18.05.2018
6739
- 1 Why are crowns needed?
- 2 Why does the crown interfere with the bite?
- 3 What to do if a temporary crown comes off?
- 4 Do I need to see a dentist?
One of the most common services provided by orthopedic dentists is the production of dental crowns. Crowns are permanent dental prostheses that can be single or fastened together. People who have undergone prosthetics often complain that the crown of the tooth interferes with chewing. Let's look at the causes and possible solutions to this problem.
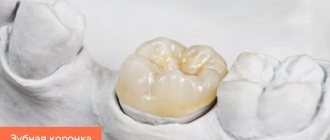
The shape of the crown matches the shape of the tooth
When making a crown, it is necessary to reproduce the anatomical shape of the tooth as accurately as possible. To do this, the technician draws the chewing tubercles, creates contact points and clearly draws the equator.
- The tubercles and pits on our teeth perform different functions, and each element has its own function. Some parts are designed for grinding food, others fix the correct bite or distribute the chewing load. The tubercles also ensure proper closure of the crown with the antagonist tooth located opposite it. If the closure is not tight enough, both teeth will move to the side, trying to take the correct position. Incorrect placement of the tubercles will be indicated by discomfort from the crown 2-3 weeks after installation. The doctor checks this point using a piece of special paper on which traces remain. This is also why temporary crowns are used, a kind of test drive.
- Equator. We are talking about a thickening, thanks to which food does not fall on the gums, but slides inside the oral cavity, as if down a slide. If the equator on the new crown is flat, then food particles will fall into the periodontal sulcus, which will lead to inflammation and discomfort. Contact point. This refers to the point at which adjacent teeth meet. It must be present, otherwise an interdental gap will form into which pieces of food will get clogged. Inflammation of the corresponding area of the gum may also appear. To test, take dental floss and pull it between your teeth. If you hear a click, there is a contact point.
Why does a crown interfere with my bite?
The low-skilled work of an orthopedic doctor can often lead to the fact that the installed prosthesis interferes with normal eating and simply living; it is constantly felt in the oral cavity. One of the reasons may also be a design defect. A dental laboratory can produce a structure with a slightly different size, or poorly polish the ceramics or coating.
When an orthopedic surgeon works with a patient and a prosthesis, he may use more cement than necessary to secure the structure. This will manifest itself in a slight overestimation of the height of the tooth and complaints that the crown interferes with the closure of the teeth. The feeling of interference can be caused by incorrect positioning of the prosthesis, for example, its rotation or immersion too deep. Such mistakes will cause pressure on other teeth, and the denture wearer will feel discomfort or pain.
If you have installed a plastic crown, and it causes discomfort, then it is likely that the material has changed in size due to the oral fluid from which it is made, and has swollen. This leads to pressure on the tissue surrounding the crown.
Sometimes painful sensations can be associated with damage to the tooth stump. If the supporting tooth suffers from the development of acute periodontitis or some kind of inflammation occurs, then exudate begins to accumulate in the periodontal gap. This leads to a slight increase in the size of the tooth, but sufficient for the sensation that the tooth has grown larger. Sometimes the adjacent gum may become inflamed, and the patient will consider this problem as a consequence of the installation of the prosthesis. How to solve a problem
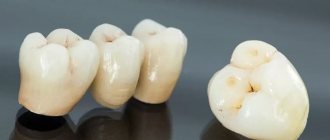
To eliminate the problem, it is necessary to determine the cause of its occurrence. If it is determined that it is associated with poor quality of the crown or the doctor’s work, then the clinic’s responsibilities include replacing the structure free of charge. There are six types of crowns:
- Of gold;
- Made of metal;
- Made of ceramics;
- Made of plastic;
- Metal-plastic;
- Metal-ceramic.
If the design is made of plastic, then it is possible to adjust it and use it again. All other dentures require a complete replacement.
If research shows that the cause of discomfort lies in slight contact with the antagonist tooth, then it is possible to perform micro-grinding of the tooth. The operation involves grinding down a small part of the opposing tooth, which eliminates premature contact and the feeling that metal ceramics are in the way in the mouth.
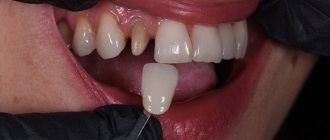
The color of the crown matches the adjacent teeth
The color of any crown, with the exception of a metal one, should match the color of the neighboring teeth. It is also important to observe a natural transition, when the tooth at the neck is slightly yellowish, and closer to the cutting edge it turns white and becomes transparent.
If the new crown causes you discomfort, you feel it like a foreign body, then we recommend that you immediately contact your dentist. It may have been installed incorrectly and requires correction. You should also come for an appointment if, after installing a metal-ceramic crown, you feel a metallic taste in your mouth.
Why are crowns needed?
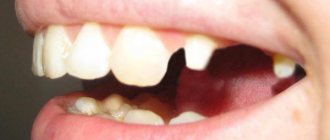
This prosthesis is necessary for people when their teeth have significant damage.
As a rule, teeth are destroyed due to advanced caries, when a course of dental canal treatment has been completed, or due to injury. All these cases can lead to the tooth being severely damaged and close to destruction. It is unreasonable to install a filling in such a situation, so it is necessary to resort to the help of prostheses. This problem most acutely concerns pulpless teeth. The fact is that in the absence of pulp, the tooth is deprived of nutrition. Because of this, its walls become more fragile over time and will sooner or later crack. It often happens that a crack runs throughout the entire tooth. This means that a tooth that was not problematic yesterday, but which could last for a long time, is completely removed by a doctor today.
Do you really have to put up with this?
Making dentures is quite a complex job, in some ways even comparable to art. Working in tandem, the orthopedic surgeon and the dental technician put a lot of effort into making an accurate and as comfortable prosthesis as possible. But in most cases, after putting it on and wearing it, it turns out that it needs some adjustment to the patient’s gums.
To regain lost comfort, you need to walk with the installed structure for 3–4 weeks. During this time, you can get used to the initially interfering prosthesis and get rid of the unpleasant sensations. If you simply remove it when discomfort appears, then you will have to describe all the inconveniences experienced in words, and the doctor will not be able to understand what exactly caused them. Do you want the correction to be effective? Be sure to come to your appointment wearing a prosthesis that causes discomfort.
Correction of dentures is carried out within 15–20 minutes. As a rule, it is possible to restore the patient’s comfort in one or two visits to the dental clinic.
Treatment
If the prosthesis is mobile, the doctor must determine the degree of displacement and instability of the artificial tooth. If the reason is weakening of the fixation, the prosthesis or abutment is removed, after which the structure is reinstalled. If dismantling the coronal part is not possible, which could lead to serious damage, fixation is carried out using a drilled hole. The cavity is then closed with filling material.
If none of the above options is suitable, the crown must be removed altogether. It is cut, after which the fastening is checked, and the connecting part is repaired. To restore the row, a new prosthesis is made and installed in place.
In some cases, the cause of the problem is peri-implantitis. In such a situation, the doctor must preserve the bone tissue to eliminate complications and avoid the need to remove the implant. Treatment methods depend on the stage of the disease, bone condition and other factors. The following actions are usually taken to eliminate inflammatory processes:
- office cleaning, removal of plaque and stone;
- ultrasonic treatment, elimination of affected areas;
- bone grafting, for which barrier membranes and bone substitutes (natural or synthetic) are used;
- therapy aimed at protecting against pathogenic bacteria (general and local with treatment of the affected surface);
- hygiene using antiseptics;
- control using radiography.
After treatment is completed, re-prosthetics are performed. Extraction of the artificial root is required only in situations where implant failure occurs. You can insert a new pin after removing it, treating the hole, removing necrotic tissue and plastic surgery. In some cases, a new rod is placed in the old socket after completion of therapy. But there is no clear opinion among experts; it all depends on the condition of the tissues and other factors.
Prevention
To avoid complications, the patient after implantation must follow a number of rules regarding oral hygiene. Poor condition and poor care are the main reason for the development of complications, any diseases of soft tissues and bones.
After completing the treatment procedure, the Patient at home must do the following:
- brushing your teeth twice a day with soft brushes that are changed every two months;
- removing food debris using irrigators or electric brushes, rinsing with antibacterial solutions;
- using dental floss to remove plaque from the cervical area;
- the use of multi-beam, cylindrical, conical brushes;
- refusal of bleaching, soda-containing or fluoridated toothpastes.
If these measures are followed and regular preventive visits to the dentist, the development of complications is reduced to a minimum. In addition, it is recommended to protect the row from excessive loads and injuries, and to exclude situations in which the prosthesis or jaw could be damaged.
Do I need to see a dentist?
If an inflammatory process occurs, then professional therapeutic treatment is necessary. To do this, the crown is removed without the possibility of reusing it. After sanitation, it is necessary to monitor the dynamics for some time, and it will be possible to resume orthopedic treatment only when the absence of inflammation is confirmed.
If you feel that the crowns are interfering with your bite, you do not need to fix the problem yourself. Seek help from a specialist as soon as possible. Without the intervention of a specialist, restoration of the bite is impossible. If the teeth meet in a certain place, and not evenly, then many problems can arise. Among them: increased tooth wear, gaps in teeth and other complications.
Important!
If for some reason your doctor does not want to redo his work, then you need to contact another specialist, but you should not delay the solution to this problem.
What to do if a temporary crown comes off?
The first thing to do in such a situation is to call your doctor.
You will discuss with him the urgent measures that need to be taken, and will also schedule an appointment to re-attach the crown. Most likely, he will suggest putting the crown back in for a while. This is necessary to protect the tooth from damage, displacement, and other things. The inserted crown may not sit completely, causing a feeling of discomfort. In this case, you do not need to insert it, just wait until you see a doctor, and before that, try not to eat hard, cold or hot foods. If it fits well, but not securely, then you can fill it from the inside with Vaseline or toothpaste.
Inflamed papillae and red spots on the tongue
Inflammation of the tongue causes many problems. It manifests itself as an increase in the papillae on the root of the tongue, their redness, and a change in sensitivity. Often the patient mistakes these symptoms for the result of tongue biting. However, as the inflammatory process intensifies, the intensity of the unpleasant sensations increases, which forces us to look for another cause of the pathology.
Causes
Implantation can cause the tongue papillae to become swollen if the muscle is injured by the prosthesis or implant. However, in most cases it is called:
- Chemical burn of mucous tissues resulting from exposure to alkalis, concentrates, acids, regular long-term resorption of tablets.
- Thermal damage - consuming too hot or cold foods or drinks.
- Injury to the mucous membrane by gastric juice in gastroesophageal reflux disease.
- Burn of the tongue with hydrochloric acid during vomiting.
- Mechanical damage to the muscular organ of the oral cavity - bite, scratch, puncture;
- Resorption of food, as a result of which the tongue rubs.
- Damage to the tongue due to aggressive hygiene procedures, the use of toothpicks, matches, pencils to clean the oral cavity.
- Damage caused by the sharp edge of a decayed tooth.
- Infection in the mouth, throat, stomach.
- Injury to the muscle by teeth due to malocclusion.
- Development of glossitis. The disease is caused by bacteria, viruses, and fungi that spread when a muscle organ is damaged. Glossitis can result from rubbing with dentures or diseases (HIV, cancer, iron deficiency, lichen). A clear sign of glossitis, in addition to enlarged tongue papillae, is the appearance of red spots.
Treatment options
Therapy for the inflammatory process depends on the cause of its development. If the receptors are inflamed due to mechanical damage, chemical or thermal burn, local healing drugs are prescribed (Vetoron, Karotolin, Chlorophyllipt, Lugol's spray). Antiseptic healing ointments (Cholisal, Solcoseryl) will also help get rid of enlarged papillae on the root of the tongue. For severe pain, local anesthesia is indicated (Lidocaine solution, Strepsils spray, Emla ointment).
Drugs that stimulate the immune system may be prescribed. If the cause of swelling of the papillae is the influence of microorganisms, antifungal, antiviral or antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
Possible causes of pain
Most often, before installing a crown, the dentist performs depulpation. Pulp is a loose tissue that is located inside the tooth and is penetrated by many blood vessels and nerve endings. Therefore, this procedure is colloquially referred to as nerve removal. It is generally accepted that pulpless teeth do not hurt and do not cause problems. In fact, this is not entirely true, since inflammatory processes often spread to surrounding tissues.
Inflammation is one of the most common causes of pain in a pulpless tooth under the crown. It is important to note that the factors that provoke the development of the inflammatory process are:
- Inadequate tooth preparation. A correctly performed procedure assumes that the pulp will be completely removed, and the canals will be disinfected and sealed to a physiological level. If the canal is not completely sealed, the resulting cavity creates conditions favorable for the development of bacteria. The same thing happens when using low-quality filling materials - over time, they sag and form voids into which infection penetrates, resulting in inflammation.
- Root canal perforation. As a rule, the thickness of the canal walls is small, so in complex anatomical cases they can be damaged. Perforation is the formation of a through hole, which is an “open door” for pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, if this complication occurs, it is necessary to close it carefully.
- Incorrect fit of the prosthesis. If the crown is not installed correctly, a small gap remains between its edge and the gum or the crown and the tooth. Over time, food particles accumulate in it, which causes an increase in the number of bacteria. The result is inflammation and pain under the crown again.
- Failure to follow doctor's recommendations. Poor oral hygiene, excessive consumption of sweets, the habit of opening lids with teeth - all this can also become a factor that provokes pain. In this case, the inflammatory process occurs due to the proliferation of bacteria or traumatic damage to the tissues surrounding the tooth.
- Crack or fracture of a tooth. If a prosthetic design is chosen that is inadequate to the case or the tooth was previously severely weakened, then a root crack may occur, and then a fracture.