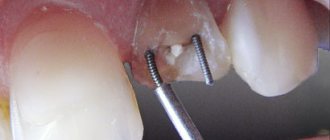
About two years ago, a filling with a pin was placed on the 7th lower tooth. The filling recently broke off, I went to the hospital, they put a new filling on the same pin, and when they aligned the filling with the bite, the pin became visible. Either it’s translucent, or it’s already polished along with the filling, but it’s visible on the cutting edge, although I can’t feel it.
Today I went and told the doctor that the pin was visible, she told me that this happens. Is this normal?
No, this is not normal, if only because in your case, if the coronal part is damaged by more than 30%, it is necessary to install not a filling with a pin, but a stump inlay and a crown.
In this case, you run the risk of chipping the tooth wall and, if the outcome is negative, you may lose the tooth altogether if the wall chip is below the gum.
I recommend that you go to paid dentistry and get quality service.
Contact phone number
Comments and reviews 10
After installing the fiberglass pin, the tooth was closed with a temporary filling. Part of this filling fell out. Installation of a temporary filling is planned in 4 days. Do I need to see a doctor soon or can I wait for a scheduled appointment? Answer
It is better to inform your doctor about the current situation. Answer
General dentist
Today I had a filling placed on a fiberglass pin on my front lower incisor (4, I think). On the inner surface of the tooth, on the filling, at home I saw a small white spot, is this the edge of the pin? Photos are not high quality, unfortunately. If it’s a pin, then what does this mean for me? Answer
The lower incisor or even the fourth tooth are not large in size, so it is quite possible that the edge of the fiberglass post is showing through or even reaching the surface. Ideally, it should be completely immersed in the composite structure, but if the translucency occurs on the inner surface, then there is nothing to worry about, because apart from aesthetic disturbances, which are important only on the front surface, there are no other negative consequences from the surface location of the fiberglass pin. Answer
Contact phone number
My wife got a filling on a pin today. I looked and was surprised that the golden pin was very visible from the tooth. My wife can't feel it with her tongue. Is it generally normal that it can be seen so clearly? Will it interfere later if the filling sags or wears off? The tooth is chewing! Answer
Of course this is not normal! The dentist selected a pin that was too large. Call for a follow-up appointment. Answer
Contact phone number
A month ago I got a light filling with a pin. For the whole month I have been feeling discomfort in the tooth (as if something was stuck), the pin is visible, the filling does not completely cover it, and when I touch the tooth with my tongue, I feel the border between the tooth and the filling! Should I redo it or is this the norm? Answer
Of course, it needs to be redone. This phenomenon has nothing to do with quality work. Answer
The pin from the filling is visible
We placed a filling on the 6th upper tooth, the golden pin is very visible. What should I do? Should I go to the doctor to have it redone? Or is this normal? What could be the consequences?
Hello. If the filling does not interfere with your height and there are no negative changes on the x-ray, this restoration does not have any negative consequences other than aesthetics and there is no point in redoing it. It is recommended to take an X-ray of this tooth to control the quality of treatment and with this image go to a face-to-face consultation with a dentist-therapist. Sincerely, dentist Andrey Aleksandrovich Syomkin.
Good afternoon. It needs to be redone.
There are no consequences, if you are not satisfied only with the aesthetics, then redo it.
A dentist I know told me that they haven’t used anchor pins on chewing teeth for 10 years. And they put composite posts or a stump inlay, and a crown on top. And that in any case it will be necessary to redo it later, since the anchor pin may crack the tooth root.
Yesterday I took x-rays, a dentist friend said that the pin was screwed in too large and was located too close to the edge of the root wall. I don't know what to do now? I'm very worried.
Good afternoon. There is no point in panicking. It is difficult to judge why the doctor did not install the pin deeper; perhaps the conditions were difficult, but in general there is nothing to worry about.
Tooth pin
The pin is quite widely used in modern dentistry - it is a permanent prosthesis that is installed on the crown of the tooth. It consists of the pin itself and the crown part.
To strengthen the tooth from the inside, there are several types of pins.
- Anchor
- Fiberglass
Anchor pins are made from titanium.
They are fixed in the root part of the tooth using chemicals and sekloionomer cement. In case of complications, such a pin is easy to remove, because it appears on an x-ray.
Fiberglass pin.
Fixed with double-curing cement. This pin is more durable, but it is quite difficult to remove in case of complications of tooth disease, because it is absolutely invisible on an x-ray.
Pins can also be divided into active and passive.
Active pins have a thread for screwing it into the tooth bone; passive pins do not have such a thread and are installed using cement.
Similar questions
Hello! I have a problem. A piece of either a tooth or a filling broke off, I went to the dentist. I was told that my tooth had already been treated as deep, possibly...
Hello! I am 23 years old! Even in childhood, the lower tooth 6 was healed, the tooth was very bad, all rotten, and when the doctor put a filling he said that there were guarantees on how long the tooth would last...
Hello! Please consult! There is no way to see a doctor in the near future. I need an approximate diagnosis. I took an x-ray of the healthy tooth and everything was fine. 3 from the edge...
Good afternoon, dear dentists! I ask for your help and advice. The fact is that in August I was given a large light-curing filling (I understand that this is it, because...
Pin visible
Moderator: Lesya
Pin visible
Post by Alena310893 » Tue Jan 30, 2018 13:14
Re: Pin visible
Post by Lesya » Fri Feb 16, 2022 13:22
The tooth is very badly damaged, and it is not surprising that you were advised to remove it. It's easier, but not better. So you're lucky to have found a doctor willing to keep him. The fact that the doctor restored it unfortunately does not mean that this is all. With such destruction, a crown must be placed on the tooth. I'm sure the doctor told you about this. Therefore, if you plan to install a crown in the near future, then it’s not scary that you see the pin. If you don’t install a crown, then such a tooth will not serve you for long. The fact that there are no bumps on it, and it is clearly lower in bite, indicates that the doctor is going to put a crown.
And here is the main question about the channels and the old pin. I would still remove it, since it is not exactly along the channel. And I also treated the canals, because judging by the pictures, the filling in the canals is far from good. If the tooth has been standing like this for more than 10 years and has never hurt, then you can take a risk. But if this filling is a year or two old, the tooth bothers you not even much, but periodically, then it will be wrong to put a crown on it, without treating the canals. After all, if he gets sick under the crown, then it will have to be cut and thrown away, and the canals will still have to be re-treated. Conclusion: If the tooth has never bothered you and the filling (of the canals) is more than 7-10 years old, get a crown. If the tooth sometimes bothers you, the filling is 1-2 years old - you need to re-treat the canals, and only then put on a crown. But I would recommend a crown in any case. Without it, you will lose your tooth. After all, the doctor is not a magician. He molded a huge filling on the pin for you, and the walls of the tooth are almost completely gone. Such a tooth will not last long for chewing.
View full version : Pins visible
Olgi I will support the previous speakers, a crown is definitely needed. Concerning
2. Will this affect the faster destruction of the filling due to the heterogeneity of the chewing surface. What you call a filling is actually a tooth stump, that is, the doctor did everything correctly, preparing the tooth for prosthetics, removing it from the bite. And in this case, the goal is usually not to make a relief chewing surface, outlining all the anatomical features of the tooth. By refusing a crown in this case, you take full responsibility for this tooth, since without a crown, even if something breaks (as already said, thin walls), no one will most likely redo it for free (I wouldn’t) . Discuss this issue with your doctor so that it doesn’t come as a surprise to you later. And it will definitely break sooner or later.
I don’t agree about stamping crowns. If I were you (if the reasons are financial), having found the funds to restore a tooth with pins, I would rather save up and eventually make metal-ceramics.
Vector is very effective, in my opinion (more precisely, my opinion on the results after the treatment), the price justifies itself.
With the advent of the German Vector device, there is no longer any doubt about the effectiveness of ultrasonic methods for treating periodontitis, since thanks to its unique design, the main problem is eliminated - the randomness of the beating of the cleaning instrument. Ultrasonic vibrations are transmitted to the tool through a resonant circuit, as a result, ordered vibrations are imparted to the tool - it moves strictly along the tooth surface being cleaned. Lateral vibrations no longer irritate the gum tissue in the periodontal pockets and do not destroy the surface of the tooth roots, so Vector is even suitable for the treatment of periodontitis in patients with high sensitivity. Due to the orderliness of the vibrations, the depth of penetration of ultrasound also increases - up to 11 mm, which in many cases makes it possible to do without surgical treatment methods. During the treatment of a periodontal pocket, a mixture containing hydroxyapatite particles 10 nm in size is supplied to the working instrument. Vibrating in an orderly manner in an ultrasonic field, these particles completely remove subgingival deposits and endotoxins from the periodontal pocket and polish the tooth surface. In addition, hydroxyapatite promotes rapid gum recovery after the procedure. Patients respond very well to the treatment carried out with the Vector device, since during and after cleaning the periodontal pockets there is practically no discomfort. Therefore, in many cases it is possible to do without anesthesia. Thanks to the orderliness of the vibrations, the depth of penetration of ultrasound also increases - up to 11 mm, which in many cases makes it possible to do without surgical treatment methods.
Why is a pin inserted into a tooth?
A pin is a special rod-shaped structure made of metal (titanium, brass, steel, precious metal alloys) or non-metallic materials (fiberglass, ceramics, carbon fiber), which is inserted into the dental root canals and helps strengthen the damaged tooth. It can have different shapes: conical, cylindrical, screw, and can be installed in an active way (screwing into dentin) or passively (fixed with filling material when filling tooth canals).
The dentist selects pins depending on the condition of the dental tissues and root canals, as well as depending on the method of restoring the tooth on a pin. The load to which the restored dental unit will be subjected is also taken into account: it will be different for chewing and front teeth, and it also matters whether the tooth will be a support for a prosthetic structure or a free-standing unit. Very often, pin restoration precedes the installation of a metal-ceramic crown, either a separate crown or a supporting crown of a bridge.
If a tooth unit still has healthy roots or can be successfully treated, it is not necessary to remove it at all - installing pin structures will allow you to save the tooth root and “grow” a new crown onto it. But you need to know that if the thickness of the root canal wall is less than 2 mm, if there is a complete absence of crowns on the teeth in the “smile zone,” as well as with some serious diseases of the internal organs, the method of restoring a tooth on a pin cannot be used.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Filling on a tooth using a pin, restoration of a tooth on a pin
Petrov Oleg Viktorovich
Chief physician, director of the clinic, implant surgeon, candidate of medical sciences at the branch of the street. 8th Krasnoarmeyskaya, 3
He began studying maxillofacial surgery and dentistry at the department of the same name at the Military Medical Academy, and almost all subsequent postgraduate education was associated with training at this oldest educational institution. After graduating in 1992, he underwent advanced training at the faculty of retraining and advanced training in the “surgical dentistry” cycle. And in the period from 1996 to 1999, he studied at the faculty of medical management, specializing in “maxillofacial surgery and dentistry.” Candidate of Medical Sciences.
For six years he was the head of the dental department of the hospital. During this period, he repeatedly underwent advanced training in various areas of dentistry from “therapeutic dentistry” to “implantology”. Out of love for his specialty, two rationalization proposals were born. When treating patients, I prefer a systematic approach, using all knowledge to solve the patient’s problems.
Knowledge of implantology and improvement of implant treatment methods in complex clinical cases took place at the bases of well-known European universities: a one-year cycle in implantology at the Frankfurt University. Goethe; cycle on bone grafting at the Medical University of Vienna. Participated in international implantological congresses in Italy, England, Monaco. This made it possible to use the acquired knowledge and skills to solve practical problems of restoring patients’ missing teeth.
I have been working at the Astra Clinic since 2005. Managing a friendly team of doctors, I try to use all known modern methods of dental restoration to achieve aesthetic and functional results.
Nemchenko Dmitry Vladimirovich
Surgeon, surgeon-implantologist at the branch of Tikhoretsky Ave., 22/13
Graduated from the Military Medical Academy named after. Kirova S.M. in 1992. In the specialty of maxillofacial surgery, he specialized at the MAPO and continued to work as a maxillofacial surgeon at city hospital No. 15. Having gained rich clinical experience in the treatment of various diseases of the maxillofacial region, he noted that in Russia very little attention is paid to the rehabilitation of patients and, in particular, implantation. In the nineties, implantation in Russia was in its infancy, and to obtain practical skills and theoretical knowledge it was necessary to turn to foreign sources. For this purpose, he interned and assisted in operations at the maxillofacial department in the clinic in Luleå (Sweden) under the guidance of prof. Ulf Blomback. I acquired the basics of my knowledge of implantology under the guidance of the head. Member of MAPO Professor Vasiliev A.V. While continuing to work on implantation, he took part in international symposiums and congresses dedicated to this topic. In 2010-2011 he studied at the University. Goethe in Frankfurt am Main and, after successfully passing theoretical and practical exams, received a European certificate as an implantologist. In 2014, he completed training in Berlin on plastic surgery of soft tissues in the area of installed implants to create aesthetic restorations of the dentition. I have been working at the ASTRA-3 LLC clinic on Tikhorektsky Prospekt 22/13 since 2008. Every year I perform about 1000 successful operations to install implants. I pay great attention to the problem of bone tissue deficiency and ways to solve it. I am proficient in various methods of bone tissue augmentation: sinus lifting, harvesting and transplantation of bone blocks, 3D restoration of the bone crest using the Curie technique. Extensive knowledge, existing experience and modern technologies help me in the work that I consider my calling.
Beginning of the implantation operation with Nemchenko D.V.
Patient's review of the work of Zybina M.O. and Nemchenko D.V.
Review of a foreign patient about the work of Nemchenko D.V.
Elimination of defects in hard dental tissues can be carried out by using pin structures, such as:
- pin tooth;
- pin stump structures;
- restorations on pins.
A pin restoration is a microprosthesis designed to replace a defect and restore the coronal part of a tooth and is tightly fixed to the tissues using a special rod. In fact, such a filling with a pin is installed when there is doubt about the effectiveness that a tooth restoration without a pin (a simple filling) can demonstrate.
We speak of restoration on root pins when the shank of the rod is located inside the canal (filling root canals with pins). When restoring with parapulp pins, the rod is placed in the thickest areas of dentin. This design makes it possible to restore the coronal zone of chewing and anterior teeth without removing the pulp and installing artificial crowns.
What to do if a tooth is destroyed
Modern dentistry has a large arsenal of tools for its restoration. The most popular way to restore a tooth in such a situation is restoration using pins.
With the help of pin structures, it is possible not only to restore the destroyed supragingival part of the tooth, but also to normalize its position if the tooth was not level.
With the help of pin structures, it is possible to normalize the bite, in cases where significant grinding of the dental tissues is necessary due to their incorrect position.
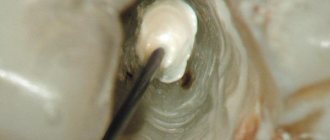
In the photo: a pin for tooth restoration
The main myth associated with pinned teeth
There are several fears associated with restoring teeth with pins.
Some of them arise while reading information on the Internet, some are due to the uncertainty of a doctor who has insufficient experience in restoring teeth with a pin.
The main fear is the possibility of tooth root destruction from the pressure of the pin.
Can a pin destroy the root or walls of a restored tooth?
The answer is simple: this method of tooth restoration, like any treatment method, has its indications and contraindications. A properly restored tooth with a pin by an experienced dentist will last for decades or more.
This can be compared to building a house. The metal beams also put pressure on the foundation of the house, causing the house to collapse? Of course not, even at the planning stage the pressure exerted and the number of those same metal structures are calculated.
Likewise, the dentist, at the stage of treatment planning, evaluates the possibility of restoring a damaged tooth with pin structures.
In order to fully and reliably restore a tooth stump using a pin structure, the tooth root must meet a number of strict requirements:
- The root canal must be of sufficient length
- The root canal should not be too narrow or curved
- The walls of the tooth root should not be thinned
- The tissues of the tooth being restored should not be subject to caries.
- Tooth tissues should not be fragile and should be able to withstand stress.
Depending on the anatomy of different groups of teeth, the tooth stump can be restored not with one, but with several pins at once.
Now let's look at the basic requirements that pins for restoring teeth must meet:
- Pin structures must have a long service life and have sufficient wear resistance.
- The shape of the pin must match the shape of the root canal.
- The length of the pin must be sufficient for reliable retention.
- The material from which the pin is made must be bioinert, not subject to corrosion, and must not adversely affect tooth tissue.
- The pin should create a tight seal and prevent infection from entering the tooth.
- The material of the pin must have a good connection with the cement on which it is fixed.
- It should be possible to remove the pin if re-treatment of the root canals is necessary.
The decision to restore a tooth with one or another pin structure should always be made by a doctor, based on the individual anatomy of the root canal: its length, diameter and degree of curvature.
Each pin is for a specific situation, and there is no such universal pin that suits everyone, but standard pins do exist.
Usually these are pins made of special medical metals or alloys, presented in sets with various diameters and lengths of pins, complete with tools for preparing the root canal and giving it the appropriate shape. This creates a bed for the pin and allows for a perfect fit of the structure.
The most reliable are pins made of precious and semi-precious metals, as well as titanium. The surface of the pins is usually specially treated: either sandblasted or acid-etched. This is done for better adhesion to cement and improved fixation.
The surface of the pin can be smooth, grooved, or have a thread, in which case the pin looks like a small self-tapping screw. Recently, combined pins that combine several types of surfaces are becoming increasingly common.
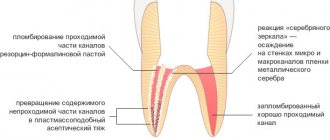
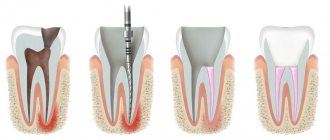
How to install a pin in a tooth.
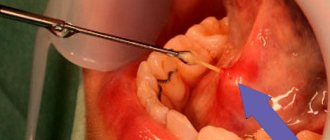
Before placing the pin, the supragingival part of the tooth is prepared, the mouth of the root canal is widened, after which the canal is processed and filled. After that, a bed for the pin is formed using a special reamer.
Then the canal is thoroughly washed, treated with antimicrobial agents, dried and degreased. Cement is pumped into the tooth canal with a special tool, eliminating the formation of pores, and a pin coated with cement is inserted. After the cement has hardened, the dentist begins to restore the supragingival part of the tooth on the free part of the pin, slightly rising above the gum. This is done either by hand using a composite material, or using special forms filled with a composite material and placed on the pin.
After such restoration, the tooth stump is polished with burs, removing excess material and giving the correct shape, after which the orthopedist takes impressions and restores the tooth with a crown.
General indications and contraindications
Typically, pin filling methods are used when the nerve has been removed and at least one tooth wall has been preserved. A similar need may arise when a tooth is damaged due to untimely treatment of caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, etc. It is important to understand that in case of severe tooth decay, the absence of a crown part, this method is not applicable and requires consultation with a dentist regarding the installation of a pin tooth or an artificial dental crown with core pin insert.
Restoration of teeth using cast core inlays
This is one of the most reliable and proven methods of restoring a tooth stump.
A cast stump inlay is essentially an individual pin cast from metal, strengthened in the tooth canal with cement, and restoring the supragingival part of the tooth.
This is a monolithic structure without seams or joints, and therefore very durable and resistant to significant loads. Do you still have questions about restoring a damaged tooth using a therapeutic method? Get a free consultation from specialists. Registration is open online on the clinic website!
Parapulpal pins (aka pins)
Parapulpal pin – a rod about 5 mm in length, with a radius of mainly 0.35 -0.4 mm, without/with thread, which is installed in dental hard tissues when it is necessary to hold fillings in cavities of the IV and II classes, severe destruction of the dental crown and preserved pulp (not used in the treatment of pulpless teeth).
The material of the rod can be titanium, steel, gold alloys .
The pin is usually inserted into the subgingival dental area, due to the properties of root dentin that are suitable for this purpose. The pin is located at a distance of 0.5 mm from the enamel/dentin border and from the pulp, 1-1.5 mm from the marginal area of the tooth.
In accordance with the decay of the tooth, the required number of pins is inserted. Thus, when intervening in the area of the front teeth, one rod is sufficient, while to restore chewing teeth it is necessary to use as many pins as there are no chewing drills.
Stages of restoring a filling on pins
- cleaning the cavity and leveling its walls;
- formation of a pin channel;
- installing a pin into the channel and securing it;
- installation of a seal.
The parapulpal pin is an additional device, which is why, to ensure the quality, strength and duration of the result, other methods are used in parallel to ensure the retention of the filling. Professionalism in working with channels plays an important role.
Sometimes the pin can be seen through the filling. To prevent such defects, special coatings are used, for example, gold plating (yellow color is more natural than steel), plastic.
Indications for installation of anchor pins
- strengthening teeth without pulp before restoration with filling materials;
- strengthening teeth without pulp that are more than half destroyed before temporary restoration with composite materials (if orthopedic intervention is planned in the future) - the so-called. temporary filling of the root canals of teeth with pins;
- restoration of pulpless teeth to retain the filling in a situation where further crown coverage is expected;
- preventive strengthening of teeth in case of severe thinning of the dental crown due to endodontic intervention.
Posts are not used for the purpose of strengthening a tooth root that has been weakened due to endodontic manipulation . They only improve the fixation of the filling. It is also important to consider that the presence of a structure increases the risk of root fracture due to excessive forces.
The intracanal rod can be characterized by active fixation (with a thread for screwing in) or passive (fixation of the pin in the root canal is achieved by cementing).
Pin in a tooth - what is it?
Phrases from the series “putting a tooth on a pin,” “building a tooth on a pin,” or “tooth under a pin” sound quite scary for many patients. However, in reality, restoring a tooth with a pin will help avoid its removal, and the design itself does not cause any discomfort. A dental pin is placed into the root canal. The device performs a supporting function and helps to optimally distribute the load on the tooth. Since a pin is placed in the root of the tooth, a number of therapeutic and endodontic procedures must be carried out before starting treatment.
Indications for installing a pin in a tooth
- Serious damage to the coronal part. A tooth without a post has a higher risk of destruction after treatment if more than 50% of its visible part is initially damaged.
- Repeated dental treatment due to secondary caries or destruction of tooth tissue due to other reasons.
- The need for additional supporting and fixing elements for installing a crown.
- When preparing the abutment tooth for fixing the prosthesis.
- For the treatment of advanced forms of periodontitis and periodontal disease. Pins are installed on loose teeth for subsequent splinting.
- During tooth replantation (in rare cases).
Contraindications to the procedure are related to the condition of the tooth (severe damage, too thin walls), anatomical features and pathologies of the root canal structure, as well as concomitant diseases (caries, acute periodontitis, cyst, granuloma, abscess, mental disorders) and body conditions (pregnancy) .
The use of posts (anchor pins) is possible only with:
- high-quality tooth treatment endodontically;
- absence of pathologies in the peri-apical zone of the tooth root;
- complete removal of dentin affected by caries;
- the ratio of the coronal part of the rod and its part inside the canal = 1:2;
- careful filling of the canal fragment from the apex of the root to the end of the rod (from 0.5 cm);
- the ratio of the width of the walls of the tooth root canal and the thickness of the rod = 1:1 (the root wall is a millimeter thick!).
If the tooth has thin roots, then conical rods are usually installed, while thick ones are cylindrical. The selection of a specific design for a tooth is carried out on the basis of an x-ray.
Dental restoration with pins
Dental restoration is one of the most complex and important areas of modern dentistry. Restoration is important because, among other things, missing teeth have a negative effect on the entire digestive system. For example, if food is poorly chewed, problems may begin in the stomach or intestines. It is also worth noting that even if even one tooth is missing in the oral cavity, chewing food, especially hard food, will be complicated. For these and not only these reasons, dentists advise preserving teeth, even if they have been seriously damaged.
Restoration can be done using fillings, but only if tooth decay is minimal. What if most of the tooth is lost? and the filling will no longer be able to restore either chewing activity or a decent appearance, the method of tooth restoration using anchor pins is used.
What is an anchor pin?
A pin is a special dental structure that is fixed in the root of the tooth. If the outer part of the tooth is destroyed by more than half, then the pin will not only preserve it, but also ensure its functioning for 10-15 years. The pin consists of two main parts: the pin itself and its crown part. The pin is a permanent prosthesis that is fixed in the oral cavity in two main ways:
- screwing into the bone;
— fixation using specialized solutions.
According to this classification, active and passive pins are distinguished.
Anchor pins, as a rule, are made of the most durable metal - titanium; other materials are less commonly used, for example, gold-based alloys, palladium or stainless steel. They are installed in the root part of the tooth and, thanks to the material from which they are made, they reliably serve for many years.
After the pin is installed, external restoration of the tooth begins, that is, building up its visible part - the crown. The crown part is made of filling material that best matches the shade of a person’s teeth. In case of negative reactions, the anchor pin can be removed without any problems. It is necessary to remember that absolutely all types of teeth can be restored using pins.
It is also worth mentioning the fundamental difference between implantation and dental restoration using pins. When restoring teeth with pins, the tooth root remains in place. This means that the living nerves of the root will provide the pin with even greater and more reliable fixation.
How to install the pin?
The process of installing a pin, like any other process in dentistry, begins with a diagnosis. After the patient contacts, the doctor will determine how damaged the tooth is, how thick it is, in what form the root is preserved, what function the destroyed tooth performs in the chewing process, etc. Only after this the specialist begins the restoration process, which can be divided into several stages:
— preparation of tooth root canals. At this stage, the dentist must fully prepare the still living tooth root for fixation of the pin: clean, seal the canals, and also, with special care, seal the area at the top of the root, the so-called apical region.
- insertion of the pin. The key point of this stage is fixing the pin directly into the jaw bone, which will ensure maximum reliability and stability of the prosthesis in the future.
- additional fixation. The pin must be additionally fixed in the oral cavity using special cement.
- extension of the upper, coronal part. This part of the work relates to a greater extent to aesthetic dentistry, since we are talking about working with the visible part of the tooth. The crown can be made (most often) from a filling material, the color of which is selected by the dentist based on the color of the patient's teeth, or the crown can be a ceramic or composite inlay.
What other pins are there?
In addition to the metal pins described above, in modern dentistry there are also pins made without the use of iron. In recent years, the following have found widespread use among practicing dentists:
- fiberglass pins. Their main competitive advantage is lightness, flexibility and, at the same time, incredible strength. In the first months of use, fiberglass pins change their shape slightly, but later return to their original shape. The pin itself has a translucent white color, and its properties make it possible to produce a fairly thin (compared to its iron counterpart) product.
- ceramic pins. This type of pin is used most often because of its appearance. After all, ceramics has a color that is as close as possible to the natural color of human teeth. Among the main disadvantages, experts cite the low degree of elasticity and flexibility of ceramic pins.
- carbon pins. At the moment this is the least common type of pin. The main reason for this is the low strength of the products.
Benefits of restoring teeth using pins
Among the key advantages of dental restoration using pins it is worth noting:
— comparative ease and speed of installation;
— long service life: up to 20 years;
— no long-term adaptation to the pin;
— high reliability of the product;
— the possibility of complete restoration of hard tooth tissue;
- high aesthetics, especially in cases of using fiberglass and ceramic pins.
At the EuroStom clinic, we offer our clients only the most modern dental technologies and the highest quality materials. Our specialists have been successfully working in the area of dental restoration using pins for many years. Professionalism, thorough diagnostics and care for each client are what we are valued for. Come to the EuroStom clinic and we will provide you with prompt and qualified assistance at affordable prices.
Recovery and care after treatment
To prevent unwanted consequences and ensure full recovery, it is important to follow a number of rules:
- take medications prescribed by your doctor and follow dietary recommendations;
- exclude the consumption of rough foods that injure the mucous membranes;
- carry out thorough hygienic care without injuring the tooth;
- Get regular check-ups with your dentist.
Painful sensations after filling should gradually subside over several days. If the tooth continues to hurt, the canals are bothering you, the pain increases, if the filling with the pin falls out, you need to consult a doctor.
In a situation where the pin is visible from under the filling, you should also visit a specialist, since this phenomenon may be the result of errors in installing the structure on the tooth, a violation of the seal, the development of secondary caries around the filling, etc.
What to do if a tooth with a pin hurts?
Painful sensations may well occur after installation of the pin, since surrounding tissues were affected during the treatment process. Often, unpleasant sensations occur after depulpation, especially with the use of arsenic. A tooth without a nerve and a pin should not hurt, since it is dead. If a tooth hurts after installing a pin and these sensations do not go away for several days, there is a risk that the treatment was carried out with errors and complications arose. In this case, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.