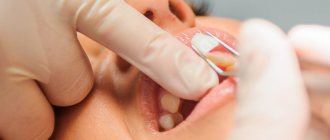
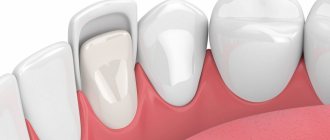
What problems do veneers solve?
Darkening and discoloration of enamel.
The procedure is relevant in cases where bleaching does not bring the desired result. You can achieve radiant white teeth without the use of chemicals. Damage to enamel. Cracks and chips in teeth are the main cause of dangerous oral diseases, since damage becomes an optimal environment for the development of bacteria.
Gaps between teeth. You can restore the beauty of your smile without the use of orthodontic treatment and installation of braces. Veneers will help hide too large gaps between teeth.
Other dental defects. If the enamel is worn away, the teeth are too short or of unequal length, there are minor curvatures and wedge-shaped defects, then it’s time to install veneers.
Veneers are the solution to my problem
As I already wrote, on the Internet I saw an advertisement about Perfect Smile veneers, which told me how good they were and, in my opinion, at that time they could solve my problem.
They then cost 1,780.00 rubles, and since I worked, I could afford such an easy solution to the problem than going to the dentist and treating my teeth for who knows what money.
Without thinking for a long time and without consulting with my children, I decided to order these Perfect Smile veneers so that I could have beautiful teeth. Moreover, the price was not particularly bad.
Indications for installing veneers on teeth
Veneers are aesthetic microprostheses in the form of plates. They are fixed with a composite adhesive on the outside of the tooth, giving it a beautiful and natural appearance. It is recommended to install veneers in the following cases:
- there are enamel or dentin defects;
- demineralization of the tooth has occurred;
- there is a slight curvature of the bite;
- the color of old fillings or the enamel itself has changed.
These problems may appear due to injury, age-related changes, poor oral hygiene, or be congenital. In any case, installing onlays is an effective solution that allows you to get a luxurious smile and improve the aesthetics of your teeth.
Place veneers on your front teeth in dental clinics in Kemerovo
- Good afternoon
- Sobornaya street, house 12
- +7 (3842) 90-… show all
- Mon-Fri 9:00–21:00; Sat, Sun 10:00–16:00
3.9 ratings: 9
- Dentistry Diamond Premium
3.9 ratings: 8
- Doctor hare
3.8 ratings: 6
- Star
3.9 ratings: 9
- Smile
4.2 ratings: 12
- Alyona
4.0 ratings: 9
- Smile Studio
3.8 ratings: 9
Types of veneers
Dentistry knows three common types of veneers:
Ceramic or E-max.
Such plates are made indirectly, that is, from impressions in the laboratory, then they are attached with special cement, which reliably fixes the structure. Such veneers are placed on the front teeth due to their high aesthetics.
Porcelain.
They are made in two ways - the first consists of applying layer-by-layer material to the teeth and firing it, the second is pressed porcelain and is made separately. The second option is more durable.
Composite.
Veneers are installed directly in the mouth and require just one visit to the dentist. The composite has a less natural appearance and is more fragile compared to the first methods, but it is quite inexpensive. The first variety is considered the most popular.
Advantages of dental restoration with veneers
The main reasons why it is recommended to install veneers on ceramic teeth are: minimum installation time (2-3 visits); careful selection of onlays to match the color of the patient’s teeth; full fit; resistance to discoloration of the overlays due to smoking or food; high quality aesthetics; protection of dentin from damage; long service life with proper care. price. Veneers are cheaper than lumineers. Composite veneers will also hide defects, chips or darkening of teeth. With proper care (daily hygiene, absence of dyes in consumed products, etc.), such pads can last quite a long time.
Price-list
| Order number | Name of service | price, rub. | Service code |
| 1. | Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with an orthodontist | 600 | B01.063.001 |
| 2. | Repeated appointment (examination, consultation) with an orthodontist | 300 | B01.063.002 |
| 3. | Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with a pediatric dentist | 600 | B01.064.003 |
| 4. | Repeated appointment (examination, consultation) with a pediatric dentist | 300 | B01.064.004 |
| 5. | Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with a dentist-therapist | 600 | B01.065.001 |
| 6. | Repeated appointment (examination, consultation) with a dentist-therapist | 300 | B01.065.002 |
| 7. | Initial consultation with diagnostic images from a dentist-therapist | 1000 | B01.065.003 |
| 8. | Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with a dental hygienist | 600 | B01.065.005 |
| 9. | Repeated appointment (examination, consultation) with a dental hygienist | 300 | B01.065.006 |
| 10. | Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with an orthopedic dentist | 600 | B01.066.001 |
| 11. | Repeated appointment (examination, consultation) with an orthopedic dentist | 300 | B01.066.002 |
| 12. | Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with a dentist-surgeon | 600 | B01.067.001 |
| 13. | Repeated appointment (examination, consultation) with a dentist-surgeon | 300 | B01.067.002 |
X-ray examination
| 14. | Targeted intraoral contact radiography (1 image) | 400 | A06.07.003 |
Physiotherapy
| 15. | Photodynamic therapy (Foto San) | 500 | A22.07.010 |
ANESTHESIA
| 16. | Conduction anesthesia | 650 | B01.003.004.002 |
| 17. | Infiltration anesthesia | 650 | B01.003.004.005 |
| 18. | Working field isolation (rubberdam, optragate) | 350 | A11.07.017 |
Injections
| 19. | Injection administration of drugs, without the cost of the drug | 300 | A11.07.011 |
| 20. | Introduction of hyaluronic acid hyalripayer into the gingival papillae | 6600 | A11.07.011.001 |
| 21. | Application of the drug to the oral mucosa | 300 | A11.07.022 |
THERAPY Professional oral hygiene and prevention of dental diseases in adults
| 22. | Electroodontometry of 1 tooth | 110 | A05.07.001 |
| 23. | Selective polishing of 1 tooth | 450 | A16.07.025.001 |
| 24. | Professional intracoronal teeth whitening for non-vital changes in tooth color (1 tooth) | 450 | A16.07.050.004 |
| 25. | Professional clinical teeth whitening (2 jaws in the smile line) | 11000 | A16.07.050.006 |
| 26. | Removal of white and brown spots (ICOH Opalustre) (1 tooth) | 2500 | А16.07.050.007 |
| 27. | Professional oral and dental hygiene (good condition) | 3500 | A16.07.051 |
| 28. | Professional hygiene of the oral cavity and teeth (satisfactory condition) | 4500 | A16.07.051.001 |
| 29. | Professional hygiene of the oral cavity and teeth (unsatisfactory condition) | 5500 | A16.07.051.002 |
| 30. | Professional oral hygiene (brush + paste + gel application) | 2800 | A16.07.051.004 |
| 31. | Sealing the tooth fissure with sealant | 1500 | A16.07.057 |
| 32. | Grinding of hard tooth tissues using an operating microscope | 1200 | A16.07.082.100 |
Professional oral hygiene and prevention of dental diseases in children
| 33. | Deep fluoridation of enamel (liquid enamel, 1 tooth) | 250 | A11.07.012 |
| 34. | Tooth-Moussi Dental Remineralization Therapy (fluoride-free) | 2500 | A11.07.012.1 |
| 35. | Application of the tooth silvering method (1 tooth) | 150 | A11.07.023 |
| 36. | Professional oral hygiene of baby teeth (brush + paste) | 1500 | A16.07.051.003 |
| 37. | Professional oral hygiene of baby teeth (brush + paste + gel application) | 2800 | A16.07.051.005 |
| 38. | School of psychological prevention for patients and relatives (adaptive reception) | 600 | В04.070.001 |
Treatment of pathology of hard dental tissues. Aesthetic dental restoration in adults
| 39. | Diagnostic tooth preparation for further prognosis | 3000 | А16.07.002.002 |
| 40. | Tooth restoration with a temporary filling | 600 | А16.07.002.003 |
| 41. | Tooth restoration (wedge-shaped defect) | 3000 | A16.07.002.004 |
| 42. | Tooth restoration with IV filling; II, III class according to Black (Vitremer) | 4100 | A16.07.002.005 |
| 43. | Tooth restoration with a filling I, III, V, VI class according to Black | 3900 | A16.07.002.010 |
| 44. | Restoration of a tooth with a filling in violation of the contact point II, III, IV class according to Black | 4600 | A16.07.002.011 |
| 45. | Restoring a tooth with a filling (chip restoration) | 3000 | A16.07.002.013 |
| 46. | Aesthetic and functional tooth restoration | 7000 | A16.07.003. 003 |
| 47. | Biological method of treating pulpitis (using MTA + filling) | 6600 | A16.07.009.001 |
| 48. | Temporary splinting for periodontal diseases (2 teeth) | 2100 | A16.07.019 |
| 49. | Fixation of intracanal pin (fiberglass, anchor pin) | 2100 | A16.07.093 |
Treatment of pathology of hard dental tissues in children.
| 51. | Restoring a baby tooth with a filling | 2100 | A16.07.002.013 |
| 52. | Filling 1 root canal of a baby tooth | 500 | A16.07.008.011 |
| 53. | Temporary filling of 1 canal of a baby tooth | 300 | A16.07.008.010 |
Root canal endodontics in adults
| 54. | Application of devitalizing paste + temporary filling | 1000 | А11.07.027 |
| 55. | Pulp extirpation (1 channel) | 300 | А16.07.010 |
| 56. | Instrumental and medicinal root canal treatment | 1900 | A16.07.030 |
| 57. | Temporary filling of the root canal with a drug | 450 | A16.07.030.003 |
| 58. | Ultrasound expansion of the root canal of a tooth, unfilling of 1 root canal of a tooth | 2600 | A22.07.004.003 |
| 59. | Removing the intracanal pin/inlay | 2000 | A16.07.094 |
| 60. | Instrumental and medicinal treatment of the root canal using an operating microscope | 1200 | A16.07.030.100 |
| 61. | Filling the root canal of a tooth (with gutta-percha pins) | 1500 | A16.07.008.001 |
| 62. | Filling the root canal of a tooth (thermafil) | 2000 | А16.07.008.002 |
| 63. | Filling the root canal of the tooth, closing the perforation and the bottom of the tooth cavity MTA | 1700 | A16.07.008.009 |
Root canal endodontics in children
| 64. | Treatment of chronic periodontitis of a baby tooth – 1 visit | 650 | A16.07.009.001 |
| 65. | Treatment of chronic periodontitis of a baby tooth – 2nd visit | 650 | A16.07.009.002 |
| 66. | Treatment of chronic pulpitis of a baby tooth – 1 visit | 650 | A16.07.009.003 |
| 67. | Treatment of chronic pulpitis of a baby tooth – 2nd visit | 650 | A16.07.009.004 |
| 68. | Coronal pulp amputation | 300 | A16.07.009 |
ORTHOPEDICS
Impressions
| 69. | Orthopedics impression taking | 2500 | А02.07.010.002 |
| 70. | Taking an impression from one jaw to make a silicone key | 500 | А02.07.010.011 |
| 71. | Making a boxing mouth guard | 6000 | A23.07.002.043 |
| 72. | Making a removable plastic plate without elements (bite block) | 3000 | A23.07.002.063 |
| 73. | Study on diagnostic jaw models | 500 | A02.07.010 |
Fixed prosthetics
| 74. | Tooth restoration with a metal-ceramic crown | 8000 | A16.07.004.007 |
| 75. | Tooth restoration with a metal-plastic crown | 7000 | A16.07.004.008 |
| 76. | Tooth restoration with a cast metal crown | 6000 | A16.07.004.009 |
| 77. | Tooth restoration with a plastic crown | 6000 | A16.07.004.0010 |
| 78. | Restoration of a tooth with a facet | 6000 | A16.07.004.0011 |
| 79. | Restoration of a cast tooth | 6000 | A16.07.004.0012 |
| 80. | Tooth restoration with a temporary crown using the direct method | 1000 | A16.07.004.001 |
| 81. | Tooth restoration with a permanent metal-ceramic crown with shoulder mass and individual reproduction of aesthetics on teeth in the smile line | 15000 | A16.07.004.004 |
| 82. | Tooth restoration with a permanent metal-free crown made of zirconium dioxide, standard aesthetics (staining method) | 18000 | A16.07.004.005 |
| 83. | Tooth restoration with a permanent metal-free all-ceramic zirconium dioxide or Imax crown with individual aesthetics (application method) | 18000 | A16.07.004.006 |
| 84. | Tooth restoration with inlays, veneers, half-crowns | 15000 | A16.07.003 |
| 85. | Tooth restoration with KHS inlays | 4000 | A16.07.003.001 |
| 86. | Tooth restoration with collapsible KHS inlays | 6000 | A16.07.003.002 |
| 87. | Tooth restoration with zirconium dioxide inlays | 8000 | A16.07.003.003 |
| 88. | Tooth restoration with an inlay, veneer, half-crown made of Imax or zirconium dioxide with individual aesthetics | 15000 | A16.07.003.001 |
| 89. | Tooth restoration with an inlay, veneer, half-crown made of Imax material (refractor) | 15000 | A16.07.003.002 |
Removable dentures
| 90. | Bite correction using removable and non-removable orthopedic structures - mouthguard | 5000 | A16.07.021.003 |
| 91. | Aesthetic mouthguard | 12500 | A16.07.021.004 |
| 92. | Custom mouthguard for bruxism | 5000 | А16.07.021.005 |
| 93. | Prosthetics with partial removable lamellar dentures (1 jaw) | 25000 | A16.07.035 |
| 94. | Dental prosthetics with complete removable plate dentures (1 jaw) | 30000 | A16.07.023 |
| 95. | Prosthetics with removable clasp dentures with clasp fixation (1 jaw) | 35000 | A16.07.036.001 |
| 96. | Prosthetics with removable clasp dentures with locking fixation (1 jaw) | 42000 | A16.07.036.002 |
| 97. | Relining a removable denture (Mucopren Soft) | 5000 | A16.07.036.003 |
| 98. | Prosthetics with partial removable plate dentures made of nylon (1 jaw) | 30000 | A16.07.035.001 |
| 99. | Prosthetics with partial removable plate dentures for temporary replacement of 1-3 missing teeth (immediate denture) | 12500 | A16.07.035.003 |
| 100. | Prosthetics with partial removable laminar dentures for the temporary replacement of 4-6 missing teeth (immediate denture) | 25000 | A16.07.035.004 |
Implant-supported prosthetics
| 101. | Dental prosthetics using an implant, metal-ceramic crown (individual abutment) | 21000 | A16.07.006.008 |
| 102. | Dental prosthetics using an implant, metal-ceramic crown (standard abutment) | 20000 | A16.07.006.001 |
| 103. | Dental prosthetics using an implant with a metal-plastic crown (standard abutment) | 20000 | A16.07.006.002 |
| 104. | Dental prosthetics using an implant, metal-free ceramic crown (ceramic abutment) | 39000 | A16.07.006.011 |
| 105. | Dental prosthetics using an implant with Ca, metal-ceramic crown (standard abutment) | 24000 | A16.07.006.005 |
| 106. | Dental prosthetics using an implant with Ca, a metal-plastic crown (individual abutment) | 21000 | A16.07.006.012 |
| 107. | Dental prosthetics using an implant with a Ca crown, metal-free ceramics + zirconium abutment | 43000 | A16.07.006.013 |
| 108. | Dental prosthetics using a metal-ceramic implant in a bridge | 9000 | A16.07.006.010 |
| 109. | Dental prosthetics using an implant with a temporary plastic crown | 17000 | A16.07.006.009 |
Other orthopedic services
| 110. | Repeated fixation of permanent orthopedic structures with temporary cement (1 unit) | 500 | A16.07.049.001 |
| 111. | Repeated fixation of permanent orthopedic structures with permanent cement (1 unit) | 500 | A16.07.049.002 |
| 112. | Removal of a permanent fixed orthopedic structure (1 unit) | 1000 | A16.07.053.010 |
| 113. | Removal of a temporary fixed orthopedic structure (1 unit) | 500 | A16.07.053.020 |
SURGERY
Outpatient surgical procedures in adults
| 114. | Removal of postoperative sutures (ligatures) | 100 | A16.30.069 |
| 115. | Tooth extraction (simple) | 2000 | A16.07.001 |
| 116. | Tooth extraction (complicated) | 3500 | A16.07.001.003 |
| 117. | Tooth extraction with the formation of a mucoperiosteal flap and partial alveolotomy | 7700 | A16.07.001.004 |
| 118. | Removal of an impacted, dystopic or supernumerary tooth | 3300 | A16.07.024 |
| 119. | Collapan | 2500 | A16.07.041.003 |
| 120. | Opening a submucosal or subperiosteal inflammation in the oral cavity | 600 | A16.07.011 |
| 121. | Opening and drainage of odontogenic abscess | 600 | A16.07.012 |
| 122. | Delayed curettage of the extracted tooth socket | 10100 | A16.07.013 |
| 123. | Opening and draining an oral abscess | 600 | A16.07.014 |
| 124. | BIO GIDE Bone Membrane | 25000 | A16.07.041.002 |
| 125. | Alveolar ridge plastic surgery | 11000 | A16.07.017 |
| 126. | Autologous bone transplantation (bone block, autologous bone during augmentation) | 25000 | A16.03.019 |
| 127. | Correction of the volume and shape of the alveolar process | 5500 | A16.07.017.002 |
| 128. | Plastic surgery of the alveolar process using a gum former on an implant | 4400 | A16.07.017.003 |
| 129. | Osteotomy of the jaw to expose the crown of an unerupted tooth | 5500 | A16.07.027.001 |
| 130. | Jaw osteotomy with implant removal | 11000 | A16.07.027.002 |
| 131. | Open curettage for periodontal diseases in the tooth area | 3000 | А16.07.038 |
| 132. | Closed curettage for periodontal diseases in the tooth area | 1500 | A16.07.039 |
| 133. | Flap surgery in the oral cavity | 5000 | A16.07.040 |
| 134. | Flap surgery in the oral cavity when collecting a graft from the tubercle of the upper jaw | 8000 | А16.07.040.001 |
| 135. | Flap surgery in the oral cavity when taking a graft from the palate | 10000 | A16.07.040.002 |
| 136. | Flap surgery in the oral cavity with plastic surgery of gum recession in the area of 1 tooth | 2500 | A16.07.040.003 |
| 137. | Flap surgery in the oral cavity with removal of the membrane and pins | 15000 | А16.07.040.004 |
| 138. | Bone grafting of the maxillofacial area using biodegradable materials | 16000 | A16.07.041.001 |
| 139. | Vestibuloplasty | 8000 | A16.07.045 |
| 140. | Sinus lifting (bone grafting, osteoplasty) closed | 5000 | A16.07.055.001 |
| 141. | Sinus lift (bone grafting, osteoplasty) open | 15000 | A16.07.055.002 |
| 142. | Bone substitute | 12000 | А16.07.041.004 |
| 143. | Treatment of pericoronitis (washing, cutting and/or excision of the hood) | 500 | A16.07.058 |
| 144. | Hemisection of tooth | 5000 | A16.07.059 |
| 145. | Coronary-radicular separation | 5000 | A16.07.060 |
| 146. | Gingivoplasty | 3500 | A16.07.089 |
| 147. | Gingivotomy | 2500 | A16.07.090 |
| 148. | Stopping alveolar bleeding without suturing | 200 | A16.07.095 |
| 149. | Stopping alveolar bleeding without suturing using hemostatic materials | 1000 | A16.07.095.002 |
| 150. | Plastic perforation of the maxillary sinus | 12000 | A16.07.096 |
| 151 | Suturing the oral mucosa | 500 | A16.07.097 |
Outpatient surgical procedures in children
| 152. | Milk tooth extraction (simple) | 1300 | A16.07.001.001 |
| 153. | Removal of a baby tooth (complicated) | 1900 | A16.07.001.002 |
Implantation (surgical part)
| 154. | Intraosseous dental implantation (zirconium) | 20000 | A16.07.054 |
| 155. | Intraosseous dental implantation of the “ADIN”, “SDI” system (Israel) for further dentures | 17500 | A16.07.054.001 |
| 156. | Intraosseous dental implantation with calcium coating of the ADIN system (Israel) for further dental prosthetics | 20500 | A16.07.054.002 |
| 157. | Installation of the healing abutment | 2500 | A16.07.054.003 |
| 158. | Bone transplantation - autogenous bone block | 65000 | А16.03.019.001 |
| 159. | Installation of a soft tissue plate in the area of 1 implant | 5000 | А16.07.054.004 |
| 160. | Implant removal surgery | 2500 | А16.054.109 |
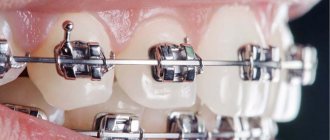
ORTHODONTICS
| 161. | Orthodontic appliance maintenance services | 500 | A23.07.001 |
| 162. | Correction of removable orthodontic appliance | 500 | A23.07.001.001 |
| 163. | Orthodontic appliance repair | 3000 | A23.07.001.002 |
| 164. | Manufacturing one element for a removable plate | 500 | A23.07.002.042 |
| 165. | Removal and installation of an orthodontic ring | 250 | A16.07.053.001 |
| 166. | Selective grinding (1 tooth) | 300 | A 16.07.025 |
| 167. | Activation of fixed orthodontic equipment (2 jaws) | 5000 | A16.07.046.003 |
| 168. | Activation of fixed orthodontic equipment (1 jaw) | 2500 | A16.07.046.002 |
| 169. | Activation of the system on a short arc | 1500 | A16.07.046.001 |
| 170. | Orthodontic correction using a removable orthodontic device “LM-activator” | 10000 | A16.07.047.001 |
| 171. | Orthodontic correction with a removable orthodontic device (trainer) | 6500 | A16.07.047.002 |
| 172. | Orthodontic correction with removable orthodontic apparatus “Myobrace” | 7500 | A16.07.047.003 |
| 173. | Orthodontic correction | 800 | A16.07.028 |
| 174. | Fitting and applying the orthodontic appliance | 1000 | A23.07.003 |
| 175. | Impression taking, diagnostics | 2500 | A02.07.010.001 |
| 176. | Making the vestibular plate | 2500 | A23.07.002.058 |
| 177. | Making a plate with a tongue barrier (without clasps) | 3000 | A23.07.002.059 |
| 178. | Making a plate with occlusal pads | 5000 | A23.07.002.060 |
| 179. | Making a removable plate with an inclined plane | 5000 | A23.07.002.068 |
| 180. | Orthodontic correction using the “Damon Q” brace system for 1 jaw (self-regulating metal) | 40000 | A 16.07.048.001 |
| 181. | Orthodontic correction using the “Damon Q” brace system for 2 jaws (self-regulating metal) | 80000 | A 16.07.048.002 |
| 182. | Orthodontic correction using the “Damon Clear” brace system for 1 jaw (self-regulating transparent top (6 pcs.) + metal) | 50000 | A 16.07.048.003 |
| 183. | Orthodontic correction using the “Damon Clear” brace system for 2 jaws (self-regulating transparent top, metal bottom) | 90000 | A 16.07.048.004 |
| 184. | Orthodontic correction using the MDM bracket system (8 pcs.) | 20000 | A 16.07.048.006 |
| 185. | Orthodontic correction using the Damon Q 2×4 bracket system (8 pcs.) | 20000 | A 16.07.048.007 |
| 186. | Installation of one orthodontic microimplant | 12000 | A 16.07.054.005 |
| 187. | Fixation of retainer (1 jaw) | 5000 | A16.07.048.011 |
| 188. | Fixing 1 link of retainer | 800 | A16.07.048.012 |
| 189. | Fixation of 1 bracket link | 800 | A16.07.048.013 |
| 190. | Removal of the bracket system with installation of a retainer (1 jaw) | 8000 | А16.07.048.008 |
| 191. | Removing the retainer (1 jaw) | 3000 | A16.07.048.009 |
| 192. | Removing the bracket system (1 jaw) | 2000 | A16.07.048.010 |
Eurocappa
| 193. | Case "Eurocappa Complete" | 179000 | A16.07.047.003.001 |
| 194. | Case "Eurocappa Light" | 129000 | A16.07.047.003.002 |
| 195. | Case "Eurocappa Express" | 99000 | A16.07.047.003.003 |
| 196. | Additional revision | 15000 | A16.07.047.003.004 |
| 197. | Re-printing 1 tray | 3000 | A16.07.047.003.005 |
| 198. | Retention mouthguard | 4000 | A16.07.047.003.006 |
| 199. | 3D modeling | 15000 | A16.07.047.003.007 |
Contraindications
The decision about the possibility of installing a veneer should be made by a doctor, since he will be able to take into account all the features of the condition of the patient’s teeth and jaw. Sometimes other treatment procedures must be completed before the onlays can be fixed. Typically contraindications include:
- Malocclusion. May have a destructive effect on renewed teeth or cause disruption of the lower temporomandibular joint
- Bruxism
- Volumetric fillings and extensive caries
- Poor hygiene
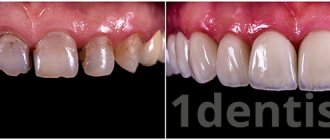
Stages of manufacturing and installation of veneers
An orthopedic surgeon can install veneers in a high-quality manner, since the work is very delicate. On average, the process of creating ceramic onlays takes a week. This period includes the following works:
- take impressions of teeth using a special spoon and impression paste;
- create a plaster model based on the cast;
- ready-made veneers are made.
Before restoration, the patient undergoes a professional cleaning to correctly determine the shade of tooth enamel. Installation can be done in one of two ways:
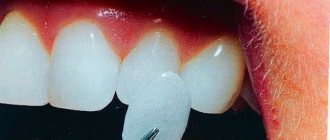
- straight. The dentist removes a thin layer of tooth enamel and then applies layers of composite material, which is then cured under the influence of a lamp. Only composite veneers can be installed this way;
- indirect. Grinding is carried out, after which an impression is taken. Based on the impression, a microprosthesis is made in the laboratory (this process may take varying amounts of time). The plate is then attached to the tooth using dental adhesive.
Veneers in a box. Truth or deception?
January 13, 2022 at 12:22 pm
Olga
Yes, the topic of the review for many is not only interesting and a warning about another deception and an attempt to make money on us, especially those who are ignorant in this matter. But it is also very painful for some in the literal sense - for example, people like me. Dentistry is my second home. Or, in another way, you can say that I go there almost as if I were going to work. From the elementary grades of Soviet childhood! Imagine what I had to endure over several decades, learn about new and old technologies, understand X-rays myself, where I can determine, just as well as a doctor, whether there is inflammation or a cyst on a tooth or not... I’m not deceiving you, readers. Pure truth. I also had to learn what implantology is. Moreover, not only theoretically, but also in practice. A terrible horror, which is quite painful, very long-term, completely devastating for the wallet and, moreover, without a guarantee “for life”. I think that when I find the time, I will write a horror story review on this topic... Someone will ask why I am listing my dental sufferings and exploits, but those who have little idea of my situation, based on their own, have already realized that , personally, I will never buy any teeth in a box for 490 rubles1 even if they offer me such miracle veneers for free. They are completely unwearable! Of course, there are many gullible people and they, not knowing the intricacies of medicine, can believe in miracle technologies and risk ordering such veneers. Someone will be tempted by the price if there is no big money. But you need to understand that simply removing the nerve and treating pulpitis can cost ten thousand or more. What kind of Hollywood for 490 rubles can we talk about? Even if you take the more expensive option, it’s all the same - everyone has a different jaw structure, a different bite, and a different size of teeth. And with age, the number of remaining teeth varies. Plus individual features that can only be shown by a computed tomography scan and seen by an experienced doctor. Well, in one go you can only do professional cleaning or cure superficial caries, and then...How can you be so naive? Advertisements for veneers sometimes appear sporadically in my gadgets, and sometimes they obsessively bare their teeth. I didn’t even have the thought of not only buying such products, but also reading about what they wanted from me. So it's clear. Apparently, given the restrictions and recommendations to go less to crowded places, which can also include clinics, the scammers decided to help deliver teeth directly to your home. Well, so that we don’t run to clinics. And those who are afraid of pain and for this reason do not go and do not have their teeth treated on time, would also be glad to see a quick solution to their problems. No, this is not the case. If you want to be healthy and have a beautiful smile, then save money and choose a competent doctor. Of course, it is also necessary to take care of them from childhood. But I, for example, have weak genetics. and no matter how I take care of them, no matter how carefully I treat them and give away, one might say, a huge amount of money for treatment, prosthetics, implants... they cannot be called beautiful and family... The highest technologies are probably available to the richer... but for 490 rubles I don't need anything either. Be careful in your choice.