October 11, 2010 - Monday
The position of a successful person today is a health fashion: playing sports, giving up bad habits, visiting cosmetologists and massage therapists... However, not everyone, not everyone, monitors the condition of their teeth. And an important role in this is played by misconceptions that have taken root in people’s minds. Indeed, in the age of developed technologies and the active implementation of innovative projects, the other side of the crazy intensification of life is the desire to get away from the hustle and bustle and the desire to believe in the miraculous and unreal.
However, if you still think that dental treatment is painful, or that a miracle paste will preserve your smile, and chewing gum will protect you from caries, congratulations, you still have not managed to separate myths and reality, and your knowledge Dentistry is full of prejudices.
How to ensure that these stereotypes, or one might say myths, do not prevent you from taking care of your smile and what really needs to be done to correct the situation, will be explained by the chief dentist of the Sverdlovsk region, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of the Regional Dental Clinic Marina Pavlovna Kharitonova .
Fact : The Sverdlovsk region is one of the regions with a high prevalence and average intensity of dental diseases: 14% of 6-year-old children already have permanent teeth affected by caries. Recently, diseases of periodontal tissues have also become much “younger” - more than half of adolescents aged 12-15 years have been diagnosed with tartar and increased bleeding of the gums. 96% of people over 35-40 years old have teeth affected by caries and inflammatory processes in the tissues surrounding the teeth (periodontitis). More than 70% of people over 65 years of age need orthopedic treatment, i.e. in prosthetics.
No one has ever died from a bad tooth
Reality: Infection coming from a diseased tooth (odontogenic infection) is one of the most dangerous. A diseased tooth is a source of pathogenic environment in the body. Numerous colonies of microorganisms live and multiply in the mouth, some of them quite aggressive. From a “neglected” diseased tooth, microbes can travel throughout the body, both independently and by causing allergization of the body, which leads to a decrease in immunity. In addition, ulcers on the roots with a decrease in immunity can lead to the development of serious complications (abscesses, phlegmon, osteomyelitis, etc.), and sometimes cause conditions incompatible with life.
Fact: Scientists have proven that the presence of multiple chronic foci of infection in untreated teeth in pregnant women leads to miscarriage and low fetal weight during childbirth.
What to do?
At least 1-2 times a year, undergo examination and professional hygiene at the dentist, which will help identify and effectively eliminate pathology in the initial stages of development.
Fact: Expenses of Russian residents, according to data at the beginning of the century, on certain types of goods and services (per year): - for vodka, beer, cigarettes - $12 billion, - for medicines - $2.2 billion, - for dental care – $600 million
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
Pathogenic microbes from the oral cavity easily migrate with food into the gastrointestinal tract. When they enter the digestive organs, they cause irritation of the mucous membrane. At best, this leads to digestive disorders, for example, bloating, heartburn, and bowel dysfunction.
But if the number and growth of pathogenic microorganisms rapidly increases, then very soon a person feels the first symptoms of gastritis, stomach ulcers or colitis.
In addition, diseased teeth are not able to cope with their main task. The process of chewing food is disrupted, the load on the digestive organs increases, which also negatively affects the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
If a tooth falls out, you can do just fine without it.
Reality: Each tooth in our wide smile is a link in the dental chain. Each group of teeth performs its own function: some bite off food, others chew it. When a tooth is removed or falls out, the shape of the teeth and jaws changes. The teeth adjacent to the missing one begin to shift and fill the vacated space, which can subsequently cause difficulties with prosthetics.
Fact: Significant tooth loss leads to eating more monotonous and less balanced food, a lack of vitamins and microelements, which can affect brain activity.
What to do?
Lost teeth need to be restored, which can be done in various ways. The options of choice are restorative orthopedic structures supported either by implants or by natural teeth. Fact: The fewer natural teeth a person has, the higher the risk of developing coronary heart disease and heart attack. People with fewer than 10 natural teeth are seven times more likely to die from a heart attack than those with more than 25 teeth.
Diabetes
The presence of microbes in circulating blood causes a change in its rheological properties. An increase in viscosity leads to disruption of transport function, a decrease in blood flow speed, and inhibition of metabolism. In turn, metabolic disorders reduce the ability of insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. Glucose concentration increases.
As a result, most people gain weight and develop diabetes. Under conditions of high sugar levels, irreversible changes occur:
- tissue nutrition is disrupted;
- the walls of blood vessels are damaged;
- stagnation develops;
- the quality and life expectancy decreases.
Chewing gum, floss and toothpaste are a panacea for caries
Reality: Even the best toothpaste in the world will not cure your tooth! Chewing gum only restores the acid-base balance disturbed during meals. Floss, or, as they more often say, dental floss, is also not a doctor for our teeth. All of the above remedies are good for preventing the occurrence of carious lesions, but given the existing pathology, they are not able to not only cure, but even stop the process.
What to do?
It is necessary to use all of the above means, but only along with systematic visits to the dental office for preventive examinations, professional hygiene and sanitation of the oral cavity, i.e. treatment and maintenance in proper condition of all teeth with one or another pathology.
Sinusitis
Appears due to constant inflammation in the oral cavity. The risk is higher if the upper molars and premolars (these are closest to the maxillary sinuses) are affected. The infection penetrates the maxillary sinuses and affects them, causing severe headaches, high fever, and constant purulent mucous discharge from the nasopharynx. Without adequate treatment, sinusitis becomes chronic and can provoke meningitis, sepsis localized near the brain, and damage to nerve endings. It cannot be treated only by relieving symptoms: antibacterial therapy and endodontic treatment are needed.
The more expensive the toothbrush and toothpaste, the better they are.
Reality: The cost of hygiene products is not an indicator of their usefulness specifically for you. The structure of dental tissues, their location, color, shape, as well as characters, are different for everyone.
What to do?
The selection of oral hygiene products should only be carried out by your treating dentist. In addition, the doctor will evaluate the correctness of your usual cleaning method and make the necessary adjustments.
Fact: The quality of teeth cleaning is influenced not so much by the toothbrush and toothpaste you choose, but by the correctness and duration of this manipulation. It has been proven that with a recommended time of about 3-5 minutes, most often the average person on the planet spends about 30 seconds brushing their teeth. Tip: To stay on time, turn on your favorite song and brush your teeth from the first chord to the last. On average, the duration of songs is the 3-5 minutes we need. Both fun and useful!
The cardiovascular system
Against the background of advanced dental diseases, a number of heart diseases can develop:
- infective endocarditis - inflammation of the heart valves due to infection, which enters them through the bloodstream from the affected tooth, more often occurs when the immune system is weakened;
- heart failure - periodontal inflammation doubles the risk of its occurrence;
- heart attack, stroke. Due to inflammation and the transfer of bacteria through the bloodstream, atherosclerotic plaques form on the walls of blood vessels. The plaque clogs the vessel and a blood clot forms. If it comes off, a stroke or heart attack occurs.
Untreated caries and constant inflammation in the oral cavity increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases by 70%.
If you take several x-rays in a row, you can get high levels of radiation
Reality: According to one of the leading specialists in dental radiology, D.V. Rogatskin, one intraoral photograph of a tooth corresponds to approximately one microsievert.
The radiation dose when taking one three-dimensional image on a dental tomograph is approximately equal to the radiation dose from a panoramic image and is about 20-50 microsieverts. What to do?
You should not apply to a peaceful dental office the same concepts that are used at a nuclear test site. During the treatment process, you can and should take as many x-rays as your doctor needs, and if necessary, do not be afraid to do 1-2 studies per year on a dental tomograph. It is necessary to understand that your attending physician takes a picture, or a series of pictures, so that the quality of treatment is at the proper level and the tooth will serve you for many more years. And such a modern method as tomography of the maxillofacial area goes beyond the boundaries of conventional x-ray examination and often allows the doctor to see in volumetric form the pathology that cannot be determined on ordinary photographs.
Pregnancy
During pregnancy, dental health can deteriorate significantly. There are fewer reserves of vitamins and minerals, the body’s defenses are reduced, and the likelihood of pathogenic microbes penetrating into the tissues of the gums and teeth increases.
And if a woman did not take care of her oral health before bearing a child, then the pathological process will only worsen until the complete loss of teeth.
The source of chronic infection is very dangerous for the unborn baby. It can lead to sepsis, which will certainly affect the development and growth of the fetus and the course of pregnancy. Therefore, during this period there is no need to postpone a visit to the dentist, but on the contrary, you should rush to see a doctor.
Heredity is to blame for bad teeth
Reality : The role of heredity in the health of our teeth is extremely small and is manifested in the structure and properties of tooth tissue: enamel and dentin. In fact, a person even with not very good heredity has every chance of keeping his teeth healthy.
What to do?
Take proper care of your teeth throughout your life and make regular visits to your dentist.
Fact: Today, there is an opposite theory that lesions of specific teeth may indicate a predisposition to the pathology of a particular organ or an already existing disease.
Correlation of teeth affected by caries with pathology of internal organs
Recommendations
The longer you ignore a bad tooth and hope that the problem will go away on its own, the more difficult and painful its treatment will be. To prevent oral diseases, it is recommended: 1.
- Carry out regular dental hygiene, annual professional teeth cleaning, and procedures to strengthen dental tissue.
- Watch your diet and limit sweets.
- Treat chronic diseases.
And of course, you should visit the dentist promptly. Even if nothing worries you, a preventative annual examination will help make sure there are no pathological processes. After all, there are diseases that make themselves felt at an advanced stage of development.
Classification of dental diseases
Pathologies of teeth eruption and formation
Early detection of dental anomalies makes it easier to carry out subsequent bite correction. Irregularities in the sequence of eruption or asymmetry of opposing teeth should be a reason to contact an orthodontist. Diagnostic accuracy is ensured through x-ray examination.
Edentia
Characterized by partial or complete absence of teeth. The disease can be hereditary or develop throughout life. Sometimes the rudiments of teeth are completely absent from birth.
Supernumerary teeth (hyperdontia)
There are too many teeth in the mouth, and the extra ones can be located both in the dentition, disturbing the arrangement of the remaining teeth, and in atypical places - on the palate or on the front surface of the gums. The anomaly occurs in 5% of the population.
Impacted teeth
The teeth remain in the bone tissue of the jaw and do not erupt completely. In most cases, this is a disease of the molars - eights.
Dystopian teeth
The teeth are located in the wrong places in the jaw, at an angle, and only partially erupt. Pathology refers to diseases of wisdom teeth.
Macrodentia/Microdentia
An increase (or decrease) in the size of teeth compared to the standard norm.
Tooth enamel diseases
There are many chemical processes going on in the mouth that wear down the enamel. Under the influence of food containing dyes or acids, as well as cleaning products, the normal mineralization of teeth is disrupted. Pathologies of the endocrine system and work in hazardous industries are additional unfavorable factors.
Fluorosis
Damage caused by an excess of fluoride in consumed water or food. Fluorosis is commonly referred to as yellow tooth disease.
Enamel hypoplasia
A disease associated with impaired formation of the enamel structure. In most cases, it develops in the first nine months of a child's life.
Wedge-shaped defect
Formation of a “protrusion” at the neck of the tooth on the front side. A disease of the front teeth that can lead to chipping of the entire crown part.
Dental disease caries and its complications
Dental caries occurs in places where microbial plaque lingers and accumulates. The likelihood of developing the disease depends on the individual resistance of both dental tissues and the body as a whole. Resistance to caries is determined by the structure and composition of the enamel, the degree of its mineralization, as well as the characteristics of the dental system - the structure of the facial skeleton, jaws, bite and location of the teeth.
Caries
A pathology that develops in the hard tissues of the tooth, accompanied by demineralization of the enamel and the formation of a cavity. If left untreated, it provokes the development of inflammation in the pulp and periodontal tissues.
Pulpitis
Inflammation of the dental nerve. Characterized by acute pain radiating to the temples. May lead to tooth loss or exacerbation of periodontitis.
Periodontitis
The inflammatory process covers the apex of the tooth root. Without treatment, there is a risk of developing a cyst or abscess. The main manifestations are swelling of the gums, increased temperature.
Periostitis (flux)
Inflammation of the periosteum due to untreated periodontitis. Accompanied by swelling of the gums and severe pain.
Granuloma
Proliferation of inflammatory tissue in the area of the tooth root. Symptoms are redness and swelling of the gums, tooth pain. Ignoring the disease leads to the appearance of a cyst on the root of the tooth, fistula and diseases of the roots of the teeth.
Tooth cyst
A formation in the form of a capsule with pus at the apex of the tooth root, resulting from the penetration of infection into the root canals. The disease is asymptomatic, in some cases there is pain when chewing. The cyst is usually noticed on x-rays.
If you find signs of dental disease presented in the table, you must go to a dental clinic as soon as possible and consult a doctor. The specialist will examine the oral cavity, prescribe diagnostic procedures and draw up an optimal treatment plan for dental diseases to restore the health and beauty of your smile.
Who will not benefit from anesthesia?
— How to relieve fear of the dental office?
— 80% of success in work depends on the professionalism of the dentist, 20% on the patient’s attitude towards treatment and his psychological comfort. I see my goal as removing all fears from patients. They need to explain in as much detail as possible what we will do and what it will look like - all the treatment tactics.
Families come to us, sometimes for decades. So we, one might say, become family doctors.
In addition, visiting the dentist is now much more convenient than before. For example, the patient does not need to sit in the corridor and wait for an X-ray image; everything comes immediately to the doctor’s computer.
Dental clinic No. 3.
Altapress.ru.
Dentistry is a field that is developing by leaps and bounds. Today, doctors sometimes have to redo work that someone else did 10-15 years ago. Because modern equipment and filling materials have appeared that provide a long-term guarantee of reliability.
Currently, all this is possible not only in commercial clinics, but also free of charge in the compulsory health insurance system.
— Basically, a person is afraid of pain. What innovations are there in terms of anesthesia?
“We are now working with modern drugs, they are effective and at the same time gentle. They can even be used when working with patients in the early stages of pregnancy.
Radmila Labyntseva.
Altapress.ru.
There are contraindications. For example, pain relief is not possible for people with cardiac arrhythmias. But even here the doctor can choose the most suitable drug. No one now endures pain in dentistry.
“People are also scared by the fact that anesthesia does not help everyone. What are the chances that pain relief will not occur?
— It depends on the individual characteristics of the organism. Most often, anesthesia does not help if a person takes certain medications. For example, a toothache, and the patient does not go to the doctor for two weeks and drinks painkillers in packs. Then the effectiveness of anesthesia decreases.
The same thing happens in advanced cases when there is a large inflammatory process.
Dental clinic No. 3.
Altapress.ru.
Can't be confused with anything
— Toothache is not always felt in the mouth. Where else can you feel it and how can you understand that its cause is a bad tooth?
— The pain can radiate to the temple, lower jaw, even to the arms. It happens that “the whole head hurts.” Sometimes there is a hole in the lower tooth, but the upper one above it hurts. Due to hidden cavities, upon visual examination the patient cannot determine which tooth hurts. Only a doctor can do this.
The cause of the headache may be neurological problems, but it is better to immediately rule out the obvious - dentistry. Sometimes patients come to us based on a neurologist’s referral.
- Why is toothache so severe?
— A tooth is not just a “bone” that cannot hurt. Inside it there is a cavity filled with nerve tissue. In addition, all the main exits of nerve endings are located on the head. Toothache is a specific pain that cannot be compared with anything.
Dental clinic No. 3.
Altapress.ru.
— How do you understand whether to preserve the nerve or remove it? Why are dental nerves so important?
— Dental nerves can be removed in some cases according to indications. If the caries has reached the nerves, then we remove it, clean the canals and fill it. But the doctor is always determined to keep the tooth viable, which means that the neurovascular bundle cannot be touched.
Living tissues must be supplied with blood; such a tooth is stronger. If we remove the nerve, the tooth dies, although it can still function. It becomes fragile and easy to lose. It is easier to treat caries and prevent the tooth from eventually dying.
Radmila Labyntseva.
Altapress.ru.
For courage
— Do you need to somehow prepare for going to the dentist’s office? I know that abroad a doctor can refuse a patient if he comes with bad breath.
— Yes, sometimes patients come who are not ready and do not understand at all that it would be worth brushing their teeth before the visit. For courage, many take strong drinks in the evening and come in with a fume.
We do not refuse admission, but we correctly explain that you should not smoke in front of the clinic or eat garlic and onions, that you need to respect yourself and the doctor. And if everything is said politely, then patients follow the recommendations, which is very pleasing.
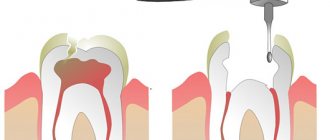
3.Treatment of tooth infection
Treatment of a tooth abscess is aimed at fighting the infection, preserving the tooth, and preventing complications. You may need to do a root canal drainage
or even
surgical root canal treatment
. During the mini-surgery, root tissue damaged due to infection is removed. And a crown can be placed on the tooth. In more serious cases, the tooth will need to be removed. And only after this is drainage done. The third way to drain and clean the affected area is through an incision in the gum.
To treat the infection, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics. And to relieve toothache and discomfort due to a tooth abscess, you can rinse your mouth with warm salt water or take a pain reliever (for example, ibuprofen).
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!