25.11.2019
“Bite” refers to the type of closure of teeth. Normally, the upper teeth should slightly overlap the lower teeth. In this case, the chewing function is performed most fully. Due to impaired jaw growth, the child experiences bite deviations: for example, the upper jaw may be overdeveloped or, conversely, underdeveloped, and the teeth may not be in their proper places.
Unfortunately, parents rarely take any effective measures to correct malocclusion in children, believing that “everything will go away on its own.” By doing this, they make a huge mistake, since a child with malocclusion suffers from digestive and swallowing disorders. Sometimes cosmetic inconveniences lead to the development of an inferiority complex; children withdraw into themselves, are reluctant to communicate with peers, and become capricious and irritable.
Causes of malocclusion in children
Among the many reasons for the formation of malocclusion, we name the following:
- Features of the structure of the jaws, which are most often inherited;
- Disturbances in the growth of jaw bones;
- Having bad habits (this includes thumb sucking);
- Using a pacifier, as well as using a pacifier that has a large hole. Parents should be aware that the hole in the nipple must be made as small as possible so that milk flows out of the bottle only if the child makes the correct sucking movements;
- Diseases of the ear, nose and throat;
- Sometimes incorrect posture also contributes to the formation of malocclusion in children;
- Prolonged stay of the child on artificial feeding;
- Keeping the child in one position while sleeping.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of pathology includes not only identifying an abnormal bite, but also determining the cause of its occurrence. To accurately assess the condition of the jaw system, a set of measures is carried out:
- Teperentgenography. Thanks to the procedure, the doctor identifies existing defects in the jaw bones and also assesses the condition of the alveolar processes.
- Tomography. It is prescribed to determine the localization of the head of the mandibular joint.
- Casts. Models are used to study the structural features of bone tissue elements.
- Electromyography. Prescribed when analyzing the chewing functions of the jaw.
- Study of the dentition using the Schwartz method. The technique allows you to identify a type of abnormal bite.
- test . Another way to determine the type of pathology.
Classification of malocclusion in children
Normal types of occlusion in children are orthognathic, progenic, direct, biprognathic. Orthognathic occlusion is ideal. In this case, the lower and upper teeth are in perfect contact. A progenic bite is characterized by the fact that at the moment of closure of the teeth, the front teeth protrude somewhat forward. In a straight bite, the upper incisors meet the lower cutting edges. Biprognathic occlusion is characterized by the fact that the lower incisors are slightly inclined towards the vestibule of the mouth.
Among the pathological types of bite, the following types are distinguished:
- Prognathia (or distal bite). In this case, the upper jaw sharply protrudes forward.
- Mesial occlusion, or progenia. In this case, the lower jaw protrudes forward.
- With a deep bite, the upper incisors overlap the lower ones by more than 50 percent.
- With a crossbite, the normal relationship of the dental arches is disrupted. Therefore, the teeth begin to move sideways relative to each other.
- An open bite is characterized by non-occlusion of the lower and upper incisors. There are its varieties. So, with an open anterior bite, the incisors do not close, and with an open lateral bite, the molars do not close.
Crowding
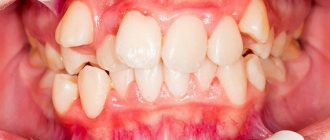
The most common drawback. Its reason is the narrowing of the upper dentition and lack of space for all the teeth. Wisdom teeth have already become a rudiment (a functionally unnecessary organ), so most people can only accommodate 14 teeth in their upper jaw. If the fifth and sixth teeth begin to erupt, then the entire row is forced to make room. This is where crowding comes from. Due to individual characteristics, sometimes even 12 teeth cannot erupt smoothly without running into each other.
Crowded teeth
Therefore, dental expansion is included in most orthodontic treatment plans. This change has a positive effect on both the smile and the face: the oval of the face and chin tighten and become clearer.
Signs of malocclusion
Often, parents do not need to carefully examine the child’s oral cavity to notice that he has an incorrect bite, since its signs are very obvious. In such children, the jaws move incorrectly (forward or backward), the dentition is uneven, and in some areas of the jaw the teeth are very crowded. The so-called hyperdentia, that is, the presence of supernumerary teeth, is often noted.
Another important sign of malocclusion in children is dystopia, that is, their incorrect position. Malocclusion is characterized by the presence of diastemas and three.
Children with malocclusion often complain of difficulty swallowing and chewing. They constantly bite their tongue and cheeks, which causes pain in the mouth, and they often develop stomatitis. Pain in the facial muscles and headaches are often noted.
You can suspect malocclusion in children based on a number of indirect signs. In such children, breathing through the mouth predominates. When swallowing, such children strain their lips and chin excessively. With significant deviations of the bite, facial asymmetry is noticeable. You may also notice a deviation in the timing of the eruption of permanent teeth.
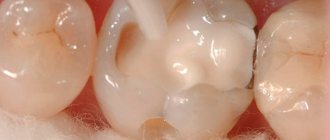
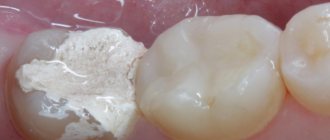
In children with malocclusion, tooth enamel wears off much faster. Increased sensitivity of the tooth occurs, i.e. reaction of the tooth surface, when it can hurt from sour, salty, sweet, as well as cold and hot. Finally, improperly positioned teeth cause the development of ulcerative inflammation of the gums, bleeding and even damage to the jaw joints.
If children have an anterior open bite, biting food becomes significantly more difficult. An open lateral bite, on the contrary, makes chewing difficult. With a deep distal bite, the child's breathing is impaired.
And finally, all types of abnormal bite lead to impaired pronunciation of sounds, which results in diction defects. And since malocclusion is also an aesthetic problem, it is easy to notice that the child becomes withdrawn, sad, and sometimes irritable.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the problem are classified into two categories - facial and oral. The main features of the first group are as follows:
- strongly pushed forward;
- crooked chin;
- shortened lower third of the skull;
- protruding upper lip;
- sharply defined supramental fold;
- parted mouth.
Among the functional signs are noted:
- the appearance sagittal fissure;
- abnormal position of the lateral teeth;
- difficulty chewing food;
- pain in the temporal region;
- impaired speech functions.
Other symptoms of pathology occur depending on the cause of the abnormal bite. One of the listed symptoms is a reason to contact an orthodontist. In a child, pathology is easier to eliminate than in adults, since in childhood the location of the teeth is not yet completely fixed.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Without medical attention, a distal bite can cause complications such as teeth grinding or bruxism. The latter type of disease often manifests itself after treatment of the problem, if the therapy was carried out too late.
Consequences of malocclusion
If a malocclusion is suspected, children should be examined by a pediatric dentist, otolaryngologist, orthodontist, or speech therapist. In this case, the main role in determining malocclusion belongs, of course, to the orthodontist. To carry out calculations and accurately diagnose, a panoramic image is required, as well as an X-ray examination of the skull. In addition, a photograph of the child's face may be required.
Finally, to determine the exact position of the teeth in the oral cavity, an alginate impression is made, on the basis of which a plaster model of the dentition can be made. With its help you can see the exact location of the teeth. To clarify the diagnosis, computed tomography and myography may be required.
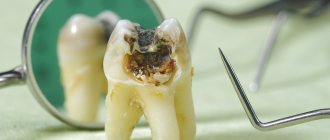
Pathological bite is not just an aesthetic problem. Any deviation from the normal position of the teeth leads to improper load on the teeth. In the process of chewing food, teeth begin to wear down excessively, which can lead to the development of bruxism, when a child grinds his teeth heavily during sleep. Because of this, the tooth begins to be affected by caries.
In addition, abnormal tooth mobility develops due to improper positioning of the teeth. If this condition is not treated, teeth will begin to fall out over time. Due to the pathological development of the temporomandibular joint, frequent headaches and clicking sounds appear when opening the mouth. Since the incorrect position of the teeth strains the joint and muscles, constant muscle pain occurs.
Aesthetic problems manifest themselves in the fact that the child’s facial profile changes. He has an ugly smile because his teeth are crooked. Sometimes the degree of tooth curvature is so pronounced that the child is completely ashamed to smile.
All these consequences together significantly worsen the child’s quality of life. So this pathology must be corrected in time.
Impacted teeth
Normally, all teeth, except for the eights, grow in by the age of 12–13 years. But if the jaw is very narrowed, then some may not have enough space and they simply will not grow, remaining in the jaw bone in a “dormant” state.
Fortunately, teeth continue to grow into adulthood. To do this, they need to prepare a place - and aligners cope with this successfully. Once the space appears, the tooth will begin to grow. Adults experience the same unpleasant sensations as children in the first year of life when their baby teeth appear: pain and itching in the gums. When the tooth has erupted a little, you can install a button with an elastic traction on it and begin to pull it out of the gums towards the rest of the teeth.
Impacted fang
If there are impacted teeth, then, as a rule, the malocclusion is serious. But this does not mean that aligners will not help: there are examples of such treatment.
Treatment of malocclusion in children
The process of correcting malocclusion in children occurs much faster than in adults. But parents do not need to take advantage of this feature of children’s jaws, but start treatment as early as possible. The optimal period for starting bite correction is 5-6 years. Before correcting the bite, it is necessary to carry out a complete sanitation of the oral cavity and professional teeth cleaning. If necessary, some teeth are removed; the dentist will tell you which ones.
Today, there are many ways to professionally correct your bite. Let's look at some of them.
Braces
Braces (bracket systems) are devices that help correct an abnormal bite. Treatment with this method involves wearing a brace system for a long time, which helps the tooth or group of teeth return to their normal position in the socket.
The position of the teeth can be changed because they do not fuse with the jaw bones, but are only tightly fixed in the sockets. When constant pressure is applied to the wall of such a hole (of course, it will not be too great), then the bone tissue in such a place gradually resolves, and this causes the tooth to change position. In place of the connective tissue, new bone tissue gradually forms, which fixes the tooth in its new position.
Braces are a non-removable system. They are fixed to the tooth thanks to the base. The bracket groove contains the main element – the orthodontic arch. It is made of materials that are able to “remember” its position. An orthodontic arch has the shape of an anatomically correct dentition. The force exerted by the arch leads to the gradual alignment of the teeth in the dentition.
Straightening teeth with braces takes a long period of time, takes place over a long period of time and under the supervision of a doctor. Treatment in some cases can take from six months to three years, and sometimes longer. All this time, patients constantly visit the dentist and follow all his instructions. Only then will treatment with braces be effective.
Mouthguards
Mouth guards are special transparent plates made of high-quality silicone that help effectively get rid of uneven teeth. Their design allows the teeth to gradually move in the dentition. The aligners are worn all day and removed at night, as well as when eating and brushing your teeth. They have a mechanical effect on the teeth, closing the gap between them and straightening the jaw.
Like braces, mouthguards are worn for a long time. They can only be purchased at specialized dental clinics. An individual model of mouth guards is made for each person. They are not felt in the mouth and are beneficial if you follow all the doctor’s instructions when wearing them.
Caring for such devices is not difficult. At night, when removing the mouth guard, rinse it with clean boiled water. Boiling water cannot be used, as the silicone may lose its properties.
Dental plates
Plates are placed on teeth if minor malocclusions need to be corrected. They are very well adapted to be installed by small children. The period of wearing them in this case is much shorter than for adults.
Such plates can be removable or non-removable. Fixed plates are worn for approximately two years. Removable plates have a simpler design and are made of high-quality plastics. They are very easy to attach using hooks.
The good thing about removable plates is that they can be removed regularly. However, they are effective only for minor violations of the structure of the dentition.
Trainers
This is an elastic splint that easily adapts to any type of jaw. They, unlike braces, eliminate the cause of malocclusion. Due to its physiological effect on the teeth, it easily corrects the bite, and therefore is most suitable for young patients.
Trainers are unnoticeable and can be worn for a short time, say, an hour. They do not cause any physical discomfort.