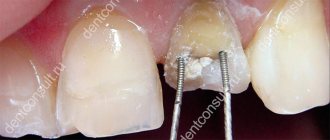
Types of fiberglass pins
Fiberglass pins in dentistry are classified depending on their shape and are:
- cylindrical - they have good retention (the ability to stay in the root canal) and do not damage the root walls;
- conical - this shape ensures accurate fit into the canal and minimal tissue loss, however, as the cone angle increases, retention decreases;
- cylindrical-conical - this option is suitable for strengthening teeth with slight destruction of the coronal part.
Fiberglass pins can have a volumetric head. This structure makes it possible to restore a badly damaged tooth. The wide coronal part of the pin structure makes it possible to create a stump with minimal use of the composite and ensures good adhesion to the restorative material. The installation of fiberglass pins of this type is especially suitable for subsequent prosthetics with metal-ceramic crowns, bridges and other orthopedic structures.
Indications and contraindications
Indications for installing fiberglass pins:
- severe damage to the teeth in the lateral and frontal areas;
- restoration by extension onto a rod;
- installation of splinting structures;
- restoration with restoration mixtures;
- in case of destruction of jaw units after serious injuries, fragmentary restoration;
- for prosthetics (it is necessary to create a reliable support when using ceramic prostheses).
Contraindications:
- pathology of hard tissues;
- blood clotting is poor;
- the root part is used for support;
- chronic diseases of the nervous system, mental illness;
- caries;
- granulomas, soft tissue cysts;
- The thickness of the root part is insufficient.
How to install a fiberglass pin
The procedure consists of several stages:
- X-ray diagnostics. To correctly place a fiberglass pin, a specialist must find out the dimensions of the tooth root, the direction of its slope, and identify all existing bends and narrowings.
- Expansion of the root canal using drills of different diameters.
- Root canal disinfection.
- Trying on a fiberglass pin. Mandatory condition: the structure should not be immersed in the canal less than the height of the tooth crown.
- Adhesive root canal preparation. It is degreased with alcohol and treated with phosphoric acid for at least two minutes. Then washed with water and dried.
- Preparation of the pin structure. To securely fix fiberglass pins, they are also treated with alcohol, dried, then sandblasted, etched with phosphoric acid, adhesive and polymerized.
- Root canal treatment. The canal walls are coated with bonding agent, dried and polymerized with a lamp. A thin layer of dual-cure cement is then applied. The rod itself is covered with the same material and placed in the channel. Excess cement is removed.
- Fixation of fiberglass pin by light polymerization.
- Restoration of the coronal part using composite materials or prosthesis.
general characteristics
A pin is a supporting device for fixing dental prostheses. The duration of use of the artificial tooth depends on the strength and reliability of the rod.
The product is made from fiberglass. The material is widely used in various fields of medicine. Its popularity is due to its hypoallergenicity, elasticity and ability to reduce stress on soft tissues.
Fiberglass pins are lightweight, durable, flexible, and able to bend and return to their original position.
Transparent color makes the product invisible in the oral cavity.
Advantages and disadvantages
Installing fiberglass pins has many advantages:
- Transparency of the design. Thanks to this property, it can be used to restore canines and incisors without damaging their appearance.
- Hypoallergenic. Fiberglass is well tolerated by the body and does not cause unwanted reactions.
- Elasticity. This parameter is close to natural dentin, which eliminates the risk of root fracture.
- No corrosion. Fiberglass pins do not oxidize, providing excellent biocompatibility and structural stability.
- Possibility of repeated endodontic treatment. If necessary, the rod can be removed using a bur, and the likelihood of damaging the tooth is very low, unlike metal structures.
Cons of installing fiberglass pins:
- Less strength compared to metal counterparts. This parameter determines the greater thickness of these products and, accordingly, the need for a significant expansion of the root canal.
- The need for special preparation of the pin structure before use. The more actions a technological process involves, the higher the risk of making a mistake.
- Cost of restoration. Prices for fiberglass pins are much higher than for metal pins.
Preparation and installation
Before you begin installing the structure, preparation is required. To do this, the channels are artificially expanded, which allows the product to be implanted. The doctor also prescribes a number of preliminary studies, including x-rays, which allows you to select the correct pins and restoration methods.
The procedure for installing pins includes the following steps:
- depulpation, preparation of canals and cavity sites;
- fitting of the structure, degreasing the canal using an alcohol solution;
- etching, drying the canal, for which paper points are used;
- rod preparation, disinfection, drying, sandblasting;
- applying a thin layer of cement mixture, introducing the structure into the channel;
- polymerization using light.
Types and manufacturers of fiberglass pins
Fiberglass restoration pins are available from a variety of manufacturers. They differ in composition, characteristics, form and features of use:
- The pins have the shape of a truncated cylinder with a rounded end. The mechanical properties of the product are almost identical to the properties of dentin and the composite used for restoration. This allows you to fully restore the tooth and return functionality to the row. But the light conductivity of the structure is lower than its analogues, although it is within acceptable limits.
- The design is distinguished by high aesthetic indicators, which allows the use of pins to restore the frontal area. In addition, the design is elastic, passive, and does not injure tissue during installation. No chemicals are used during processing, but the range of pins is quite limited.
- Relyx Fiber Post. The product is distinguished by a long tip and ease of processing, which facilitates dental procedures. The shrinkage of the cement mass is good, while the formation of pores is excluded, as well as corrosion processes. However, the cost of the design is higher than the price of analogues from other manufacturers.
- A polymer product that is resistant to coloring agents and translucency, which guarantees excellent aesthetic restoration results. Fixation is fast and reliable, the range of models is large.
- Fibrapost Lux. Modern design in the form of intra-channel conical pins. Can be cold sterilized, but has moderate radiopacity. The cost of the products is low, the quality of restoration is very good.
Service life, cost
The service life of the structure is on average 4-5 years. But with the use of high-quality materials and sufficient experience of the doctor, the period can be doubled. However, the patient must maintain hygiene and not exceed the permissible load on the restored units.
The cost of restoration depends on the manufacturer of the product and the degree of tooth destruction. On average, the price ranges from 300 rubles to 1500, the cost can be increased if treatment or other preparatory procedures are required.
Dentist advice
Osmanov Konstantin Gennadievich
Fiberglass pins can be a good alternative to metal or ceramic pins; in some cases, such pins will be the optimal solution. Teeth restored with their use “serve” for a long time (if the patient does not create factors that negatively affect the health of the teeth and the condition of the dental system as a whole) and look natural.
Introduction
Unfortunately, our teeth are not immune from injury or caries caused by us.
Too much destruction in the dental tissue cannot be saved even by modern fillings or composite veneers. Then the doctor decides on a safe and effective method of restoration using a crown, which requires a monolithic, durable structure. And it will be held on a special rod - a dental pin. Today, specialists at the scientific clinic “Dantistoff” successfully and effectively restore teeth, installing fiberglass pins as a solid foundation literally in one visit. Before prosthetics, doctors conduct a thorough examination with the obligatory identification of contraindications for the installation of such structures.
Reconstruction using a fiberglass pin. Modification and clinical protocol
Tags: Style Italiano
Adhesive tooth structure reconstruction has become the new standard since the 90s. Many aspects of treatment have been changed to make such reconstruction more feasible, predictable and long-lasting.
The advantages of this approach can be summarized as follows: good esthetics, thanks to tooth-like color, making such restorations compatible with metal-free crowns. Both biological and adhesive aspects allow for more conservative preparation while creating space to achieve retention. Mechanical aspects mean better distribution of stress along the root rather than concentrating it at the bottom of the metal structure. This homogeneity created between dentin, adhesive system, build-up and fiberglass post allows for an all-in-one concept. The purpose of this article is to present an updated clinical concept of glass fiber pin reconstructions using a case example, with the goal of making it accessible in everyday practice.
Fig.1
A 35-year-old patient had an old crown installed on tooth 1.1 five years earlier. She wanted a new restoration with “less opacity and less gray in the cervical area.” To achieve a high aesthetic result, we decided to replace the old crown and the old restoration underneath it, as well as perform a connective tissue transplant to obtain thicker gums in the cervical area.
Fig.2
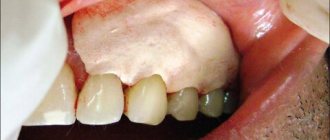
After the crown was removed, a short stump and damaged tooth structure were discovered.
Fig.3
The old bonding agent was removed and the tooth surface was cleaned to prepare it for effective bonding.
Fig.4
Wide endodontic access was discovered. In this case, restoration on a thinner post will also improve the mechanical properties of the tooth.
Fig.5
The rubber dam is positioned in such a way as to ideally isolate the tooth from biological fluids (saliva and blood).
Fig.6
When there is loss of tooth structure in contact with the gum, it is highly recommended to use dental floss to isolate the area by pushing the rubber dam into the gingival sulcus. Therefore, the doctor must have a complete peripheral occlusal view, in which all the boundaries of the tooth are visible.
Fig.7
The shape matrix of the future stump is used to give shape and uniformity to the buildup material.
Fig.8
Due to the width of the root canal preparation, a two-post restoration (LuxaPost DMG) may be an interesting option to significantly reduce the volume of the composite and therefore the polymerization stress during build-up fabrication. The larger the volume of the composite, the higher the shrinkage. This is why two small diameter pins may be preferable to one large diameter pin. Additionally, embedded bis-GMA resin fibers are our first choice for strengthening the build-up bond.
Fig.9
A larger fiberglass pin was also tested. In both cases, the mechanical key is to keep the post free in the root to avoid adjustments. This is called a passive post, allowing the buildup composite to accumulate between the dentin wall and the post and providing the mechanical benefits described previously.
Fig.10
To avoid damaging the fiber when reducing the length of the pin, it is recommended to use a diamond blade. Diamond burs destroy the fibers of the pin.
Fig.11
After shortening the fiberglass posts, the stump shape is again checked for marginal fit. After the test, the pins are placed in alcohol for 15 seconds. Since the fiberglass posts are pre-silanized, they are treated with an adhesive (LuxaBond Universal, DMG), which is then photopolymerized.
Fig.12
Phosphoric acid etching for 45 seconds is used to compensate for the loss of tubular dentin volume at the root, although the manufacturer recommends only 15-20 seconds.
Fig.13
The dual-curing adhesive system (LuxaBond Universal DMG) is applied with a special micro-brush for root access to improve rubbing into the root walls. After drying, thirty seconds are enough to remove excess bond for the chemical polymerization process to take place. A 45-second light exposure is then given.
Fig.14
A universal mixer with a flexible metal tip (Colibri breakable plus Sulzer Mixpac) is used to introduce the dual-curing composite (LuxaCore Z DMG) into the root and at the same time into the core shape to achieve perfect uniformity between the root and coronal parts.
Fig.15
A 3-second spot cure is used to remove excess material in the neck area. It is then important to maintain a setting time of two minutes until the dual-cure buildup reaches the plastic phase. Only after this setting time has passed, photopolymerization for 1 minute is recommended. Why? To avoid massive polymerization stress due to the large volume of the composite reacting. It is for this reason that LuxaCore Z (DMG) is suitable for this buildup technique.
Fig.16
The temporary crown was made using a new generation syringe-hardening resin (LuxaCrown DMG).
Fig.17
To improve the thickness of the keratinized gingiva and prevent the appearance of grayish color through the marginal gingiva, a connective tissue graft was placed into the cervical area using a flapless technique for minimal invasiveness.
Fig.18
A week later: gum healing is not yet complete, but we can already see the integration of the graft.
Fig.19
After a month, the permanent crown is cemented and finally integrated. As you can see, the pink aesthetic is only slightly modified.
Fig.20
Three years later, we can note the proliferation of the graft, which was superimposed on the ceramic. This phenomenon is common with connective tissue grafts and can be corrected with a thin gingivectomy to lengthen the crown back to its ideal proportion.
Conclusion
Fiberglass pin restorations have esthetic, biological and mechanical advantages. Preservation of the remaining tooth structure is imperative, so the clinical protocol must be strictly followed, as with any bonding protocol. Surface cleaning, choice of fiberglass post, choice of adhesive system, quality of material insertion, type of composite buildup, residual wall and clinical protocol are key factors that will make your restoration the best possible.
Source: Style Italiano
Translation from English by Dmitry Lantsuntsevich for the BELODENT.ORG portal
Similar articles:
Anna Salat
Initial caries: minimally invasive treatment
Cancellation
Dentists should choose the most appropriate treatment for patients with early caries on the proximal surfaces of the chewing teeth.
Anna Salat Read Roma Turetsky
Postorthodontic lengthening of incisors using direct restoration
Cancellation
Composite materials allow you to directly restore teeth without tissue preparation.
Roma Turetsky Read Sarmad Hijran
Compromise case of restoration using a single veneer. Recreating shape and color using composite material
Cancel
Composite restorations can last a long time and look very natural if you know the characteristics of composite materials. With experience, focus and knowledge, we can make almost anything out of them.
Sarmad Hijran Read Osama Shaalan
A simple approach to closing diastemas using layer-by-layer composite application technique
Cancellation
This article describes a clinical case of closure of multiple diastemas using the method of layer-by-layer application of several shades of composite.
Osama Shaalan Read
Sarmad Hijran
A creative approach to restoring multiple posterior teeth
Cancellation
The article describes a clinical case of replacing old failed restorations of teeth 4.5, 4.6, 4.7 with composite restorations, as well as a finishing protocol.
Sarmad Hijran Read Jordi Manauta
Optimal technique for layering composite material in a Black class 5 cavity
Withdrawal
Although the mechanism of debonding of cervical restorations has not yet been fully explored, clinical results have led to the identification of optimal treatment protocols in the long term.
Jordi Manauta Read Maroun Ghaleb
Use of composite materials for long-term restoration
Cancellation
The article describes a clinical case of replacing a composite restoration of a central incisor after 18 years of its existence.
Maroun Ghaleb Read Ali Almasoudi
Direct composite restoration of the central incisor
Cancellation
Modern dentistry allows us to rely on quick and simple protocols to achieve satisfactory results.
Ali Almasoudi Read Prashant Hatkar
Creating the perfect smile with direct composite restoration. One material, many solutions
Cancellation
This article describes a clinical case of correction of tortoanomaly of the right lateral incisor, increasing its length and closing small diastemas using composite restoration.
Prashant Hatkar Read
Osama Shaalan
Restoring natural aesthetics with direct composite restoration
Cancellation
In this clinical case, only one enamel shade was used to minimally invasively close small diastemas, correct the shape of teeth and enhance their brightness.
Osama Shaalan Read Mohammed Al Hasani
A simple way to replace an old restoration
Cancellation
Although replacing an old defective restoration may seem simple, it involves many complexities such as restoration of occlusion, contact point, etc.
Mohammed Al Hasani Read Monaldo Saracinelli
A simple approach to closing a diastema
Cancellation
Clinical case of diastema closure using composite materials.
Monaldo Saracinelli Read
- ‹
- 1
- …
Pros and cons
The positive qualities of fiberglass rods include:
- There is no significant destruction of the organ and composite.
- The elasticity of the pin corresponds to natural dentin.
- Uniform distribution of load across the dentition during chewing.
- The composition does not contain nickel, chromium or other substances that can provoke rejection.
- Light transmission.
- Matches the shade of natural enamel.
- Simplicity and painlessness of extraction.
The only drawback of the product is the likelihood of restoration chipping during prosthetics. The risk of complications increases if the dentist is insufficiently qualified.
Preparatory stage
Before you begin fixing the rod, you should prepare the dental element for manipulation. Algorithm of the dentist’s actions:
- X-ray diagnostics are performed to assess the condition of the tooth.
- An artificial expansion of the passages is performed if the natural width does not allow the implantation of the product.
The doctor must first evaluate the location of the root system, the presence of bends and branches.
Step-by-step installation
During the process of implanting the pin, the doctor performs a list of sequential actions:
- Depulpation and preparation of the cavity for fixation of the rod.
- Model fitting. The ratio of the rod to the channel is 1:4.
- The canal cavity is degreased with alcohol.
- The working surface is etched with 37% phosphoric acid. The substance is evenly distributed over the dentin and enamel coating. On the outer surface of the tooth it is maintained for up to 60 seconds, and on the inside – up to 15 seconds.
- Rinsing with distilled water.
- Drying the canals with a paper point. Purging is not recommended.
- Preparing the structure for implantation - disinfection, drying in natural conditions, sandblasting.
- Acid pickling. Polishing.
- Filling the canal with a thin layer of dental cement. Part of the composition is distributed over the pin. The product is implanted into the passage.
- Light polymerization.
- Fixation of the outer part of the unit.
The choice of crown is made by the patient.
How to choose a model
A low-quality device is fraught with the development of inflammatory processes in the jaw apparatus. Therefore, the choice of model should be approached responsibly.
The rods must have the correct shape, safe composition and quality characteristics. Popular models:
- Glassix. The product has a truncated cylindrical shape and is rounded at the end. Mechanical properties are close to those of dentin tissue and composite material.
- Ikadent. A model with a high level of aesthetics and increased elasticity. Used for restoration of the anterior zone.
- Relyx Fiber Post. Easy to process model. The extended tip ensures high-quality shrinkage of the cement and prevents the formation of porous fragments in the structure.
- EasyPost. Polymer matrix that does not change color under the influence of pigments. The possibility of translucency is excluded. Strong fixation.
- Fibrapost Lux. In-canal products of conical shape. The flexibility of the rod is almost identical to dentin tissue.