risk of complications is reduced to a minimum and is extremely rare.
Possible complications are associated with pathologies present in the patient’s body, as well as age and bad habits.
We should not forget that all manipulations in anesthesiology, up to the installation of a regular IV, carry a certain risk. However, by strictly adhering to all doctor’s prescriptions, a person in most cases manages to avoid negative consequences.
Possible complications after anesthesia include:
- headache. This negative consequence most often appears due to the fact that after anesthesia a person begins to actively move. Statistics show 1% of the total number of complications. This pain syndrome goes away on its own within a couple of days. However, during this period it would not be amiss to measure blood pressure and act based on the tonometer readings. The main rule in this case is compliance with bed rest in the postoperative period;
- decrease in blood pressure. This negative factor is caused by the introduction of an anesthetic. As a rule, it does not last long. To normalize blood pressure, special intravenous solutions are administered and it is recommended to drink more fluids. This condition occurs in 1% of patients;
- pain in the anesthesia puncture area. The discomfort goes away within 24 hours and does not require additional treatment. If the patient cannot tolerate the pain, then you can take a Paracetamol or Diclofenac tablet;
- delay in the process of urination. A common occurrence that does not require therapy and usually resolves on the second day after surgery;
- neurological complications. An extremely rare phenomenon characterized by loss of sensation, muscle weakness and tingling in the lower part of the body lasting up to two days. If this problem persists for more than three days, you should consult a doctor.
There is always a certain risk of complications after spinal anesthesia, but fortunately it is extremely small
Preventing complications
In order to eliminate the risk of developing negative consequences, it is necessary to strictly follow the recommendations of the anesthesiologist.
- 6-8 hours before surgery, do not eat or drink any liquids.
- Do not smoke tobacco products 6 hours before surgery.
- Do not wear makeup or polish your nails before surgery.
- Remove contact lenses from your eyes and remove all removable dentures, if any, from your mouth. It is necessary to inform the anesthesiologist in advance about the presence of ocular prostheses if they are worn.
- Remove rings from your fingers, earrings from your ears, chains from your neck, as well as other jewelry items. For believers, it is permissible to leave the cross on the body, but not on a chain, but on a braid.
Compliance with these recommendations significantly reduces the risk of complications.
The main thing is that the patient informs the anesthesiologist about all his diseases, previous injuries and surgical interventions, and also talks about the presence of possible allergies to medications or intolerance to any drugs. The specialist also needs to know whether the patient is taking medications. Collecting this information is the key to successful spinal anesthesia. This will also help prevent negative side effects after anesthesia.
Before administering anesthesia, the patient must inform the doctor about previous or existing diseases, taking any medications, injuries and other features
Before the operation, the patient should rest well and get enough sleep. It would be a good idea to spend some time in the fresh air and calm down. These simple steps will help you psychologically tune in to a positive wave, which will greatly facilitate the process of surgical intervention, and will also help the body recover faster after its completion.
Frequently asked questions from patients before agreeing to spinal anesthesia
How will I feel after the anesthesia is administered?
Answer. A couple of minutes after the injection of spinal anesthesia, heaviness in the lower extremities, slight numbness and warmth may be felt. After 15 minutes, the legs will be completely motionless.
How will I feel during the operation?
Answer. During a prolonged operation, a feeling of discomfort may occur due to the long static posture of the body. However, no pain will be felt. Also, discomfort during surgery can be caused by strong touches, stretching of the legs during the doctor's manipulations, or ambient noise. At the request of the patient, the anesthesiologist can put him into a state of light sleep for better comfort. At the same time, the specialist monitors his physical indicators: pulse, blood pressure, breathing and consciousness.
How will I feel after the surgery?