Installation of implants is a surgical operation that is performed under anesthesia. Most often, local anesthesia is used, that is, eliminating the sensitivity of tissue in the area of the upcoming invasive manipulation. Since the anesthetic lasts for several hours, numbness after implantation is quite normal. It may be associated with swelling, which often accompanies the installation of artificial roots in the jaw. As a rule, the numbness goes away as soon as the effect of the drug wears off. But if sensory impairment persists several days after surgery, this may indicate the development of one of the complications.
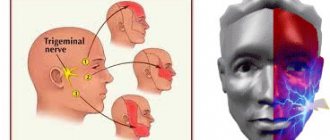
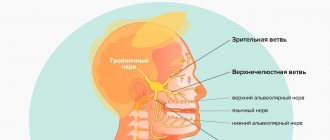
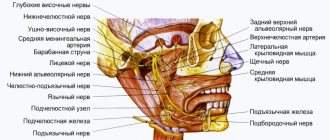
Trigeminal nerve injury
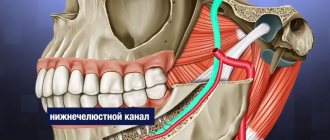
Prolonged numbness of tissues after implantation can also be caused by incorrect selection of the length of implants or their installation without taking into account the anatomical characteristics of the patient. In this case, damage to one of the processes of the trigeminal nerve is possible. Most often, when screwing in dental implants, the inferior alveolar nerve is affected. If it is damaged in the area of the lower lip, cheek and gums (up to the second molars), the following may occur:
- complete numbness of tissues;
- not disappearance, but a violation of sensitivity, without other unpleasant phenomena;
- a change in sensitivity, which is accompanied by an abnormal reaction to certain stimuli and other pathological symptoms.
If the lingual nerve is damaged during implantation, the following may also appear along with numbness:
- uncontrolled tongue biting;
- increased salivation;
- loss of taste;
- swallowing dysfunction;
- difficulties with pronouncing sounds.
If such symptoms appear and prolonged loss of sensitivity after implantation, you should contact the dentist who performed the operation.
Causes of paresthesia
Jaw numbness after wisdom teeth removal is a fairly common complication. It is due to the location of the “eights”. Their roots are located next to the jaw nerves, so during surgery the latter are often damaged, which leads to loss of sensitivity. Most often, paresthesia occurs:
- with long curved roots of the removed dental unit,
- severe bleeding during surgery,
- damage to the alveolar process.
Patients at increased risk of paresthesia after surgery include:
- over 30 years old,
- with a history of nerve ending injuries,
- endocrine diseases,
- neuralgia.
Helping the patient with numbness after implantation
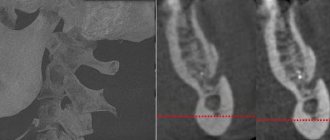
During a consultation regarding the loss or disappearance of sensitivity after installation of an implant, the dentist first of all finds out the cause. To do this, a diagnostic study is carried out, which makes it possible to determine the type and degree of damage to the nerve fibers. Then a set of therapeutic measures is prescribed.
If therapy begins at an early stage of development of disorders, sensitivity can be restored more quickly. The rehabilitation program for each patient is drawn up individually, with the participation of a dentist, neurologist and physiotherapist.
Treatment usually includes medications and physiotherapeutic procedures, such as acupressure, acupuncture, electrophoresis, and ultraphonophoresis.
Treatment
With minor damage, the tissue will go numb until the nerve fibers are restored. This may take several months or up to six months. The doctor will decide whether surgical intervention is necessary or will allow time for regeneration by the body’s natural forces.
Treatment of prolonged numbness after dental implantation, after diagnosing and determining the degree of damage, is prescribed by the implantologist or dentist who performed the operation, and this also falls within the competence of the neurologist.
Drug therapy paired with physiotherapy can quickly restore the conductivity and integrity of nerve fibers. The doctor may prescribe UHF, laser therapy, electrophoresis. From pharmacological drugs: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, antibiotics (to avoid infection).
Sometimes it is necessary to remove the implant that caused the disease. Or just unscrew it a little, changing the compression, which could cause such consequences. Microsurgery is rarely used to restore the integrity of nerve tissue. Usually a 12-week wait is given; if medications and physiotherapy do not help, the patient is referred to a microsurgeon. In any case, all actions will be aimed at restoring sensitivity and restoring a person’s normal life.
Complications after local anesthesia
The human factor plays a big role in dental procedures. Often, the inexperience or carelessness of a specialist leads to serious consequences.
General complications that arise during local anesthesia in dentistry can be of different nature:
- Discomfort at the needle insertion site. This is due to the drug being administered too quickly or too slowly.
- Hematoma at the injection site. The occurrence and growth of a hematoma indicates problems with blood vessels or an incorrect choice of the needle insertion site.
- Allergic reactions. Despite the fact that reactions to drugs are determined before anesthesia, cases of severe allergies to the composition of the anesthesia are not uncommon, especially if it consists of two or more components.
- Inflammation of the gums, development of infection. This case suggests that several mistakes were made during the procedure, as a result of which bacteria entered unprotected tissue and caused inflammation.
- Numbness of the facial muscles. The symptom is often complicated to the point of paresis, lack of control over facial expressions, inability to close lips, and sagging areas of the face.
Main causes of nerve damage during implant placement
Damage to the maxillary or mandibular processes of the trigeminal nerve, which is the main cause of long-term numbness of the lips, tongue, and chin after dental implantation, can be caused by an unintentional mistake by the dentist or negligence. Damage to the mandibular nerve, which provokes paresthesia, can occur in the following cases:
- Incorrect selection of implants (chosen too long).
- The specialist has not studied the anatomical features of the jaw and the implanted implant touches the nerve ending.
- Injury to the nerve ending by a needle during the administration of anesthesia or dental instruments during bone preparation.
If numbness in the lower part of the face is caused by injury to the nerve endings during the administration of anesthesia, the discomfort will go away on its own after the nerve fibers heal. Typically, the healing period ranges from 3 months to six months. You can understand that numbness of the lip and chin after implantation is associated with damage to the trigeminal nerve by the presence of the following signs after surgery:
- salivation increases;
- difficulty eating;
- facial expressions and articulation are impaired;
- the sensitivity of the tongue and lips decreases;
- there is pain and discomfort in the implant area;
- numbness is felt on the side where the titanium root is implanted.
Chief physician, Salatsky Dmitry Nikolaevich
Sign up for a free consultation
+7
If the feeling of numbness in the lower jaw does not decrease within several hours after implantation, then an urgent consultation with the doctor who performed the operation is necessary. Only after conducting diagnostic studies will a specialist be able to identify the extent of nerve damage and, based on this, prescribe appropriate treatment.
The main reasons why gums become numb
Among the reasons why gums become numb are the following:
- Complication resulting from tooth extraction. If your gums are numb, the cause may be related to the removal of chewing molars or wisdom teeth. This is explained by their abnormal growth at different angles with ingrowth into the nerve canal. After removal, irritation of the nerve endings occurs with a long recovery.
- Implantation with metal pins. If the gums become numb after dental implantation, the reason may be due to a mechanical effect on the nerve endings. This condition is caused by incorrect selection of the length of insertion of the pin. Therefore, at the stage of preparation for implantation, it is necessary to conduct a complete examination of the patient.
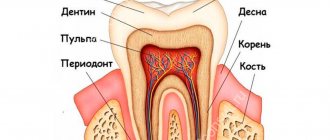
- Death of the pulp caused by a purulent or infectious process. To understand why the gums become numb, it is necessary to clarify the medical history. The main causes of pulp death include caries, pulpitis, advanced periodontal disease, gingivitis, and periodontitis.
- Trigeminal neuritis. The disease develops as a result of an infectious process, traumatic exposure, stress, as well as inflammatory processes in the ear.
In some cases, if the gums are numb, the reasons may be related to a visit to the dentist. To perform medical procedures, local anesthesia is performed, which leads to temporary loss of sensitivity. The decrease in sensitivity caused by the use of drugs goes away on its own after a few hours.
If symptoms do not disappear within 24 hours, you should consult your doctor. This is due to the fact that if the gums become numb, the cause can be life-threatening.
Complications of pulpitis without treatment
If pulpitis is not treated, the inflammation progresses, extends beyond the root canal, and affects adjacent periodontal and periodontal tissues. Most often this leads to periodontitis. Acute periodontitis is manifested by sharp pain, which is localized in the area of the affected tooth. The intensity of the pain gradually increases, it becomes throbbing when purulent inflammation begins. If treatment is not started at this stage, purulent exudate begins to separate, and the periodontal collagen fibers are destroyed. Soft tissues swell, temperature rises, and general condition worsens.
With periodontitis, the ligaments that hold the tooth in the alveolus are destroyed, and the destruction of bone tissue begins. The tooth becomes loose and falls out. Large cysts may appear.
Another possible complication of pulpitis is periostitis. With periostitis, inflammation spreads to the periosteum (tissue surrounding the bone), and a flux is formed. The gums swell and the jaw becomes painful. Periostitis can appear after pulpitis or accompany periodontitis. Without treatment, the swelling of the gums increases, the pain intensifies, the cheek and lip near the site of inflammation swell. The pain becomes shooting and can affect the temple, eye, ear. A fistula (passage) may appear in the swollen gum, through which pus comes out. After the fistula tract appears, the inflammation becomes less intense, but the tissues remain infected, and the infection continues to spread, and periostitis from an acute form becomes chronic.
Pulpitis can provoke the development of periodontitis - an inflammatory disease of the gums, dangerous by the destruction of bone tissue, gradual recession of the gums, and adentia. Against the background of acute inflammation and tissue infection, severe systemic diseases may appear: general sepsis (blood poisoning), phlegmon (breakthrough of pus into the soft tissues of the face, requiring surgical intervention), amyloidosis (occurs due to the constant toxic effect of pus).
How to treat numb gums
If the patient's gums are numb, it is necessary to begin treatment early. The problem requires an integrated approach, since it is important to establish the cause of its occurrence.
The medications that are most often used if the gums are numb include:
- ► Antibacterial drugs. To eliminate pathogenic microflora in dentistry, Amoxiclav or Clindamycin are used. Preference is given to tablet or injection forms of release. The average duration of treatment is 7-14 days.
- ► Local antiseptics. They are used in the form of an ointment, gel or rinse solution.
- ► Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The drugs reduce pain and tissue swelling. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are often taken for two weeks. The doctor selects medications individually.
- ► Traditional methods. A decoction of chamomile or calendula has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, which restores tissue sensitivity if the gums are numb. However, traditional methods can only be used on the recommendation of a dentist.
If there is no effect from the drug therapy, surgical intervention is prescribed, which is aimed at removing purulent masses or the implant. This will improve the patient's condition and prevent the spread of infection to other organs and tissues.
At the recovery stage, when the gums become numb, physiotherapeutic procedures are used:
- ► laser therapy
- ► dynamic current treatment
- ► UHF therapy
- ► electrophoresis