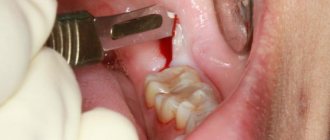
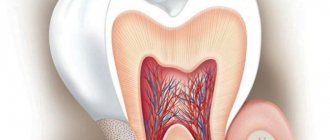
Teeth are important organs that provide several human needs at once: an aesthetic effect and calmness of the nervous system, chewing food and the proper functioning of the digestive system, the formation of a bite, and therefore correct speech. At the same time, they are very delicate, and this is fraught with serious health problems for a person. If many often encounter painful caries, cysts in the gums, and destruction of the crown, then the situation when such a terrible disease as tooth cancer develops turns out to be very unexpected. If only because many people cannot even think about this type of oncology. The director of the dental studio Fedor Zakharov told AiF.ru about how tooth cancer can be hidden behind a harmless wound on the gum or a lump on the lip .
Question and answer Which brush is better: with natural bristles or synthetic?
What is the essence of the problem
The term “dental cancer” is used in everyday life, but it is not entirely correct. Yes, tumors can develop from tooth tissue: odontoma, cementoma, etc. But these are benign formations. Malignant is adamantinoma, which develops from tooth enamel, but is extremely rare and not fully understood. Most often the problem occurs in the lower jaw. Adamantinoma, in cases where it has been discovered, affects people at a fairly young age: 18-26 years. It is located in the area of the outer chewing teeth and in the corner of the mandibular bone. It can be of two types: dense and cystic. The first is a formation with a large number of cavities. The second is a formation filled with a brown mass.
The process resembles a cystic lesion of the cavity. As the tumor grows, the bone structures begin to thicken, which later combine into one bulge.
What can provoke such a terrible disease? These can be the most trivial reasons: chronic injuries to the mucous membrane, exposure to ionizing radiation, bad habits (smoking, chewing nasvay), occupational hazards (working in hot shops or dusty rooms), unhealthy diet (excessive consumption of spicy, pungent foods). In addition, there is a risk of developing jaw cancer in cancer patients with tumors of the kidneys, stomach, and lungs. In this case, they will talk about secondary oncology.
Drink milk and chew apples. How to eat for healthy teeth Read more
Treatment and relief of edema
First you need to find out the cause of the tumor, since each case requires its own treatment to avoid deterioration.
Periodontitis in the acute phase
Periodontitis is an inflammatory process in the bone, which is associated with the fact that an infection has entered the root canals of the tooth and began to spread into the bone. If immunity is lowered, then bone inflammation goes from chronic to worsening. The amount of pus increases. Swelling and pain in the gums occur.
Periodontitis can occur both in a tooth that has been treated and filled, and in a tooth that has never been treated. In a treated tooth, it can occur due to incomplete cleaning of the tubules.
When this disease worsens, the following symptoms occur:
- A diseased tooth experiences swelling in the gum;
- The appearance of a fistula and purulent discharge;
- Pain on palpation and biting;
- Lack of reaction of the diseased tooth to high and low temperatures, to sweet foods;
- Presence of caries;
- Fever.
Swelling and pain occur due to suppuration and disappear when the pus is released. But the inflammation still goes to the bones, so a visit to the doctor is necessary.
How to treat
First, the diagnosis is clarified by the doctor. An x-ray is taken. Further treatment is of three types:
- Conservative: pus drains through the root canals, and then the canals are filled;
- Surgical: the tooth is removed and the socket is cleaned;
- Combined: the tooth is treated, an antiseptic is applied under the temporary filling, and a special incision is made to release the pus.
The choice of method depends on the location of the tooth, its condition, the course of the disease, prospects for tooth restoration, and the patient’s health status.
At home you also need to carry out the following procedures:
- Rinse with a solution of salt and soda;
- Take an antibiotic if prescribed by a doctor;
- Take anti-inflammatory drugs.
What not to do:
- Do not heat the tumor site;
- Take an antibiotic if it has not been prescribed by your dentist;
- Do not mix painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Gingivitis, periodontitis in the acute stage
Gingivitis differs from periodontitis in that the latter is an inflammation of the gums that turns into inflammation of the bone tissue, while gingivitis is a simple inflammation of the gums.
With these two diseases, your teeth should not hurt.
Causes of diseases:
- Tartar;
- Caries;
- Bad fillings;
- Incorrectly placed orthopedic structures;
- Malocclusion.
Gingivitis has an acute and chronic nature. Periodontitis is a chronic disease; there are periods during which the disease worsens.
Exacerbation may occur due to:
- Gum injuries (pricks and cuts from sharp objects);
- The presence of foreign objects in the gum pockets (bones, pieces of food, chipped tartar);
- ARVI and acute respiratory infections;
- Diabetes;
- Reduced immunity;
Symptoms
In the acute stage, gingivitis has symptoms such as:
- The occurrence of swelling and pain in the gums or jaw near a group of teeth;
- Pain when eating and brushing teeth;
- Gum bleeding due to hard foods or toothbrushing;
- Blue or red gums;
- With pressure - pain occurs;
- The gums are so swollen that they cover part of the teeth.
Periodontitis has similar symptoms, with the difference that it also reduces the height of the partitions between the teeth and their pattern becomes unclear, and the tooth roots are exposed.
How to treat
Periodontitis and gingivitis are treated by a dentist.
First, the doctor removes hard-soft deposits and polishes exposed roots and teeth. Then he examines the fillings, corrects them, and removes areas causing injury. Then the dentist removes foreign bodies and treats the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions. After this, the doctor applies anti-inflammatory drugs to the bandage.
It happens that in some cases toothbrushing, cleaning of roots and bones from stone, and suturing of tissues when they are detached and damaged are required. Here the doctor has the right to prescribe antibiotics, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, and antiseptics.
At home the patient should:
Lipoma
- Rinse the mouth with salt and soda (solution);
- Brush your teeth with special pastes;
- Treat the gums with anti-inflammatory drugs.
Abscess (periodontal)
A periodontal abscess is an inflamed area that has boundaries, in which pus accumulates under the gum. Outwardly, it looks like a formation on the gum in the form of a ball. Can be quite large.
Causes
The most common causes for this type of disease are the following:
- Accumulation of pus and its release;
- Injury of a deep nature due to a foreign object, due to which an infection entered the tissue.
Symptoms
The symptoms will be:
- A round swelling forms on the gum;
- The fabrics are elastic;
- When pressing, pain occurs and the movement of fluid inside is felt;
- Nearby tissues and cheeks swell;
- Body temperature rises.
How to treat
An abscess is treated in different ways. If it appears due to injury, then it is opened surgically, the pus is removed, and drainage is installed. If the abscess is due to periodontitis or periodontitis, then these diseases are treated first.
After the operation, you need to drink antibiotics, which the dentist will prescribe, and also take antihistamines, painkillers, and anti-inflammatory drugs.
If you suspect an abscess, then you urgently need to go to the dentist in order to prevent the risks of developing phlegmon and sepsis. There is no need to treat the abscess yourself, or heat it.
Other diseases
About ten percent of gum tumors are other diseases: precancerous, cancer, HIV infection, diabetes, hormonal disorders, etc. The symptoms of these diseases will be similar, but only a specialist will be able to accurately recognize the disease.
If you have discovered a gum tumor, contact the Onco.Rehab clinic to find out the cause of its appearance and timely treatment. Our qualified specialists will help you!
Dangerous symptoms
It is clear that diagnosing dental cancer is not so easy. It is worth being wary in cases where there is the appearance of long-term non-healing ulcers on the oral mucosa, deformations that are sometimes already noticeable to the eye, pain in untreated and intact teeth, when sensitivity changes. These are alarm bells that need to be responded to urgently and immediately run to the dentist. The earlier a tumor is detected, the greater the chance of minimizing losses.
It is also worth considering such an important sign as bleeding gums. If in a normal state, in order for blood to flow, you need to damage the gum, then in the case of cancer, light pressure will be enough. Also, swelling of the gums and increased body temperature may appear in parallel.
Tooth granuloma: symptoms
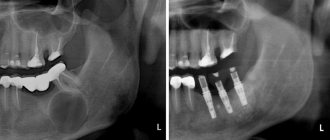
The diagnosis of “apical granuloma of the tooth” can only be made by an x-ray, on which a slight rounded darkening will be visible at the apex of the tooth root (Fig. 1). Darkening at the apex of the tooth root on an x-ray always indicates the presence of a chronic focus of inflammation and the presence of bone tissue resorption. As for the patient's complaints and other symptoms, in most cases they are not pronounced or may even be absent.
Most of the time, the tooth may not bother you at all, or periodically there may be pain when biting on the tooth or aching pain from hot foods. Those. These symptoms are standard symptoms of chronic apical periodontitis, one of the forms of which is tooth root granuloma. However, periodically (during periods of decreased immunity) an exacerbation of chronic, low-grade inflammation may occur.
An exacerbation is usually accompanied by acute pain, especially pronounced when biting on a tooth. In addition, the gums in the projection of the root apex may swell at such moments and be painful when touched. An exacerbation of the process may spontaneously subside (return to a chronic course), but can also lead to the development of severe purulent inflammation, which is popularly called gumboil. Regardless of the outcome of acute inflammation, you will ultimately need the help of a dentist to save your tooth.
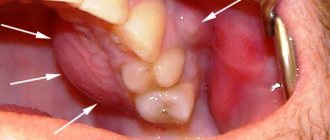
What does granuloma/cystogranuloma look like on the root of an extracted tooth:
Treatment
Tooth cancer requires surgery. And often, after tumor removal, reconstructive bone surgery may be required. Naturally, auxiliary types of therapy will also be determined if necessary: chemotherapy, radiotherapy, etc.
What happens to your teeth if you don't brush them? Infographics Read more
Types of dental cyst
The type depends on the place of occurrence. A cyst forms in the maxillary sinus, gum, root or under the crown. To determine the type of capsule with pus, the specialist examines the medical history and assesses the client’s general health. There are 5 types of dental cysts:
- Follicular - formed when the tooth was unable to grow unhindered and most of it remained inside.
- Keratocyst - develops against the background of pathological processes during the growth of the body (the growth of the neoplasm is stimulated by the pharynx-forming tissue).
- Radicular - appears from a granuloma and is a serious complication of deep caries.
- Retention – is formed during the eruption of molars in children.
- Residual – appears due to complications and inflammatory processes after tooth extraction.
Problem statistics
Tooth cancer, like any other type of oncology, is dangerous due to its active development. And here the rule also applies: the earlier it is detected, the greater the chances of recovery. According to statistics, tooth cancer cured at stages 1-2 gives an 80% chance of five-year survival, at stage 3 the prognosis is 40%, at stage 4 - less than 15%. It is important to understand that the jaw is located close to the brain, and oncology is a metastatic disease. Therefore, you should not play Russian roulette; it is better to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
At the same time, no one has canceled prevention: even if nothing bothers you, you should visit the dentist once every six months. This will allow you to identify any pathologies at an early stage. After all, prevention is easier than cure.
Granuloma on the root of the tooth - causes of appearance
There are only 2 main reasons for the occurrence of granulomas at the apexes of tooth roots. These reasons occur in 98% of cases, and we have described them in detail below. Much less often, granulomas are formed as a result of poor-quality orthodontic treatment, or mechanical trauma to the tooth (after an impact).
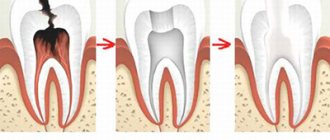
- As a consequence of untreated pulpitis (Fig. 4) - when the carious cavity of the tooth becomes deep enough - cariogenic microorganisms penetrate into the dental pulp, causing inflammation in it (it is called pulpitis). This is accompanied by sharp or aching pain. If the tooth is not treated at this stage, the nerve in the tooth dies and the pain temporarily stops.
After the death of the nerve, pathogenic microorganisms penetrate through the root canals and openings at the apex of the roots - beyond the boundaries of the tooth. This leads to the formation of foci of inflammation at the apexes of the roots (24stoma.ru). This disease is called periodontitis. There are several types of this disease, in one of which granulomas form at the tops of the roots.Keep in mind that in this case the tooth does not necessarily have to have a carious cavity, because Inflammation of the nerve in a tooth can also occur in a tooth previously treated for caries. This happens if the doctor has not completely removed the tissue affected by caries, leaving a small fragment of it under the filling (Fig. 5). In this case, caries develops under the filling and leads to the development of first pulpitis, and then periodontitis with granuloma.
- Poor-quality root canal filling - if a granuloma has formed on the root of a tooth in which root canals were previously filled (for example, during the treatment of pulpitis), then there is only one reason for its formation!
This reason is poor-quality filling of the canals, or more precisely, the fact that the root canals were not filled to the apex of the root (Fig. 6). If your doctor says that the canals are sealed well, and he does not know why a granuloma appeared after treatment, then such a doctor is lying. “The tooth is filled well, take antibiotics” - this is a standard excuse from doctors who do not want to admit to poor-quality work and, at the same time, treat the tooth for free.
Flux can occur in two forms:
- The acute form causes severe pain in the inflamed area, the temperature rises. Toothache is accompanied by pain in the head, radiating to the neck and shoulder. After the flux appears, the cheek swells, the general condition is depressed.
- The disease in its chronic form is not accompanied by such severe pain, but the temperature rises to 37.8 - 38.5 degrees, which confirms the presence of an inflammatory process. The swelling increases, extends to the temporal region, or descends towards the neck. The patient has difficulty speaking and swallowing.
Treatment after surgery
It is not easy to cure gumboil; its treatment requires a lot of patience from the patient. Tooth extraction when gumboil develops is possible, and in some cases necessary. After removal, the discomfort continues for several more days, the swelling completely subsides in only 4 days.
Treatment of gumboil in domestic circumstances is undesirable: only a professional can select medications, and he can also provide assistance if needed. With an illiterate approach, deadly complications cannot be ruled out.
After a successful operation, rehabilitation will not last long. To prevent infection, you will need to follow the rules of oral hygiene and adhere to the following instructions:
- after removing a diseased tooth, the clot of blood accumulated in the wound should be preserved, on which the process of its healing depends;
- the first two are for don't eat anything solid;
- To fight infection, use medications prescribed by your dentist;
- Brush your teeth with a soft brush, including the spaces between the teeth and without damaging the tissue adjacent to the teeth.