Author: Salatsky Dmitry Nikolaevich Chief physician, orthopedic dentist, gnathologist, maxillofacial prosthetist When treating most dental diseases, doctors do not limit themselves to simply removing the affected necrotic tissue, cleaning out the carious cavity. Very often, the dentist’s task becomes the need to remove the pulp, the neurovascular bundle located inside the tooth, and clean it with further filling of the tooth canals (endodontic treatment). In this case, the dentist must go through all the canals in the tooth without exception, since the anatomical space inside the dental unit remaining uncleaned and unsealed can lead to irreversible consequences due to which it will have to be removed.
Causes of obstruction of dental canals
The root canals of teeth can become obstructed for a variety of reasons. The most common include:
- features of the anatomical structure of the tooth - highly curved roots with small branches, flattened areas and transverse bridges;
- inflammatory processes in the neurovascular bundle - with dental injuries and chronic pulpitis with a subacute course, the root canals can become overgrown;
- age-related changes in tissues - over time, dentin deposits accumulate on the walls of the root canals, which lead to a narrowing of the lumen;
- dental procedures using phosphate cement - this material has a high density and cannot be destroyed by ultrasonic waves, instruments and solvents.
Before starting endodontic treatment, it is important to accurately determine whether the canals are patent.
How do root canals work?
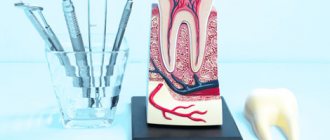
An endodontist must perfectly know the anatomical and morphological structure of the tooth canals.
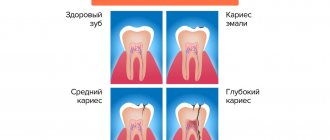
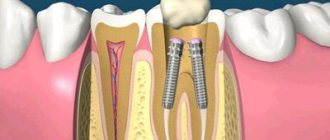
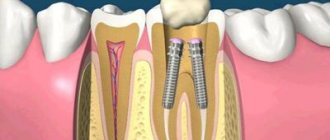
The tooth consists of three parts - crown, neck, root, and about 70% of the total volume falls on the root, around which the pulp chamber (cavity) is located, which passes into the root canals. A tooth can have one or several canals (the lateral group, as a rule, has more of them than the front). The exact number of canals can only be determined with the help of an x-ray examination, which also allows one to study the structure and characteristics of the canals in a particular patient. In modern endodontics, the most visual 3D images are used for these purposes.
It is important to know: the number of tooth roots may not coincide with the number of root canals.
Milk teeth are no different in structure from permanent teeth; their distinctive features are an enlarged apical foramen, thinner canal walls and low dentin mineralization. Treatment of pulpitis or periodontitis in patients with baby teeth is impossible without cleaning the root canals, and their mechanical treatment requires the doctor to be extremely careful and careful.
Diagnostics
Treatment of impassable root canals begins with determining their length and anatomical features. The most informative diagnostic method is radiography. To obtain accurate data on the condition of the tissues, a photograph of the tooth root is taken with the instrument inserted into it. This allows you to see:
- length of root canals,
- the presence of curvatures and perforations,
- impassable areas.
The condition of the periodontium is also assessed. This allows you to determine further treatment tactics.
How channels are processed
The effectiveness and duration of endodontic treatment depends on the method of canal treatment chosen by the doctor, namely:
- Manual - cleaning using special tools; the process is lengthy and tedious not only for the patient, but also for the doctor.
- Mechanical - cleaning using nickel-titanium tools and an endomotor; Much faster and more efficient than manual cleaning, it allows you to clean even curved channels well.
- Ultrasonic – cleaning using an ultrasonic scaler; special endodontic attachments make it possible to easily remove remaining pulp and quickly expand narrow canals; with the help of such attachments, it will not be difficult to free the canal from old gutta-percha or remove a broken instrument.
Most experts agree that high-quality irrigation of dental canals can only be achieved by combining different methods.
Important! In our clinic, the endodontist has the opportunity to use mechanical and passive ultrasonic cleaning in his practice, which, in combination with competent medicinal treatment of the canal with special disinfectants, ensures a 100% result.
The main principle of qualified endodontic treatment is the use of a microscope, which allows, under multiple magnification, to achieve the necessary efficiency of treatment, thorough disinfection and sealing of canals.
To control the quality of the work done during treatment and after its completion, control images must be taken to exclude the possibility of complications.
Features of treatment
Various techniques are used to treat impassable root canals:
- devital amputation of the pulp followed by mummification,
- depophoresis.
A special approach is required if the root canal:
- strongly curved
- completely closed,
- narrowed,
- is located next to the neighboring root.
To make the canal passable along its entire length, modern dentistry uses:
- durable extractors - nickel-titanium files, which allow you to go through the canal without preliminary tooth preparation;
- drills - special instruments with spiral blades designed for quick and safe removal of gutta-percha, pastes, cements and other filling materials;
- solvents - necessary for unsealing previously sealed canals; they cope well with soft and plastic materials.
The treatment tactics for impassable root canals in each clinical case are determined by the doctor. The procedure is performed under anesthesia. Depending on the complexity, treatment is carried out in one or several stages. To obtain the desired result, 2-3 visits to the dentist may be required.
Clinic doctors
Often during endodontic dental treatment, dentists encounter root canal obstruction (obstruction of the root canals of the teeth). But in most cases, this problem can be solved thanks to the high professionalism of specialists and the excellent equipment of the DentaBravo clinic.
Why does tooth root canal obstruction occur?
There are several causes of root canal obstruction:
- Anatomical structure of the root.
The canals may be flattened, curved, with small branches or transverse bridges.
- Inflammatory phenomena in the pulp. Chronic caries, subacute and chronic pulpitis, mechanical overload of the tooth provoke overgrowth of the canals.
- Age-related changes. Over the years, deposits of dentin or dentin-like tissue (denticles) accumulate on the walls of the canals. They narrow the lumen and often contribute to root canal obstruction.
- Treatment using phosphate cement. This is a dense material that cannot be removed by ultrasound, solvents, or mechanical methods.
How to determine tooth canal obstruction
Diagnosis of root canal obstruction is very important, because quality treatment requires careful preparation. And in order to freely manipulate during cleaning and expansion, the doctor must determine the working length.
The most common research method is radiography. A photograph of the root of a tooth with an instrument inserted into it makes it possible to see:
- tooth length;
- direction of movement of the endodontic instrument;
- obstruction of the root canals of the tooth;
- canal curvature;
- presence of perforation;
- periodontal condition, etc.
If there are symptoms of root canal obstruction, they need to be opened to the apical narrowing so that endodontic treatment can be carried out.
How is tooth canal obstruction treated?
Usually, when treating pulpitis or periodontitis, the doctor works with a pulp extractor. If there are no problems with the channels, then difficulties usually do not arise. But if the canal is curved, narrowed, closed, or adjacent to an adjacent root, a special approach is needed.
Treatment of root canal obstruction requires the use of special chemicals and a stronger extractor to avoid metal fatigue and instrument fracture. For example, nickel-titanium files (titanium needles) are used - rotating extractors, which make it possible to pass root canals without preparation and reduce the risk of pinching or breaking the instrument.
Also, in case of obstruction of the tooth canal, thin drill burs are used - instruments with spiral blades designed to eliminate old filling material (pastes, cements, gutta-percha).
Unsealing is also done using solvents that work well with soft and flexible materials. Difficulties arise with channels filled with resorcinol-formalin paste. When it hardens, it becomes very hard, and to eliminate the obstruction of the tooth canal it is necessary to use strong substances, drilling with a bur and nozzles with ultrasound. Unsealing a resorcinated canal is a long and labor-intensive procedure associated with the risk of tooth perforation. And if the patient has a phosphate-cement filling, the root is generally amputated or its apex is cut off.
Treatment methods for dental canal obstruction are selected individually. For consultation and diagnostics, sign up at the DentaBravo clinic!
When is tooth canal cleaning necessary?
Here are three common cases when a patient is required to have canal cleaning:
- Before installing the prosthesis on the tooth, the unit is depulped and ground down so that a crown can subsequently be installed on it;
- When diagnosing pulpitis (inflammation of pulp tissue). Usually pulpitis is a consequence of advanced caries and infection. The problem is accompanied by acute pain; it is painful for the patient to chew on the side of the pathological tooth, which indicates severe inflammation inside the tooth;
- If a person has been diagnosed with periodontitis - inflammation of the tissues around the tooth. Usually the problem is a consequence of untreated caries and a dynamically spreading infection.
Internal tissues and pulp become inflamed due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms. They can also get inside due to mechanical injuries (chipping off a piece of a tooth, splitting a crown due to a blow or fall, tooth dislocation), gum disease.
Note! Pain is not always the only signal to remove the pulp and clean the tubules of dead granules. Very often, cell death occurs without pronounced symptoms, when the tooth stops hurting, and the inflammatory process is already actively developing inside it. A visit to the dentist and a complete examination of the oral cavity will help you understand that there is a purulent-inflammatory process in the tooth.
It is important to thoroughly clean the canals from pulp residues, since pathogenic microflora will still provoke purulent-inflammatory processes. Therefore, it is advisable to remove inflamed tissue not only from the canals, but also from the crown part of the tooth.
In particularly complex and advanced cases, partial pulp resection is prescribed. If the dentist does not consider this method, unfortunately, the tooth is removed.
Dentistry for those who love to smile
+7
Make an appointment
Stages of canal retreatment
The procedure for re-treating the canals begins with providing access to them: removing the crown or removing (drilling out) the old filling, removing the stump inlays and pins. Then the canal cavities are freed from the filling material.
One of the stages that determines the quality of endodontic treatment is the correct measurement of the working depth of each canal. The most accurate result is obtained when using an apex locator - an electronic device connected via an electrode to a radiopaque K-file (a thin instrument immersed in the canal). As the K-file approaches the lowest point of the canal (apical constriction), the apex locator signal intensifies. An x-ray helps to clarify the readings of the device.
To ensure proper filling of the canal and adhesion (adhesion) of the filling material to its walls, preliminary mechanical treatment is necessary. Cleaning is done with hand instruments (high risk of breakage) or using an endodontic tip into which nickel-titanium profiles (thin drills) are inserted.
The intensity of rotation of the profiles is controlled by a micromotor, which triggers a reverse if the permissible pressure is exceeded. This method guarantees the absence of perforations, nicks and eliminates breakage of the instrument in the canal. Ultrasonic scalers and dentin softeners are used as auxiliary measures. This promotes maximum preservation of healthy tissue.
An important component of the canal revision process is their sterilization. The cavity is thoroughly washed and disinfected with antiseptics. In the presence of inflammatory formations, the following measures can be taken:
- opening the gums and excision of the root apex or complete removal of one of the roots (hemisection);
- laser removal of infected tissue;
- sanitation of channels through electrophoresis with calcium and copper ions.
After sterilization, filling material is placed. If the working length is incorrectly determined during machining, the top of the channel opens and the material flows beyond its limits. As a result, the patient will be bothered by prolonged pain, inflammation and neuralgia. At the IMEZA clinic, such errors in treatment are excluded.
The retreatment procedure is associated with additional damage to the coronal part, therefore, in some cases, its position is strengthened using an intracanal pin. Manipulation is possible if the layer of dentin surrounding the pin is at least 2 mm. Installation includes the following steps:
- preparing the bed using a calibration tool;
- adjusting the length of the pin;
- etching and drying the bed;
- applying adhesive material directly to the pin or into the cavity of the bed;
- installation of the rod, polymerization of the adhesive mass.
After completing the canal filling work, the dental cavity is closed with a temporary filling. At the next visit, the doctor begins to restore the upper part of the tooth using an artificial crown, inlays or volumetric restoration techniques.
After treatment, discomfort when biting on a tooth may persist for 3-5 days. If there are no complications, you should return for a routine examination in a year.
Stages of treatment
The Dentpremium Center provides dental canal treatment in stages. At the first appointment, the endodontist conducts an examination and diagnosis.
If root canal inflammation is suspected, radiography must be performed to determine the location of the lesion. Additionally, a computed tomography or orthopantomogram may be performed. After receiving all the data, the doctor determines the method of therapy.
Main stages of endodontic treatment.
- Pulpectomy. The endodontist anesthetizes the affected area, opens the tooth, and removes all necrotic and inflamed tissue. Giving the desired shape to the channels. Antiseptic treatment.
- Filling. Hermetically filling open cavities with a high-quality and safe filling composition: plastic (paste, gutta-percha), hard (pins) or hardening (cement materials). Filling using hot gutta-percha is considered the most effective.
- Crown restoration. The specialist’s task at this stage is to restore the anatomical shape of the tooth. For this, a filling (direct method) or a crown (indirect method) is used.
In case of inflammation of the dental canals, treatment is performed using strong anesthetics. Insufficient anesthesia can lead to pain, since the dental canals and pulp are connective and soft tissues equipped with nerve receptors.
At the Dentpremium clinic, specialists use only modern anesthetic drugs, which effectively anesthetize the area where the endodontist works for 2 hours. Treatment lasts from 30 minutes to 1 hour. In severe cases, it can take up to 2 hours. If sensation is restored during the procedure, another injection of anesthetic may be given.
Conservative treatment method
This method allows you to keep the nerve alive. This is a more preferable option, which is possible in case of a minor inflammatory process, or in the presence of a deep carious lesion, in which the lesion is close to the root, but has not yet had time to fully move to the pulp. In addition, complete and rapid nerve regeneration is possible mainly in young patients under 25-30 years of age due to the physiological characteristics of the structure and functioning of the pulp.
During the conservative treatment method, carious tissue is removed, after which a special medication is applied on top of the nerve. A temporary filling is fixed, which will reliably cover the area from bacteria and plaque. Such treatment can be repeated - the doctor assesses the condition of the dental nerve using X-rays and if the pulp regeneration is insufficient, the medicine can be prescribed for a few more days. After therapeutic treatment, the temporary filling is removed and replaced with a permanent one.
Surgical method of treatment
The surgical method is more common in the treatment of pulpitis, since the pulp most often cannot be cured and it is necessary to remove it so that the inflammatory process does not spread to the tissues around the tooth. This procedure is called depulpation or endodontic treatment.
Signs of canal infection
In some cases, patients can independently determine the presence of problems with a previously treated tooth. The main signs of canal infection are:
- pain that did not go away after treatment or occurred some time after it;
- a feeling of fullness in the gums, discomfort when pressing on the tooth;
- the presence of swelling, swelling on the gums, as well as the formation of a fistulous tract (cyst breakthrough);
- changing the shade of the dental crown from light to gray. This may indicate dentin destruction;
- persistent unpleasant odor.
If you have the above symptoms, you should not waste time by self-medicating. At the IMEZA clinic, the patient can count on a quick, accurate diagnosis and adequate treatment.