1744
Medicine is constantly moving forward, and dentistry is no exception. Its arsenal is constantly updated with new technologies, drugs and high-tech equipment.
One such advancement is the microscope. Thanks to this device, most problems that were previously beyond the power of dentists are solved, and 80% of previously removed teeth can be saved.
Use of a microscope in dentistry: indications, advantages, features of dental treatment
Dental treatment is a very delicate job, because the tooth itself is small, and the root canals inside it are even smaller. Therefore, the clearer the doctor sees the picture, the more effectively he will carry out all the manipulations. To perform their work efficiently, modern specialists use equipment, for example, they perform dental treatment under a microscope. This procedure is gaining more and more popularity today, and we offer to learn about all its nuances, advantages, disadvantages and features. Details in the article!
Prices
Of course, the cost of treating dental pathologies under a microscope exceeds the payment for the same disease, the treatment of which was carried out according to the standard protocol. Thus, the cost of treating some diseases is:
- pulpitis will cost 10 thousand rubles;
- periodontitis - 13-15 thousand rubles;
- granulomas and cysts – from 10 thousand rubles;
- caries - about 8 thousand rubles.
Typically, this price already includes payment for processing and filling of root canals. The approximate payment for retreatment is 4-6 thousand rubles, diagnostic measures - 1 thousand rubles. Prices at different clinics will vary slightly, as they largely depend on the following factors:
- clinic status;
- location;
- cost of drugs.
The high cost of the service is explained by the high cost of the device, as well as the need to improve the dentist’s qualifications. But when it comes to preserving the tooth and minimizing complications, such material expenses are justified.
The video provides additional information on the topic of the article.
What is a dental microscope
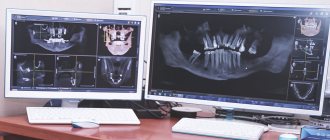
A dental microscope is a high-precision optical device that can magnify an image of a tooth, as well as everything inside it, 20 times or more. This allows the endodontist or endodontist to carry out quite sophisticated work on cleaning canals, removing cysts or resection of the root apex. The dentist may also be able to see if there are abnormal or infected areas or may notice a foreign object inside the root canal.
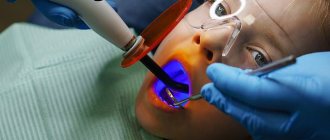
Important! Many patients are afraid of using optical equipment in treatment because they think that the device will be placed in their mouth. However, this is not true. The device is located above the patient, at a distance of 20-30 cm from his face, which is convenient for both the patient and the doctor. The endodontist carries out therapy looking through the eyepieces, but the image from the device is also displayed on the monitor so that the assistant can observe the process and provide the doctor with the necessary tools.
Areas of application of a dental microscope
A microscope is a highly accurate and rather expensive device, so its use in conventional caries treatment is unlikely to be justified. But those who believe that this optics are used only during complex surgical interventions will also be wrong.
In dentistry, such sensitive equipment has its own area of application:
- identifying the structure of channels, their number and branches,
- filling of tortuous canals,
- diagnosis of caries in the initial stage,
- detection of cracks in the enamel or canal wall,
- detection and removal of foreign objects (pieces of instruments, remains of filling materials, etc.) from root canals,
- diagnosis and treatment of canal or root perforation,
- assessment of the tightness of fit of restoration materials or prostheses (performed both during fitting and during their installation),
- tissue treatment before prosthetics to prevent damage to soft tissues or loss of healthy tooth structure,
- quality control of restoration or orthopedic work,
- removal of cysts, granulomas,
- some types of surgical work, including maxillofacial surgery.
Indications for using the microscope
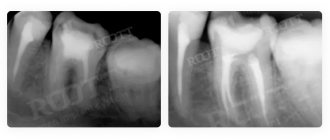
There are no specific diseases in dentistry that cannot be treated without high-precision optics, but the quality of medical care greatly benefits from its use. This is especially true for complex cases, for example, dental treatment with any anomaly in the development of the jaw or with an atypical structure of the root canals (when they are highly branched or tortuous). The use of electronic optics when re-sealing canals is justified, because this requires first unsealing1 and cleaning the canals without damaging their walls. The doctor must make sure that no particles of the previous filling, medication, pin, etc. remain in their branches.
The use of a microscope in the treatment of cysts, granulomas and other neoplasms at the apex of the roots allows for high-precision resection or cystectomy without damaging the surrounding tissues, and most importantly, preserving the tooth. This is a very important point when removing a cyst or root tip, because improper operation or injury to adjacent tissues can lead to re-infection and growth of the cyst.
And of course, such a device is used in all organ-saving and minimally invasive (low-traumatic) endodontic operations.
Progress of the procedure
Treatment using optical magnification is more comfortable for the patient. He reclines in a chair, which helps him relax better. In addition, the instruments that the doctor uses are much smaller than usual, and therefore do not cause discomfort or a gag reflex. This also allows the patient to swallow saliva normally. In addition, multiple magnification of the image allows the doctor to see the work area in great detail, and the patient does not need to open his mouth wide.
How to determine caries at home -
- The presence of pain syndrome, which we wrote about above.
- The cavity may have sharp edges and irregularities, which can be perfectly felt (in some cases) by the tongue.
- Bad breath may indicate the presence of caries. Food debris is retained in the carious cavity, which is difficult to clean; under the influence of the microflora of the oral cavity, they begin to rot, causing an unpleasant odor.
- Inspection of visually accessible surfaces of teeth (for example, in a mirror). At the same time, even if the surface layer of enamel is preserved, darkening may be visible underneath it. Such darkening may indicate caries.
Advantages of working with a microscope
Despite the fact that many dentists continue to treat teeth using conventional methods, many advanced clinics have already appreciated the quality of work using a microscope, because this method has a number of advantages:
- diagnostic accuracy: the use of high-precision optics allows you to diagnose caries at an early stage, when a drill is not required for its treatment. Multiple magnification allows you to examine hard-to-reach places (fissures, the junction of the crowns of adjacent teeth) and identify the beginning of pathological changes in the enamel,
- reduction of radiation exposure to the body: thanks to sensitive optics, the doctor can see with his own eyes the condition of the hard tissues of the tooth, its roots and canals, which means there is no need for radiography, which is especially valuable for pediatric dentistry,
- minimally invasive technologies: the endodontist can see the clinical picture in the smallest detail, which means that during his work he will not damage healthy tissue - gums, dentin, canal walls,
- high quality of work: when filling canals (especially if they have some anatomical features), it is very important to fill the entire cavity with filling material, leaving no voids or branches, so as not to create conditions for the development of microbes. In addition, the microscope allows you to verify the tightness of fillings or restoration overlays, to accurately fit the crown to the tooth,
- reduction of the rehabilitation period: often after canal filling, the patient experiences pain in the treated tooth for several days. This occurs due to the fact that nerve endings that have not been removed remain in the canal. The use of dental optics makes it possible to see and remove these particles, which relieves the patient of pain in the post-therapeutic period,
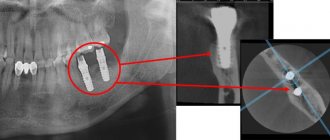
- monitoring the progress of work: since the high-resolution digital camera located inside the device displays the image on a large screen, the doctor can take a picture of any stage of work and any area of intervention. This allows him to adequately assess the quality of the work himself or invite colleagues to a consultation if a complex case requires consultation with another specialist - an orthopedist, surgeon, or orthodontist.
Important aspects
The use of optics is most relevant and justified in endodontics , i.e. in the treatment of dental canals. Without a microscope, doctors relied only on their knowledge of anatomy (they acted by touch), and radiography came to their aid.
But here you need to understand that x-rays are one of the diagnostic methods, and all responsibility for the quality of treatment lies with the dentist. The advent of optics has greatly facilitated his work, and now a specialist can treat canals with great accuracy.
A microscope is also indispensable for diagnostics. It helps to detect diseases at their earliest stages, see hidden caries, and find the smallest cracks invisible to the eye. There is no need for additional procedures, which means it protects the patient from unnecessary material costs.
No less often, optics are used to re-treat canals in cases where the previous treatment was of poor quality, and in order to eliminate the problem, the canals need to be unsealed.
Not so long ago, after a poorly performed manipulation, a tooth had to be removed. The microscope helps to examine the structure and direction of the canal , see the old composite in it, determines the exact direction of treatment, and reduces the likelihood of complications and injury to a minimum.
When working with the device, the doctor is always sure that the canals are completely traversed, well processed and sealed. It can also be used to find and remove fragments of a broken instrument left in the tooth cavity.
Complications after working under a microscope
As a rule, there are no complications after therapy where a detailed microscope was used. The risk is minimized, since the doctor has the opportunity to see the area of work in detail and control the process at all its stages. All complications arise when working without a microscope, because the doctor does not see the nuances, can injure neighboring tissues, accidentally pierce the walls of the canal, break the tip of the instrument in the root branch and not even notice it.
Attention! If after treatment with the use of optics a complication does occur, then this indicates a low qualification of the endodontist or a malfunction of the equipment.
Reviews
A microscope is a universal dental equipment that gives a real chance to save a seemingly hopeless tooth and diagnose pathologies at the initial stage of their development.
It allows you to make the treatment process predictable, improve quality and accurately predict its outcome.
If you have similar experience and would like to express your opinion on the effectiveness and advisability of optical treatment, please share them in the comments to this article.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags toothache treatment dental treatment under a microscope
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
On the effectiveness of tooth restoration in dentistry using an anchor pin
Next article
Intraligamentary anesthesia is a step towards painless treatment