Content:
- Methods used in dental practice
- Medicines that are most often used in the dental office
- What affects the duration of the anesthetic effect?
- What to do to quickly forget about dental intervention
- After what time can you eat?
Most people are afraid to have their teeth treated because they are afraid of pain.
It seems to them that any medical manipulation will cause them serious discomfort. Fortunately, the days of painful dental procedures are far behind us. Today, using highly effective anesthetics, doctors manage to make even the most complex procedures comfortable for the patient and completely painless. Meanwhile, some clients have a question about how long the anesthesia wears off after tooth extraction or pulpitis treatment. They are embarrassed by a long-lasting feeling of numbness. Let's consider this issue in more detail.
Local anesthesia in dentistry for children
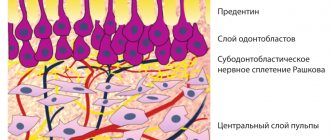
Local anesthesia is an anesthesia that temporarily blocks the transmission of nerve impulses. This means that during the treatment the child does not feel pain or discomfort. Dentists use local anesthetics as medications, selecting the composition after determining the patient’s allergic reactions.
Local anesthesia for children's teeth is usually carried out in two stages:
- application - for primary reduction of sensitivity;
- injection - administration of an anesthetic composition through an injection of an anesthetic.
Anesthesia for the treatment of baby teeth in very young patients takes place in three stages. The first is application “freezing”. The second and third are injection anesthesia. The first injection of anesthetic is performed with a minimum dose, a drop. Anesthesia takes effect almost immediately, after which the entire volume of the drug is administered.
Rodikova Tatyana
With children 3-4 years old we usually play a fairy tale - based on Frozen or invent our own. First, we smear the gums with “magic ice jam”, then we cast a spell like Elsa “to freeze microbes.” And after that we “make Olaf the snowman” or simply “freeze everything around.” Kids are happy to listen and help, which eliminates tears and whims during dental treatment.
Methods used in dental practice
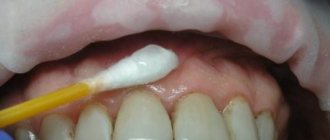
How long it takes for the anesthesia effect to disappear depends directly on the method of anesthesia used. The sensitivity of tissues is restored most quickly when using an application. The doctor applies a special gel to the area of upcoming manipulations, which “freezes” for about fifteen minutes.
If the anesthetic medication was administered using a syringe and needle, the area will remain numb for up to one to three hours. The exact time is determined by the location of the treated area, the dose and type of drug.
Basic painkillers
Not any anesthesia can be used when extracting a tooth. In dentistry, only the most common and effective medications are used. And almost every hospital has Novocaine.
But in modern treatment, novocaine is used much less frequently. If previously not a single operation could be done without it, now this drug causes an allergic reaction in most people. It has a number of side effects:
- dizziness;
- lethargy;
- lowering blood pressure.
Today there are more intense anesthetics, and therefore novocaine is used only in combination. It is injected into the body with a small dose of adrenaline. In combination, these drugs have the best analgesic functions. But such a mixture should not be prescribed to people whose blood pressure is off the charts.
For infiltration anesthesia, a 0.5% lidocaine solution is used. This drug can be used for the conduction method; only a 1–2% solution is required. For an adult, the norm is 300–400 mg. Side effects of this medicine include:
- headache;
- fatigue;
- loss of sensation in the lips and tongue;
- heart rhythm is disturbed;
- blood pressure decreases;
- there may be hives.
The most modern anesthesia is a medicine based on the substance articaine. Such drugs can provide long-term and reliable pain relief. It is used by a large number of dental surgeons. The substance reaches its maximum effect after 10 minutes and maintains its result for 1–3.5 hours. But no matter how good the drug is, it always has side effects:
- muscle twitching;
- headache;
- tremor;
- nausea;
- vomiting reflex;
- diarrhea.
These are the most common side effects. But sometimes others happen:
- blood pressure decreases;
- cardiac arrhythmia is disturbed;
- rashes appear on the skin;
- angioedema may occur.
These painkillers cannot be used for meningitis, tumors, osteochondrosis, spondylitis, tuberculosis, metastatic lesions of the spine, heart failure, tumors in the abdominal area, severe arterial hypotension, and hemostasis disorders.
Use with caution during pregnancy. The drug may cause a decrease in the fetal heart rate.
A very good drug based on articaine is Ubistezin. It also contains adrenaline. It reduces blood vessels in the area where anesthesia was administered. This makes it difficult to absorb the substance. As a result, the analgesic effect begins to act within 3 minutes. In addition to the above listed side effects that drugs based on articaine have, Ubistezin also adds the likelihood of an ischemic zone in the area where anesthesia was administered. This occurs if a blood vessel has been hit or a nerve has been damaged.
Medicines that are most often used in the dental office
If you need to numb a tooth, the doctor may use different drugs. The list of the most popular includes:
- Novocaine. Has a short period of action.
- Lidocaine and products containing articaine. Provides a medium-duration analgesic effect.
- Bupivacaine, Hirocaine, Ropivacaine. They have a long period of action.
The doctor determines which drug to choose taking into account the complexity of the upcoming treatment procedures. It is important that the patient is not allergic to the prescribed anesthetic.
Types of anesthesia in pediatric dentistry
Modern dental technologies are very diverse.
Hypnosis, musical sound analgesia, laughing gas, electroanesthesia, and infiltration anesthesia can be used as anesthesia for children during dental treatment. But more often they use methods based on proven medications and compounds. Protocols can be classified according to a variety of criteria. General gradation:
- local anesthesia;
- Oxygen sedation;
- deep sedation;
- general anesthesia.
There are also different methods of how dental anesthesia is given to children:
- topical anesthesia - smearing the gums with an anesthetic to locally “freeze” the nerve endings;
- injection anesthesia - administration of the drug using a carpule syringe with a particularly thin needle;
- mask for children - used in dentistry to administer anesthesia or a nitrogen mixture.
The names of drugs for pediatric anesthesia during dental treatment deserve special mention. Most often this is:
- Sevoran for general anesthesia is a highly effective inhalation anesthetic with the highest safety profile.
- Propofol for deep sedation is a completely safe composition for intravenous anesthesia.
The method of pain relief is selected taking into account the patient’s age, indications for use, and the amount of planned dental work.
What affects the duration of the anesthetic effect?
The same drug may work differently in different people. For example, for some the analgesic effect disappears in one hour, while for others it lasts two or even three hours. What affects the duration of anesthesia, besides the pharmacological characteristics of the drug itself? There are several fundamental factors:
- The presence of inflammation in the anesthetized area. For example, after the removal of a wisdom tooth that was painful, the rehabilitation period is always delayed. The fact is that the active compounds of anesthetics have an alkaline environment, and in a localized inflammatory focus it is acidic. The combination of the two media causes neutralization of the alkaline composition of the drug. Because of this, the pain relief effect either does not develop at all or disappears very quickly. With advanced inflammation, it is very important to correctly calculate the optimal amount of pain medication so that the patient does not feel acute pain during treatment.
- The inclusion of components in the administered drug that promote spasm of blood vessels. Such substances make the anesthetic more effective and increase the duration of its action.
- Patient's age. It is more difficult for older people to obtain pain relief, and the anesthetic effect lasts longer.
- The presence of diseases of internal organs. Metabolites of dental drugs are eliminated from the body due to the work of the kidneys and liver. If there are diseases of these organs, anesthesia lasts longer.
- Experience and accuracy of the dentist. When giving an injection, the doctor must follow the injection technique and accurately calculate the dose. Any mistake makes the result of using an anesthetic unpredictable.
What can I do to make the anesthesia wear off faster?
If the patient does not want the anesthesia to wear off for a long time and cause unnecessary discomfort, you can follow simple tips:
- When planning a trip to the dentist, you should exclude fatty foods and alcohol from your diet. This will help relieve the liver and other glands that produce secretions to speed up metabolism. Thus, the anesthetic will be removed from the body faster, and the frozen area will recover from anesthesia more quickly. It is worth limiting the intake of medications except for those that are necessarily prescribed by the doctor and the refusal of which can lead to negative consequences.
- After minor dental procedures, significant volumes of liquid and massage of the freezing zone will help relieve anesthesia.
- In case of complex operations, on the contrary, it is necessary to exclude impact on the place where the intervention took place. Eating food and liquids is possible no earlier than four to five hours later.
If the numbing, pain-relieving effect does not subside for quite some time after visiting the dental office, this may indicate that a nerve has been affected. In this case, you should consult a doctor for additional help and advice to avoid negative consequences.
Before going to an appointment, each patient at a dental clinic must be sure that there are no allergic reactions to anesthesia. Otherwise, before using anesthesia, the doctor must conduct testing by administering a small dose of the drug. This will allow you to get rid of possible problems and side effects after visiting the dentist.
Category: Tooth extraction Published by Mister stomatolog
What to do to quickly forget about dental intervention
Very often, upon returning home, the patient continues to feel numbness in part of the jaw. This condition can cause discomfort and even mild aching pain. In order for tissue sensitivity to be restored as quickly as possible, the following rules should be followed:
- On the eve of planned dental procedures, avoid drinking alcohol , fatty and heavy foods. If a specialist recommends taking any medications, it is important to follow his prescription.
- In the case of treating caries , removing tartar, grinding down the top layer of enamel under a crown, it is permissible to massage the gums. You can also drink warm tea or heated water. These simple methods will increase local blood circulation and create conditions for the speedy release of anesthesia. But, if anesthesia was administered before tooth extraction, there should be no talk of any self-massage - touching the hole with your hands is strictly prohibited. Otherwise, you can damage the blood clot that protects the wound from the penetration of bacteria and germs. This will lead to severe inflammation and bleeding.
Don't be alarmed if the anesthetic continues to work for up to six hours. The situation will normalize on its own. If the numbness does not go away longer, this is a reason to consult a dentist again.
What to do if the numbness does not go away?
There is no need to be afraid of prolonged tissue numbness; after a couple of hours, sensitivity will definitely return. If numbness in your teeth, tongue, jaw, or nose after anesthesia does not go away by the end of the day, you should call your doctor and report the situation. In rare cases, complications of anesthesia occur in the form of paresis and paresthesia - disruption of tissue innervation. They appear when a nerve is accidentally injured by a needle. In this case, you need to visit a doctor who will prescribe treatment for the pathology. When the anesthesia of the tooth wears off, discomfort and unpleasant sensations may appear.
In most cases, tissue anesthesia passes without a trace, so if there are indications for anesthesia, there is no need to be afraid to perform it. If you have had an unpleasant experience with pain relief or need emergency treatment under anesthesia, you should simply tell your dentist about it. The doctor will definitely take into account your wishes and will be able to control the amount of the drug and the duration of its action.
Anesthesia doesn't work
There are cases when the anesthesia does not work and the person feels pain. There are several factors why this happens:
- Alcohol. The chemical composition of ethyl alcohol can block the effects of the anesthetic. Therefore, it is not recommended to go to the dentist if you have recently consumed strong drinks.
- Using large amounts of painkillers. If a person is taking medications that contain painkillers, they should not be taken before seeing a doctor.
- A person may have individual immunity to certain anesthetics. This factor is very rare.
If the anesthesia does not work, then it is worth understanding the reason. Having received the result, the treatment is postponed to another day.
Removing baby teeth
Milk teeth that can no longer be cured, but they provoke the development of acute inflammation of the bone or periosteum, must be removed. Which method to use will depend on the specific situation.
For example, the milk tooth being removed is already well loosened and the pain when pulled out will be minimal. In this case, the doctor may advise putting on an application, gel or aerosol.
Lidocaine aerosol is used quite often. There are 3 mg per 1 kg of body weight. For children, it is better to apply this substance using a cotton swab.
For more serious dental problems, children are given infiltration anesthesia. Lidocaine, Ubistezin Forte and similar medications are used. Two injections are made - from the gum and from the tongue.
Children tolerate these painkillers well. But before using them, it is necessary to undergo tests to identify allergens. It is also worth clarifying whether the child has problems with the cardiovascular system.
Children
It should be noted separately the features of local anesthesia in children. The technique of local anesthesia in children must be planned so that 100% pain relief is achieved at all stages of treatment, otherwise it will be impossible to carry out the necessary manipulations.
As mentioned above, children under 5 years of age are given an anesthetic without adrenaline (3% scandonest SVC, or septanest 4% SVC).
Children over 5 years old can use an anesthetic with low concentration adrenaline (1:200,000 - Ultracaine DS). The dose of drugs is selected depending on age. Pain relief is performed in children in 3 stages:
- First, a superficial anesthetic gel is applied
- then a small dose (0.1-0.2 ml) of anesthetic is administered;
- after which, after 60-90 seconds (time sufficient for effective anesthesia of the needle path in the soft tissues), the remaining amount of the planned dose of anesthetic is administered.
We wait 5-10 minutes until complete anesthesia occurs. The child, feeling a complete absence of pain, gains confidence in the doctor and gives the opportunity to carry out the necessary intervention.
Scandonest SVC
If the patient belongs to a risk group (with severe concomitant diseases , in particular cardiovascular pathology ), the use of an anesthetic solution with adrenaline, a vasoconstrictor, should be completely abandoned. In such cases we use Scandonest SVC . This anesthetic exhibits a vasoconstrictor effect, i.e. has vasoconstrictor properties and can therefore be used without adrenaline, which means that the drug does not contain sulfites and can also be used in patients with bronchial asthma and allergic conditions (after an allergy test). Scandonest SVC is a medium-strength anesthetic; provides anesthesia, depending on which part of the jaw the doctor disconnects from pain sensitivity, for 20 - 90 minutes, which sets it apart from the group of other non-adrenaline anesthetics.