Changing children's baby teeth to permanent ones is always an exciting time for parents. This process is quite lengthy and often painful for the child, because it can be accompanied by various inflammations and discomfort. To help parents, for a better understanding of the physiological processes associated with the formation of teeth, dentists offer to look at the pattern of loss of baby teeth in children.
Content:
- Why is it necessary to replace baby teeth with permanent ones?
- When do the first baby teeth fall out?
- Which baby teeth fall out first?
- Drop order
- At what age do radical units appear?
- Possible abnormalities in the child
- Why do empty spaces remain unoccupied for a long time?
As the child grows, the baby teeth are replaced by permanent ones. This is a natural process, without which the full functioning of the dentofacial apparatus is impossible. But parents should treat it with the utmost responsibility, since very often violations in the sequence of loss of temporary units cause serious malocclusions that have to be treated in the future.
How does teeth change?
The rudiments of future permanent units are located under the root of the baby tooth and are separated from it by a thin bone septum. At 6–7 years of age, osteoclasts of the connective tissue surrounding the baby tooth dissolve the mineral component of the septum and destroy it. At the same time, the pulp of the temporary unit is gradually transformed into granulation connective tissue rich in osteoclasts, which gradually destroy the dentin of the primary tooth. At the same time, the roots of the temporary units dissolve and, in fact, only the crown of the baby tooth remains. It can be easily removed on its own, with the help of the dentist’s manipulations, or it can be pushed out by an actively growing molar (permanent) tooth.
Anatomy of permanent teeth The permanent units of a child (and an adult) have a complex anatomy.
Visually, the tooth consists of three parts - crown, neck, roots.
- The crown is the visible part of the tooth that rises above the gum.
- The neck is the part of the tooth at the gum level, in the place where the crown meets the root, and the enamel of the unit turns into cement.
- The root is the part of the unit invisible to the eye, located in the alveolar socket. The base of each unit is made of dentin, a hard tissue. In the coronal part, dentin is covered with enamel, and in the root part there is cement. Inside the dentin is the dental pulp - loose fibrous soft connective tissue, penetrated by a large number of blood and lymphatic vessels and nerve endings. Passing along the root canal, through the apical foramen located on the upper part of the root, they communicate with the main neurovascular bundle, providing nutrition to the tooth, drainage of excess fluid and its innervation.
Normally, by the age of 13, when a permanent bite is formed, a child has 28 permanent teeth. At the age of 17 - 25 years, third molars (wisdom teeth) erupt and the number of units may increase - 32 teeth.
Why is it necessary to replace baby teeth with permanent ones?
The chewing apparatus is improving and developing. In infancy, it is adapted exclusively for the intake of liquid food - breast milk. But closer to six months, you can already see baby teeth in children’s mouths. They allow the baby to get acquainted with the variety of solid adult foods.
There are few temporary teeth - ten pieces in each jaw. This is quite enough for the baby to eat well and talk normally. Closer to primary school age, the jaw grows. She is ready to cope with more serious chewing loads. Then children's incisors, canines and molars begin to wobble. They are replaced by a constant shift.
Doctor's advice when the process of changing teeth begins:
- After tooth loss, let your baby not eat for 3 hours, and you should also not drink very cold or hot drinks.
- Protect your child from sour, spicy and very sweet, astringent foods. All this has a negative impact on teeth.
- If your baby is bothered by discomfort or pain after a baby tooth falls out, then buy a special gel, but it is better to choose it on the recommendation of a dentist.
- Do not let your child touch the hole where a tooth has fallen out, as it may become infected.
- To soothe your mouth, make a decoction of chamomile.
Which baby teeth fall out first?
According to the standard pattern for replacing baby teeth, the lower incisors are the first to fall out. They are located in the center of the jaw. They can loosen one by one or almost simultaneously.
Following them, the opposite upper units begin to move. This is why you can often see children five or six years old with a funny toothless smile.
Which teeth should an eight-year-old child have?
Every child who has reached the age of eight should normally have the following permanent teeth - 4 lower and 4 upper incisors, sixth molars. Sometimes there may be individual deviations in teething within plus or minus six months.
Why is it necessary to treat caries in childhood if you then have to remove baby teeth with filled roots?
If an empty space forms in the dentition, this contributes to the fact that the remaining milk teeth shift, and along with them, the rudiments of permanent teeth also shift and they begin to grow incorrectly under them - in one place the formation of cracks begins, and in another - the teeth fit alone another. A filled, treated baby tooth will save space for a permanent tooth. Untreated teeth infect the rudiments of permanent teeth with infection, which causes their deformation and even complete absence.
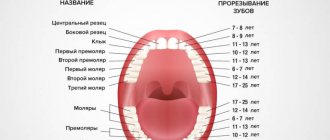
Drop order
The dropout pattern looks like this:
- 5-7 years - central incisors;
- 7-8 - lateral incisors;
- 9-11 - first molars of the upper jaw and second molars of the lower jaw;
- 9-12 - fangs;
- 10-13 - second molars of the upper dentition and first lower ones.
The diagram shows that the timing of changing units is quite arbitrary and quite long. This is why some children already have a permanent bite at the age of ten, while others still walk around at the age of 12 with actively loose baby teeth.
At what age should a bite be corrected?
You can start correcting your bite at 4-5 years of age. In this case, the growth of permanent teeth will be even, in the place intended by nature. Therefore, there is no need to carry out subsequent long-term bite correction. In any case, if there is a malocclusion, the problem can be eliminated efficiently and as quickly as possible by contacting a qualified orthodontist as early as possible.
| Teeth | Dairy (temporary) | Permanent | ||
| Jaw | Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper |
| Central incisors | 6-12 months | 8-12 months | 6-7 years | 6-8 years |
| Lateral incisors | 10-16 months | 9-13 months | 7-8 years | 7-8 years |
| Fangs | 17-23 months | 16-22 months | 9-10 years | 11-12 years old |
| First Premolars | — | — | 10-12 years | 10-11 years |
| Second Premolars | — | — | 11-12 years old | 10-12 years |
| First Molars | 14-18 months | 13-19 months | 6-7 years | 6-7 years |
| Second Molars | 23-33 months | 25-33 months | 11-12 years old | 11-13 years old |
At what age do radical units appear?
We can talk about adult occlusion only a few years after the start of the change in time units. Typically, a stronger replacement will erupt several weeks or months (or, if pulled out prematurely, years) after the baby teeth fall out.
Central incisors grow from 6 to 8 years of age, lateral incisors from 7 to 9, premolars and canines from 9 to 12. Molars begin to grow at approximately six years of age. They immediately grow permanently, replacing the empty space.
Why can a lot of time pass between the loss of baby teeth and the eruption of permanent teeth?
Most often, the front teeth grow quickly. And canines and baby molars (premolars) can be delayed. After a temporary tooth falls out, it may even take 4-6 months until a permanent tooth erupts in that place. Just expect it and take good oral care. But if this period begins to exceed six months, so as not to worry, it is better to visit a doctor. After examining the child, he will be able to decide whether the permanent tooth needs to be stimulated to grow.
Possible abnormalities in the child
Parents should know when to expect changes in their child's bite . Late change of baby teeth, like premature change, is undesirable. They speak of lateness when an eight-year-old child has not yet lost any of his incisors; they speak of early eruption if a five-year-old child has already lost many of his incisors and fallen out. It is important to find out the cause of the changes occurring and, if possible, eliminate it.
Factors due to which the bite changes earlier than standard periods:
- severe jaw injuries;
- congenital diseases leading to anomalies in the eruption of temporary and permanent units;
- advanced caries, due to which crowns and roots are destroyed faster than necessary.
As for a late shift, it is possible due to:
- rickets, calcium and vitamin D deficiency in the child’s body;
- hereditary characteristics of the dentofacial apparatus;
- some infectious pathologies.
What problems do children and their parents face when replacing baby teeth with molars?
As mentioned above, first the root of the baby tooth is absorbed. In this case, the loss occurs painlessly on its own or under the influence of external signs (constant loosening by the child or eating fairly solid food). But it may also happen that the root of the tooth has not yet been sufficiently absorbed, the baby tooth has not yet fallen out, but the molar has already begun to grow. If you do not consult a dentist in time to remove a tooth that is interfering with natural growth, a significant malocclusion may occur: a molar may simply grow next to the baby tooth. Such changes in the oral cavity may be accompanied by an increase in body temperature and significant pain.
Another significant problem is teeth falling out too early. It can be caused by various gum diseases or physical trauma. If you do not seek advice from a specialist in time, the gums may become overgrown at the site of tooth loss, which will subsequently prevent the eruption of a molar at this site and the curvature of the dentition. In this case, they usually resort to prosthetics. A structure made of hypoallergenic materials is installed on the damaged area, completely identical in appearance to a natural tooth. It maintains the child’s neighboring teeth in an even state, preventing the formation of an incorrect bite.
Another significant problem is the delay in tooth loss, when the molar is already beginning to erupt, but the milk tooth is still quite firmly “sitting” in its place. This may be due to a lack of nutrients, delays in the development of the body in general and the oral cavity in particular. In this case, you should contact a dentist, who will examine the little patient in detail and prescribe the necessary measures. In most cases, the tooth that is preventing growth is simply removed. In this case, local anesthesia is used, which will make the process of tooth extraction almost painless.
Newly erupted molars are not yet strong enough; their tooth enamel is thinned. Therefore, during the period when baby teeth are replaced by molars, there is an increased risk of acquiring dental diseases. The most significant of them is caries. It can occur due to poor oral hygiene and consumption of large amounts of sweet foods. If caries is not treated in time, complications in the form of pulpitis and other dangerous dental diseases are possible. There is also a possible risk of damage to the oral cavity during this period by various types of infections, which often lead to inflammation of the gums and loss of newly grown teeth.
Replacing baby teeth with molars is a very important process for a child. Parents should do everything possible to make it enjoyable and painless. Therefore, it is very important to visit the pediatric dentist on time.
Why do empty spaces remain unoccupied for a long time?
It often happens that a child walks around with a toothless smile for a long time, but the situation still does not change. When examining his oral cavity, the parents do not see even a hint of an imminent full bite. This happens when:
- Retentions. Dental pathology in which a segment of gum tissue is shown very little or not at all. The violation may be complete or partial. In any case, if it occurs, you should consult your dentist. Sometimes the situation can only be corrected through surgery.
- Edentia. The banal absence of a permanent germ. So, for example, a temporary fang falls out, and there is nothing to replace it with. The anomaly can be confirmed using x-ray diagnostics - the images show that the rudiment is missing. Fortunately, congenital adentia is rarely diagnosed in young patients. If it is, only prosthetics will save you.
- Impacts. Difficulties with eruption with this diagnosis are explained by the fact that the crowns of the “neighbors” are too close to each other and do not leave room for the crown, which should be between them. Deviations can also be detected using x-rays.
If there are any problems with the bite, parents should show the baby to the doctor. Moreover, children should have annual checkups at the dentist's office. This simple measure serves as an excellent prevention of serious complications and reduces the likelihood of an unattractive smile in adulthood.
Care instructions
Since the enamel is not yet fully formed during the eruption of molars, great attention should be paid to proper oral hygiene and preventive measures to prevent the development of caries.
- In the morning and evening, teeth should be brushed using a soft brush that does not damage the gums. Children are recommended to use special toothpastes with a high content of calcium and fluoride. It is better to brush your teeth under adult supervision, as children often do it too quickly and not thoroughly enough.
- All children should visit the dentist twice a year for an examination, professional cleaning, and timely detection and treatment of tooth decay.
- After any meal, children should rinse their mouths with plain water, a special baby mouthwash, or chamomile infusion. Thanks to this, plaque will not accumulate on the teeth and the likelihood of developing an inflammatory process in the eruption zone of the molar will decrease.
Molars in children: symptoms of eruption
- Fever. When teething in children, body temperature may rise, usually not higher than 38 degrees.
- Itching and pain at the site where the molar appears. Various gels and ointments, as well as gum massage, will help relieve children from unpleasant sensations.
- Increased salivation and runny nose.
Important!
The growth of molars in children, especially at the initial stage, leads to weakened immunity. Take vitamins and do not forget about preventive visits to the dentist.
Common problems with molars in children
| Problems with molars | How to fix? |
| Molar tooth is loose | A common occurrence with injuries and bruises. To avoid tooth loss, an urgent visit to the dentist and the application of a special splint are necessary, especially if the child’s molar sways when touched. |
| Broken molar tooth | Severe chips may require orthopedic treatment. If a child's front molar has chipped, aesthetic restoration with veneers or crowns may be required. |
| Molar caries | When the first molars erupt, it is important to prevent the occurrence of caries. If this happens, then it is necessary to stop the disease in its infancy, otherwise it will affect the deeper layers of the tooth. |
| A child's molar has fallen out | The most unpleasant thing that can happen. If a child knocks out a molar along with the root, then there is a chance to save it. To do this, you need to place the knocked out tooth back into the oral cavity, saline solution or into a glass of milk and urgently rush to the dentist (you need to do it within 30 - 40 minutes after the injury). If a child’s molar tooth has been removed, then there is only one way out - installing a prosthesis. |
Features of care
A permanent bite requires careful care and attention. First of all, parents should teach their child the rules of hygiene:
- using a toothbrush twice a day (at least 3 minutes);
- if possible, rinse your mouth after eating, especially when it comes to sweets;
- using dental floss to clean the interdental space.
In addition, preventive visits to the dentist are mandatory. At an early age, the enamel is more susceptible to the influence of external factors, so caries progresses quickly. The pathological process can also affect the pulp (its size in a child is larger than in an adult), which will require long-term and painful treatment.
Particular attention should be paid to a balanced diet, active recreation, and walks in the fresh air. If you live in a region where the number of sunny days per year is small, you should discuss with your pediatrician the issue of using vitamin D and preparations containing calcium.
Teething sequence
Almost all parents believe that the first molars should be incisors, which replace temporary elements of the dentition. But this opinion is wrong. Even before baby teeth fall out, at the age of 5-6 years, children receive their first molars, which are not on the list of primary teeth.
After this, the sequence of formation of a permanent bite is almost no different from the order of eruption of primary teeth:
- the lower and upper central incisors grow;
- lateral incisors appear on both jaws;
- lower and upper first premolars;
- fangs;
- upper and lower second premolars;
- second and third molars (you must understand that the so-called “wisdom teeth” sometimes do not penetrate the surface of the gums at all).
Teeth cutting in this order does not happen just like that, because it ideally corresponds to the speed of development and formation of the maxillofacial system. If the optimal sequence is followed, correct bite development occurs.
How to determine that a child will soon have molars?
According to some of the signs, interdental intervals initially increase. This happens due to the growth of the jaw bones - the teeth begin to not fit tightly together, as happens in adults. Then the temporary teeth gradually become loose - due to the gradual disappearance of the temporary root, which can no longer reliably hold such a tooth, and itself is gradually pushed out of the soft and semi-soft tissues on the jaw. The loss of a temporary tooth is a clear sign that the permanent tooth is already growing in full force, and the top of its crown will soon push apart the gum tissue. The appearance of a new tooth is also accompanied by slight redness and swelling. If a child or teenager has a fever, their health has worsened, and their gums hurt, go to the doctor immediately.