Dental implantation is a complex procedure that requires intervention in the soft tissues of the oral cavity. To avoid all sorts of complications, it is very important to follow the dentist’s recommendations. Swelling and redness may be observed for several days after surgery, which is considered normal. If other unpleasant symptoms appear, you should consult a specialist to prevent rejection of the prosthesis and other pathological conditions.
Normal gum condition after implantation
Because the gums are exposed during surgery, your gums may appear inflamed in the first few days after surgery. The patient may experience the following symptoms:
- bleeding;
- pain;
- hematoma.
If symptoms do not subside after a week, you should consult an implantologist.
The implant adaptation period can take from 2 to 6 months, depending on the complexity of the manipulation and the individual characteristics of the body. For example, artificial roots take root faster on the lower jaw than on the upper jaw.
How are gum tissues exposed?
It all depends on which implant you choose.
The subosseous one is implanted into the jawbone, but the periosteal one is implanted into the soft tissue. Sometimes the hole of an extracted tooth is suitable for an implant, and then the impact is minimal, but this is not always the case. In some cases, it is necessary to either deepen the hole or completely cut through the gum with a laser - and then it is necessary to put sutures on it to hold the tissues in place before they grow together.
There are also cases when, after installing an implant, gum surgery is required - then healing takes even longer.
Possible complications
In most cases, swelling, discomfort, and pain disappear 5-7 days after implantation. If after this time the symptoms do not disappear or increase, you should consult a specialist to rule out the following pathologies:
- hyperplasia. Rapid proliferation of mucous membranes at the implantation site. Elimination will require partial removal of mucous tissue;
- fistulas, purulent foci. A characteristic sign of such consequences may be white dotted plaque on the gums. Inflammation can result from infection during surgery, medical negligence, injury to the nasal sinuses, incorrect choice of implant, poor oral hygiene, and bad habits;
- peri-implantitis. Beginning of prosthesis rejection. Bleeding, severe swelling, redness, pain, and numbness may indicate pathology. In this case, immediate treatment and curettage are required;
- implant rejection. It is rarely recorded in dental practice. Characterized by the mobility of the installed rod. The cause of the violation may be physiological characteristics, doctor errors, chronic diseases in the acute phase, poor hygiene, and bad habits.
To minimize the risk of such conditions, you should follow your doctor's postoperative recommendations.
How to care for your gums during the adaptation period
The rehabilitation period after implantation and prosthetics usually takes at least five months. At this time, it is important to follow all doctor's recommendations. Typically the list of appointments includes:
- regular visits to the dentist;
- brushing your teeth with a soft-bristled brush;
- daily rinsing of the mouth with antiseptic solutions;
- avoidance of the implantation area during hygiene procedures;
- gently cleansing gums that have been injured with a cotton swab;
- use of floss, irrigator;
- refusal to visit the sauna, bathhouse, or take a hot bath;
- limiting the consumption of solid foods;
- exclusion from the diet of spicy, sour, hot, cold foods;
- strict control over the healing process.
An important point for gum health is quitting smoking. Tobacco smoke negatively affects the condition of the mucous membrane and is the main provocateur of implant rejection. Therefore, it is better to get rid of a bad habit.
- Complete restoration of the dentition in just 4 days!
more detailsRoott Pterygoid Implants Sinus lift is no longer needed!
more details
Once and for life! Express implantation in 4 days with a permanent ReSmile prosthesis
more details
All-on-4, All-on-6, ReSmile, Zygomatic implantation We use all modern methods of dentition restoration
more details
Treatment of postoperative complications
In some cases, after implantation, the patient is prescribed antibiotic treatment, which helps prevent infectious processes. In addition, drugs with an antiseptic wound-healing effect are prescribed:
- chlorhexidine (0.05%). It has a disinfecting effect and is used in the first days after manipulation. The composition should be kept on the side where the implant is installed for several minutes. It is recommended to repeat the procedure 3-4 times a day;
- betadine (10%). Three drops of the composition are diluted with water (100 ml). Rinsing the postoperative area relieves inflammation and heals wounds. The drug provides protection to damaged tissues. Should be used up to 6 times a day;
- dexalgin. Has anti-inflammatory analgesic properties. Relieves pain for 3-6 hours, reduces swelling.
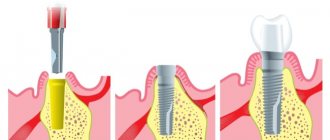
Orthopedic stage of implantation: impact on the gums
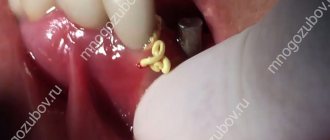
- Creating a gum contour
Before prosthetics, a former is installed - this is necessary to form the contour of the gums. Installation takes no more than 20 minutes and looks like this:
- making a small incision;
- unscrewing the plug;
- fixation of the former.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. Prosthetics can begin in one to two weeks.
After installing the former, the abutment is fixed to connect the implant and crown.
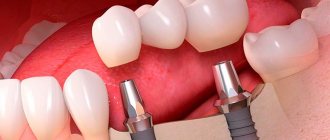
- Installing a prosthesis over an implant
The main task of prosthetics is to restore the integrity of the dentition. At the same time, it is important not only to preserve the external aesthetics of the prostheses, but also to ensure functionality. This is achieved through the joint efforts of the orthopedist and implantologist.
To make a crown, preliminary impressions are made. Before the final installation, the required number of fittings and corrections are carried out. The duration of the process is 2-4 weeks.
Oral care after implantation
The rehabilitation period takes at least 5 months. At this time, it is important to follow your doctor's recommendations:
- regular scheduled examination;
- using a brush with soft bristles;
- daily hygiene using antiseptics;
- minimizing impacts on the operating area;
- use of an irrigator;
- limiting warming bath procedures;
- adherence to the recommended diet;
- monitoring the condition of the prosthesis;
- to give up smoking.
How does healing occur and what are the normal consequences?
- In the first few days, the area undergoing surgery will be painful - you don’t have to endure this at all, just use painkillers that the doctor recommends. Also, your gums may be swollen, and you may have a fever - this is not surprising, and there is no need to be alarmed.
- During the first week, you may experience itching in your gums - this is completely normal.
- If you have had stitches, you should come in for checkups weekly—or as often as your doctor advises. After 3-4 weeks, the stitches should be removed.
- By the end of the month you should completely stop experiencing discomfort. If this does not happen, be sure to see a specialist.
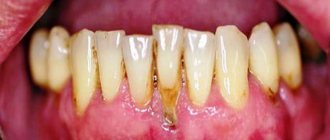
Causes of the inflammatory process
Several factors can cause inflammation of the gums after installation of an implant: from a medical professional’s error to the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. The most common and common reasons include:
- Excessive tissue trauma that accompanies the process of implantation into the bone.
- Violation of the patient's medication regimen.
- Exceeding the permissible load on the implant during the healing period.
- Infection: either the instrument was poorly sterilized before surgery, or the patient did not maintain oral hygiene.
- The presence of allergic reactions to the implant material;
- Bad habits (smoking);
- Low quality implants.
Inflammation of gum tissue can also be due to the patient’s reduced immunity, chronic diseases of the oral cavity and nasopharynx, problems with blood vessels and the heart, etc. In addition, there are medical errors, for example, incorrectly selected design parameters for the implant, erroneous position of the rod, non-compliance with the installation technique, ignoring contraindications, etc.
Is it possible to re-install a failed implant after removal?
When performing classic two-stage implantation, after removal of the implants, their re-installation is almost impossible. This is due to severe bone atrophy caused by inflammation. To reinstall an artificial tooth, bone grafting is required. Initially, you need to completely eliminate the inflammation, then carry out surgery. Engraftment of bone material can last for 3-6 months. When choosing a complex implantation method with immediate loading, rejection of the prosthesis occurs extremely rarely, but even in this case, the implant can be reinstalled.
The main advantages of implantation:
- No interference with the structures of neighboring teeth.
- Long service life of the denture structure (15 years or more).
- Lightweight and physiological denture structure (root - implant, tooth - crown).
Dental implantation as a method of replacing lost teeth was most suitable for the patient. The patient chose treatment at the Dial-Dent clinic for several reasons:
- The presence in the clinic of an experienced implant surgeon with extensive experience Alaverdova V.P.
- The Dial-Dent clinic demonstrated the features of various tooth replacement options using real clinical cases as examples. The use of animation and computer modeling during consultation helped the patient to fully understand the essence of the proposed manipulations.
- The use of the “Implant Assistant” computer program in the clinic, which allows for a virtual operation to install implants.
- The patient could undergo all the necessary consultations and studies at the clinic.
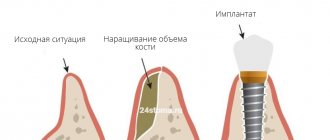
How does gum growth occur?
Today we will look in more detail at how to increase gum volume and which donor sites are used for this.
So, in order to change the volume of gum tissue near a tooth or implant, it is necessary to work in two directions:
- It is necessary to process and change the location of local tissues in the planned area
- It is necessary to take tissue from the donor site and plant it in the surgical area.
Local tissues of the operated area most often stratify and move in space. After the surgeon’s work, they should be completely pliable, without tension or any obstacles to movement.
Thus, the tissue in the hands of the surgeon is a kind of plasticine! They move to the place that the doctor intended.
There are many surgical techniques in the operation area and they are chosen by the attending physician himself.
Now let's look at the options for donor zones, as well as the advantages of each of them:
1. If the defect is large in extent (for example, several recessions), the most successful donor site is the palate
A thin long strip of tissue is taken from the arch of the hard palate near the teeth and immediately covers the entire defect.
Pros:
- Possibility to close an extended defect.
- Simplicity of the fence.
Minuses:
- Possibility of bleeding due to the vascular network of the palate.
- Sensitivity and sometimes pain of the wound.
- The ability to perform only 2 operations, since there are only two halves of the sky. If it is necessary to close recessions everywhere, then some operations are postponed for 3-4 months until the tissues of the palate are restored.
You can clearly see the use of a donor site on the palate below:
2. If a small plastic surgery is required, but a large tissue gain is required, then the best option is the tubercle of the upper jaw.
This is the place where wisdom teeth grow/grew.
Pros:
- Simplicity of the fence.
- The tissue in this area has the ability to grow, so the visual effect of the operation can change up to a year!
- Little risk of bleeding.
- After the operation there is no pain at all, the wound is like after a tooth extraction.
Minuses:
- If you have wisdom teeth, they will have to be removed in advance.
- If the removal was very traumatic, there may be little tissue of the tubercle; in this case, the doctor will have to use a different area.
In the photo below you see the use of the upper jaw tubercle when implanting a tooth:
3. And finally, another compromise zone. For small defects, you can use mucous membrane from the area of the extracted tooth.
Pros:
- Simplicity of the fence.
- There is no pain, the wound is small, the sensations are similar to healing after removal.
- If there is no chewing tooth in the upper jaw, the mucous membrane may also be capable of growth.
Minuses:
- If you have all your teeth, this option is not suitable for you.
- The tissue must be formed, so at least 3 months must pass after removal. Fresh mucous membrane should not be used.
- You cannot cover an extended defect.
Thus, there are a lot of combinations of using different techniques and different donor sites.
You should trust your doctor and visualize the beauty of the mucous membrane after your joint efforts. After all, the patient and the doctor are one team, trying for the common good. And if you work together, everything will be just wonderful!
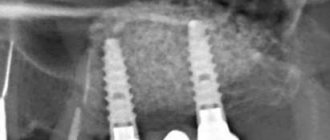
Is it possible to do MRI and CT with a dental implant?
Contrary to popular reviews on the Internet, magnetic resonance imaging (or MRI) with dental implants is allowed. Just be sure to warn the radiologist or laboratory technician that you have implants (and what they are made of - titanium, tantalum or Roxolid alloy) even before the examination. Typically, metals and metal alloys used for dental implants are not magnetized, but may create interference or “artifacts” in the image. Therefore, the laboratory technician changes the tomograph settings to eliminate distortions. The procedure itself is safe, the implant will not be pulled out of the bone by a magnet - it will not move at all.