Tongue cancer is a fairly common pathology in the structure of malignant neoplasms of the head and neck organs (about 55% of cases), and in the general structure of malignant neoplasms it accounts for 0.45%. The average age of those affected is 60 years, men suffer from it 3 times more often than women. But the tumor can also occur in young people and even children.
- Causes of tongue cancer
- Symptoms of tongue cancer
- Methods for diagnosing tongue cancer
- Treatment of tongue cancer
- Prevention
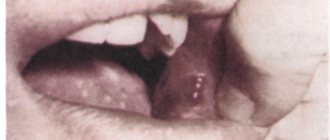
Most often, cancer is localized on the lateral surface, a little less often on the root of the tongue, and very rarely in the area of its back and tip. [1,2]
Anatomical structure of the tongue
Bloody marks on the tongue - what can cause the symptom and what to do about it
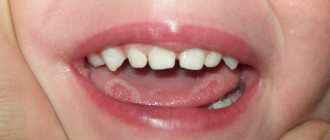
There are many possible reasons why your tongue may bleed. Most often, the prerequisite for this unpleasant phenomenon is banal damage to the organ during talking or chewing. However, in other cases, this symptom may indicate serious health problems. Such manifestations as a thick coating on the tongue, enlarged papillae, and even more so traces of blood, should at least alert you and also become a good reason to contact a specialist. Today we will look at the most common causes of blood above and below the tongue, and also find out what to do with this symptom.
Structure and purpose of the language organ
The tongue is a digestive organ. Essentially, this is a muscle that consists of striated tissue. It is covered with a protective layer - the mucous membrane. The anatomical structure of the organ includes two parts: the body and the root. The upper region is called the back, and under the organ is the frenulum. There are also terminal and longitudinal grooves - the first is located at the junction of the root and the body, and the second divides the organ vertically.
On a note! On the surface of the tongue there are many papillae, which contain taste buds. For example, those responsible for recognizing sweet taste are located on the tip, and salty taste is located on the sides. On the side, closer to the root, there are receptors that react to sour things, but the base of the organ is susceptible to bitter tastes.
The tongue not only allows us to enjoy the taste of our favorite treats, but also takes a very direct part in the conversational function. It also helps us chew food and is responsible for the production of salivary fluid, which, in turn, helps break down food particles and therefore participates in digestion.
Special types of glossitis and their treatment
In addition to the above types of glossitis, dentists distinguish special types of glossitis, characterized by the development of limited specific changes in the tongue. These include:
Desquamative glossitis
It appears in the form of a “geographical” tongue, which has a “variegated” pinkish-red appearance, somewhat reminiscent of the outlines of the continents on a geographical map. In some cases, with the development of the inflammatory process, thinned areas cleared of plaque may change their position and shape within a short period of time (2 - 4 days). In such cases, desquamative glossitis is also called wandering glossitis. This can usually be observed with exudative diathesis, diseases of the digestive system, helminthic infestations, metabolic disorders, blood diseases, pregnant women, etc. Desquamative glossitis involves standard treatment, which leads to a gradual cleansing of the surface of the tongue and the disappearance of associated complaints in the patient.
Median rhomboid glossitis
It is characterized by the presence of a local thickening of the epithelium, usually located in the middle of the back of the tongue. In this case, the thickened area of the epithelium has a diamond-shaped or oval shape and can change its color from red to bluish. Rhomboid glossitis most often occurs in chronic diseases of the digestive system and is prone to chronicity and recurrence. Depending on the form of glossitis (flat, tuberculate, papillomatous), appropriate treatment is carried out: laser therapy, surgery, etc.
Atrophic glossitis
It often develops with insufficient intake of vitamins A and E. It usually appears as a single bright red, smooth spot that occupies the entire surface of the tongue. The focus of atrophy can persist for quite a long time without progressing. Sometimes the tongue decreases in size. Histological examination reveals dilation of blood and lymphatic vessels, swelling and inflammation in the papillary layer. Often, atrophic glossitis is a symptom of tongue damage due to gonorrhea.
Gunter's glossitis
Appears with a deficiency of vitamin B12 and folic acid. It most often occurs with blood diseases (usually anemia associated with impaired hematopoietic processes). In this form of the disease, the surface of the tongue is bright crimson in color and, due to atrophy of the papillae, has a “varnished” appearance. Gunter's glossitis involves treatment of the underlying disease by a therapist or hematologist.
Mycotic, candidal, or yeast glossitis
As a rule, it is a consequence of intensive antibacterial therapy, as a result of which the normal microflora in the patient’s body was suppressed. The disease manifests itself as swelling of the tongue, an accumulation of white plaque on it, with pronounced longitudinal and transverse grooves. Very often, mycotic glossitis occurs in young children and the elderly, as well as in people with weakened immune systems. Candidal glossitis requires treatment with antifungal drugs.
As an additional means for the treatment and prevention of glossitis, many experts have recently begun to recommend the use of an ultrasonic brush for oral hygiene.
Why might your tongue bleed?
Now let's figure out why blood still appears on the tongue. There are many potential causes of blood marks, but the most common is careless biting of an organ while speaking or chewing. Most often the tip suffers for this reason. As a result, painful ulcers may form on the surface of the epithelium. The choice of a specific treatment method in this case will directly depend on the extent of the damage. If the wound is small, but there is bleeding, it will be enough to treat the defect with an antiseptic solution. However, before using a pharmaceutical product, you should consult your doctor.
Why does the tongue bleed?
If the wound is serious and requires stitches, then you cannot do without the help of a specialist. In addition to banal biting, there are many other reasons that can lead to bleeding. Let's take a closer look at them.
Mechanical causes of bleeding
As noted above, the most common cause of blood is mechanical damage. However, this phenomenon is not always caused by careless tongue biting. The oral mucosa can be damaged as a result of careless cleaning of the tongue, injury from a sharp nut shell, seed or fish bone. It’s even more difficult with babies, because when children start teething, they diligently put everything they can get their hands on into their mouths. At this time, the risk of soft tissue injury increases significantly.
“For example, it used to often happen to me that I wake up in the morning and blood is flowing from my tongue. It doesn’t whip, of course, but still. True, after brushing my teeth everything went away. And then I finally decided to get braces and went to see an orthodontist. While talking to the doctor, I told her about my problem, and then she explained that it was all due to an incorrect bite and crooked teeth. It’s just that at night, when I involuntarily clenched my jaws, my teeth began to rub my tongue, which then caused bleeding. Now I’m in braces, which, by the way, also seriously scratched all the mucous membranes, but here wax saves me ... "
Camilla R., 28 years old, from correspondence on the forum www.32top.ru
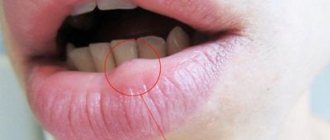
Tongue injury is a common cause of bleeding.
Other common external factors include a fall or blow to the face. At high risk are people with damaged teeth, the sharp edges of which can easily damage the integrity of soft tissues. Also, many problems are caused by incorrectly installed fillings, worn-out prosthetic structures that require relining or replacement, as well as orthodontic devices, which contain many small parts that can injure surrounding tissues.
I would like to pay special attention to hematomas that form directly on the body of the tongue as a result of mechanical influences. A bruise appears when a vessel located inside an organ bursts. This situation can lead to swelling of the soft tissues, which can lead to difficulty breathing and other serious consequences.
Pathological causes of bleeding
Why else might bloody marks appear on the tongue? There are a number of potential pathological causes for this symptom, but the most common condition in this case is glossitis. It is this disease that leads to the appearance of traces of blood on the organ, and it develops for several reasons:
- entry of harmful microorganisms into an open wound,
- allergies to hygiene products,
- exposure to chemicals, acrid tobacco smoke or low quality alcohol,
- frequent consumption of spicy and acidic foods.
The photo shows glossitis of the tongue.
The spread of infection into soft tissues sometimes leads to the appearance of cracks, blisters and bleeding ulcers. Such neoplasms can also result from disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and central nervous system. By the way, cracks very often become an allergic reaction or the result of a deficiency in the body of vitamins B, A, PP1.
What is glossitis?
Glossitis (from the Greek glossa (tongue) + suffix –itis) is an inflammation of the tongue. The reasons for its occurrence are different. Glossitis can develop as a result of a viral or bacterial infection, or as a result of another disease in the body. In addition, there are some other factors that provoke the development of the disease. These include mechanical, chemical and thermal damage to the oral cavity; nicotine; food that is too spicy or too hot; alcohol; caramel; some components present in toothpastes.
Glossitis has the following forms:
- folded
- diamond-shaped median
- desquamative
- hairy black
- Gunter's
- interstitial
According to the duration of the inflammatory process, acute and chronic glossitis are distinguished. The acute form of glossitis manifests itself as inflammation of the tongue, a change in its structure or color. Symptoms of the chronic form are more varied, but in most cases the disease is diagnosed by the presence or absence of papillomas - fungal growths on the tissues of the tongue. There are cases when the cause of the disease can be identified only after comprehensive medical research. True, this happens quite rarely and, as a rule, is associated with the presence of congenital, hereditary diseases.
Treatment of bleeding
What to do if bleeding comes from the tongue, and how to quickly stop it? First of all, it should be noted that treatment here will directly depend on the cause of the problem and the extent of the injury. To reduce bleeding and relieve pain, dental experts advise you to adhere to the following recommendations:
- first you need to thoroughly wash your hands and treat them with an antiseptic, for example, wipe them with alcohol or a special pharmaceutical solution. You can also use sterile gloves. The most important thing is not to allow infection to enter the open wound,
- after this, you should go to the mirror, tilt your head slightly forward to prevent blood from flowing down your throat and obstructing your breathing. It is imperative to remove all foreign objects from the oral cavity: chewing gum, piercings, dentures, if any,
- To stop the bleeding, you will have to put a little pressure on the organ. To do this, you will need a clean bandage, gauze or cotton wool, which must be applied to the damaged area. You need to keep the napkin in this position for at least 10 minutes. The tongue is characterized by an intense blood supply, so coping with the problem will not be difficult. After the specified time has passed, you need to remove the napkin and make sure that the blood has stopped flowing,
- After this, you need to rinse your mouth with cool water - cold causes blood vessels to constrict. Only after this can treatment be carried out with an antiseptic.
To stop bleeding, you need to cover the wound with a bandage.
If your tongue hurts a lot, try applying a piece of ice wrapped in sterile gauze to the wound. To alleviate the condition, you can take a painkiller tablet. If the wound is quite deep, be sure to go to the doctor.
What you should absolutely not do
If blood appears on the tongue, it means there is an open wound on its surface. In order not to aggravate the situation and not provoke the development of inflammatory processes, it is important to adhere to some restrictions. So, if you inadvertently injured the main speech organ, refrain from the following actions:
- cauterizing the wound with alcohol - this will only further injure the mucous membrane,
- drinking hot tea will increase bleeding,
- treating the wound with brilliant green or iodine,
- pressing the wound with a bare finger or teeth, trying to stop the bleeding by pressing the tongue to the roof of the mouth.
Until the bleeding has completely stopped, do not eat or put anything foreign in your mouth until the wound has completely healed. It is also strictly forbidden to self-medicate with antibacterial drugs - they can only be prescribed by the attending physician.
How to treat a blood bladder?
General therapy
Depending on the type of pathological condition that caused the appearance of a blood bubble in the mouth, treatment can be carried out with the following medications:
- In case of traumatic formations that go away on their own over time, the oral cavity is treated with antiseptic agents
For candidal stomatitis, antifungal drugs such as Levorin and Nystanin are effective.
- For diseases of viral etiology, the treatment regimen includes Viferon, Amoxicillin, Tsiprolet, Azithromycin.
- To combat gingivostomatitis, where it is expected to remove areas affected by necrosis, antiallergic medications, antibacterial agents, and vitamin complexes are used.
- In case of traumatic formations that go away on their own over time, the oral cavity is treated with antiseptic agents. If there is pain, the doctor may prescribe Cholisal, Ketoprofen, Voltaren, Lornoxicam, Kamistad.
- To eliminate tuberculosis, appropriate chemotherapy is prescribed, which includes Rifampicin, Ioniazid, Pyrazinamide.
Local therapy
To speed up the healing process, regularly rinse with antiseptic agents. Furacilin, Chlorhexidine, Stomatidine, Betadine, Miramistin, hydrogen peroxide solution, Iodoform, Chlorophyllipt show good results.
Treatment of the affected tongue with disinfectant solutions should be performed twice a day, at a minimum, but before that you must brush your teeth and remove any remaining food.
It is advisable to eat food after the procedures within 30-60 minutes, which will significantly increase their effectiveness.
Traditional methods
Aloe or Kalanchoe juice has a wound healing effect
To alleviate the condition, it is good to use healing decoctions based on chamomile, sage, yarrow, St. John's wort, and viburnum fruits.
They are prepared at the rate of 1 tbsp. herbal raw materials per 1 glass of water.
The mixture is brought to a boil and left for 2-3 hours to infuse. Before use you need to strain.
Aloe or Kalanchoe juice has a wound-healing effect.
Oil from sea buckthorn and rosehip also has the same property. They are applied directly to the affected area.
These agents accelerate the regeneration process, prevent the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and anesthetize the lesion.
A solution prepared from salt (1 tsp), 3 drops of iodine and soda (1 tsp) is a universal remedy in the fight against inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
These components are mixed in one glass of warm boiled water and used for lotions and rinses. It is also good to treat the affected areas with hydrogen peroxide.
When to see a doctor
In some situations, there may be a need for emergency assistance from a specialist. You should consult a doctor if you cannot stop the bleeding on your own, and if there is severe swelling of the soft tissue in the area of injury. A hematoma has appeared on the tongue, pharmaceutical products do not help cope with severe pain, and pus begins to leak from the wound - all this is a serious reason for concern and an urgent visit to the doctor.
If pus appears, you should definitely contact a specialist.
You should also definitely visit a dentist if, some time after the injury, a thick coating with obvious grooves begins to form on the tongue, and there is a burning sensation and discomfort when eating. Remember: a consultation with a specialist is never superfluous, especially if we are talking about an open wound on the oral mucosa.
- Gorbacheva I.A., Integrated approaches to the treatment of patients with combined diseases of internal organs and inflammatory periodontal lesions, 2004.
What not to do?
If you have blood blisters, you should not:
- Pierce and burst them yourself. This technique will only worsen the situation; as a result of additional injury, a fungal infection will join the existing problem, which will prolong the disease.
- Ignore the hematoma, lump, or clot that appears in the oral cavity. If there are any changes in the mucous membrane of the tongue, gums, palate, or cheeks, it is recommended to contact a qualified specialist who will identify the true cause of the disease and prescribe an appropriate treatment regimen.