Many of us remember from school that adults have 32 teeth, 16 of which are located both at the top and bottom of the oral cavity. You can often hear this information in advertising on television. But not everyone knows at what period teeth should erupt or how the absence of, say, wisdom teeth affects our body.
Every person, especially young parents, needs to know well how many baby teeth there are, when the molars appear, and what they are used for. All this information is needed to combat diseases of the oral cavity and the human body as a whole.
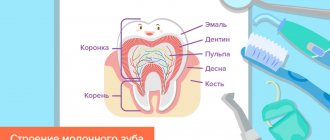
Anatomy of permanent teeth
Each molar consists of certain parts:
- crown. This is the part of the tooth that protrudes from the top;
- the root, it goes deep into the alveoli. At the same time, it is attached thanks to special connective tissue bundles. There can be different numbers of roots (1-5 pieces). This moment affects the number of nerves and channels;
- neck. This part is located between the root and the crown.
Tooth tissues are distinguished by their heterogeneity. The enamel is on top and is known for its durability. Once the tooth has erupted, it is covered with a transparent thin layer. This is the cuticle, which eventually changes to the pellicle. The latter is a film that is created from what saliva produces.
Beneath the enamel is dentin, the tissue of the tooth. Dentin is similar to bone when you study how it is built. However, it is more durable because there is a high level of mineralization. In the area where the root is located, the dental tissue is covered with cement. The latter is rich in mineral compounds and is also associated with periodontium. Collagen fibers are used for this.
As for the part of the tooth that is inside, this is the crown and root canal. They are filled with pulp. This is loose connective tissue; it contains nerve endings and blood vessels.
How to care for children's teeth -
Oral hygiene should begin even before the first teeth erupt. Typically, infants' gums are cleaned twice a day. It is done either using a special fabric fingertip, or a clean bandage wrapped around the finger and moistened with boiled water. When teeth erupt, special hygiene products are needed (special toothbrushes, as well as toothpastes or tooth foams).
Remember that the enamel of children's teeth is more porous and rough, because... it contains few microelements (compared to already mature mineralized enamel in adults). Consequently, in the absence of proper hygiene and diet, there is a very high risk of developing multiple early dental caries. We hope that our article on the topic: Timing and order of teething in children was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Dental education of the author of the article, 2. Based on personal 20 years of experience as a dentist, 3. The European Academy of Paediatric Dentistry (EU), 4. National Library of Medicine (USA), 5. “Pediatric therapeutic dentistry. National leadership" (Leontyev).
Differences between baby teeth and permanent teeth
Permanent and temporary teeth are built in the same way, but still have certain differences between themselves:
- The enamel on baby teeth is whiter. And the enamel on permanent teeth has a yellowish tint;
- the best indicators of density and mineralization are noted behind the molars;
- the pulp of a baby tooth is large in size, and the dense tissues and their walls are thinner;
- permanent teeth are larger in size, here the length is greater than the width;
- The root of baby teeth is short and thin compared to permanent teeth. When the root of temporary teeth is formed, they expand in width. Therefore, the permanent bud has free space to grow.
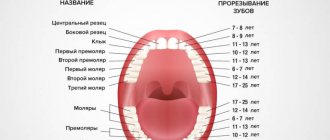
Diagram of teething of primary occlusion
A newborn child has 20 primary tooth buds inside the upper and lower jaws (10 follicles for each jaw). The timing of teething in children, according to different authors, can vary greatly, and in diagram No. 1 below you can see generally accepted figures from the “National Guide to Pediatric Dentistry”. In this diagram you can see the timing of the eruption of baby teeth in completely healthy children who do not have any pathology.
Scheme of teething in children without pathology (scheme No. 1) –
According to statistics, the normal schedule for teething in children is observed only in 42% of cases. A delay in the timing of eruption is observed in approximately 48% of children, which is associated with illnesses suffered - both by the mother during pregnancy and by the newborn child (you can read about the main reasons for the delay in eruption below). Approximately 10% of all children experience early eruption of primary teeth, and in a small percentage of cases this can occur even during fetal development.
What may cause delayed teething?
Many factors can influence the delay in the eruption of primary teeth. For example, in premature children with general somatic pathology, the eruption of the first teeth in 61% of cases occurs only at the age of 8 months and older. Moreover, if a premature baby has suffered an intracranial birth injury or a severe infectious-inflammatory disease, then eruption may begin even later - at 11-12 months and older.
The timing of the onset of teething also depends on the duration of natural feeding. In bottle-fed children, in 60% of cases, the first temporary teeth erupt only at 8 months or later. In mixed-fed children, delayed eruption was observed in only 30% of cases. A lot depends on the state of health of the mother during pregnancy, as well as on the course of pregnancy. For example, when examining children under 3 years of age whose mothers suffered severe toxicosis, it was found that the start of the eruption of primary teeth in them shifted to 8-10 months.
It is also worth noting that delayed eruption in a small percentage of cases can occur even in completely healthy children, which is associated with a genetic factor (for example, when late eruption was observed in one of the child’s parents). The “National Guide to Pediatric Dentistry” published a table that clearly shows what the delay in eruption may be if a child has various diseases.
Table No. 1 - timing of the onset of eruption in the presence of pathology
List of reasons for delayed eruption of baby teeth:
1) The first group of reasons includes diseases of a woman during pregnancy, as well as features of the course of pregnancy. Moreover, it is worth noting that all these reasons have only a moderate effect (unlike diseases in the 1st year of a child’s life). These reasons include:
- toxicosis of the 2nd half of pregnancy,
- kidney disease,
- previous pneumonia or acute respiratory infection with high fever,
- herpes infection, rubella, toxoplasmosis,
- constant chronic or short-term severe stress.
2) The greatest influence on the delay in the eruption of primary teeth is caused by diseases suffered during the 1st year of the child’s life:
- neonatal sepsis,
- pneumonia, frequent acute respiratory infections,
- atopic dermatitis, rickets,
- general somatic pathology,
- convulsive states,
- intestinal toxicosis,
- prematurity and postmaturity,
- hypothyroidism (lack of iodine intake),
- poor unbalanced diet,
- for epilepsy.
Causes of early teething: studies have found that early teething is most often characteristic of children born with a large body weight. Moreover, there is a clear correlation - the greater the child’s body weight, the earlier the eruption of temporary teeth begins. Also, premature eruption is observed with adrenal tumors accompanied by hyperfunction (24stoma.ru).
Violation of the sequence of teething in children -
Physiological teething is characterized not only by timing, but also by such characteristics as pairing and sequence. Those. all teeth should erupt in pairs, for example, first 2 central incisors of the lower jaw erupt at once, then 2 central incisors of the upper jaw, etc. See diagram No. 1 above for the timing and sequence of baby teeth eruption. In healthy children, there are usually no violations of pairing and sequence during teething.
But in children who have suffered from rickets, sequence violations occur in approximately 52% of all cases, pairing disorders occur in approximately 35% of cases. In children with rickets, the eruption of primary teeth very often begins with the central and lateral incisors of the upper jaw, and when the crowns of the teeth erupt approximately halfway, the eruption process may stop for many months. The latter is associated with a violation of the formation of the roots of milk teeth, because when milk teeth just begin to erupt, their roots are still only 25-50% formed.
Where do teeth come from?
Teeth begin to form and develop when the fetus is still inside the womb (at about 6 weeks). They have their source - the epithelial dental plate. Already by 14 weeks, active formation of dental tissues, which are hard, occurs. Initially, this occurs in the area where the crown will be, and later at the root.
Molars, namely their first rudiments, appear by the 5th month of the embryo. They are located higher than the child’s baby teeth or lower. By the time the child is born, the rudiments are already practically formed in the tissues of the jaw.
Teeth that belong to an additional group (have no predecessors) are formed later. This occurs after about 1 year of life. Why? Because the baby's jaw is still very small and there is not enough space for them.
Causes of abnormal deviation from the norm
It’s great if the teeth erupt on time and do not change in color, shape, or size. In this case, the baby definitely develops in a normal rhythm, he has no deviations in physical and general somatic health.
The culprits of dental defects, including lack of teeth at the age of three, may be:
- Heredity.
- Congenital malformations.
- Undeveloped gum muscles.
- Bad ecology.
- Adenoids, chronic rhinitis, otitis.
- Non-compliance with the diet by the mother during pregnancy.
- Deficiency of vitamins, minerals (after birth, inside the womb).
- Trisomies (chromosomal abnormalities).
The true cause of jaw development abnormalities in children can be identified using laboratory tests, an external examination of a small patient, and a survey of parents. Early diagnosis of diseases and malfunctions of internal organs and systems will help prevent the disease from developing and prescribe timely treatment.
What does a dental formula look like?
To make it more convenient to describe teeth and their number, special formulas are usually used. Each tooth has its own number, which is used to decipher its location.
When describing a milk bite, Roman numerals are used:
- incisors – I, II;
- canine – III;
- molars – IV, V.
If we talk about the formula for adult teeth, here the teeth are counted starting from the center:
- incisors – 1.2;
- fang – 3;
- molars (small) – 4.5;
- molars (large) – 6,7,8.
8 is a wisdom tooth; not every person has it.
How many teeth should a child have?
It all depends on age. The maximum number of teeth in the period from birth to 5-6 years is 20 - these are milk teeth. Then, until the age of 15-16, the molars begin to erupt, pushing out the milk teeth. Ultimately, their number grows to 28.
The latest are the third molars. They grow only after 18 years of age, but not everyone has them.
It is worth noting that the period of formation and eruption of baby teeth is very individual. In some children, all 20 teeth grow by the age of 2, while in others - by 2.5 or later. Such delays within a year are considered normal and are not a developmental anomaly.
If teeth do not start cutting in the first year of the baby’s life, you should consult a doctor to find out the reasons.
To the list of posts
Teething order
Typically, all children start teething at about the same time. Teeth emerge from the molar set at the age of 5, and it is the molars (large ones) that emerge. Then the diagram is as follows:
- Initially, the incisors on the lower jaw change, which are located in the center;
- then the central incisors appear on the upper jaw and the incisors on the sides on the lower jaw;
- at about 8-9 years old, the incisors on the top and sides change;
- up to 12 years of age, molars (small) grow;
- at the age of 13, the fangs change;
- after the child turns 14 years old, the second molars (large ones) come in. They were not included in the milk kit;
- and after another 1 year the third molars (large) appear. This is a wisdom tooth. But he may not appear at all.
Scheme - schedule for changing teeth in children:
- The central incisors are subject to renewal at the age of about 5 or 7 years, soon followed by the lateral ones.
- From 9 to 11 years the first molars are expected.
- At the same time as the molars, the canines also change.
- In the period of 10-13 years, the second molars also emerge.
By the age of 13, a teenager’s mouth can already count about 28 teeth. If there is a one-year delay in their appearance, it is recommended to consult a dentist. An adult must have at least 28 or 32 teeth. It must be remembered that from the age of five there begins a period of replacement of milk teeth with those that will be with a person throughout his life.
How to determine that a child will soon have molars?
There are certain signs that indicate that permanent teeth will soon begin to erupt:
- The spaces between the teeth increase. The jaw grows and the free space increases;
- baby teeth become loose as the root gradually dissolves. It cannot be firmly fixed in the jaw tissues;
- in case of loss of a temporary tooth. This confirms that the molar will soon come out as it has pushed out the previous one;
- The gums are slightly swollen and red.
When permanent teeth erupt, the child’s general well-being usually remains the same, the temperature does not rise, and there is no pain.
Oral care
Going to the pediatric dentist with a swollen cheek and molars destroyed by caries is the worst option. It is better to prevent dental diseases by following the rules of oral care.
Follow these guidelines:
- Buy your daughter or son a beautiful toothbrush and tasty toothpaste without fluoride.
- Shop together to choose what your baby will definitely like.
- Apply the paste to the brush in a minimal amount, no more than a pea.
- Record the time for cleaning, spend at least 3 minutes on the procedure.
- Conduct preventative conversations about the benefits of oral hygiene.
- Tell a scary tale about dental monsters that destroy molars if you don't brush them before bed.
- Watch an educational cartoon together, read a fairy tale, or make up one yourself so that your child understands why his teeth hurt.
- Don't trust three-year-old toddlers to clean their mouths on their own. It is better to carry out a control procedure for several months.
- Treat the initial stages of caries with silvering.
This is a safe and beneficial procedure. It helps to avoid early removal of incisors, is used as a prevention of destruction, and replaces filling.
Possible problems
Permanent teeth have just appeared, but this does not mean that there will not immediately be any problems associated with them. Parents should be aware of possible dental problems:
- lack of molars;
- pain in the molar area;
- crooked position of molars;
- molars fall out;
- injuries.
For any of these problems, it is important to contact a specialist in time to receive qualified help.
Adviсe
While the baby is still toothless, parents carefully monitor the growth of the first tooth, often look into the mouth, and monitor the condition of the gums. When a lot of molars grow, they forget about it. We will give some useful tips on how to prevent serious dental problems in young children.
- Examine your baby's mouth frequently at home. Check for stains, chips, and plaque.
- Every mother should have a dental chart for children under 3 years of age.
With its help, it is easy to track the pattern of incisor eruption, the norm by number and age. - Teach your child to brush their teeth 2 times a day. Use games, tasty pasta and other methods of teaching hygiene, set an example.
- Visit your dentist regularly, at least 2-4 times a year. The doctor will notice defects in jaw development in time, tell you how and in what order teeth should be cut, and why they are deteriorating.
Important! The most important condition for maintaining dental health is attention and control from parents.